前言
虽然webpack5已经发布了一段时间了,但一直都没有研究过,最近正好在做微前端相关的调研,恰好看到了webpack5的模块联邦与微前端的相关方案,便想着探究下模块联邦的相关源码。(ps:关于微前端,稍微说一句,个人觉得在选取微前端方案的时候可有结合现有资源以及形态进行相关取舍,从共享能力、隔离机制、数据方案、路由鉴权等不同维度综合考量,个人使用最小的迁移成本,渐进式的过渡,才是最优的选择。)
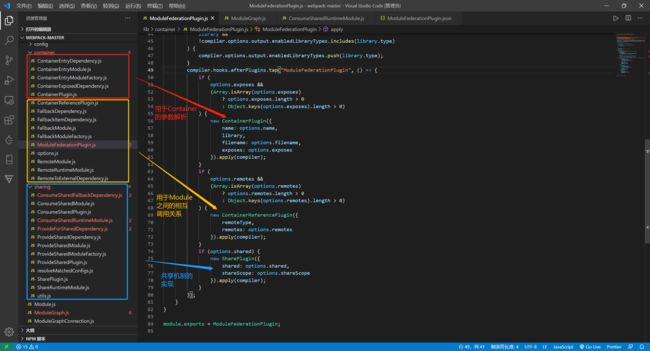
目录结构
container
ModuleFederationPlugin.js (核心,重点分析)
options.js (用户输入的option)
ContainerEntryDependency.js
ContainerEntryModule.js
ContainerEntryModuleFactory.js
ContainerExposedDependency.js
ContainerPlugin.js (核心,重点分析)
ContainerReferencePlugin.js (核心,重点分析)
FallbackDependency.js
FallbackItemDependency.js
FallbackModule.js
FallbackModuleFactory.js
RemoteModule.js
RemoteRuntimeModule.js
RemoteToExternalDependency.js
sharing
SharePlugin.js (核心,重点分析)
ShareRuntimeModule.js
utils.js
resolveMatchedConfigs.js
ConsumeSharedFallbackDependency.js
ConsumeSharedModule.js
ConsumeSharedPlugin.js
ConsumeSharedRuntimeModule.js
ProvideForSharedDependency.js
ProvideSharedModule.js
ProvideSharedModuleFactory.js
ProvideSharedPlugin.js
Module.js (webpack的module)
ModuleGraph.js (module图的依赖)
源码解析
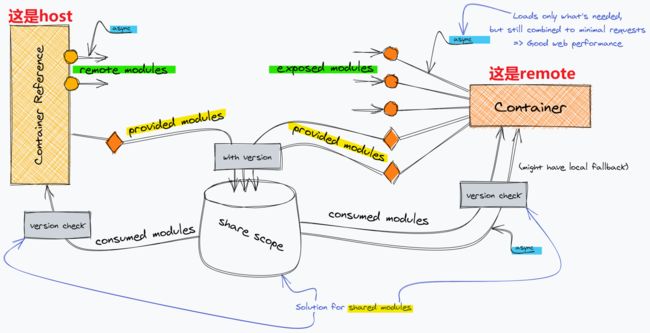
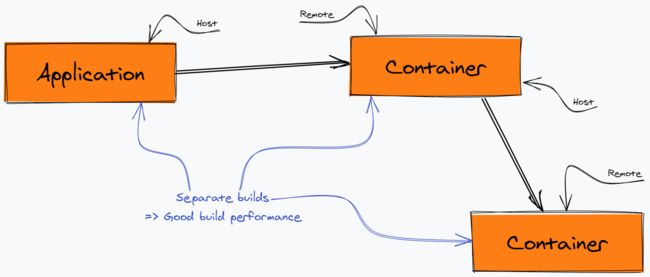
整体webpack5的模块联邦 Module Federation是基于ModuleFedreationPlugin.js的,其最后是以webapck插件的形式接入webpack中,其内部主要设计ContainerPlugin用于解析Container的配置信息,ContainerReferencePlugin用于两个或多个不同Container的调用关系的判断,SharePlugin是共享机制的实现,通过ProviderModule和ConsumerModule进行模块的消费和提供
Module
Webpack的module整合了不同的模块,抹平了不同的差异,模块联邦正是基于webpack的模块实现的依赖共享及传递
class Module extends DependenciesBlock { constructor(type, context = null, layer = null) { super(); // 模块的类型 this.type = type; // 模块的上下文 this.context = context; // 层数 this.layer = layer; this.needId = true; // 模块的id this.debugId = debugId++; } // webpack6中将被移除 get id() {} set id(value) {} // 模块的hash,Module图中依赖关系的唯一判定 get hash() {} get renderedHash() {} // 获取文件 get profile() {} set profile(value) {} // 模块的入口顺序值 webpack模块加载的穿针引线机制 get index() {} set index(value) {} // 模块的出口信息值 webpack模块加载的穿针引线机制 get index2() {} set index2(value) {} // 图的深度 get depth() {} set depth(value) {} // chunk相关 addChunk(chunk) {} removeChunk(chunk) {} isInChunk(chunk) {} getChunks() {} getNumberOfChunks() {} get chunksIterable() {} // 序列化和反序列化上下文 serialize(context) {} deserialize(context) {} }
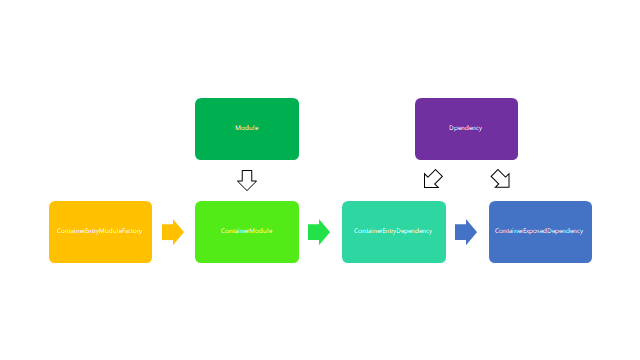
ContainerPlugin
class ContainerPlugin { constructor(options) {} apply(compiler) { compiler.hooks.make.tapAsync(PLUGIN_NAME, (compilation, callback) => { const dep = new ContainerEntryDependency(name, exposes, shareScope); dep.loc = { name }; compilation.addEntry( compilation.options.context, dep, { name, filename, library }, error => { if (error) return callback(error); callback(); } ); }); compiler.hooks.thisCompilation.tap( PLUGIN_NAME, (compilation, { normalModuleFactory }) => { compilation.dependencyFactories.set( ContainerEntryDependency, new ContainerEntryModuleFactory() ); compilation.dependencyFactories.set( ContainerExposedDependency, normalModuleFactory ); } ); } }
ContainerPlugin的核心是实现容器的模块的加载与导出,从而在模块外侧进行一层的包装为了对模块进行传递与依赖分析
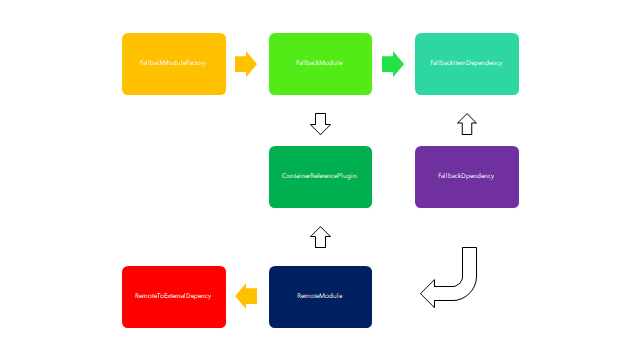
ContainerReferencePlugin
class ContainerReferencePlugin { constructor(options) {} apply(compiler) { const { _remotes: remotes, _remoteType: remoteType } = this; const remoteExternals = {}; new ExternalsPlugin(remoteType, remoteExternals).apply(compiler); compiler.hooks.compilation.tap( "ContainerReferencePlugin", (compilation, { normalModuleFactory }) => { compilation.dependencyFactories.set( RemoteToExternalDependency, normalModuleFactory ); compilation.dependencyFactories.set( FallbackItemDependency, normalModuleFactory ); compilation.dependencyFactories.set( FallbackDependency, new FallbackModuleFactory() ); normalModuleFactory.hooks.factorize.tap( "ContainerReferencePlugin", data => { if (!data.request.includes("!")) { for (const [key, config] of remotes) { if ( data.request.startsWith(${key}) && (data.request.length === key.length || data.request.charCodeAt(key.length) === slashCode) ) { return new RemoteModule( data.request, config.external.map((external, i) => external.startsWith("internal ") ? external.slice(9) : webpack/container/reference/${key}${ i ?/fallback-{data.request.slice(key.length)}`, config.shareScope ); } } } } ); compilation.hooks.runtimeRequirementInTree .for(RuntimeGlobals.ensureChunkHandlers) .tap("ContainerReferencePlugin", (chunk, set) => { set.add(RuntimeGlobals.module); set.add(RuntimeGlobals.moduleFactoriesAddOnly); set.add(RuntimeGlobals.hasOwnProperty); set.add(RuntimeGlobals.initializeSharing); set.add(RuntimeGlobals.shareScopeMap); compilation.addRuntimeModule(chunk, new RemoteRuntimeModule()); }); } ); } }
ContainerReferencePlugin核心是为了实现模块的通信与传递,通过调用反馈的机制实现模块间的传递
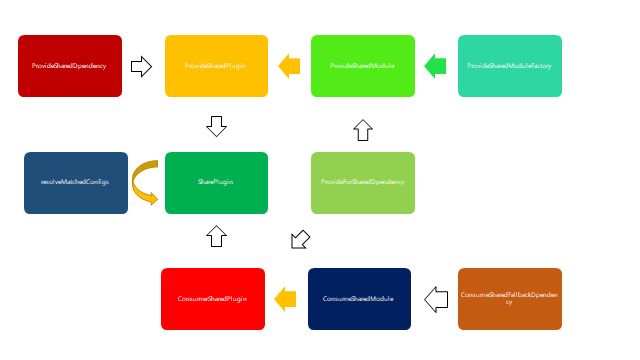
sharing
class SharePlugin { constructor(options) { const sharedOptions = parseOptions( options.shared, (item, key) => { if (typeof item !== "string") throw new Error("Unexpected array in shared"); /** @type {SharedConfig} */ const config = item === key || !isRequiredVersion(item) ? { import: item } : { import: key, requiredVersion: item }; return config; }, item => item ); const consumes = sharedOptions.map(([key, options]) => ({ [key]: { import: options.import, shareKey: options.shareKey || key, shareScope: options.shareScope, requiredVersion: options.requiredVersion, strictVersion: options.strictVersion, singleton: options.singleton, packageName: options.packageName, eager: options.eager } })); const provides = sharedOptions .filter(([, options]) => options.import !== false) .map(([key, options]) => ({ [options.import || key]: { shareKey: options.shareKey || key, shareScope: options.shareScope, version: options.version, eager: options.eager } })); this._shareScope = options.shareScope; this._consumes = consumes; this._provides = provides; } apply(compiler) { new ConsumeSharedPlugin({ shareScope: this._shareScope, consumes: this._consumes }).apply(compiler); new ProvideSharedPlugin({ shareScope: this._shareScope, provides: this._provides }).apply(compiler); } }
sharing的整个模块都在实现共享的功能,其利用Provider进行提供,Consumer进行消费的机制,将共享的数据隔离在特定的shareScope中,通过resolveMatchedConfigs实现了对provider依赖及consumer依赖的过滤,从而对共有依赖只进行一遍请求
总结
webpack5的模块联邦是在通过自定义Container容器来实现对每个不同module的处理,Container Reference作为host去调度容器,各个容器以异步方式exposed modules;对于共享部分,对于provider提供的请求内容,每个module都有一个对应的runtime机制,其在分析完模块之间的调用关系及依赖关系之后,才会调用consumer中的运行时进行加载,而且shared的代码无需自己手动打包。webapck5的模块联邦可以实现微前端应用的模块间的相互调用,并且其共享与隔离平衡也把控的较好,对于想研究模块联邦实现微前端的同学可以参考这篇文章【第2154期】EMP微前端解决方案,随着webpack5的推广及各大脚手架的跟进,相信webpack5的模块联邦方案会是未来微前端方案的主流。
参考
- webpack官方仓库
- Module federation 原理研究
- 精读《Webpack5 新特性 - 模块联邦》
- Webpack 5 Module Federation: A game-changer in JavaScript architecture