参考博客https://www.cnblogs.com/aylin/p/5770888.html
pymysql
- 下载安装
pip install pymysql - 操作数据库
import pymysql
class MysqlSearch(object):
def __init__(self):
self.get_conn()
def get_conn(self):
""" 获取连接 """
try:
self.conn = pymysql.connect(
host='localhost',
port=3306,
user='root',
passwd='',
db='news',
charset='utf8')
except Exception as e:
print('Error:%s' %e)
def close_conn(self):
try:
# 关闭连接
if self.conn:
self.conn.close()
except Exception as e:
print('Error: %s' %e)
def get_one(self):
# 准备SQL
sql = 'SELECT * FROM news;'
# 找到cursor
cursor = self.conn.cursor()
# 执行SQL
cursor.execute(sql)
# print(dir(cursor))
# print(cursor.description)
# 拿到结果
data = cursor.fetchone()
# print(data)
# 将列名和数据组合成字典形式方便查询
data = dict(zip([k[0] for k in cursor.description], data))
# 处理数据
print(data)
print(data['title'])
# 关闭cursor/连接
cursor.close()
self.close_conn()
return data
def get_more(self, page, page_size):
# 准备SQL
offset = (page - 1) * page_size # 利用LIMIT实现翻页
sql = f'SELECT * FROM news ORDER BY id LIMIT {offset}, {page_size};'
# 找到cursor
cursor = self.conn.cursor()
# 执行SQL
cursor.execute(sql)
# print(dir(cursor))
# print(cursor.description)
# 拿到结果
data = cursor.fetchall()
# print(data)
# 将列名和每一条数据组合成字典形式
data = [dict(zip([k[0] for k in cursor.description], row)) for row in data]
# 处理数据
# print(data)
# print(data['title'])
# 关闭cursor/连接
cursor.close()
self.close_conn()
return data
def add_one(self):
try:
# 准备SQL
sql = (
"""
INSERT INTO news(title, image, content, types, created_at, is_valid) VALUE
(%s, %s, %s, %s, NOW(), %s);
"""
)
# 准备连接和cursor
cursor = self.conn.cursor()
# 执行SQL
cursor.execute(sql, ('title0', 'image_url', '新闻内容', '类型', 0))
cursor.execute(sql, ('title1', 'image_url', '新闻内容', '类型', 1))
# 提交数据到数据库
# 提交事务
self.conn.commit()
# 关闭cursor和连接
cursor.close()
except Exception as e:
print("Error: %s" %e)
self.conn.rollback() # 若出现一条错误则都不提交成功
self.close_conn()
def delete_one(self):
try:
# 准备SQL
sql = (
"""
DELETE FROM news WHERE title='title0' or title = 'title1';
"""
)
# 准备连接和cursor
cursor = self.conn.cursor()
# 执行SQL
cursor.execute(sql)
# 提交事务
self.conn.commit()
# 关闭cursor和连接
cursor.close()
except Exception as e:
print("Error: %s" %e)
self.conn.rollback()
self.close_conn()
def main():
obj = MysqlSearch()
# data = obj.get_one()
# print(data)
# obj.add_one()
# obj.delete_one()
# data = obj.get_more(1, 20)
# for item in data:
# print('\n', item)
# print('\n', item['title'])
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
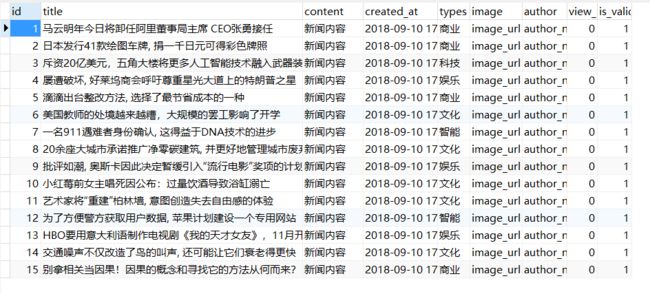
下面是我创建的一张表:
下面分别演示各个方法的结果:
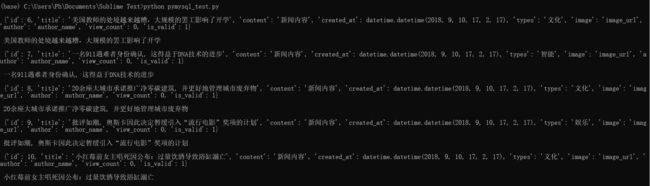
obj = MysqlSearch()
data = obj.get_one()
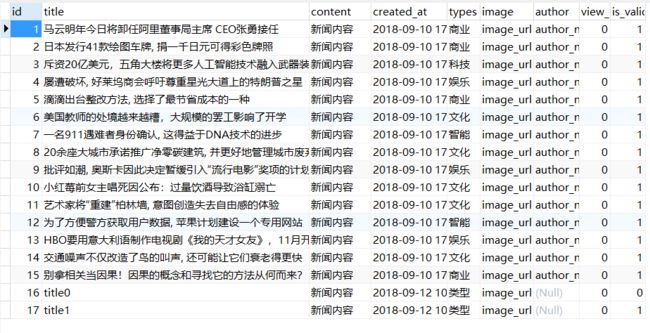
obj.add_one()
可以看到数据库中成功插入了两条我想要插入的数据
obj.delete_one()
可以看到我刚刚插入的两条title0和title1数据已经被删除了
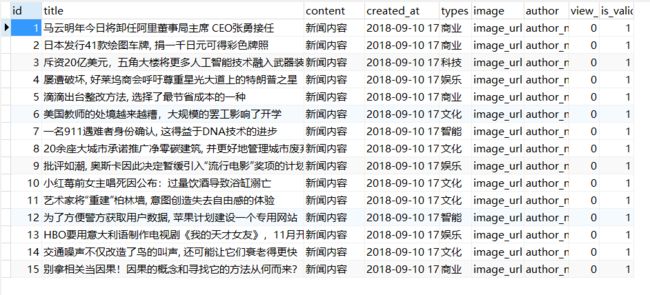
data = obj.get_more(2, 5)
for item in data:
print('\n', item)
print('\n', item['title'])
可以看到如期输入了id为6-10的第二页数据,并在每一条数据下面输出了title信息
sqlalchemy简介
SQLAlchemy是Python编程语言下的一款开源软件。提供了SQL工具包及对象关系映射(ORM)工具,使用MIT许可证发行。
SQLAlchemy“采用简单的Python语言,为高效和高性能的数据库访问设计,实现了完整的企业级持久模型”。SQLAlchemy的理念是,SQL数据库的量级和性能重要于对象集合;而对象集合的抽象又重要于表和行。因此,SQLAlchmey采用了类似于Java里Hibernate的数据映射模型,而不是其他ORM框架采用的Active Record模型。不过,Elixir和declarative等可选插件可以让用户使用声明语法。
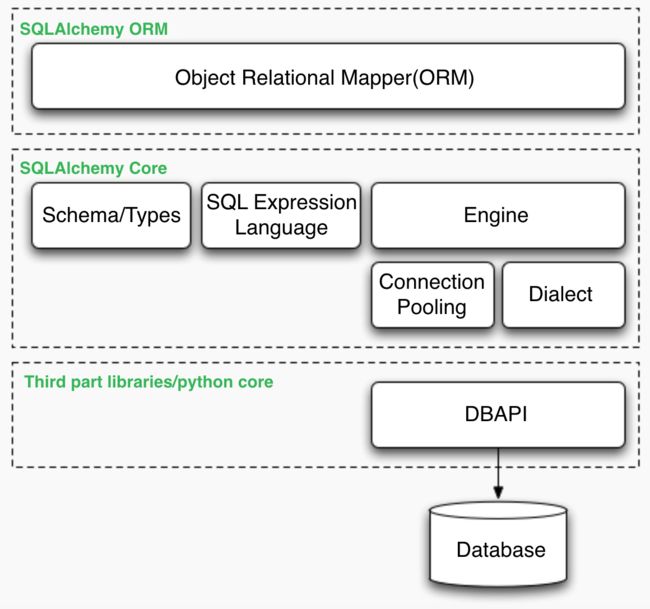
SQLAlchemy与数据库关系图如下:
sqlalchemy基本操作
- 安装sqlalchemy
==> 本文用的是mysql案例,所以需要一台有安装mysql数据库的机器
==> 使用Python的pip安装pip install sqlalchemy(如果既有Python2又有Python3的用pip3 install sqlalchemy)
安装完后查看版本信息
import sqlalchemy
sqlalchemy.__version__
- 操作数据库
# ORM: Object Relational Mapping 对象关系映射
# https://bugs.mysql.com/bug.php?id=82414 Bug report // Warning
# Warning: (1366, "Incorrect string value: '\\xD6\\xD0\\xB9\\xFA\\xB1\\xEA...' for column 'VARIABLE_VALUE' at row 481")
# result = self._query(query)
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
from sqlalchemy import Column, Integer, String, DateTime, Boolean
engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://username:passwd@localhost:port/db?charset=utf8', max_overflow=5) # max_overflow 最多多几个连接
Base = declarative_base()
Session = sessionmaker(bind=engine)
class News(Base):
__tablename__ = 'news'
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
title = Column(String(200), nullable=False)
content = Column(String(2000), nullable=False)
types = Column(String(10), nullable=False)
created_at = Column(DateTime)
image = Column(String(300), )
author = Column(String(20), )
view_count = Column(Integer)
is_valid = Column(Boolean)
class OrmTest(object):
def __init__(self):
self.session = Session()
def add_one(self):
''' 添加数据 '''
new_obj = News(
title='ORM标题',
content='content',
types='技术'
)
new_obj2 = News(
title='title',
content='content',
types='types'
)
self.session.add(new_obj)
self.session.add(new_obj2)
self.session.commit()
return new_obj
def get_one(self):
''' 查询一条数据 '''
return self.session.query(News).get(3)
def get_more(self):
''' 查询多条数据 '''
return self.session.query(News).filter_by(is_valid=True)
def update_data(self, pk):
''' 修改数据 '''
# 修改多条数据
data_list = self.session.query(News).filter(News.id>2)
# data_list = self.session.query(News).filter_by(is_valid=False)
for item in data_list:
item.is_valid = 1
self.session.add(item)
self.session.commit()
# 修改单条数据
new_obj = self.session.query(News).get(pk)
if new_obj:
new_obj.is_valid = 0
self.session.add(new_obj)
self.session.commit()
return True
return False
def delete_data(self, pk):
''' 删除数据 '''
# 获取要删除的数据
new_obj = self.session.query(News).get(pk)
if new_obj:
self.session.delete(new_obj)
self.session.commit()
def main():
obj = OrmTest()
# test = obj.add_one()
# print(test.id)
# test = obj.get_one()
# if test:
# print(f'ID:{test.id} => title:{test.title}')
# else:
# print('Not exist.')
# result = obj.get_more()
# print(result.count())
# for new_obj in result:
# print(f'ID:{new_obj.id} => title:{new_obj.title}')
# print(obj.update_data(3))
# print(obj.delete_data(1))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
我电脑里的MySQL是5.7版本,这里有一个不影响使用但会报Warning的BUG,Bug report:https://bugs.mysql.com/bug.php?id=82414
更多详细的可以参考官方文档
以及这篇邹业盛的中文博客