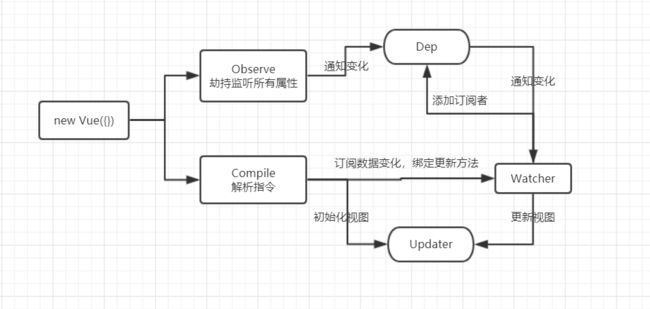
简单实现vue框架实例,实现的目的主要看下几个知识点如何进行的:
- Vue工作机制
- Vue响应式的原理
- 依赖收集与追踪
- 编译compile
以及一些相关操作,代码如下
mvue-test-html
{{name}}
{{age}}
如上, 我们需要实现几点:
- 根组件初始化,el挂载
- data实现数据双向绑定,视图层响应更新, 如 this.name = '刘翔' 赋值后视图层自动更新
- created生命周期简单实现
- 指令v-text、表达式{{name}}、@click、v-model双向数据绑定的实现
- data、方法等挂载到this上,可以直接调用
这里分两块去处理这些东西,一部分是我们vue实例的处理,还一部分是编译到html的处理。我这里写了两个文件,先实现vue实例,然后又写了个compile的js文件。
MVue
这个里面首先包含一个vue实例,在constructor中我们做一些初始化的事情,然后执行响应式处理,将data中的值都做好拦截及监听处理,最后调用compile渲染出指定的el
observe 这个方法主要做响应式处理,遍历data中的所有键名一一调用defineReactive进行数据响应式处理,然后代理到this实例上。
defineReactive 这个方法主要是给每个属性的get、set定义拦截,做一些拦截处理。同时生成dep和key一一对应,对所有的依赖进行管理。
proxyData 顾名思义就是把data中的值代理到实例上面,方便this.name这样去调用。
这里面还有一个Dep和Watcher两个类,他们主要做依赖收集及管理,Dep里面会管理所有的watcher
// 定义KVue构造函数
class MVue {
constructor(options) {
// 保存传入的选项
this.$options = options;
// 传入data
this.$data = options.data;
// 响应式处理
this.observe(this.$data);
this.$methods = options.methods;
new Compile(options.el, this)
if (options.created) {
options.created.call(this)
}
}
// 响应式处理
observe(data) {
if (!data || typeof data !== "object") {
return;
}
// 遍历data
Object.keys(data).forEach(key => {
// 响应式处理
this.defineReactive(data, key, data[key]);
// 代理data中的属性
this.proxyData(key);
});
}
defineReactive(data, key, val) {
this.observe(val);
// 定义一个Dep
const dep = new Dep(); // 每个dep实例都与key值一一对应
// 给obj的每个key定义拦截
Object.defineProperty(data, key, {
get() {
// 依赖收集
Dep.target && dep.addDep(Dep.target);
return val;
},
set(v) {
if (v !== val) {
val = v;
dep.notify();
}
}
});
}
// 讲$data中的属性代理到实例上
proxyData(key) {
Object.defineProperty(this, key, {
get() {
return this.$data[key];
},
set(v) {
this.$data[key] = v;
}
});
}
}
// 创建dep:管理所有的watcher
class Dep {
constructor() {
// 存储所有的依赖
this.deps = [];
}
addDep(dep) {
this.deps.push(dep);
}
// 通知更新
notify() {
this.deps.forEach(dep => dep.update());
}
}
// 创建watcher: 保存data中的数值和页面中的挂钩关系
class Watcher {
constructor(vm, key, cb) {
// 创建实例时立刻将该实例指向Dep.target便于依赖收集
this.vm = vm;
this.cb = cb;
this.key = key;
// 触发依赖收集
Dep.target = this;
this.vm[this.key]; // 触发依赖收集
Dep.target = null;
}
// 更新
update() {
console.log(this.key + "更新了");
this.cb.call(this.vm, this.vm[this.key])
}
}
compile 主要做一些指令等一系列操作的处理,包括实例中的el元素经过处理后挂载到dom上等操作
这里主要使用了正则去匹配相应的表达式、指令等,然后做出相关操作处理。具体看代码操作即可。
// 遍历dom,解析指令和插值表达式
class Compile {
// el 待编译的模板, vm-MVue实例
constructor(el, vm) {
this.$vm = vm;
this.$el = document.querySelector(el);
// 把模版中的内容移到片段操作
this.$fragment = this.node2Fragment(this.$el);
// 执行编译
this.compile(this.$fragment)
// 放回至el中
this.$el.appendChild(this.$fragment)
}
node2Fragment(el) {
// 创建片段
const fragment = document.createDocumentFragment();
let child;
while(child = el.firstChild) {
fragment.appendChild(child)
}
return fragment;
}
compile(el) {
const childNodes = el.childNodes
Array.from(childNodes).forEach(node => {
if (node.nodeType == 1) {
// 元素
// console.log('编译元素' + node.nodeName)
this.compileEle(node)
} else if (this.isInter(node)) {
// 只关心{{XXX}}
// console.log('编译插值文本' + node.textContent)
this.compileText(node)
}
// 递归子节点
if (node.children && node.childNodes.length > 0) {
this.compile(node)
}
})
}
isInter(node) {
return node.nodeType == 3 && /\{\{(.*)\}\}/.test(node.textContent)
}
compileEle(node) {
const nodeAttr = node.attributes;
// 匹配 m-xxx
Array.from(nodeAttr).forEach(attr => {
// 规定 m-xxx="yyyy"
const attrName = attr.name;
const exp = attr.value;
if (attrName.indexOf('m-') == 0) {
// 指令
const dir = attrName.substring(2);
// 执行
this[dir] && this[dir](node, this.$vm, exp)
} else if (attrName.indexOf('@') == 0) {
// 事件
const method = attrName.substring(1)
this.addEvent(node, this.$vm, exp, method)
}
})
}
// 文本替换
compileText(node) {
// console.log(RegExp.$1);
// console.log(this.$vm[RegExp.$1])
// 表达式
const exp = RegExp.$1
this.update(node, this.$vm, exp, 'text')
}
update(node, vm, exp, type) {
const updater = this[type + 'Updater']
updater && updater(node, vm[exp])
new Watcher(vm, exp, function(val) {
updater && updater(node, val)
})
}
textUpdater(node, val) {
node.textContent = val
}
htmlUpdater(node, val) {
node.innerHTML = val
}
modelUpdater(node, val) {
node.value = val
}
text(node, vm, exp) {
this.update(node, vm, exp, 'text')
}
html(node, vm, exp) {
this.update(node, vm, exp, 'html')
}
model(node, vm, exp) {
this.update(node, vm, exp, 'model')
node.addEventListener('input', (e) => {
vm[exp] = e.target.value
})
}
addEvent(node, vm, exp, method) {
const fn = vm.$options.methods && vm.$options.methods[exp]
node.addEventListener(method, fn.bind(vm))
}
}
这只是一个非常简单的vue模仿,距离框架真正处理差了十万八千里,不过里面的一些思路还是比较温和的,仅供vue框架源码初探,后面会具体分析vue的源码。