使用 pod lib create 新建工程
这种方式创建的工程,pod会做好相关的配置,可以直接开发
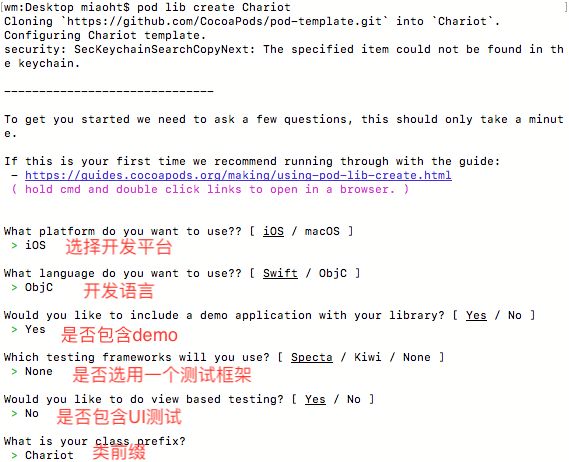
pod lib create Chariot
会有六个选项需要自己设置
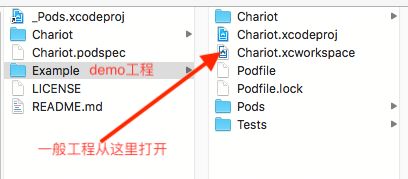
创建成功后得到工程文件夹,文件结构如下:
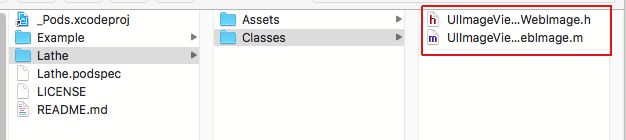
开发时,将要制作成库的.h和.m文件拖拽到Classes文件夹,将相关的资源文件拖拽到Assets
打开Example文件夹中的.xcworkspace,编辑.podspec文件
这里只列举了常用的设置项
Pod::Spec.new do |s|
# 库名
s.name = 'Lathe'
# 版本,这个版本是可用的tag
s.version = '0.1.0'
# 概要
s.summary = 'lathe summary'
# 描述
s.description = <<-DESC
lathe description
DESC
# 主页,用来介绍你的库
s.homepage = 'http://***.com/auto/ilathe/wikis/home'
# 屏幕截图
# s.screenshots = 'www.example.com/screenshots_1', 'www.example.com/screenshots_2'
# 库支持的许可证
s.license = { :type => 'MIT', :file => 'LICENSE' }
# 库作者
s.author = { 'mht' => '***@***.com' }
# 库位置
s.source = { :git => 'git@***.com:***.git', :tag => s.version.to_s }
# s.social_media_url = 'https://twitter.com/'
# 部署target需要版本(8.0以上)
s.ios.deployment_target = '8.0'
# 源码位置
s.source_files = 'Lathe/Classes/**/*'
# 资源文件位置(图片 plist json xml 等)
# s.resource_bundles = {
# 'Lathe' => ['Lathe/Assets/*.png']
# }
# 公共头文件
# s.public_header_files = 'Pod/Classes/**/*.h'
# 依赖的系统框架
# s.frameworks = 'UIKit', 'MapKit'
# 依赖的三方库 多个库直接在后面追加dependency
# s.dependency 'AFNetworking', '~> 2.3'
# s.dependency 'Mock', '~> 2.3'
# s.dependency 'YYKit', '~> 2.3'
end
将库文件拖拽到Classes文件夹
cd到Example工程目录下,并执行pod install
cd /Users/miaoht/Desktop/Lathe/Example
pod install
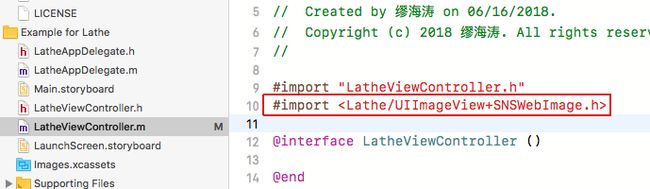
执行完成后,打开Example工程,编译一次(有很多时候不编译一次,没法引用库),就可以使用#import <>的方式引用自己的库了
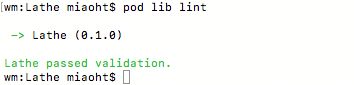
接下来校验podspec文件的正确性
cd /Users/miaoht/Desktop/Lathe
pod lib lint
绿色字提示通过
其中
s.source = { :git => 'git@***.com:auto/ilathe.git', :tag => s.version.to_s }会警告,可以忽略
s.source = { :git => 'http://***.com/auto/ilathe.git', :tag => s.version.to_s } 这样写没有警告
在git服务器上(自己部署的gitlab或GitHub、码云等)创建并checkout出工程
上传刚刚创建好的工程,使用sourcetree或者命令行新建对应的tag,这个tag号对应着.podspec中的版本号,pod时会自动拉取对应版本,创建tag时一定要在服务器上创建,或者本地创建tag推送到服务器,总之保证服务器上存在.podspec中对应版本的tag
cd进入cd /Users/miaoht/Desktop/Lathe 校验podspec文件的正确性(如果有无关紧要的warning可以忽略)
pod repo lint
关键点:创建私有库
在git服务器上创建存放podspec文件的库,就跟创建代码库一样,只不过这个库是用来存放podspec文件的。
向本地pod库中添加podspec文件的库 ,REPO_NAME是库名,SOURCE_URL是podspec库地址
pod repo add REPO_NAME SOURCE_URL
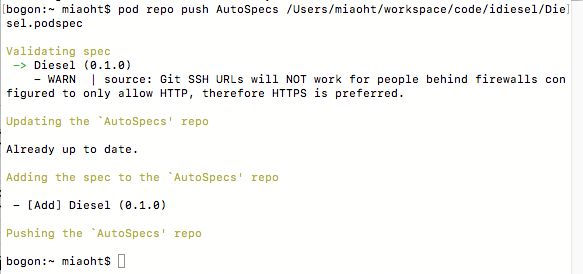
将podspec推送到podspec库(如果podspec文件存在警告这个操作也会失败,可以在后面加--allow-warnings允许警告)
pod repo push REPO_NAME SPEC_NAME.podspec
推送成功后,就可以使用pod引入库了
这里写podfile的时候要加上 source 'podspec 库 的 url',这样pod会去指定的podspec库检出依赖库
# Uncomment the next line to define a global platform for your project
platform :ios, '9.0'
source 'git@***.com:888/HelloPodSpecs.git'
target 'PodTest' do
# Uncomment the next line if you're using Swift or would like to use dynamic frameworks
# use_frameworks!
# Pods for PodTest
pod 'HelloPod'
end
最后执行pod install ,就可以看到自己的库被引用进工程了
配置库的层次
s.subspec 'Router' do |ss|
ss.source_files = 'HelloPod/Classes/Router/*.{h,m}'
end
使用上述方法可以配置工程的层次,别人在使用的时候可以只pod出指定的库文件
例如:pod 'HelloPod/Router'
Pod::Spec.new do |s|
s.name = 'HelloPod'
s.version = '0.1.1'
s.summary = 'A short description of HelloPod.'
s.description = <<-DESC
TODO: Add description of the pod here.
DESC
s.homepage = 'http://opensource.cnsuning.com/888/HelloPod/wikis/home'
# s.screenshots = 'www.example.com/screenshots_1', 'www.example.com/screenshots_2'
s.license = { :type => 'MIT', :file => 'LICENSE' }
s.author = { '缪海涛' => '[email protected]' }
s.source = { :git => '[email protected]:888/HelloPod.git', :tag => s.version.to_s }
s.ios.deployment_target = '8.0'
s.source_files = 'HelloPod/Classes/*.{h,m}'
s.subspec 'Router' do |ss|
ss.source_files = 'HelloPod/Classes/IMAGE/*.{h,m}'
end
end