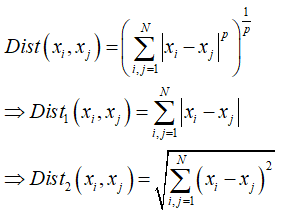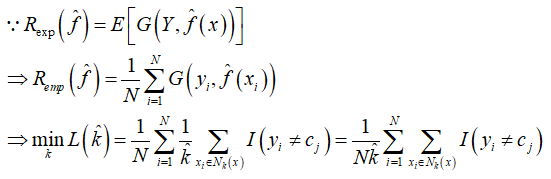返回主页
k 最近邻算法(k-nearest neighbor, k-NN)是一种基本的分类方法(二分类 / 多分类),由 Cover 和 Hart 于1968年提出。它的输入为特征向量,通过距离度量与多数表决,输出类别标记。该算法不具有显式的学习过程,且 k 值的选择对结果会产生重大的影响,因此对于 k-NN 而言,k 的选择至关重要。
1、定义数据集
2、假设空间
关于距离的度量一般有曼哈顿距离和欧氏距离等等:
3、目标函数
4、优化算法
k-NN 不具有显式的学习过程,一般在预测的过程中通过线性扫描或KD树的方法执行判断
手写 k-NN 算法并与 Sklearn 作比较
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from __future__ import (absolute_import, division, print_function)
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import scipy.spatial.distance as dist
from sklearn.utils import shuffle
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
#import random as rd
#import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
class KnnModel(object):
@staticmethod
def check_k(K, x_train):
if not isinstance(K, np.ndarray):
raise TypeError("K must be as type of np.ndarray")
if (min(K) <= 0) or (max(K) > len(x_train)):
raise ValueError("K must be in range [1, N]")
for k in K:
if not isinstance(k, np.int32):
raise TypeError("the element of K must be as type of np.int32")
return None
def __init__(self, K, metric):
self.K = K
self.metric = metric
def z_scale(self, x_train):
'''z标准化,在动用距离度量的算法中,必须先进行标准化以消除数据量纲的影响'''
mu = np.mean(x_train, axis=0)
std = np.std(x_train, axis=0)
return mu, std
def data_transform(self, mu, std, x_train, x_test):
'''数据变换,执行标准化操作'''
x_train_scale = (x_train - mu) / std
x_test_scale = (x_test - mu) / std
return x_train_scale, x_test_scale
def l1(self, x1, x2):
'''曼哈顿距离'''
return np.sum(np.abs(x1 - x2))
def l2(self, x1, x2):
'''欧氏距离'''
return np.sqrt(np.sum((x1 - x2)**2))
def cosine(self, x1, x2):
'''余弦距离'''
return 1 - x1.dot(x2) / (np.sqrt(np.sum(x1**2)) * np.sqrt(np.sum(x2**2)))
def fit(self, x_train_scale, y_train):
'''模型训练,针对KNN,其实没有显示的学习过程,所谓的训练其主要目的就是选择合适的k值'''
# 训练样本量
N = len(x_train_scale)
# 适配距离函数
if self.metric == "l1":
m = self.l1
elif self.metric == "l2":
m = self.l2
elif self.metric == "cosine":
m = self.cosine
else:
raise ValueError("metric must be 'l1', 'l2' or 'cosine'")
# 计算样本两两距离,形成距离方阵
#dist_train = dist.cdist(x_train_scale, x_train_scale, metric="euclidean")
dist_train = dist.cdist(x_train_scale, x_train_scale, metric=m)
dist_train = pd.DataFrame(dist_train)
# 迭代,选择最优的k值
loss_list = []
for k in K:
loss_res = 0
for idx in dist_train.index:
# 为每个样本计算k近邻索引
k_nearest_idx = dist_train.iloc[idx, :].sort_values(ascending=True)[1:k+1].index
# 得到k近邻的类别标记
c = y_train[k_nearest_idx]
# 计算误分类率
loss = sum(y_train[idx] != c) / k
loss_res += loss
# 总体误分类率
loss_res /= N
loss_list.append(loss_res)
# 取误分类率最小的k为最优值
k_best = K[np.argmin(loss_list)]
print(f"误分类率列表:\n{loss_list} \n最优的k:{k_best}")
return k_best
def predict(self, x_train_scale, x_test_scale, y_train, k_best):
'''模型预测,每个样本的预测类别 = 该样本所属的以 k 为范围的邻域内所有训练样本类别的投票值'''
# 适配距离函数
if self.metric == "l1":
m = self.l1
elif self.metric == "l2":
m = self.l2
elif self.metric == "cosine":
m = self.cosine
else:
raise ValueError("metric must be 'l1', 'l2' or 'cosine'")
# 计算测试集样本与训练集样本的两两距离
dist_test = dist.cdist(x_test_scale, x_train_scale, metric=m)
dist_test = pd.DataFrame(dist_test)
# 执行预测,找到以 k 为范围的邻域内所有训练样本类别的投票值
y_pred = []
for i in range(len(dist_test)):
k_nearest_idx = dist_test.iloc[i, :].sort_values(ascending=True)[0:k_best].index
c = y_train[k_nearest_idx]
label, label_count = np.unique(c, return_counts=True)
y_hat = label[np.argmax(label_count)]
y_pred.append(y_hat)
return y_pred
def get_score(self, y_true, y_pred):
'''模型评估'''
score = sum(y_true == y_pred) / len(y_true)
return score
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 构造多分类数据集
n1 = 20
x1 = np.random.uniform(low=1, high=5, size=[n1, 4]) + np.random.randn(n1, 4)*0.01
y1 = np.tile(0, n1)
n2 = 10
x2 = np.random.uniform(low=6, high=10, size=[n2, 4]) + np.random.randn(n2, 4)*0.01
y2 = np.tile(1, n2)
n3 = 30
x3 = np.random.uniform(low=8, high=20, size=[n3, 4]) + np.random.randn(n3, 4)*0.01
y3 = np.tile(2, n3)
x = np.concatenate([x1, x2, x3], axis=0)
y = np.concatenate([y1, y2, y3])
x, y = shuffle(x, y, random_state=0)
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.2)
K = np.array([3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 15, 20]).astype(np.int32)
# 手写 k-NN
model = KnnModel(K=K, metric="l2")
model.check_k(K, x_train)
mu, std = model.z_scale(x_train)
x_train_scale, x_test_scale = model.data_transform(mu, std, x_train, x_test)
k_best = model.fit(x_train_scale, y_train)
y_pred = model.predict(x_train_scale, x_test_scale, y_train, k_best)
score = model.get_score(y_test, y_pred)
print(f"KnnModel 预测准确率:{score}")
# sklearn
scale = StandardScaler(with_mean=True, with_std=True)
scale.fit(x_train)
x_train_scale = scale.transform(x_train)
x_test_scale = scale.transform(x_test)
clf = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5, algorithm="kd_tree", metric="euclidean")
clf.fit(x_train_scale, y_train)
y_pred = clf.predict(x_test_scale)
score = sum(y_test == y_pred) / len(y_test)
print(f"KnnSklearn 预测准确率:{score}")
误分类率列表:
[0.020833333333333332, 0.024999999999999998, 0.029761904761904757, 0.05324074074074075, 0.0890151515151515, 0.14444444444444446, 0.25]
最优的k:3
KnnModel 预测准确率:1.0
KnnSklearn 预测准确率:1.0
返回主页