ES3/ES5
focus implicit conversion [ɪmˈplɪsɪt]
function test(x, y){
x = x || 1;
y = y || 2;
console.log( x + y );
}
test(2,0);
//解析:打印结果4 0遇到||往后走 解决方式es6参数默认值 es5 x = typeof(x) !== 'undefined' ? x : 1;
what is the correct output?
for(var i = 0; i < 10; i++){
i = 'a';
console.log(i);
}
for(var i = 0; i < 10; i++){
var i = 'a';
console.log(i);
}
写一个函数,可以接受任意一个字符串,算出这个字符串的总字节数。
function charSum(str){
var str = arguments[0] || '',
sum = 0;
for(var i = 0; i < str.length; i++){
sum += str.charCodeAt(i) > 255 ? 2 : 1;
}
console.log(sum);
return sum;
}
charSum('ab我'); //4
what to output
var str = "undefined";
str += 10;
var type = typeof(str);
if(type.length === 6){
type.text = 'string';
}
console.log(type.text); undefined
what to output
function b(x, y, a){
arguments[2] = 10;
console.log(a);
}
function c(x, y, a){
a = 10;
console.log(arguments[2]);
}
b(1,2,3);
c(1,2,3);
what to output
function foo1(x){
console.log(arguments);
return x;
}
foo1(1,2,3,4,5);
function foo2(x){
console.log(arguments);
return x;
}(1,2,3,4,5); 结果为5 原因是浏览器会把(1,2,3,4,5)优先解析为一个表达式,单独运行(1,2)的输出结果是2,因此结果是5。而()只能用于执行函数,单独运行()会报错。
(function foo3(x){
console.log(arguments);
return x;
})(1,2,3,4,5);
what to output
function foo1(x){
console.log(arguments);
return x;
}
foo1(1,2,3,4,5);
function foo2(x){
console.log(arguments);
return x;
}();
(function foo3(x){
console.log(arguments);
return x;
})(1,2,3,4,5);
what to output
function Test(a, b, c){
var d = 0;
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
this.c = c;
function e(){
d++;
console.log(d);
}
this.f = e;
}
var t = new Test();
t.f();
t.f();
var t1 = new Test();
t1.f();
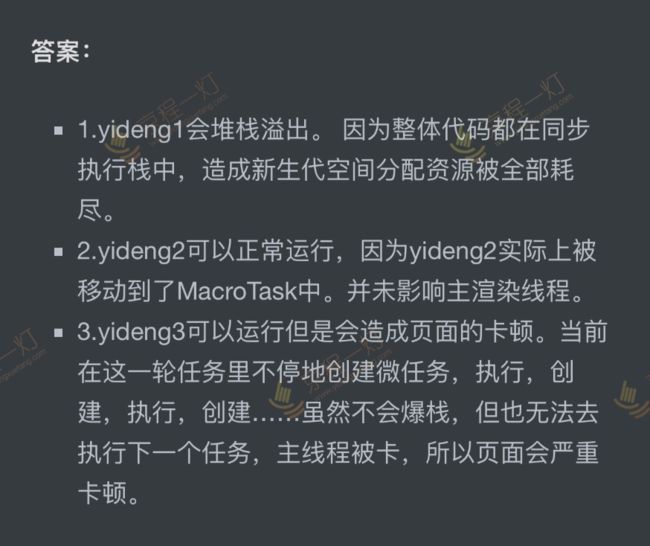
output: 1 2 1
what to output 如何让下面的结果输出0-9
function test(){
var arr = [];
for(var i = 0; i < 10; i++){
arr[i] = function(){
console.log(i);
}
}
return arr;
}
var arr = test();
for(var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
arr[i]();
}
-------------------------answer-----------------------
function test(){
var arr = [];
for(var i = 0; i < 10; i++){
arr[i] = (function(j){
return function(){
console.log(j)
}
})(i)
}
return arr;
}
var arr = test();
for(var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
arr[i]();
}
what is the correct output?
var arr = []
for(var i = 0; i < 10; i++){
arr[i] = function(){
console.log(i);
}
}
for(var i = 0; i < 10; i++){
arr[i]();
}
for(var k = 0; k < 10; k++){
arr[k]();
}
output: 前者:0-9 后者 10个10 解析原因是再次声明i的时候,会改变全局的i值,当运行arr[i]()时,拿到的是全局的i值
what is the correct output ?
function Test() { }
Test.prototype.name = 1;
var t = new Test();
Test.prototype.name = 2;
Test.prototype = {
name: 3
}
console.log(t.name);
output: 2 解析 t的原型对应的是一个引用值,而非Test.prototype。Test.prototype未被重新赋值前,t的原型和Test.prototype指向的是同一个引用值地址。
写一个isNaN功能的函数 考点 NaN + ""
function isNaN(num){
console.log(num);
var res = Number(num) + '';
if(res === 'NaN'){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
what is the correct output ? 考点 实参 形参映射
function test(a, b, c){
c = 2;
console.log(arguments[2]);
}
test(1, 2);
output: undefined 解析:arguments是和实参一一映射
what is the correct output? focus:this
var name = '111';
var a = {
name: '222',
fun: function(){
console.log(this.name);
}
}
var b = {
name: '333',
fun: function(fun){
fun();
}
}
var fun = a.fun;
fun();
a.fun();
b.fun(a.fun);
b.fun = a.fun;
b.fun();
output: 111 222 111 333 解析: 第三个输出结果为111的原因是:函数无论在哪定义,当其独立执行,而非对象调用的形式执行,其this指向则为window。如果是箭头函数,则为其所在环境;字面量对象不属于箭头函数的所在环境。
[] == ![] 和 {} == !{}的结果
[] == ![] true 解析 == 会将两边的原始值转为数字,由于右边使用了! 会将[]转为原始值,因此结果为true
[] == ![] false 解析 与上面同理 左边为'[object Object]',因此为false
what is the correct output? focus: call
function test(){
this.name = 'test';
}
test.prototype.print = function(){
console.log(this.name);
}
function test1(){
this.name = 'test1';
}
function test2(){
this.name = 'test2';
}
function test3(){
this.name = 'test3';
}
test.prototype.print.call(new test1());
test.prototype.print.apply(new test2());
test3.prototype = test.prototype;
var test3 = new test3();
test3.print();
var test = new test();
test.print();
what is the correct output?
function Foo(){
getName = function(){
console.log(1);
}
return this;
}
Foo.getName = function(){
console.log(2);
}
Foo.prototype.getName = function(){
console.log(3);
}
var getName = function(){
console.log(4);
}
function getName(){
console.log(5);
}
Foo.getName(); //-----------------------------------------------------------result:2 直接执行构造函数对象上的方法
getName(); //-----------------------------------------------------------result:4 由于变量提升的缘故,所以var getName被后赋值
Foo().getName(); //-----------------------------------------------------------result:1 函数执行后,函数体重的getName被挂载到全局,覆盖掉之前的getName
new Foo.getName(); //-----------------------------------------------------------result:2 “.”的优先级高于new,因此先执行Foo.getName()
new Foo().getName(); //-----------------------------------------------------------result:3 ()的优先级高度".",因此先执行 new Foo()
new new Foo().getName(); //-----------------------------------------------------------result:3 ()的优先级高于“.”,因此先执行 new Foo() 这里没有报错的原因是 最后一个new 执行的是 Foo.prototype.getName
what is the correct output?
function test( x = y, y = 2 ){
console.log(x, y);
}
what is the correct output?
console.log(typeof a);
let a;
focus this
var name = '222';
var a = {
name : '111',
say : function(){
console.log(this.name);
}
}
var fun = a.say;
fun();
a.say();
var b = {
name: '333',
say: function (fun){
fun();
}
}
b.say(a.say);
b.say = a.say;
b.say();
//result:222 111 222 333 函数也是一种引用值,除了对象.属性的方式外执行函数,都属于独立执行函数。
focus unique
- 编写一个方法,找出字符串中第一个不重复的字母
var str = "afdjaqskljwdsadseafkdja";
function unique (str) {
var obj = {};
for( var i = 0; i < str.length; i++ ) {
if(obj.hasOwnProperty(str[i])) {
obj[str[i]]++;
}else{
obj[str[i]] = 1;
}
}
for( var key in obj ) {
if(obj[key] === 1) {
return key;
}
}
}
focus function expression
var test = function a () {
console.log(a);
}
console.log(typeof(a)); //----------------------------------------------------------- 'undefined'
console.log(test.name); //----------------------------------------------------------- 'a'
test(); //----------------------------------------------------------- function a(){...}
console.log(a); //----------------------------------------------------------- 报错
focus array index
function week(day){
switch(day){
case 1:
console.log('Monday');
break;
case 2:
console.log('Tuesday');
break;
case 3:
console.log('Wednesday');
break;
case 4:
console.log('Thursday');
break;
case 5:
console.log('Friday');
break;
case 6:
console.log('Saturday');
break;
case 7:
console.log('Sunday');
break;
default:
console.log('please input the correct day');
}
}
- 将以上方法通过数组优化
function weekday(day){
var weeks = [ 'Monday', 'Tuesday', 'Wednesday', 'Thursday', 'Friday', 'Saturday', 'Sunday' ];
if(weeks[day-1]){
console.log(weeks[day - 1]);
}else{
console.log('please input correct day');
}
}
what's the correct output
function test(){ return 1; }
const t = new test();
console.log(t);
output: test(){} 解析:通过new 实例化构造函数时,如果函数返回的是原始值,则会通过this对原始值覆盖,如果返回的是引用值,则直接将引用值赋值给t。
write the code about formatNumber
const str = '1234567890';
function formatNumber(str){
// your code
}
console.log(formatNumber(str)); // 1,234,567,890
answer1: return parseInt(str).toLocaleString('en-US'); 解析:toLocaleString获取数字在特定语言下以字符串的表示形式
answer2: return new Intl.NumberFormat().format(str); 解析:Intl 是一个国际化命名空间,提供了 DateTimeFormat NumberFormat的构造函数作为其属性。
what's the correct output
function addToList(item, list){
return list.push(item);
}
const result = addToList('company', ['yideng']);
console.log(result);
output: 2 解析:push属于改变原数组的方法,它的返回值为数组的长度。pop返回的是最后一个被删除的值,unshift返回的是数组长度,shift返回的是第一个被删除的值。
what's the correct output
var A = function(){};
A.prototype = {};
var a = new A();
A.prototype = {};
var b = new A();
console.log(a instanceof A);
console.log(b instanceof A);
output: false true 解析 instanceof 是要检查 构造函数的原型属性 是否在实例化对象的原型链上,如果不存在则返回false。由于A的原型属性被重写了,所以最终A的原型属性不在a的原型链上了。所以结果是false true。
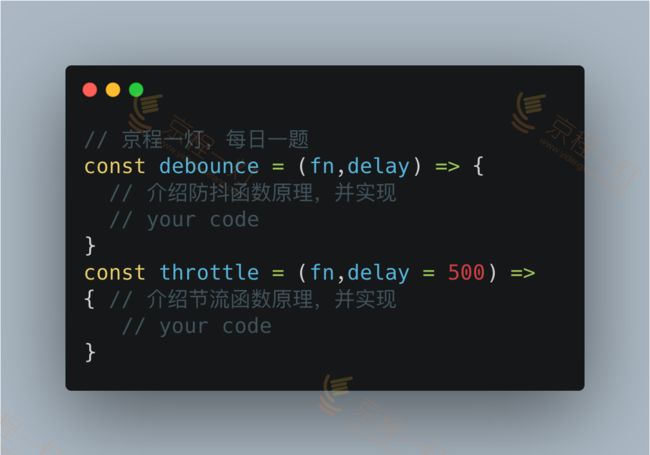
// 防抖函数解决的问题是:当一个事件在指定的时间内多次被触发时,只有最后一次生效。意味着一个函数,被多次重复调用时,只执行最后一次。
// 解题思路:利用定时器setTimeout回调要执行的函数,利用clearTimeout在setTimeout之前清除掉之前的定时器。
const debounce = (fn, delay) => {
let tid = null;
return function (...args) { // 此处不要用箭头函数,否则里面的this指向window
tid && clearTimeout(tid);
tid = setTimeout(() => {
fn.apply(this, delay);
}, 500);
}
}
// 节流:当同一个事件短时间内再次被触发时,依旧执行之前的事件。例如输入框、拖拽、动画等事件。
// 解题思路:通过setTimeout回调函数,时间未到时,不会再触发setTimeout
const throttle = (fn, delay) => {
let tId = null;
return function (...args) {
if(!tId){
setTimeout(() => {
fn.apply(this, args);
tId = null;
}, 500);
}
}
}
const throttle1 = (fn, delay) => {
let preTime = Date.now();
return function (...args) {
let nowTime = Date.now();
if( nowTime - preTime > delay ){
preTime = Date.now();
fn.apply(this, args);
}
}
}
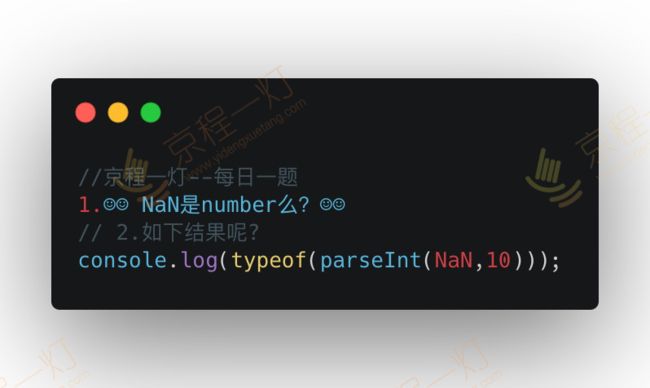
答案:number bumber 原因:parseInt(NaN, 10)结果依旧是NaN
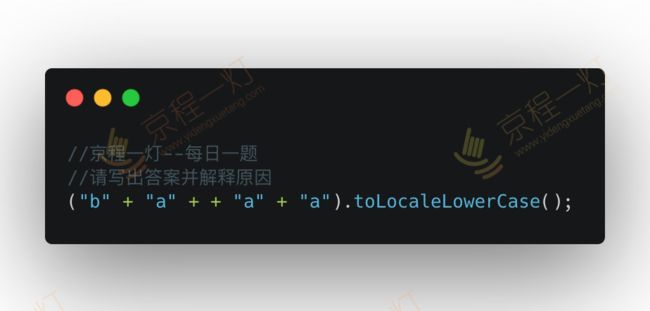
答案: banana 解析:+"a" 正"a"为NaN
答案:false false true
解析:null 除了和undefined及自己相当外 和其他的都不相当 所以第一个为false null进行比较运算时会经过Number转换 所以0 < 0 为false 0 <= 0为true
答案 : true true true false
解析:1. [] 和原始值比较时,会调用其toString方法[]tostring后为"" 所以为true
- 遇到!时,会变成false,"" == false 为true
- 字符串数字和数字比较时,会转成数字
-
"" == "0" 为false
解析:
返回值为iframe和frame的个数
foo的执行期上下文存储在全局中,所以在bar中运行foo时,foo里的length会去全局寻找length,而window.length为iframe的个数