基本信息
设备号的数据类型:dev_t
typedef unsigned int dev_t;设备号是一个统称,分为主设备号和次设备号。
主设备号保存在高12位;
次设备号保存在低20位。设备号的功能
主设备号:一个设备驱动对应一个主设备号。应用程序通过设备文件中的主设备号在内核中找到对应的设备驱动。
次设备号:一个设备对应一个次设备号。当一个驱动程序管理多个设备时,驱动程序通过设备文件中的次设备号,找到需要操作的设备。
操作宏
/* 通过已知的主次设备号,合成设备号 */
dev_t dev = MKDEV(major, minor);
/* 通过已知的设备号,获取主设备号 */
major = MAJOR(dev);
/* 通过已知的设备号,获取次设备号 */
minor = MINOR(dev);
上述宏的实现:
#define MINORBITS 20
#define MINORMASK ((1U << MINORBITS) - 1)
#define MAJOR(dev) ((unsigned int) ((dev) >> MINORBITS))
#define MINOR(dev) ((unsigned int) ((dev) & MINORMASK))
#define MKDEV(ma,mi) (((ma) << MINORBITS) | (mi))
相关结构体
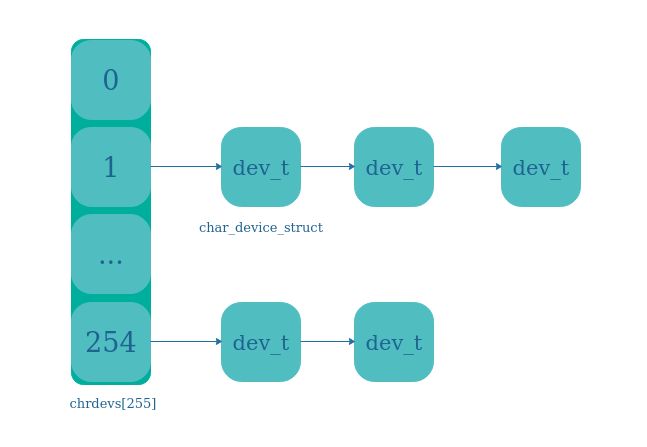
kernel用来保存设备号的结构体char_device_struct,来来看看这个结构体:
static struct char_device_struct {
struct char_device_struct *next;
unsigned int major;
unsigned int baseminor;
int minorct;
char name[64];
struct cdev *cdev; /* will die */
} *chrdevs[CHRDEV_MAJOR_HASH_SIZE];
内核为了管理设备号,维护了一个char_device_struct结构的散列表——chrdevs。
chrdevs的每一个成员,都是一个以char_device_struct结构体指针为元素的 单项链表的 头指针。
每条链表中的所有元素拥有相同的主设备号,及该链表所在chrdevs数组的下标。
操作函数
内核提供的可以用来申请设备号的函数,知道的有三个。专门用来申请设备号的函数有两个,分别是:
register_chrdev_region()和alloc_chrdev_region()。
name是设备名称,可通过cat /proc/devices查看
如果我们明确的知道所需要的设备号时,可以使用下面的函数:
/**
* register_chrdev_region() - register a range of device numbers
* @from: the first in the desired range of device numbers; must include
* the major number.
* @count: the number of consecutive device numbers required
* @name: the name of the device or driver.
*
* Return value is zero on success, a negative error code on failure.
*/
int register_chrdev_region(dev_t from, unsigned count, const char *name)
{
struct char_device_struct *cd;
dev_t to = from + count;
dev_t n, next;
for (n = from; n < to; n = next) {
next = MKDEV(MAJOR(n)+1, 0);
if (next > to)
next = to;
cd = __register_chrdev_region(MAJOR(n), MINOR(n),
next - n, name);
if (IS_ERR(cd))
goto fail;
}
return 0;
fail:
to = n;
for (n = from; n < to; n = next) {
next = MKDEV(MAJOR(n)+1, 0);
kfree(__unregister_chrdev_region(MAJOR(n), MINOR(n), next - n));
}
return PTR_ERR(cd);
}
需要注意的一个细节是,使用next和to进行比较,如果next 如果需要内核帮我们动态的分配设备号,使用下面的函数: 上面个两个申请设备号的函数都调用了 __register_chrdev_region第一个参数是主设备号,在alloc_chrdev_region中第一个参数给了0,也就是要求动态分配主设备号。 __register_chrdev_region第一个参数是主设备号,如果传递0,进入上述if语句,从最大值( major_to_index()是个取模操作: 由这个函数也可以了解到,主设备号可以大于255。当然了如果是动态分配,是不会出现这种情况的。 上述的for循环的目的,是为即将被分配的设备号寻找一个合适的位置(*cp指向的位置)。 上面的for循环有两个遗留问题需要进一步check,下面的就是检查minior是否重叠的代码: 这就是两个集合是否重叠的问题。画图更容易理解。 将cd插入到*cp指向的节点前面。 最后是设备号释放的方法:/**
* alloc_chrdev_region() - register a range of char device numbers
* @dev: output parameter for first assigned number
* @baseminor: first of the requested range of minor numbers
* @count: the number of minor numbers required
* @name: the name of the associated device or driver
*
* Allocates a range of char device numbers. The major number will be
* chosen dynamically, and returned (along with the first minor number)
* in @dev. Returns zero or a negative error code.
*/
int alloc_chrdev_region(dev_t *dev, unsigned baseminor, unsigned count,
const char *name)
{
struct char_device_struct *cd;
cd = __register_chrdev_region(0, baseminor, count, name);
if (IS_ERR(cd))
return PTR_ERR(cd);
*dev = MKDEV(cd->major, cd->baseminor);
return 0;
}
__register_chrdev_region函数,下面具体看一下这个真正分配设备号的函数:/*
* Register a single major with a specified minor range.
*
* If major == 0 this functions will dynamically allocate a major and return
* its number.
*
* If major > 0 this function will attempt to reserve the passed range of
* minors and will return zero on success.
*
* Returns a -ve errno on failure.
*/
static struct char_device_struct *
__register_chrdev_region(unsigned int major, unsigned int baseminor,
int minorct, const char *name)
{
struct char_device_struct *cd, **cp;
int ret = 0;
int i;
cd = kzalloc(sizeof(struct char_device_struct), GFP_KERNEL);
if (cd == NULL)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
mutex_lock(&chrdevs_lock);
/* temporary */
if (major == 0) {
for (i = ARRAY_SIZE(chrdevs)-1; i > 0; i--) {
if (chrdevs[i] == NULL)
break;
}
if (i == 0) {
ret = -EBUSY;
goto out;
}
major = i;
}
cd->major = major;
cd->baseminor = baseminor;
cd->minorct = minorct;
strlcpy(cd->name, name, sizeof(cd->name));
i = major_to_index(major);
for (cp = &chrdevs[i]; *cp; cp = &(*cp)->next)
if ((*cp)->major > major ||
((*cp)->major == major &&
(((*cp)->baseminor >= baseminor) ||
((*cp)->baseminor + (*cp)->minorct > baseminor))))
break;
/* Check for overlapping minor ranges. */
if (*cp && (*cp)->major == major) {
int old_min = (*cp)->baseminor;
int old_max = (*cp)->baseminor + (*cp)->minorct - 1;
int new_min = baseminor;
int new_max = baseminor + minorct - 1;
/* New driver overlaps from the left. */
if (new_max >= old_min && new_max <= old_max) {
ret = -EBUSY;
goto out;
}
/* New driver overlaps from the right. */
if (new_min <= old_max && new_min >= old_min) {
ret = -EBUSY;
goto out;
}
}
cd->next = *cp;
*cp = cd;
mutex_unlock(&chrdevs_lock);
return cd;
out:
mutex_unlock(&chrdevs_lock);
kfree(cd);
return ERR_PTR(ret);
}
/* temporary */
if (major == 0) {
for (i = ARRAY_SIZE(chrdevs)-1; i > 0; i--) {
if (chrdevs[i] == NULL)
break;
}
if (i == 0) {
ret = -EBUSY;
goto out;
}
major = i;
}
ARRAY_SIZE(chrdevs)的大小为#define CHRDEV_MAJOR_HASH_SIZE 255)开始遍历chrdevs数组,直到chrdevs[1]或者遇到chrdevspi[ == NULL为止。(也就是说,主设备号0和255不会被动态分配)
如果1到244没有空闲的主设备号,则分配失败。i = major_to_index(major);
for (cp = &chrdevs[i]; *cp; cp = &(*cp)->next)
if ((*cp)->major > major ||
((*cp)->major == major &&
(((*cp)->baseminor >= baseminor) ||
((*cp)->baseminor + (*cp)->minorct > baseminor))))
break;
/* fs/char_dev.c */
#define CHRDEV_MAJOR_HASH_SIZE 255
/* index in the above */
static inline int major_to_index(unsigned major)
{
return major % CHRDEV_MAJOR_HASH_SIZE;
}
上述for循环break的条件:
/* Check for overlapping minor ranges. */
if (*cp && (*cp)->major == major) {
int old_min = (*cp)->baseminor;
int old_max = (*cp)->baseminor + (*cp)->minorct - 1;
int new_min = baseminor;
int new_max = baseminor + minorct - 1;
/* New driver overlaps from the left. */
if (new_max >= old_min && new_max <= old_max) {
ret = -EBUSY;
goto out;
}
/* New driver overlaps from the right. */
if (new_min <= old_max && new_min >= old_min) {
ret = -EBUSY;
goto out;
}
}
cd->next = *cp;
*cp = cd;
mutex_unlock(&chrdevs_lock);
return cd;
/**
* unregister_chrdev_region() - unregister a range of device numbers
* @from: the first in the range of numbers to unregister
* @count: the number of device numbers to unregister
*
* This function will unregister a range of @count device numbers,
* starting with @from. The caller should normally be the one who
* allocated those numbers in the first place...
*/
void unregister_chrdev_region(dev_t from, unsigned count);