在上一篇文章iOS原理探索10-应用程序的加载流程
中,我们梳理了dyld的加载流程,应用程序的加载流程,本篇文章主要 来阐述一下dyld是如何关联objc的。在探索之前,我们首先找到libObjc中的_objc_init方法源码。
一、libObjc中的_objc_init方法源码
void _objc_init(void)
{
static bool initialized = false;
if (initialized) return;
initialized = true;
// fixme defer initialization until an objc-using image is found?
//读取环境变量
environ_init();
//线程key的绑定
tls_init();
//运行c++静态构造函数,在dyld调用我们的静态析构函数之前,libc会调用_objc_init(),因此我们必须自己做
static_init();
//runtime运行时环境初始化,里面主要是unattachedCategories、allocatedClasses -- 分类初始化
runtime_init();
//初始化libobjc的异常处理系统
exception_init();
//缓存条件的初始化
cache_init();
//启动回调机制,通常这不会做什么,因为所有的初始化都是惰性的,但是对于某些进程,我们会迫不及待地加载trampolines dylib
_imp_implementationWithBlock_init();
// 什么时候调用? images 镜像文件
// map_images()
// load_images()
_dyld_objc_notify_register(& map_images, load_images, unmap_image);
#if __OBJC2__
didCallDyldNotifyRegister = true;
#endif
}
1、 environ_init();:主要是读取环境变量;
2、 tls_init();:线程key的绑定,主要是本地线程池的绑定。
void tls_init(void)
{
#if SUPPORT_DIRECT_THREAD_KEYS//本地线程池,用来进行处理
pthread_key_init_np(TLS_DIRECT_KEY, &_objc_pthread_destroyspecific);//初始init
#else
_objc_pthread_key = tls_create(&_objc_pthread_destroyspecific);//析构
#endif
}
3、 static_init();:运行c++静态构造函数,在dyld调用我们的静态析构函数之前,libc会调用_objc_init(),因此我们必须自己做。
/***********************************************************************
* static_init
* Run C++ static constructor functions.
* libc calls _objc_init() before dyld would call our static constructors,
* so we have to do it ourselves.
**********************************************************************/
static void static_init()
{
size_t count;
auto inits = getLibobjcInitializers(&_mh_dylib_header, &count);
for (size_t i = 0; i < count; i++) {
inits[i]();
}
}
4、 runtime_init();:runtime运行时环境初始化,里面主要是unattachedCategories、allocatedClasses -- 分类初始化。
void runtime_init(void)
{
objc::unattachedCategories.init(32);
objc::allocatedClasses.init();
}
5、 exception_init();:主要是初始化libobjc的异常处理系统,注册异常处理的回调,从而监控异常的处理。
/***********************************************************************
* exception_init
* Initialize libobjc's exception handling system.
* Called by map_images().
**********************************************************************/
void exception_init(void)
{
old_terminate = std::set_terminate(&_objc_terminate);
}
- 当有
crash(crash是指系统发生的不允许的一些指令,然后系统给的一些信号)发生时,会来到_objc_terminate方法,走到uncaught_handler扔出异常。
static void (*old_terminate)(void) = nil;
static void _objc_terminate(void)
{
if (PrintExceptions) {
_objc_inform("EXCEPTIONS: terminating");
}
if (! __cxa_current_exception_type()) {
// No current exception.
(*old_terminate)();
}
else {
// There is a current exception. Check if it's an objc exception.
@try {
__cxa_rethrow();
} @catch (id e) {
// It's an objc object. Call Foundation's handler, if any.
(*uncaught_handler)((id)e);
(*old_terminate)();
} @catch (...) {
// It's not an objc object. Continue to C++ terminate.
(*old_terminate)();
}
}
}
-
objc_setUncaughtExceptionHandler抛出异常的函数。fn为外界传入的函数。
objc_uncaught_exception_handler
objc_setUncaughtExceptionHandler(objc_uncaught_exception_handler fn)
{
// fn为设置的异常句柄 传入的函数,为外界给的
objc_uncaught_exception_handler result = uncaught_handler;
uncaught_handler = fn; //赋值
return result;
}
6、 cache_init(); :初始化缓存
void cache_init()
{
#if HAVE_TASK_RESTARTABLE_RANGES
mach_msg_type_number_t count = 0;
kern_return_t kr;
while (objc_restartableRanges[count].location) {
count++;
}
//为当前任务注册一组可重新启动的缓存
kr = task_restartable_ranges_register(mach_task_self(),
objc_restartableRanges, count);
if (kr == KERN_SUCCESS) return;
_objc_fatal("task_restartable_ranges_register failed (result 0x%x: %s)",
kr, mach_error_string(kr));
#endif // HAVE_TASK_RESTARTABLE_RANGES
}
7、 _imp_implementationWithBlock_init();:启动回调机制
void
_imp_implementationWithBlock_init(void)
{
#if TARGET_OS_OSX
// Eagerly load libobjc-trampolines.dylib in certain processes. Some
// programs (most notably QtWebEngineProcess used by older versions of
// embedded Chromium) enable a highly restrictive sandbox profile which
// blocks access to that dylib. If anything calls
// imp_implementationWithBlock (as AppKit has started doing) then we'll
// crash trying to load it. Loading it here sets it up before the sandbox
// profile is enabled and blocks it.
// 在某些进程中渴望加载libobjc-trampolines.dylib。一些程序(最著名的是嵌入式Chromium的较早版本使用的QtWebEngineProcess)启用了严格限制的沙箱配置文件,从而阻止了对该dylib的访问。如果有任何调用imp_implementationWithBlock的操作(如AppKit开始执行的操作),那么我们将在尝试加载它时崩溃。将其加载到此处可在启用沙箱配置文件之前对其进行设置并阻止它。
// This fixes EA Origin (rdar://problem/50813789)
// and Steam (rdar://problem/55286131)
if (__progname &&
(strcmp(__progname, "QtWebEngineProcess") == 0 ||
strcmp(__progname, "Steam Helper") == 0)) {
Trampolines.Initialize();
}
#endif
}
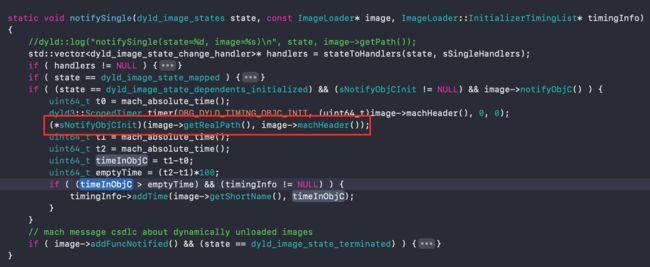
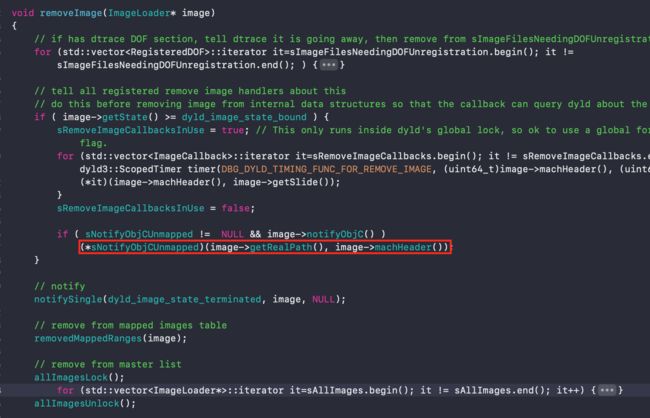
8、 _dyld_objc_notify_register(& map_images, load_images, unmap_image);:这个方法的具体实现在iOS原理探索10-应用程序的加载流程有详细的讲述,它的源码实现是在dyld源码中,以下是_dyld_objc_notify_register方法的声明,主要是在运行时使用,来注册处理程序,以便于映射、取消映射以及初始化obj对象时候使用。
void _dyld_objc_notify_register(_dyld_objc_notify_mapped mapped,
_dyld_objc_notify_init init,
_dyld_objc_notify_unmapped unmapped);
map_images : dyld将image镜像加载进内存;
load_images : dyld初始化image镜像文件会触发该函数;
unmap_image: dyld将image镜像文件移除的时候触发该函数;
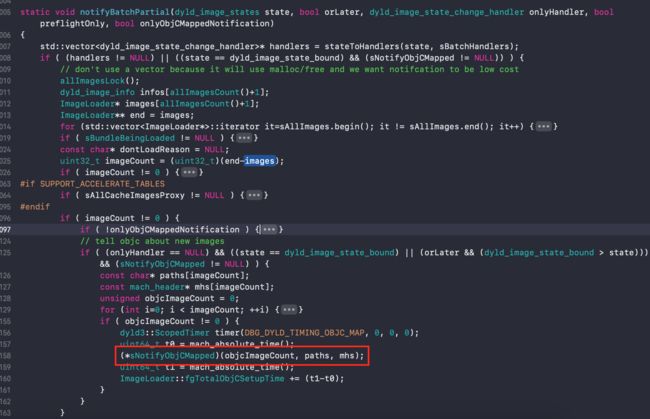
二、map_images函数
- map_images我们结合上篇iOS原理探索10-应用程序的加载流程,知道在dyld的源码中的调用顺序为:
_dyld_objc_notify_register ---> registerObjCNotifiers --> sNotifyObjCMapped
void _dyld_objc_notify_register(_dyld_objc_notify_mapped mapped,
_dyld_objc_notify_init init,
_dyld_objc_notify_unmapped unmapped)
{
dyld::registerObjCNotifiers(mapped, init, unmapped);
}
------------------------
void registerObjCNotifiers(_dyld_objc_notify_mapped mapped, _dyld_objc_notify_init init, _dyld_objc_notify_unmapped unmapped)
{
// record functions to call
sNotifyObjCMapped = mapped;
sNotifyObjCInit = init;
sNotifyObjCUnmapped = unmapped;
... 省略部分代码 ....
}
- 根据
sNotifyObjCMapped,在项目中查找调用的地方