Net设计模式实例之享元模式( Flyweight Pattern)
一、享元模式简介(Brief Introduction)
享元模式(Flyweight Pattern),运用共享技术有效支持大量细粒度的对象。
Use sharing to support large numbers of fine-g
享元模式可以避免大量非常相似类的开销。在程序设计中有时需要生成大量细粒度的类实例来表示数据。如果发现这些实例除了几个参数外基本伤都是相同的,有时就能够受大幅度第减少需要实例化的类的数量。如果能把这些参数移到类实例外面,在方法调用时将他们传递进来,就可以通过共享大幅度地减少单个实例的数目。
享元对象的内部状态与外部状态:
内部状态,在享元对象的内部并且不会随环境改变而改变的共享部分。
外部状态,随环境改变而改变的,不可以共享的状态。
二、解决的问题(What To Solve)
如果一个应用程序使用了大量的对象,而大量的这些对象造成了很大的存储开销,这时可以考虑使用享元模式。
当对象的大多数状态是外部状态,如果删除对象的外部状态,那么可以用相对较少的共享对象取代很多组对象,这时也可以考虑使用享元模式。
三、享元模式分析(Analysis)
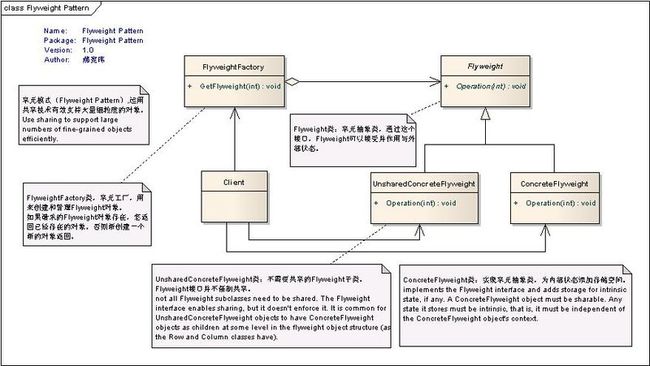
1、享元模式结构
FlyweightFactory类:享元工厂,用来创建和管理Flyweight对象。如果请求的Flyweight对象存在,怎返回已经存在的对象。否则新创建一个新的对象返回。
Flyweight类:享元抽象类,通过这个接口,Flyweight可以接受并作用与外部状态。
UnsharedConcreteFlyweight类:不需要共享的Flyweight子类。Flyweight接口并不强制共享。
ConcreteFlyweight类:实现享元抽象类,为内部状态添加存储空间。
2、代码
| 1、享元工厂类FlyweightFactory
|
| public class FlyweightFactory
{
public Hashtable flyweights = new Hashtable();
public FlyweightFactory()
{
flyweights.Add("A", new ConcreteFlyweight());
flyweights.Add("B", new ConcreteFlyweight());
flyweights.Add("C", new ConcreteFlyweight());
}
public Flyweight GetFlyweight(string key)
{
return flyweights[key] as Flyweight;
}
}
|
| 2、享元抽象类Flyweight 及其具体实现类UnsharedConcreteFlyweight
和ConcreteFlyweight
|
| public abstract class Flyweight
{
public abstract void Operation(int extrinsicstate);
}
public class UnsharedConcreteFlyweight:Flyweight
{
public override void Operation(int extrinsicstate)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}:{1}",this.GetType().Name,extrinsicstate);
}
}
public class ConcreteFlyweight:Flyweight
{
public override void Operation(int extrinsicstate)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}:{1}", this.GetType().Name, extrinsicstate);
}
}
|
| 3、客户端代码
|
| static void
{
// Arbitrary extrinsic state
int extrinsicstate = 20;
FlyweightFactory factory = new FlyweightFactory();
// Work with different flyweight instances
Flyweight fx = factory.GetFlyweight("A");
fx.Operation(--extrinsicstate);
Flyweight fy = factory.GetFlyweight("B");
fy.Operation(--extrinsicstate);
Flyweight fz = factory.GetFlyweight("C");
fz.Operation(--extrinsicstate);
UnsharedConcreteFlyweight fu = new UnsharedConcreteFlyweight();
fu.Operation(--extrinsicstate);
Console.ReadKey();
}
|
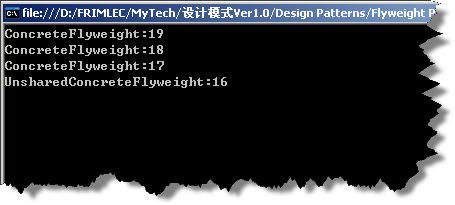
3、实例运行结果
四.享元模式实例分析(Example)
1、场景
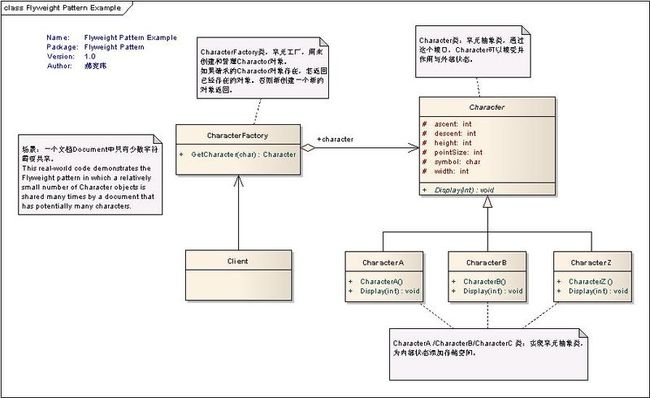
一个文档Document中只有少数字符需要共享。结构如下图所示
CharacterFactory类,享元工厂,用来创建和管理Charactor对象。如果请求的Charactor对象存在,怎返回已经存在的对象。否则新创建一个新的对象返回。
Character类:享元抽象类,通过这个接口,Character可以接受并作用与外部状态。
CharacterA /CharacterB/CharacterC 类:实现享元抽象类,为内部状态添加存储空间。
2、代码
| 1、字符工厂类CharacterFactory
|
| class CharacterFactory
{
private Dictionary<char, Character> _characters = new Dictionary<char, Character>();
public Character GetCharacter(char key)
{
// Uses "lazy initialization"
Character character = nu
if (_characters.ContainsKey(key))
{
character = _characters[key];
}
else
{
switch (key)
{
case 'A': character = new CharacterA(); break;
case 'B': character = new CharacterB(); break;
//...
case 'Z': character = new CharacterZ(); break;
}
_characters.Add(key, character);
}
return character;
}
}
|
| 2、抽象数据对象类DataObject及其具体实现类CustomersData
|
| /// <summary>
/// The 'Flyweight' abstract class
/// </summary>
abstract class Character
{
protected char symbol;
protected int width;
protected int height;
protected int ascent;
protected int descent;
protected int pointSize;
public abstract void Display(int pointSize);
}
/// <summary>
/// A 'ConcreteFlyweight' class
/// </summary>
class CharacterA : Character
{
public CharacterA()
{
this.symbol = 'A';
this.height = 100;
this.width = 120;
this.ascent = 70;
this.descent = 0;
}
public override void Display(int pointSize)
{
this.pointSize = pointSize;
Console.WriteLine(this.symbol + " (pointsize " + this.pointSize + ")");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// A 'ConcreteFlyweight' class
/// </summary>
class CharacterB : Character
{
public CharacterB()
{
this.symbol = 'B';
this.height = 100;
this.width = 140;
this.ascent = 72;
this.descent = 0;
}
public override void Display(int pointSize)
{
this.pointSize = pointSize;
Console.WriteLine(this.symbol + " (pointsize " + this.pointSize + ")");
}
}
// ... C, D, E, etc.
/// <summary>
/// A 'ConcreteFlyweight' class
/// </summary>
class CharacterZ : Character
{
// Constructor
public CharacterZ()
{
this.symbol = 'Z';
this.height = 100;
this.width = 100;
this.ascent = 68;
this.descent = 0;
}
public override void Display(int pointSize)
{
this.pointSize = pointSize;
Console.WriteLine(this.symbol +" (pointsize " + this.pointSize + ")");
}
}
|
| 3、客户端代码
|
| static void
{
// Build a document with text
string document = "AAZZBBZB";
char[] chars = document.ToCharAr
CharacterFactory factory = new CharacterFactory();
// extrinsic state
int pointSize = 10;
// For each character use a flyweight object
foreach (char c in chars)
{
pointSize++;
Character character = factory.GetCharacter(c);
character.Display(pointSize);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
|
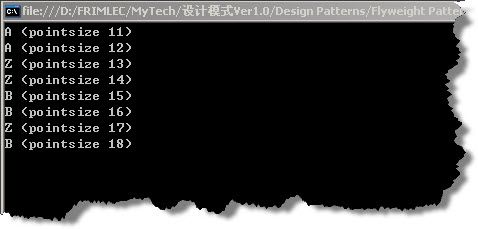
3、实例运行结果
五、总结(Summary)
本文对享元模式(Flyweight Pattern)的概念、设计结构图、代码、使用场景、进行了描述。以一个享元模式实例进行了说明。如果一个应用程序使用了大量的对象,而大量的这些对象造成了很大的存储开销,这时可以考虑使用享元模式。