前言
NestedScrolling 是Andorid 5.0推出的一个嵌套滑动机制,主要是利用 NestedScrollingParent 和 NestedScrollingChild 让父View和子View在滚动时互相协调配合,极大的方便了我们对于嵌套滑动的处理。通过 NestedScrolling 我们可以很简单的实现类似知乎首页,QQ空间首页等非常漂亮的交互效果。
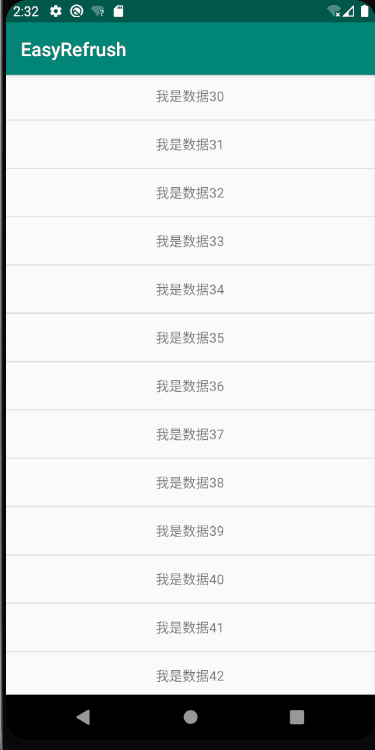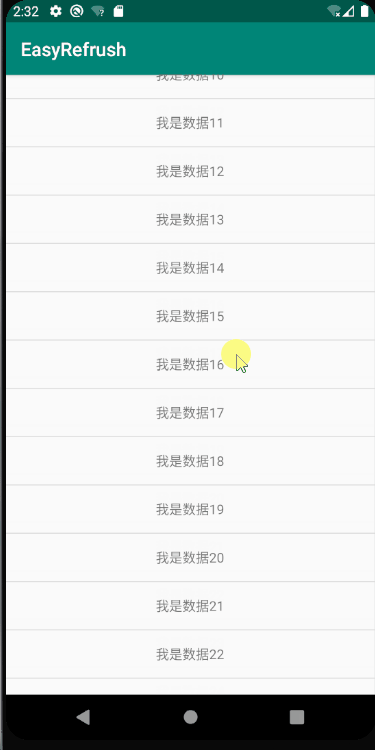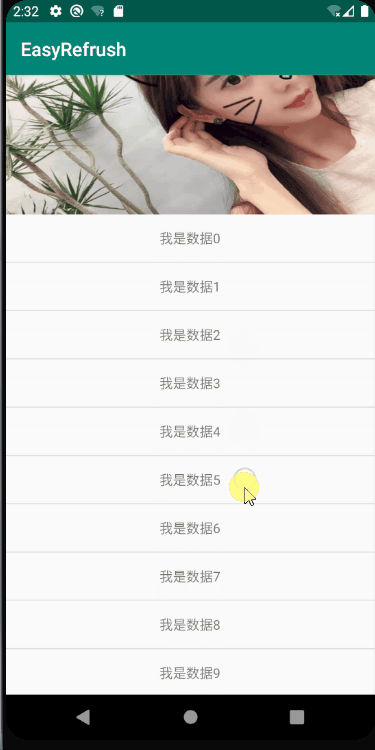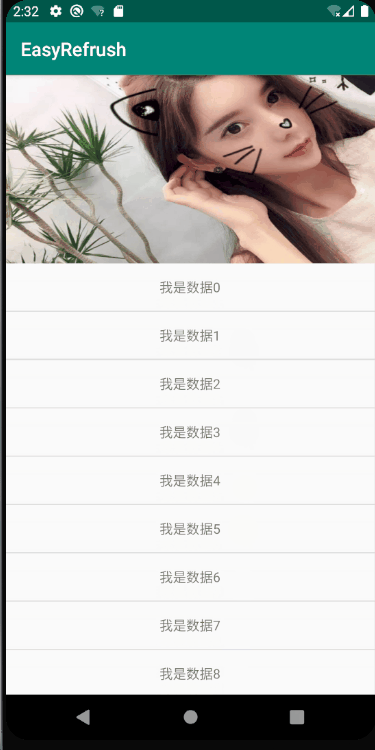
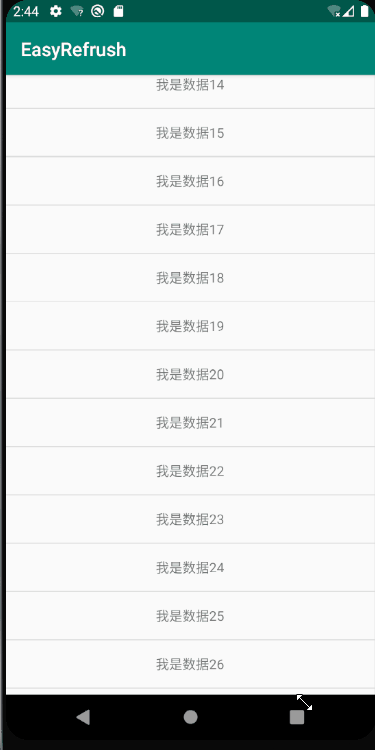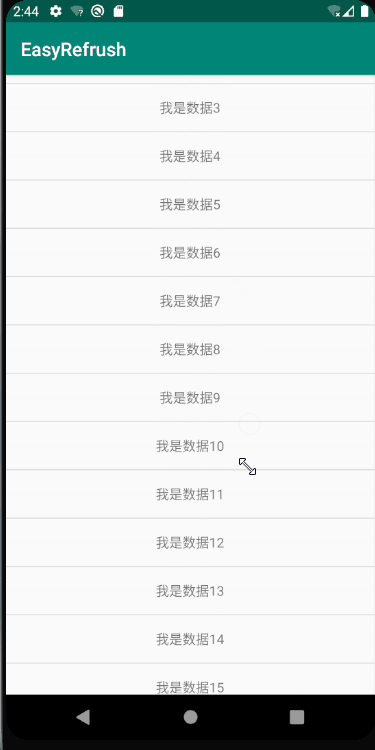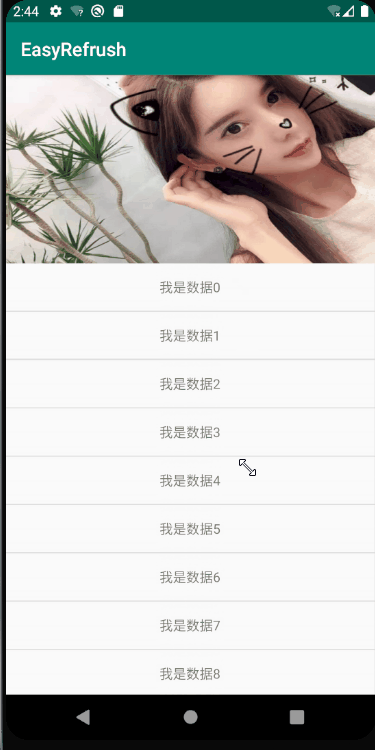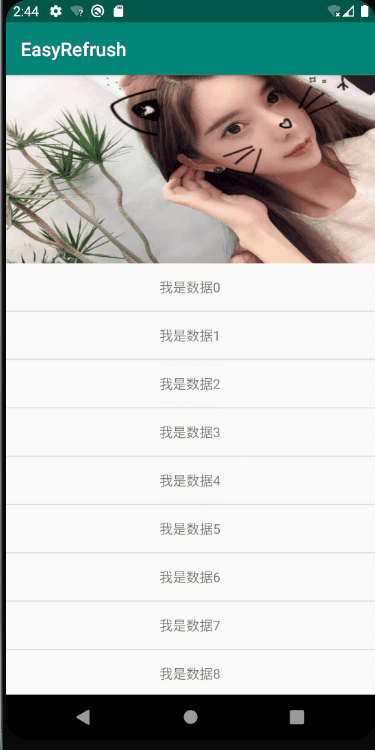
但是有一个问题,对于fling的传递,NestedScrolling的处理并不友好,child只是简单粗暴的将fling结果抛给parent。对于fling,要么child处理,要么parent处理。当我们想要先由child处理一部分,剩余的再交个parent来处理的时候,就显得比较乏力了;
老规矩,直接上图:
很明显,列表处理了fling,在滑动到顶端的时候就停下来了,需要在再次触摸滑动,才能显示出顶部的图片;这种情况下,如果和UI进行斗智斗勇,我们是必败无疑。
不过,在Andorid 8.0 ,google爸爸应该也了解到了这种情况,推出了一个升级版本 NestedScrollingParent2 和 NestedScrollingChild2 ,友好的处理了fling的分配问题,可以实现非常丝滑柔顺的滑动效果,直接看图:
在这个版本中,列表在消耗fling之后滑动到第一个item之后,将剩余的fling交个parent来处理,滑动出顶部的图片,整个流程非常流程,没有任何卡顿;接下来本文将详细的剖析一下NestedScrollingParent2 和 NestedScrollingChild2 的工作原理;
正文
NestedScrollingParent 和 NestedScrollingChild 已经有很多的教程,大家可以自行学习,本片文章主要对 NestedScrollingParent2 和 NestedScrollingChild2 进行分析;
1、先了解API
- NestedScrollingParent2
public interface NestedScrollingParent2 extends NestedScrollingParent {
/**
* 即将开始嵌套滑动,此时嵌套滑动尚未开始,由子控件的 startNestedScroll 方法调用
*
* @param child 嵌套滑动对应的父类的子类(因为嵌套滑动对于的父控件不一定是一级就能找到的,可能挑了两级父控件的父控件,child的辈分>=target)
* @param target 具体嵌套滑动的那个子类
* @param axes 嵌套滑动支持的滚动方向
* @param type 嵌套滑动的类型,有两种ViewCompat.TYPE_NON_TOUCH fling效果,ViewCompat.TYPE_TOUCH 手势滑动
* @return true 表示此父类开始接受嵌套滑动,只有true时候,才会执行下面的 onNestedScrollAccepted 等操作
*/
boolean onStartNestedScroll(@NonNull View child, @NonNull View target, @ScrollAxis int axes,
@NestedScrollType int type);
/**
* 当onStartNestedScroll返回为true时,也就是父控件接受嵌套滑动时,该方法才会调用
*
* @param child
* @param target
* @param axes
* @param type
*/
void onNestedScrollAccepted(@NonNull View child, @NonNull View target, @ScrollAxis int axes,
@NestedScrollType int type);
/**
* 在子控件开始滑动之前,会先调用父控件的此方法,由父控件先消耗一部分滑动距离,并且将消耗的距离存在consumed中,传递给子控件
* 在嵌套滑动的子View未滑动之前
* ,判断父view是否优先与子view处理(也就是父view可以先消耗,然后给子view消耗)
*
* @param target 具体嵌套滑动的那个子类
* @param dx 水平方向嵌套滑动的子View想要变化的距离
* @param dy 垂直方向嵌套滑动的子View想要变化的距离 dy<0向下滑动 dy>0 向上滑动
* @param consumed 这个参数要我们在实现这个函数的时候指定,回头告诉子View当前父View消耗的距离
* consumed[0] 水平消耗的距离,consumed[1] 垂直消耗的距离 好让子view做出相应的调整
* @param type 滑动类型,ViewCompat.TYPE_NON_TOUCH fling效果,ViewCompat.TYPE_TOUCH 手势滑动
*/
void onNestedPreScroll(@NonNull View target, int dx, int dy, @NonNull int[] consumed,
@NestedScrollType int type);
/**
* 在 onNestedPreScroll 中,父控件消耗一部分距离之后,剩余的再次给子控件,
* 子控件消耗之后,如果还有剩余,则把剩余的再次还给父控件
*
* @param target 具体嵌套滑动的那个子类
* @param dxConsumed 水平方向嵌套滑动的子控件滑动的距离(消耗的距离)
* @param dyConsumed 垂直方向嵌套滑动的子控件滑动的距离(消耗的距离)
* @param dxUnconsumed 水平方向嵌套滑动的子控件未滑动的距离(未消耗的距离)
* @param dyUnconsumed 垂直方向嵌套滑动的子控件未滑动的距离(未消耗的距离)
* @param type 滑动类型,ViewCompat.TYPE_NON_TOUCH fling效果,ViewCompat.TYPE_TOUCH 手势滑动
*/
void onNestedScroll(@NonNull View target, int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed,
int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed, @NestedScrollType int type);
/**
* 停止滑动
*
* @param target
* @param type 滑动类型,ViewCompat.TYPE_NON_TOUCH fling效果,ViewCompat.TYPE_TOUCH 手势滑动
*/
void onStopNestedScroll(@NonNull View target, @NestedScrollType int type);
}
- NestedScrollingParent2
public interface NestedScrollingChild2 extends NestedScrollingChild {
/**
* 开始滑动前调用,在惯性滑动和触摸滑动前都会进行调用,此方法一般在 onInterceptTouchEvent或者onTouch中,通知父类方法开始滑动
* 会调用父类方法的 onStartNestedScroll onNestedScrollAccepted 两个方法
*
* @param axes 滑动方向
* @param type 开始滑动的类型 the type of input which cause this scroll event
* @return 有父视图并且开始滑动,则返回true 实际上就是看parent的 onStartNestedScroll 方法
*/
boolean startNestedScroll(@ScrollAxis int axes, @NestedScrollType int type);
/**
* 子控件停止滑动,例如手指抬起,惯性滑动结束
*
* @param type 停止滑动的类型 TYPE_TOUCH,TYPE_NON_TOUCH
*/
void stopNestedScroll(@NestedScrollType int type);
/**
* 判断是否有父View 支持嵌套滑动
*/
boolean hasNestedScrollingParent(@NestedScrollType int type);
/**
* 在dispatchNestedPreScroll 之后进行调用
* 当滑动的距离父控件消耗后,父控件将剩余的距离再次交个子控件,
* 子控件再次消耗部分距离后,又继续将剩余的距离分发给父控件,由父控件判断是否消耗剩下的距离。
* 如果四个消耗的距离都是0,则表示没有神可以消耗的了,会直接返回false,否则会调用父控件的
* onNestedScroll 方法,父控件继续消耗剩余的距离
* 会调用父控件的
*
* @param dxConsumed 水平方向嵌套滑动的子控件滑动的距离(消耗的距离) dx<0 向右滑动 dx>0 向左滑动 (保持和 RecycleView 一致)
* @param dyConsumed 垂直方向嵌套滑动的子控件滑动的距离(消耗的距离) dy<0 向下滑动 dy>0 向上滑动 (保持和 RecycleView 一致)
* @param dxUnconsumed 水平方向嵌套滑动的子控件未滑动的距离(未消耗的距离)dx<0 向右滑动 dx>0 向左滑动 (保持和 RecycleView 一致)
* @param dyUnconsumed 垂直方向嵌套滑动的子控件未滑动的距离(未消耗的距离)dy<0 向下滑动 dy>0 向上滑动 (保持和 RecycleView 一致)
* @param offsetInWindow 子控件在当前window的偏移量
* @return 如果返回true, 表示父控件又继续消耗了
*/
boolean dispatchNestedScroll(int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed,
int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed, @Nullable int[] offsetInWindow,
@NestedScrollType int type);
/**
* 子控件在开始滑动前,通知父控件开始滑动,同时由父控件先消耗滑动时间
* 在子View的onInterceptTouchEvent或者onTouch中,调用该方法通知父View滑动的距离
* 最终会调用父view的 onNestedPreScroll 方法
*
* @param dx 水平方向嵌套滑动的子控件想要变化的距离 dx<0 向右滑动 dx>0 向左滑动 (保持和 RecycleView 一致)
* @param dy 垂直方向嵌套滑动的子控件想要变化的距离 dy<0 向下滑动 dy>0 向上滑动 (保持和 RecycleView 一致)
* @param consumed 父控件消耗的距离,父控件消耗完成之后,剩余的才会给子控件,子控件需要使用consumed来进行实际滑动距离的处理
* @param offsetInWindow 子控件在当前window的偏移量
* @param type 滑动类型,ViewCompat.TYPE_NON_TOUCH fling效果,ViewCompat.TYPE_TOUCH 手势滑动
* @return true 表示父控件进行了滑动消耗,需要处理 consumed 的值,false表示父控件不对滑动距离进行消耗,可以不考虑consumed数据的处理,此时consumed中两个数据都应该为0
*/
boolean dispatchNestedPreScroll(int dx, int dy, @Nullable int[] consumed,
@Nullable int[] offsetInWindow, @NestedScrollType int type);
}
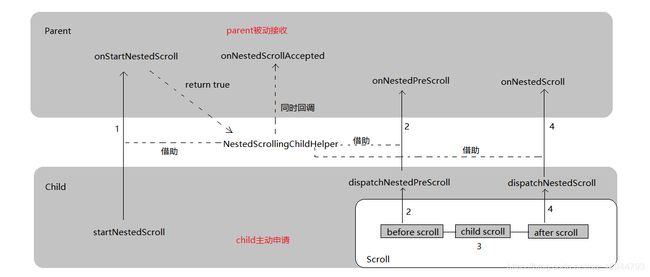
- 调用流程
上面的API我已经做了很详细的注释,应该不难理解,梳理下拉,大概流程就是:
一般情况下,事件是从child的触摸事件开始的,
首先调用child.startNestedScroll()方法,此方法内部通过 NestedScrollingChildHelper 调用并返回parent.onStartNestedScroll()方法的结果,为true,说明parent接受了嵌套滑动,同时调用了parent.onNestedScrollAccepted()方法,此时开始嵌套滑动;
在滑动事件中,child通过child.dispatchNestedPreScroll()方法分配滑动的距离,child.dispatchNestedPreScroll()内部会先调用parent.onNestedPreScroll()方法,由parent先处理滑动距离。
parent消耗完成之后,再将剩余的距离传递给child,child拿到parent使用完成之后的距离之后,自己再处理剩余的距离。
如果此时子控件还有未处理的距离,则将剩余的距离再次通过 child.dispatchNestedScroll()方法调用parent.onNestedScroll()方法,将剩余的距离交个parent来进行处理
滑动结束之后,调用 child.stopNestedScroll()通知parent滑动结束,至此,触摸滑动结束
触摸滑动结束之后,child会继续进行惯性滑动,惯性滑动可以通过 Scroller 实现,具体滑动可以自己来处理,在fling过程中,和触摸滑动调用流程一样,需要注意type参数的区分,用来通知parent两种不同的滑动流程
至此, NestedScrollingParent2 和 NestedScrollingChild2 的流程和主要方法已经很清晰了;但是没有仅仅看到这里应该还有比较难以理解,毕竟没有代码的API和耍流氓没什么区别,接下来,还是上源码;
2、通过RecycleView学习 NestedScrollingChild2
没有什么知识点是从源码里获取不到的,RecycleView是我们最常用的列表组件,同时也是嵌套滑动需求最多的组件,它本身也实现了 NestedScrollingChild2 ,这里就以此为例进行分析;
1、 RecycleView中的 NestedScrollingChild2
首先,我们先找到RecycleView中的 NestedScrollingChild2 的方法;
@Override
public boolean startNestedScroll(int axes, int type) {
return getScrollingChildHelper().startNestedScroll(axes, type);
}
@Override
public void stopNestedScroll(int type) {
getScrollingChildHelper().stopNestedScroll(type);
}
@Override
public boolean hasNestedScrollingParent(int type) {
return getScrollingChildHelper().hasNestedScrollingParent(type);
}
@Override
public boolean dispatchNestedScroll(int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed, int dxUnconsumed,
int dyUnconsumed, int[] offsetInWindow, int type) {
return getScrollingChildHelper().dispatchNestedScroll(dxConsumed, dyConsumed,
dxUnconsumed, dyUnconsumed, offsetInWindow, type);
}
@Override
public boolean dispatchNestedPreScroll(int dx, int dy, int[] consumed, int[] offsetInWindow,
int type) {
return getScrollingChildHelper().dispatchNestedPreScroll(dx, dy, consumed, offsetInWindow,
type);
}
private NestedScrollingChildHelper getScrollingChildHelper() {
if (mScrollingChildHelper == null) {
mScrollingChildHelper = new NestedScrollingChildHelper(this);
}
return mScrollingChildHelper;
}
从上面可以看到,RecycleView 本身并没有去处理 NestedScrollingChild2 方法,而是交给 NestedScrollingChildHelper 方法进行处理,NestedScrollingChildHelper 主要作用是和 parent 之间进行一些数据的传递处理,逻辑比较简单,篇幅有限,就不详细叙述了。
2、 NestedScrollingChild2在 RecycleView 触摸滑动过程的逻辑
RecycleView 源码本身非常复杂,为了便于理解这里我剔除掉一些与本次逻辑无关的代码,根据上面的逻辑逻辑,首先找到 startNestedScroll()方法,并以此开始一步步的跟进:
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent e) {
// ... 此处剔除了部分和嵌套滑动关系不大的逻辑
switch (action) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: {
mLastTouchX = (int) (e.getX() + 0.5f);
mLastTouchY = (int) (e.getY() + 0.5f);
//此处开始进行嵌套滑动
startNestedScroll(nestedScrollAxis, TYPE_TOUCH);
} break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: {
//省略部分无关逻辑
int dx = mLastTouchX - x;
int dy = mLastTouchY - y;
//在开始滑动前,将手指一动距离交个parent处理
if (dispatchNestedPreScroll(dx, dy, mScrollConsumed, mScrollOffset, TYPE_TOUCH)) {
//如果parent 消耗掉部分距离,此处进行处理
dx -= mScrollConsumed[0];
dy -= mScrollConsumed[1];
}
//省略RecycleView 本身的滑动逻辑
//......
//scrollByInternal()本质调用的还是 dispatchNestedScroll()方法,在父控件消耗完成之后,且自己也消耗之后,将剩余的距离再次交个父控件处理
scrollByInternal(
canScrollHorizontally ? dx : 0,
canScrollVertically ? dy : 0,
vtev);
} break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: {
//省略速度计算相关代码
// ....
fling((int) xvel, (int) yvel);
resetTouch();
} break;
}
return true;
}
去除掉不相关的逻辑之后,触摸事件就变得非常简单明晰
1. MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN 中,开始滑动,调用child.startNestedScroll()方法
2. MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE 中,调用 dispatchNestedPreScroll()和dispatchNestedScroll()方法
从源码中可以看到,在 MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE 中,首先调用了 dispatchNestedPreScroll()方法,如果返回true,表示父控件消耗了部分距离,此时 RecycleView 调用了两行代码
dx -= mScrollConsumed[0];
dy -= mScrollConsumed[1];
在父控件消耗这段距离这会,RecycleView也相应的减少了这部分的滑动距离;
在RecycleView处理完成滑动之后,如果还有剩余的距离,则调用dispatchNestedScroll(),将剩余的距离再次交给parent处理;
3.MotionEvent.ACTION_UP 中开启惯性滑动,同时调用 stopNestedScroll()通知停止触摸滑动
ACTION_UP 事件中,主要调用了 fling((int) xvel, (int) yvel)和 resetTouch();fling开始进行惯性滑动,而resetTouch()源码如下,主要通知调用stopNestedScroll()方法,通知父控件停止触摸滑动
private void resetTouch() {
if (mVelocityTracker != null) {
mVelocityTracker.clear();
}
stopNestedScroll(TYPE_TOUCH);
releaseGlows();
}
至此RecycleView在嵌套互动过程中的触摸滑动已经完成,同时也开始了fling滑动
3、NestedScrollingChild2 在 RecycleView 惯性滑动过程的逻辑
在上一小节中,MotionEvent.ACTION_UP 事件已经出发了 fling((int) xvel, (int) yvel) 方法,并且开始惯性滑动,这里就从fling()方法开始,理解NestedScrollingChild2 在惯性滑动时候的逻辑处理:
1.开始惯性滑动,调用 startNestedScroll()方法
老规矩,先剔除掉一些不相干代码,可以看到,
public boolean fling(int velocityX, int velocityY) {
//... 剔除掉部分不相干的代码
startNestedScroll(nestedScrollAxis, TYPE_NON_TOUCH);
velocityX = Math.max(-mMaxFlingVelocity, Math.min(velocityX, mMaxFlingVelocity));
velocityY = Math.max(-mMaxFlingVelocity, Math.min(velocityY, mMaxFlingVelocity));
mViewFlinger.fling(velocityX, velocityY);
return true;
}
可以看到,fling()方法实质上仅仅做了两件事
- 调用 startNestedScroll(nestedScrollAxis, TYPE_NON_TOUCH) 通知 parent 开始惯性滑动。注意第二个参数TYPE_NON_TOUCH,和触摸滑动时候的 TYPE_TOUCH 区别开,是父控件区分滑动状态的重要参数
- 开始惯性滑动
2.开始惯性滑动后的逻辑处理
在开始惯性滑动之后,我们来看一下fling过程中的逻辑处理,代码主要在 ViewFlinger 的run()方法中,我们去除掉一些并不重要的代码之后,得到下面的伪代码:
public void run() {
final OverScroller scroller = mScroller;
final SmoothScroller smoothScroller = mLayout.mSmoothScroller;
//开始惯性滑动前,先将数据交个父控件处理
if (dispatchNestedPreScroll(dx, dy, scrollConsumed, null, TYPE_NON_TOUCH)) {
//处理被父控件消耗掉的
dx -= scrollConsumed[0];
dy -= scrollConsumed[1];
}
//... 省略RecycleView本身惯性滑动逻辑处理
//将剩余的距离交个父控件进行处理
if (!dispatchNestedScroll(hresult, vresult, overscrollX, overscrollY, null,
TYPE_NON_TOUCH)
&& (overscrollX != 0 || overscrollY != 0)) {
}
//处理完成之后,通知父控件此次惯性滑动结束
stopNestedScroll(TYPE_NON_TOUCH);
}
惯性滑动的过程和触摸滑动非常相似,虽然仅仅加了一个参数,但是已经将惯性滑动的数据传递给了父控件,非常简单的完成了整个流程的处理,不得不说,google爸爸永远是google爸爸;
到此为止,我们已经完整的分析了RecycleView作为child的逻辑流程,相信对于 NestedScrollingChild2 也已经有了一个初步的了解;
NestedScrollingParent2 相对来说比较简单,这里就不进行详细的分析了,只要根据 NestedScrollingChild2 传来的数据,进行处理就好了
3、实战,自己写一个完整的嵌套滑动
光说不练都是假把式,在已经初步了解RecycleView的流程的情况下,自己写一个小小的Demo,实现开头的效果,直接上代码:
1、NestedScrollingParent2Layout 继承NestedScrollingParent2 实现parent 代码逻辑
使用这个代码直接包裹RecycleView和一个ImageView就可以直接实现开头的效果了
package com.sang.refrush;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
import androidx.annotation.NonNull;
import androidx.annotation.Nullable;
import androidx.core.view.NestedScrollingParent2;
import androidx.core.view.NestedScrollingParentHelper;
import androidx.core.view.ViewCompat;
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView;
import com.sang.refrush.utils.FRLog;
/**
* Description:NestedScrolling2机制下的嵌套滑动,实现NestedScrollingParent2接口下,处理fling效果的区别
*/
public class NestedScrollingParent2Layout extends LinearLayout implements NestedScrollingParent2 {
private View mTopView;
private View mContentView;
private View mBottomView;
private int mTopViewHeight;
private int mGap;
private int mBottomViewHeight;
private NestedScrollingParentHelper mNestedScrollingParentHelper = new NestedScrollingParentHelper(this);
public NestedScrollingParent2Layout(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public NestedScrollingParent2Layout(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public NestedScrollingParent2Layout(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
setOrientation(VERTICAL);
}
/**
* 即将开始嵌套滑动,此时嵌套滑动尚未开始,由子控件的 startNestedScroll 方法调用
*
* @param child 嵌套滑动对应的父类的子类(因为嵌套滑动对于的父控件不一定是一级就能找到的,可能挑了两级父控件的父控件,child的辈分>=target)
* @param target 具体嵌套滑动的那个子类
* @param axes 嵌套滑动支持的滚动方向
* @param type 嵌套滑动的类型,有两种ViewCompat.TYPE_NON_TOUCH fling效果,ViewCompat.TYPE_TOUCH 手势滑动
* @return true 表示此父类开始接受嵌套滑动,只有true时候,才会执行下面的 onNestedScrollAccepted 等操作
*/
@Override
public boolean onStartNestedScroll(@NonNull View child, @NonNull View target, int axes, int type) {
if (mContentView != null && mContentView instanceof RecyclerView) {
((RecyclerView) mContentView).stopScroll();
}
mTopView.stopNestedScroll();
return (axes & ViewCompat.SCROLL_AXIS_VERTICAL) != 0;
}
/**
* 当onStartNestedScroll返回为true时,也就是父控件接受嵌套滑动时,该方法才会调用
*
* @param child
* @param target
* @param axes
* @param type
*/
@Override
public void onNestedScrollAccepted(@NonNull View child, @NonNull View target, int axes, int type) {
mNestedScrollingParentHelper.onNestedScrollAccepted(child, target, axes, type);
}
/**
* 在子控件开始滑动之前,会先调用父控件的此方法,由父控件先消耗一部分滑动距离,并且将消耗的距离存在consumed中,传递给子控件
* 在嵌套滑动的子View未滑动之前
* ,判断父view是否优先与子view处理(也就是父view可以先消耗,然后给子view消耗)
*
* @param target 具体嵌套滑动的那个子类
* @param dx 水平方向嵌套滑动的子View想要变化的距离
* @param dy 垂直方向嵌套滑动的子View想要变化的距离 dy<0向下滑动 dy>0 向上滑动
* @param consumed 这个参数要我们在实现这个函数的时候指定,回头告诉子View当前父View消耗的距离
* consumed[0] 水平消耗的距离,consumed[1] 垂直消耗的距离 好让子view做出相应的调整
* @param type 滑动类型,ViewCompat.TYPE_NON_TOUCH fling效果,ViewCompat.TYPE_TOUCH 手势滑动
*/
@Override
public void onNestedPreScroll(@NonNull View target, int dx, int dy, @NonNull int[] consumed, int type) {
//这里不管手势滚动还是fling都处理
boolean hideTop = dy > 0 && getScrollY() < mTopViewHeight ;
boolean showTop = dy < 0
&& getScrollY() >= 0
&& !target.canScrollVertically(-1)
&& !mContentView.canScrollVertically(-1)
&&target!=mBottomView
;
boolean cunsumedTop = hideTop || showTop;
//对于底部布局
boolean hideBottom = dy < 0 && getScrollY() > mTopViewHeight;
boolean showBottom = dy > 0
&& getScrollY() >= mTopViewHeight
&& !target.canScrollVertically(1)
&& !mContentView.canScrollVertically(1)
&&target!=mTopView
;
boolean cunsumedBottom = hideBottom || showBottom;
if (cunsumedTop) {
scrollBy(0, dy);
consumed[1] = dy;
} else if (cunsumedBottom) {
scrollBy(0, dy);
consumed[1] = dy;
}
}
/**
* 在 onNestedPreScroll 中,父控件消耗一部分距离之后,剩余的再次给子控件,
* 子控件消耗之后,如果还有剩余,则把剩余的再次还给父控件
*
* @param target 具体嵌套滑动的那个子类
* @param dxConsumed 水平方向嵌套滑动的子控件滑动的距离(消耗的距离)
* @param dyConsumed 垂直方向嵌套滑动的子控件滑动的距离(消耗的距离)
* @param dxUnconsumed 水平方向嵌套滑动的子控件未滑动的距离(未消耗的距离)
* @param dyUnconsumed 垂直方向嵌套滑动的子控件未滑动的距离(未消耗的距离)
*/
@Override
public void onNestedScroll(@NonNull View target, int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed, int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed, int type) {
if (dyUnconsumed<0){
//对于向下滑动
if (target == mBottomView){
mContentView.scrollBy(0, dyUnconsumed);
}
}else {
if (target == mTopView){
mContentView.scrollBy(0, dyUnconsumed);
}
}
}
/**
* 停止滑动
*
* @param target
* @param type
*/
@Override
public void onStopNestedScroll(@NonNull View target, int type) {
if (type == ViewCompat.TYPE_NON_TOUCH) {
System.out.println("onStopNestedScroll");
}
mNestedScrollingParentHelper.onStopNestedScroll(target, type);
}
@Override
public int getNestedScrollAxes() {
return mNestedScrollingParentHelper.getNestedScrollAxes();
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//ViewPager修改后的高度= 总高度-导航栏高度
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
ViewGroup.LayoutParams layoutParams = mContentView.getLayoutParams();
layoutParams.height = getMeasuredHeight();
mContentView.setLayoutParams(layoutParams);
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
@Override
protected void onFinishInflate() {
super.onFinishInflate();
if (getChildCount() > 0) {
mTopView = getChildAt(0);
}
if (getChildCount() > 1) {
mContentView = getChildAt(1);
}
if (getChildCount() > 2) {
mBottomView = getChildAt(2);
}
}
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
if (mTopView != null) {
mTopViewHeight = mTopView.getMeasuredHeight() ;
}
if (mBottomView != null) {
mBottomViewHeight = mBottomView.getMeasuredHeight();
}
}
@Override
public void scrollTo(int x, int y) {
FRLog.d("scrollTo:" + y);
if (y < 0) {
y = 0;
}
//对滑动距离进行修正
if (mContentView.canScrollVertically(1)) {
//可以向上滑栋
if (y > mTopViewHeight) {
y = mTopViewHeight-mGap;
}
} else if ((mContentView.canScrollVertically(-1))) {
if (y < mTopViewHeight) {
y = mTopViewHeight+mGap ;
}
}
if (y > mTopViewHeight + mBottomViewHeight) {
y = mTopViewHeight + mBottomViewHeight;
}
super.scrollTo(x, y);
}
}
2、NestedScrollingChild2View 继承 NestedScrollingChild2 实现 child 代码逻辑
当然,仅仅使用parent ,我们会发现顶部图片并不具备滑动功能,有时候我我们也需要顶部布局拥有触摸滑动和惯性滑动事件,还好,RecycleView 的源码我们已经学习过了,照葫芦画瓢,我们也来实现以下child的代码吧;代码逻辑先相对来说复杂一些,我已经尽可能的进行了详细的注释,应该很容易理解,重点请关注onTouchEvent() 和惯性滑动的代码
public class NestedScrollingChild2View extends LinearLayout implements NestedScrollingChild2 {
private NestedScrollingChildHelper mScrollingChildHelper = new NestedScrollingChildHelper(this);
private final int mMinFlingVelocity;
private final int mMaxFlingVelocity;
private Scroller mScroller;
private int lastY = -1;
private int lastX = -1;
private int[] offset = new int[2];
private int[] consumed = new int[2];
private int mOrientation;
private boolean fling;//判断当前是否是可以进行惯性滑动
public NestedScrollingChild2View(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public NestedScrollingChild2View(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public NestedScrollingChild2View(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
setOrientation(VERTICAL);
mOrientation = getOrientation();
setNestedScrollingEnabled(true);
ViewConfiguration vc = ViewConfiguration.get(context);
mMinFlingVelocity = vc.getScaledMinimumFlingVelocity();
mMaxFlingVelocity = vc.getScaledMaximumFlingVelocity();
mScroller = new Scroller(context);
}
/**
* 开始滑动前调用,在惯性滑动和触摸滑动前都会进行调用,此方法一般在 onInterceptTouchEvent或者onTouch中,通知父类方法开始滑动
* 会调用父类方法的 onStartNestedScroll onNestedScrollAccepted 两个方法
*
* @param axes 滑动方向
* @param type 开始滑动的类型 the type of input which cause this scroll event
* @return 有父视图并且开始滑动,则返回true 实际上就是看parent的 onStartNestedScroll 方法
*/
@Override
public boolean startNestedScroll(int axes, int type) {
return mScrollingChildHelper.startNestedScroll(axes, type);
}
/**
* 子控件在开始滑动前,通知父控件开始滑动,同时由父控件先消耗滑动时间
* 在子View的onInterceptTouchEvent或者onTouch中,调用该方法通知父View滑动的距离
* 最终会调用父view的 onNestedPreScroll 方法
*
* @param dx 水平方向嵌套滑动的子控件想要变化的距离 dx<0 向右滑动 dx>0 向左滑动 (保持和 RecycleView 一致)
* @param dy 垂直方向嵌套滑动的子控件想要变化的距离 dy<0 向下滑动 dy>0 向上滑动 (保持和 RecycleView 一致)
* @param consumed 父控件消耗的距离,父控件消耗完成之后,剩余的才会给子控件,子控件需要使用consumed来进行实际滑动距离的处理
* @param offsetInWindow 子控件在当前window的偏移量
* @param type 滑动类型,ViewCompat.TYPE_NON_TOUCH fling效果,ViewCompat.TYPE_TOUCH 手势滑动
* @return true 表示父控件进行了滑动消耗,需要处理 consumed 的值,false表示父控件不对滑动距离进行消耗,可以不考虑consumed数据的处理,此时consumed中两个数据都应该为0
*/
@Override
public boolean dispatchNestedPreScroll(int dx, int dy, @Nullable int[] consumed, @Nullable int[] offsetInWindow, int type) {
return mScrollingChildHelper.dispatchNestedPreScroll(dx, dy, consumed, offsetInWindow, type);
}
/**
* 在dispatchNestedPreScroll 之后进行调用
* 当滑动的距离父控件消耗后,父控件将剩余的距离再次交个子控件,
* 子控件再次消耗部分距离后,又继续将剩余的距离分发给父控件,由父控件判断是否消耗剩下的距离。
* 如果四个消耗的距离都是0,则表示没有神可以消耗的了,会直接返回false,否则会调用父控件的
* onNestedScroll 方法,父控件继续消耗剩余的距离
* 会调用父控件的
*
* @param dxConsumed 水平方向嵌套滑动的子控件滑动的距离(消耗的距离) dx<0 向右滑动 dx>0 向左滑动 (保持和 RecycleView 一致)
* @param dyConsumed 垂直方向嵌套滑动的子控件滑动的距离(消耗的距离) dy<0 向下滑动 dy>0 向上滑动 (保持和 RecycleView 一致)
* @param dxUnconsumed 水平方向嵌套滑动的子控件未滑动的距离(未消耗的距离)dx<0 向右滑动 dx>0 向左滑动 (保持和 RecycleView 一致)
* @param dyUnconsumed 垂直方向嵌套滑动的子控件未滑动的距离(未消耗的距离)dy<0 向下滑动 dy>0 向上滑动 (保持和 RecycleView 一致)
* @param offsetInWindow 子控件在当前window的偏移量
* @return 如果返回true, 表示父控件又继续消耗了
*/
@Override
public boolean dispatchNestedScroll(int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed, int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed, @Nullable int[] offsetInWindow, int type) {
return mScrollingChildHelper.dispatchNestedScroll(dxConsumed, dyConsumed, dxUnconsumed, dyUnconsumed, offsetInWindow, type);
}
/**
* 子控件停止滑动,例如手指抬起,惯性滑动结束
*
* @param type 停止滑动的类型 TYPE_TOUCH,TYPE_NON_TOUCH
*/
@Override
public void stopNestedScroll(int type) {
mScrollingChildHelper.stopNestedScroll(type);
}
/**
* 设置当前子控件是否支持嵌套滑动,如果不支持,那么父控件是不能够响应嵌套滑动的
*
* @param enabled true 支持
*/
@Override
public void setNestedScrollingEnabled(boolean enabled) {
mScrollingChildHelper.setNestedScrollingEnabled(enabled);
}
/**
* 当前子控件是否支持嵌套滑动
*/
@Override
public boolean isNestedScrollingEnabled() {
return mScrollingChildHelper.isNestedScrollingEnabled();
}
/**
* 判断当前子控件是否拥有嵌套滑动的父控件
*/
@Override
public boolean hasNestedScrollingParent(int type) {
return mScrollingChildHelper.hasNestedScrollingParent(type);
}
private VelocityTracker mVelocityTracker;
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
int action = event.getActionMasked();
cancleFling();//停止惯性滑动
if (lastX == -1 || lastY == -1) {
lastY = (int) event.getRawY();
lastX = (int) event.getRawX();
}
//添加速度检测器,用于处理fling效果
if (mVelocityTracker == null) {
mVelocityTracker = VelocityTracker.obtain();
}
mVelocityTracker.addMovement(event);
switch (action) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: {//当手指按下
lastY = (int) event.getRawY();
lastX = (int) event.getRawX();
//即将开始滑动,支持垂直方向的滑动
if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {
//此方法确定开始滑动的方向和类型,为垂直方向,触摸滑动
startNestedScroll(ViewCompat.SCROLL_AXIS_VERTICAL, TYPE_TOUCH);
} else {
startNestedScroll(ViewCompat.SCROLL_AXIS_HORIZONTAL, TYPE_TOUCH);
}
break;
}
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE://当手指滑动
int currentY = (int) (event.getRawY());
int currentX = (int) (event.getRawX());
int dy = lastY - currentY;
int dx = lastX - currentX;
//即将开始滑动,在开始滑动前,先通知父控件,确认父控件是否需要先消耗一部分滑动
//true 表示需要先消耗一部分
if (dispatchNestedPreScroll(dx, dy, consumed, offset, TYPE_TOUCH)) {
//如果父控件需要消耗,则处理父控件消耗的部分数据
dy -= consumed[1];
dx -= consumed[0];
}
//剩余的自己再次消耗,
int consumedX = 0, consumedY = 0;
if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {
consumedY = childConsumedY(dy);
} else {
consumedX = childConsumeX(dx);
}
//子控件的滑动事件处理完成之后,剩余的再次传递给父控件,让父控件进行消耗
//因为没有滑动事件,因此次数自己滑动距离为0,剩余的再次全部还给父控件
dispatchNestedScroll(consumedX, consumedY, dx - consumedX, dy - consumedY, null, TYPE_TOUCH);
lastY = currentY;
lastX = currentX;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: //当手指抬起的时,结束嵌套滑动传递,并判断是否产生了fling效果
case MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL: //取消的时候,结束嵌套滑动传递,并判断是否产生了fling效果
//触摸滑动停止
stopNestedScroll(TYPE_TOUCH);
//开始判断是否需要惯性滑动
mVelocityTracker.computeCurrentVelocity(1000, mMaxFlingVelocity);
int xvel = (int) mVelocityTracker.getXVelocity();
int yvel = (int) mVelocityTracker.getYVelocity();
fling(xvel, yvel);
if (mVelocityTracker != null) {
mVelocityTracker.clear();
}
lastY = -1;
lastX = -1;
break;
}
return true;
}
private boolean fling(int velocityX, int velocityY) {
//判断速度是否足够大。如果够大才执行fling
if (Math.abs(velocityX) < mMinFlingVelocity) {
velocityX = 0;
}
if (Math.abs(velocityY) < mMinFlingVelocity) {
velocityY = 0;
}
if (velocityX == 0 && velocityY == 0) {
return false;
}
//通知父控件,开始进行惯性滑动
if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {
//此方法确定开始滑动的方向和类型,为垂直方向,触摸滑动
startNestedScroll(ViewCompat.SCROLL_AXIS_VERTICAL, ViewCompat.TYPE_NON_TOUCH);
} else {
startNestedScroll(ViewCompat.SCROLL_AXIS_HORIZONTAL, ViewCompat.TYPE_NON_TOUCH);
}
velocityX = Math.max(-mMaxFlingVelocity, Math.min(velocityX, mMaxFlingVelocity));
velocityY = Math.max(-mMaxFlingVelocity, Math.min(velocityY, mMaxFlingVelocity));
//开始惯性滑动
doFling(velocityX, velocityY);
return true;
}
private int mLastFlingX;
private int mLastFlingY;
private final int[] mScrollConsumed = new int[2];
/**
* 实际的fling处理效果
*/
private void doFling(int velocityX, int velocityY) {
fling = true;
mScroller.fling(0, 0, velocityX, velocityY, Integer.MIN_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE, Integer.MIN_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
postInvalidate();
}
@Override
public void computeScroll() {
if (mScroller.computeScrollOffset() && fling) {
int x = mScroller.getCurrX();
int y = mScroller.getCurrY();
int dx = mLastFlingX - x;
int dy = mLastFlingY - y;
FRLog.i("y: " + y + " X: " + x + " dx: " + dx + " dy: " + dy);
mLastFlingX = x;
mLastFlingY = y;
//在子控件处理fling之前,先判断父控件是否消耗
if (dispatchNestedPreScroll(dx, dy, mScrollConsumed, null, ViewCompat.TYPE_NON_TOUCH)) {
//计算父控件消耗后,剩下的距离
dx -= mScrollConsumed[0];
dy -= mScrollConsumed[1];
}
//因为之前默认向父控件传递的竖直方向,所以这里子控件也消耗剩下的竖直方向
int hResult = 0;
int vResult = 0;
int leaveDx = 0;//子控件水平fling 消耗的距离
int leaveDy = 0;//父控件竖直fling 消耗的距离
//在父控件消耗完之后,子控件开始消耗
if (dx != 0) {
leaveDx = childFlingX(dx);
hResult = dx - leaveDx;//得到子控件消耗后剩下的水平距离
}
if (dy != 0) {
leaveDy = childFlingY(dy);//得到子控件消耗后剩下的竖直距离
vResult = dy - leaveDy;
}
//将最后剩余的部分,再次还给父控件
dispatchNestedScroll(leaveDx, leaveDy, hResult, vResult, null, ViewCompat.TYPE_NON_TOUCH);
postInvalidate();
} else {
stopNestedScroll(ViewCompat.TYPE_NON_TOUCH);
cancleFling();
}
}
private void cancleFling() {
fling = false;
mLastFlingX = 0;
mLastFlingY = 0;
}
/**
* 判断子子控件是否能够滑动,只有能滑动才能处理fling
*/
private boolean canScroll() {
//具体逻辑自己实现
return true;
}
/**
* 子控件消耗多少竖直方向上的fling,由子控件自己决定
*
* @param dy 父控件消耗部分竖直fling后,剩余的距离
* @return 子控件竖直fling,消耗的距离
*/
private int childFlingY(int dy) {
return 0;
}
/**
* 子控件消耗多少竖直方向上的fling,由子控件自己决定
*
* @param dx 父控件消耗部分水平fling后,剩余的距离
* @return 子控件水平fling,消耗的距离
*/
private int childFlingX(int dx) {
return 0;
}
/**
* 触摸滑动时候子控件消耗多少竖直方向上的 ,由子控件自己决定
*
* @param dy 父控件消耗部分竖直fling后,剩余的距离
* @return 子控件竖直fling,消耗的距离
*/
private int childConsumedY(int dy) {
return 0;
}
/**
* 触摸滑动子控件消耗多少竖直方向上的,由子控件自己决定
*
* @param dx 父控件消耗部分水平fling后,剩余的距离
* @return 子控件水平fling,消耗的距离
*/
private int childConsumeX(int dx) {
return 0;
}
在顶部的图片用child进行包裹,你会发现,图片也有了触摸滑动和惯性滑动效果,并且能将剩余的滑动距离传递给RecycleView;
到此为止,我们已经完成了嵌套滑动的学习,时间比较仓促,如果有还不完善的地方,请多多指正
最后,部分内容参考一些大佬的代码,因为时间太久已经记不清楚了,没办吧一一注明,如果引起不适请留言或者私信我;
最后的最后:源码