如果我们的hashMap源码单纯的用数组实现,那么它们的增加和查找的时间复杂度为o(n),因为在增加的时候要遍历一次查询key是否存在,在查找的时候要遍历一次查找key。但是HashMap使用了散列表来存储数据,可以使得增加和查找的时间复杂度为o(1)。
散列表
数组的各个下标相当于一个个桶,通过hashCode(key)就可以拿到每个桶的下标,桶里面的数据用链表存储, 因此如果此时桶里只有一个链节点就只要o(1),有两个节点就只要o(2),一个桶装的链表节点太多还可以转换成红黑树。这就是散列表的好处。
源码分析
如下是我自己写的简易版的hashMap:
public class HashMapSample {
/**
* 散列表(桶)
*/
public MapEntry[] tables;
/**
*存放的个数
*/
transient int size;
/**
* 扩容阈值
*/
int threshold = 12;
/**
* 加载因子
*/
final float loadFactor = 0.75f;
public class MapEntry{
K key;
V value;
MapEntry next; //链表
int hash;
public MapEntry(int hash,K key,V value,MapEntry next){
this.hash=hash;
this.key=key;
this.value=value;
this.next=next;
}
}
private int getIndext(int hash,int length) {
//大小为2的幂次方,因为&操作符是:两个1为1,其他为0。2的幂次方-1的二进制全是1,可避免过度哈希冲突
return hash&length-1;
}
//哈希code得到哈希值
private int hash(K key) {
int h = 0;
return key==null?0:(h=key.hashCode()^(h>>>16));
//两对象hash相等,两个对象可能相等;两个对象hash不等,则俩对象一定不等
//原理: value>16,是对象的32位地址向右移了16位,剩下的16位可能相等
}
/**
* Get区域
* @param key
* @return
*/
public V get(K key){
if(key == null){
return null;
}
//判断有没有该key
MapEntry mapEntry =getEntry(key);
return mapEntry==null?null:mapEntry.value;
}
private MapEntry getEntry(K key) {
//判断同一个桶是否有这个key
int hash=hash(key);
int indext = getIndext(hash,tables.length);
for(MapEntry mapEntry = tables[indext];mapEntry!=null;mapEntry=mapEntry.next){
Object k;
if(mapEntry.hash == hash && ((k=mapEntry.key)==key || key.equals(k))){
return mapEntry;
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* Put区域
* @param key
* @param value
* @return
*/
public V put(K key,V value){
if(tables == null){
tables=new MapEntry[16];
}
if(key==null){
return null;
}
//1.找到table的位置
int hash = hash(key);
int index = getIndext(hash,tables.length);
//2.判断有没有重复key
for(MapEntry table = tables[index];table!=null;table=table.next){
Object k;
if(table.hash == hash && ((k=table.key)==key || key.equals(k))){
V oldValue = table.value;
table.value=value;
return oldValue;
}
}
//3.添加一个新的mapEntry
addEntry(hash,key,value,index);
return null;
}
/**
* 添加一个新的entry
* @param hash
* @param key
* @param value
* @param index
*/
private void addEntry(int hash,K key,V value,int index){
//判断要不要扩容
if(size>=threshold && tables[index] != null){
resize(size<<1);
//跟新添加的index
index = getIndext(hash,tables.length);
}
//真正的执行添加
createEntry(hash,key,value,index);
}
private void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int index) {
MapEntry newMapEntry = new MapEntry<>(hash,key,value,tables[index]);
newMapEntry.next=tables[index];
tables[index]=newMapEntry;
}
private void resize(int newCapacity) {
MapEntry[] newTable = new MapEntry[newCapacity];
//重新计算index
transform(newTable);
tables = newTable;
threshold =(int)(newCapacity*loadFactor);
}
private void transform(MapEntry[] newTable) {
//重新计算index
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (MapEntry e:tables){
//这里的节点会变成逆序排序,如1-2-3变成3-2-1
//在多线程执行时会造成死循环,如两个对象的next相互调用
while (null != e){
MapEntry next = e.next;
int index = getIndext(e.hash,newCapacity);
//先把newTable[index]的值存到e.next
e.next= newTable[index];
//把e存到第一个newTable[index]
newTable[index] = e;
//给e继续遍历旧table的链节点
e=next;
}
}
}
}
加载因子:为什么是0.75?不是1
因为:如果加载因子太小,就会导致太快的扩容(扩容要进行遍历一次重新计算index)。如果加载因子太大,比如100,就是导致散列表的每个桶存放太多的节点。为什么不是1,是因为用一个空间换时间的概念。
为什么hashMap的大小是2的幂次方
因为使用hash&length-1这个公式把得到的hash值&(求%)时2的幂次方-1的二进制全都是1,对哈希值的影响小。可避免过度的哈希碰撞。
hashcode的计算原理
利用对象的地址(32位),然后右移16位,即取后面的16位的二进制作为hash值。所以hash值相等,两对象可能不等;hash值不相等,两对象一定不相等。
初始化大小
hashMap的初始化的大小为16,因为扩容对性能比较消耗,所以我们在知道数据大小的情况下要尽量不扩容,我们可以手动初始化大小为:count*0.75+1
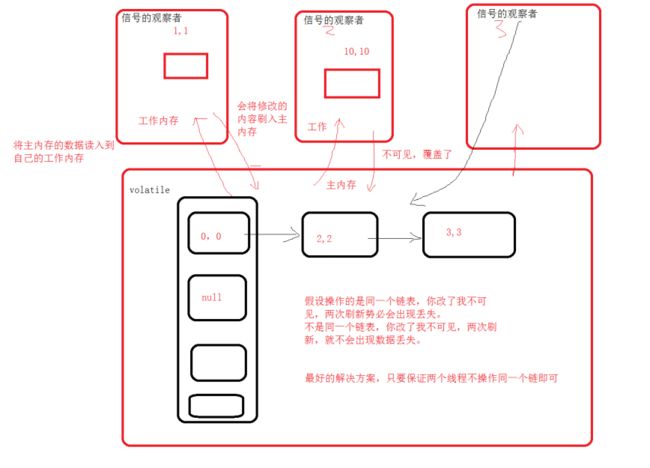
多线程下在hashMap中put导致的问题
数据丢失,死循环:每个子线程都有自己的工作内存,通过拷贝需要的部分在主内存的资源到子线程的工作内存,子线程修改好后就将资源更新到主内存。hashMap就在主内存,所以会造成子线程的获取资源的不同步。
1.死循环,在扩容时旧表的元素重新计算index时,多线程情况下,链节点可能会形成环,从而造成死循环。
2.多线程同时对同一链表增加数据,更新后可能会导致数据丢失,前面存储的数据被覆盖。不同链表的增加数据,更新后不会影响。
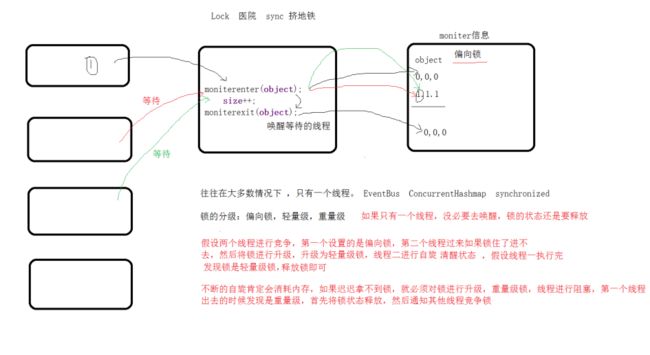
解决方案:1.hashTable、2.Collections.synchronizedMap() 3.ConcurrentHashMap :前两个方法都是锁住方法,conCurrentHashMap利用:分段锁 Lock , 分段锁 (synchronized,CAS)。
当put方法synchronized时,其他线程也不可以get()操作。
hashTable、ConcurrentHashMap的分析:
1.hashTable是将整个方法加上synchronized,整个方法锁住比较消耗性能,因为整个hash表都被锁住了,其他线程只能阻塞等待重新去抢资源。一个线程在 put 的时候,另外一个线程不能再 put 和 get 必须进入等待状态。
2.concurrentHashMap则是把需要改变的链表锁住,而不是把整个hash表锁住,其他线程的就可以访问hash表里未被锁住的链表。这样多线程就不会同时改动同一个链表造成数据丢失和死循环,也提高了性能。
concurrentHashMap源码:
// volatile 保证可见性
transient volatile Node[] table;
// 新增元素的方法
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
// 二次 hash
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
for (Node[] tab = table;;) {
Node f; int n, i, fh;
// 如果 tab 为空,初始化 tab
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0){
tab = initTable();
}
// 当前 tab 的 index 链表为 null
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null, new Node(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
V oldVal = null;
// 锁住当前 tab 的 index 链表(分段锁)
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
// ......
public V get(Object key) {
Node[] tab; Node e, p; int n, eh; K ek;
int h = spread(key.hashCode());
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
// CAS 操作
(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {
if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {
if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))
return e.val;
}
else if (eh < 0)
return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;
// 遍历当前列表
while ((e = e.next) != null) {
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))
return e.val;
}
}
return null;
}
synchronized 底层实现原理
// 1.对于普通同步方法,锁是当前实例对象。this
public synchronized void method(){
}
// 2.对于静态同步方法,锁是当前类的Class对象。this.class
public static synchronized void method(){
}
// 3.对于同步方法块,锁是Synchonized括号里配置的对象。object
public static synchronized void method(){
synchronized(object){
}
}
其实 synchronized 同步的代码块,虚拟机在同步代码块开始前会插入一条 monitorenter 指令,在代码块的末尾会插入一条 monitorexit 指令。而每个对象的 Mark Word 头信息里都会存储 Monitor 信息,也就是当前对象的锁信息,当然 Mark Word 头信息还包含对象的 hashCode 和 GC 的分代年龄
LinkedHashMap分析
hashMap不是一个有序的map,所以LinkedHashMap出现了。
hashMap用散列表"数组+单链表实现",LinedList用"双向链表实现"实现顺序存储数据。LinedHashMap就是用"hashMap+LinkedList"的散列表的双链回环实现。
小demo
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new LinkedHashMap();
map.put("apple", "苹果");
map.put("watermelon", "西瓜");
map.put("banana", "香蕉");
map.put("peach", "桃子");
Iterator iter = map.entrySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) iter.next();
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "=" + entry.getValue());
}
}
输出:
apple=苹果
watermelon=西瓜
banana=香蕉
peach=桃子
还可以再根据访问顺序再排序:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new LinkedHashMap(16,0.75f,true);
map.put("apple", "苹果");
map.put("watermelon", "西瓜");
map.put("banana", "香蕉");
map.put("peach", "桃子");
map.get("banana");
map.get("apple");
Iterator iter = map.entrySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) iter.next();
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "=" + entry.getValue());
}
}
输出:
watermelon=西瓜
peach=桃子
banana=香蕉
apple=苹果
LinkedHashMap源码实现
先总结:
- LinkedHashMap继承自HashMap,它的新增(put)和获取(get)方法都是复用父类的HashMap的代码,只是自己重写了put给get内部的某些接口来搞事情。
- LinkedHashMap的数据存储和HashMap的结构一样采用(数组+单向链表)的形式,只是在每次节点Entry中增加了用于维护顺序的before和after变量维护了一个双向链表来保存LinkedHashMap的存储顺序,当调用迭代器的时候不再使用HashMap的的迭代器,而是自己写迭代器来遍历这个双向链表即可。
第一:给entry加上befor,after这个前指针:
next是用于维护HashMap指定table位置上连接的Entry的顺序的,before、After是用于维护Entry插入的先后顺序的(为了维护双向链表)。
private static class Entry extends HashMap.Entry {
// These fields comprise the doubly linked list used for iteration.
Entry before;
Entry after;
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, HashMap.Entry next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
...
}
第二:初始化
public LinkedHashMap() {
super();
accessOrder = false; //LinkedHashMap特有的元素
}
public HashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
threshold = (int)(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY * DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
table = new Entry[DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY];
init(); //此方法LinkedHashMap进行了重写
}
void init() {
header = new Entry(-1, null, null, null);
header.before = header.after = header;
}
可以看到header就是我们双链表的表头。
LinkedHashMap添加元素
HashMap的put方法:
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
////1.找到table的位置
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
//查看是否有相同的Key
for (Entry e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
//没有相同的key
modCount++;
//这个方法先检查要不要扩容,再添加entry
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
void recordAccess(HashMap m) {
LinkedHashMap lm = (LinkedHashMap)m;
//设置accessOrder为true才执行,重排序
if (lm.accessOrder) {
lm.modCount++;
remove();
addBefore(lm.header);
}
}
private void remove() {
//如果这个entry没有前后节点则不执行。
this.before.after = after;
this.after.before = before;
}
private void addBefore(Entry existingEntry) {
//表头
after = existingEntry;
//通过双向链表的表头找到最后一个元素
before = existingEntry.before;
before.after = this; //把最新的元素排到最后
after.before = this; //更新表头的前指针
}
LinkedHashMap中重写了addEntry
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
// Remove eldest entry if instructed, else grow capacity if appropriate
Entry eldest = header.after;
if (removeEldestEntry(eldest)) {
removeEntryForKey(eldest.key);
} else {
if (size >= threshold)
resize(2 * table.length);
}
}
void createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
// Remove eldest entry if instructed, else grow capacity if appropriate
Entry eldest = header.after;
if (removeEldestEntry(eldest)) {
removeEntryForKey(eldest.key);
} else {
if (size >= threshold)
resize(2 * table.length);
}
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
HashMap.Entry old = table[bucketIndex];
Entry e = new Entry(hash, key, value, old);
table[bucketIndex] = e;
e.addBefore(header);
size++;
}
get方法
public V get(Object key) {
Entry e = (Entry)getEntry(key);
if (e == null)
return null;
e.recordAccess(this);
return e.value;
}
3. 利用LinkedHashMap实现LRU缓存
就是利用LinedHashMap把accessOrder设置为ture,在(put/get)重排序双链表,这样表头就是"最近最少使用数据"即LRU
LinkedHashMap的删除头结点的方法:
void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { // possibly remove eldest
LinkedHashMap.Entry first;
if (evict && (first = head) != null && removeEldestEntry(first)) {
K key = first.key;
removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true);
}
}
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(java.util.Map.Entry var1) {
return false; //默认实现空
}
简易版的lru
public class LRUCache extends LinkedHashMap
{
public LRUCache(int maxSize)
{
super(maxSize, 0.75F, true);
maxElements = maxSize;
}
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(java.util.Map.Entry eldest)
{
//逻辑很简单,当大小超出了Map的容量,就移除掉双向队列头部的元素,给其他元素腾出点地来。
return size() > maxElements;
}
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
protected int maxElements;
}