这里总结下runtime的几个使用场景,至于前面的概念和原理大家可参考这篇文章。
我提供了一个和本次笔记同步的demo
),可供参考。
一、objc_msgSend
Objective-C的方法调用实则为“发送消息”,[per msgsendTest]实际上会被转化为
objc_msgSend(per, SEL)
如果包含参数,则objc_msgSend(per, SEL, arg1, arg2, ...)
详细代码如下代码:
/*
1、初始化一个对象
Person *per = [[Person alloc] init];
return [per msgsendTest:@"我是参数1"];
*/
/*
2、可以拆分为
Person *per = [Person alloc];
[per init];
return [per msgsendTest:@"我是参数2"];
*/
/*
3、通过msgsend改写为
Person *per = objc_msgSend([Person class], @selector(alloc));
per = objc_msgSend(per, @selector(init));
return objc_msgSend(per, @selector(msgsendTest:), @"我是参数3");
*/
/*
4、在3中依然可以看到@selector这种方法,于是可以进一步改成
*/
Person *per = objc_msgSend(objc_getClass("Person"), sel_registerName("alloc"));
per = objc_msgSend(per, sel_registerName("init"));
return objc_msgSend(per, sel_registerName("msgsendTest:"), @"我是参数4");
注意:新建项目引入#import 头文件后,使用objc_msgSend会报
objc_msgSend()报错Too many arguments to function call ,expected 0,have3
解决方法如下图:
消息发送步骤:
- 检测这个 消息 是不是要忽略的。比如 Mac OS X 开发,在ARC中有了垃圾回收就不理会MRC的 retain, release 这些函数了。
- 检测这个 目标对象 是不是 nil 对象。ObjC 的特性是允许对一个 nil 对象执行任何一个方法不会 Crash,因为会被忽略掉。
- 如果上面两个都过了,那就开始查找这个类的 IMP,先从 cache 里面找,完了找得到就跳到对应的函数去执行。
- 如果 cache 找不到就找一下方法分发表。
- 如果分发表找不到就到超类的分发表去找,一直找,直到找到NSObject类为止。
- 如果还找不到就要开始进入动态方法解析,或者重定向或者消息转发。
二、 对象归解档
Person有如下属性:
@interface Person : NSObject
//下面四个属性用来归解档
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *name;
@property (nonatomic, assign) int age;
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *school;
@property (nonatomic, assign) int height;
@end
通常情况下:
//归档
-(void)encodeWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aCoder{
[aCoder encodeObject:_name forKey:@"name"];
[aCoder encodeInt:_age forKey:@"age"];
[aCoder encodeInt:_height forKey:@"height"];
[aCoder encodeObject:_school forKey:@"school"];
}
//解档
- (instancetype)initWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aDecoder{
if (self = [super init]) {
_name = [aDecoder decodeObjectForKey:@"name"];
_age = [aDecoder decodeIntForKey:@"age"];
_height = [aDecoder decodeIntForKey:@"height"];
_school = [aDecoder decodeObjectForKey:@"school"];
}
return self;
}
这样做的话,在属性很多或者后期需要增加属性的时候,就需要修改归解档方法,维护起来有一定工作量。
可以通过runtime实现归解档:
//告诉(NSKeyedArchiver),归档那些属性
-(void)encodeWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aCoder{
//记录成员变量个数
unsigned int count = 0;
/*
很多需要传递基本数据类型的指针,这么做是为了改变值,经过下一句代码,count的值为Person中其成员变量的真正数量,在runtime中没有.h和.m之分
ivars 不是数组,是一个指针,ivars[0]代表指向成员变量Ivar的第0个
*/
Ivar *ivars = class_copyIvarList([self class], &count);
for (int i=0; i-(instancetype)initWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aDecoder{
if (self = [super init]) {
unsigned int count = 0;
Ivar *ivars = class_copyIvarList([self class], &count);
for (int i=0; i验证结果:
//归档
Person *per = [[Person alloc] init];
per.name = @"寒江";
per.age = 18;
per.school = @"哈哈高中";
per.height = 179;
NSString *filePath = [self.temPath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"hanjiang.han"];
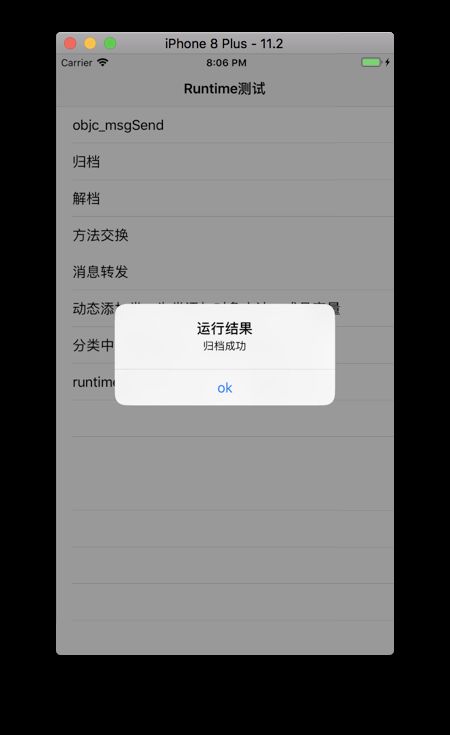
[NSKeyedArchiver archiveRootObject:per toFile:filePath]? [self alertView:@"归档成功"]: [self alertView:@"归档失败"];
//解档
NSString *filePath = [self.temPath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"hanjiang.han"];
Person *per = [NSKeyedUnarchiver unarchiveObjectWithFile:filePath];
[self alertView:[NSString stringWithFormat:@"解档成功:%@同学、身高%d、今年%d岁了、在%@上学!", per.name, per.height, per.age, per.school]];
三、 方法交换Swizzling
该场景在项目中用的好可以解决很多项目问题,而且便于项目开发与维护。
这里举一个例子,不论在什么项目都会无法避免的涉及网络请求,在使用[NSURL URLWithString:]时,如果传入的url不合法,严重的话会导致程序崩溃。当然可以在使用的地方均加入判断,但是这么做会增加很多相同代码,而且在多人开发或者有新人时很可能忘记判断,造成程序异常。
我们通过Swizzling来解决这个问题
+(void)load{
[super load];
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
//系统待交换方法
Method oldMethod = class_getClassMethod([self class], @selector(URLWithString:));
//准备与系统方法交换的新方法
Method newMethod = class_getClassMethod([self class], @selector(WG_URLWithString:));
//这里要加一个判断,在没有实现新方法时,不进行交换
if (oldMethod && newMethod) {
method_exchangeImplementations(oldMethod, newMethod);
}
});
}
+(instancetype)WG_URLWithString:(NSString *)urlStr{
if ([urlStr hasPrefix:@"http"]) {
//注意这里不会导致死循环,因为已经进行了方法交换,所以执行[self WG_URLWithString:urlStr]时相当于执行的是[self URLWithString:urlStr]
NSURL *url = [self WG_URLWithString:urlStr];
if (!url) {
return nil;
}else{
return url;
}
}else{
return nil;
}
}
验证:
NSURL *url01 = [NSURL URLWithString:@"http://www.baidu.com/中文"];
NSURL *url02 = [NSURL URLWithString:@"6666"];
NSURL *url03 = [NSURL URLWithString:@"http://www.baidu.com"];
[self alertView:[NSString stringWithFormat:@"URL含有中文:%@,没有http:%@、正确格式:%@", url01, url02, url03]];
在url含有中文或者不是http开头的时候认为不合法,返回nil;当然具体判断需求可以在方法里自己改动,这里我只是做个测试。
四、消息转发
在前面已经知道消息发送步骤,在当runtime在缓存和本类以及父类的方法列表中找不到执行的方法时,会调用resolveIntanceMethod或者resolveClassMethod来给一次动态添加的机会。
测试代码:
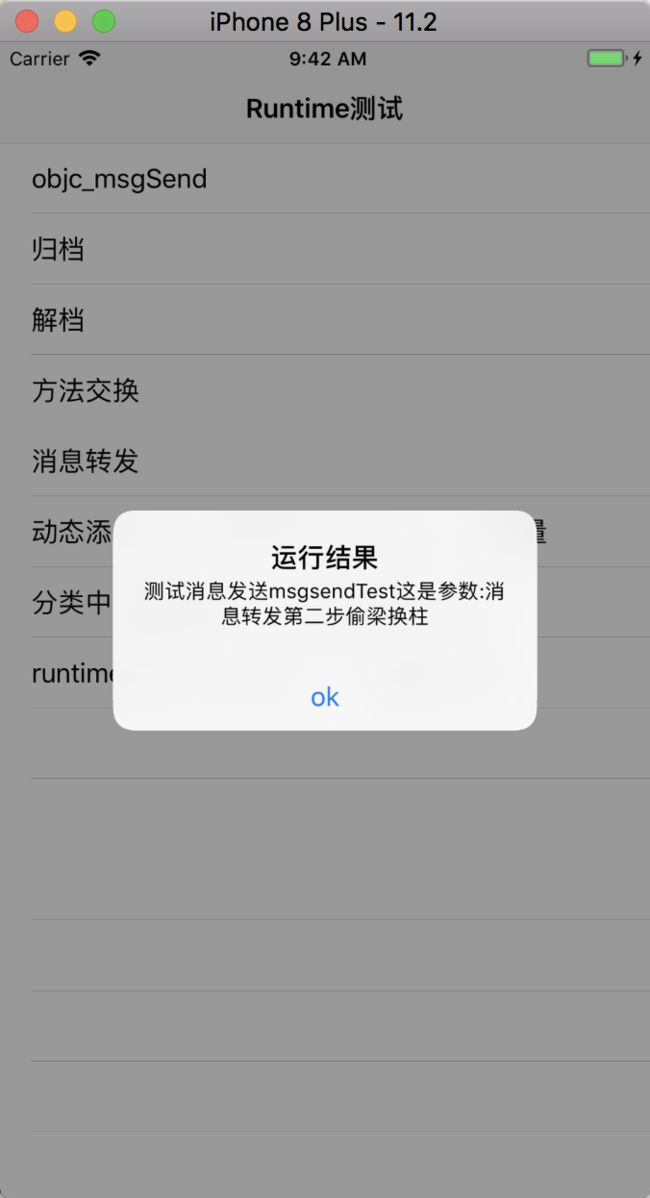
MsgZFPerson *zfPer = [[MsgZFPerson alloc] init];
[self alertView:[zfPer performSelector:@selector(msgsendTest:) withObject:@"消息转发第二步偷梁换柱"]];
//第1步
//当调用一个没有实现的类方法
//+(BOOL)resolveClassMethod:(SEL)sel
//调用了未实现的对象方法
+(BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel{
/*
IMP方法实现,一个函数指针
下面这么做相当于:只要调用了未实现的对象方法,都会拦截执行commonMethod这个方法。
当然也可以针对某个方法做实现处理
*/
class_addMethod([self class], sel, (IMP)commonMethod, "");
return YES;
// return NO;
}
//注意:需要传参数的话:前两个参数是默认参数,必填上,后面才跟上自己的参数。如果没有参数,则默认可以不填
id commonMethod(id objc, SEL _cmd, id name){
/*
这里如果需要给一个通用提示的话,可以不接受传过来的参数,写成定值
*/
NSString *className = NSStringFromClass([objc class]);
NSString *selName = NSStringFromSelector(_cmd);
return [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@中%@方法未实现,会导致崩溃",className, selName];
}
当第1步返回NO时,在消息转发机制执行前,Runtime 系统会再给我们一次偷梁换柱的机会,即通过重载- (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector 方法替换消息的接受者为其他对象:
//第2步
/*
在第1步返回NO时。
Runtime 系统会再给我们一次偷梁换柱的机会,即通过重载下面方法替换消息的接受者为其他对象。
这里MsgZFPerson并没有msgsendTest:方法,在转发之前把消息接受对象改为了Person,该类有此方法。
*/
- (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector{
if (aSelector == @selector(msgsendTest:)) {
return self.p;
}
return [super forwardingTargetForSelector:aSelector];
}
- (Person *)p{
if (!_p) {
_p = [[Person alloc] init];
}
return _p;
}
//在Person类中
- (NSString *)msgsendTest:(NSString *)str{
return [NSString stringWithFormat:@"测试消息发送msgsendTest这是参数:%@", str];
}
//第3步
//如果前两步都没有拦截的话,则可以消息转发,防止崩溃
-(NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector{
if (aSelector == @selector(msgsendTest:)) {
return [NSMethodSignature signatureWithObjCTypes:"v@:"];
}
return [super methodSignatureForSelector:aSelector];
}
-(void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation{
if ([self.p respondsToSelector:[anInvocation selector]]) {
[anInvocation invokeWithTarget:self.p];
}else{
[super forwardInvocation:anInvocation];
}
// [anInvocation setSelector:@selector(dance:)];
// [anInvocation invokeWithTarget:self];
}
- (NSString *)dance:(NSString *)str{
return str;
}
forwardInvocation: 方法就像一个不能识别的消息的分发中心,将这些消息转发给不同接收对象。或者它也可以象一个运输站将所有的消息都发送给同一个接收对象。它可以将一个消息翻译成另外一个消息,或者简单的”吃掉“某些消息,因此没有响应也没有错误。forwardInvocation:方法也可以对不同的消息提供同样的响应,这一切都取决于方法的具体实现。该方法所提供是将不同的对象链接到消息链的能力。
五、 动态添加类,类成员变量,实例方法
- (NSString *)addClassTest{
Class WGPerson = objc_allocateClassPair([NSObject class], "WGPerson", 0);
//添加成员变量name,age
class_addIvar(WGPerson, "_name", sizeof(NSString *), log2(sizeof(NSString *)), @encode(NSString *));
class_addIvar(WGPerson, "_age", sizeof(int), log2(sizeof(int)), @encode(int));
//添加实例方法
SEL method = sel_registerName("say:");
class_addMethod(WGPerson, method, (IMP)sayFunction, "v@:@");
//注册一个类
objc_registerClassPair(WGPerson);
//创建类的实例
id wgp = [[WGPerson alloc] init];
//通过KVC赋值
[wgp setValue:@"hanjiang" forKey:@"name"];
//通过从类中获取成员变量_age,再为pepleShare的成员变量赋值
Ivar ivar = class_getInstanceVariable(WGPerson, "_age");
object_setIvar(wgp, ivar, @18);
//发送消息
NSString *str = objc_msgSend(wgp, method, @"动态添加类,给类添加成员变量,给变量赋值成功");
//当WGPerson类或者它的子类的实例还存在,则不能调用objc_disposeClassPair这个方法;因此这里要先销毁实例对象后才能销毁类;
wgp = nil;
//销毁类
objc_disposeClassPair(WGPerson);
return str;
}
id sayFunction(id objc, SEL _cmd, id some){
return [NSString stringWithFormat:@"今年%@岁的%@说:%@",object_getIvar(objc, class_getInstanceVariable([objc class], "_age")),[objc valueForKey:@"name"], some];
}
测试:
WGAddClass *add = [[WGAddClass alloc] init];
self alertView:[add addClassTest]];
结果:
六、分类中添加属性探索
在CPerson分类中添加两个属性,
#import "CPerson.h"
typedef void(^CodingCallback)(void);
@interface CPerson (Associate)
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSNumber *height;
@property (nonatomic, copy) CodingCallback associatedCallback;
在CPerson类中有如下属性和实例方法
@interface CPerson : NSObject{
NSString *_occupation;//职业
NSString *_nationality;//国籍
}
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *name;
@property (nonatomic, assign) NSUInteger age;
- (NSDictionary *)allProperties;
- (NSDictionary *)allIvars;
- (NSDictionary *)allMethods;
接下来获取CPerson所有的属性,成员变量和实例方法
- (NSDictionary *)allProperties{
unsigned int count = 0;
NSMutableDictionary *resultDict = [[NSMutableDictionary alloc] init];
objc_property_t *properties = class_copyPropertyList([self class], &count);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
objc_property_t property = properties[i];
const char *pro = property_getName(property);
NSString *proName = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:pro];
id proValue = [self valueForKey:proName];
if (proValue) {
resultDict[proName] = proValue;
}else{
resultDict[proName] = @"属性字典中key对应的值不存在";
}
}
free(properties);
return resultDict;
}
- (NSDictionary *)allIvars{
unsigned int count = 0;
NSMutableDictionary *resultDict = [[NSMutableDictionary alloc] init];
Ivar *ivars = class_copyIvarList([self class], &count);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
Ivar ivar = ivars[i];
const char *iva = ivar_getName(ivar);
NSString *ivaName = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:iva];
id ivaValue = [self valueForKey:ivaName];
if (ivaValue) {
resultDict[ivaName] = ivaValue;
}else{
resultDict[ivaName] = @"成员变量字典中key对应的值不存在";
}
}
free(ivars);
return resultDict;
}
- (NSDictionary *)allMethods{
unsigned int count = 0;
NSMutableDictionary *resultDic = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];
Method *methods = class_copyMethodList([self class], &count);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
Method method = methods[i];
SEL metdsel = method_getName(method);
const char *metd = sel_getName(metdsel);
NSString *metdName = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:metd];
//获取参数个数
unsigned int arguments = method_getNumberOfArguments(method);
//其中有两个默认参数,id self, SEL _cmd
resultDic[metdName] = @(arguments - 2);
}
free(methods);
return resultDic;
}
结果如下:
从结果可以看出,即使为分类添加了set和get方法,外界可以通过.语法调用改属性,但是在成员变量列表中依然没有height和associatedCallback,可见在分类里是不能添加成员变量的。
在category中不能添加属性的原因:
在分类里使用@property声明属性,只是将该属性添加到该类的属性列表,并声明了setter和getter方法,但是没有生成相应的成员变量,也没有实现setter和getter方法。所以说分类不能添加属性。但是当我们在分类里使用@property声明属性,而且自己实现了setter和getter方法后,那么在这个类以外可以正常通过点语法给该属性赋值和取值。就是说,在分类里使用@property声明属性,又实现了setter和getter方法后,可以认为给这个类添加上了属性。
七、 runtime实现字典和model之间的转换
字典转模型:思路就是每个属性都有对应的set方法,这里根据字典中对应KEY生成对应的set方法,然后发送set消息。
模型转字典:遍历所有属性,然后根据属性名称生成对应get方法,然后发送get消息。
-(instancetype)initWithDictionary:(NSDictionary *)dictionary{
if (self=[super init]) {
NSArray *keyArr = [dictionary allKeys];
for (int i = 0; i0) {
for (int i=0; i 测试:
NSDictionary *dic = @{@"name":@"寒江",
@"age":@18,
@"occupation":@"老师",
@"captionality":@"中国"
};
//字典转模型
PersonModel *dp = [[PersonModel alloc] initWithDictionary:dic];
// [self alertView:[NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@今年%@岁在%@做%@!",dp.name, dp.age, dp.captionality, dp.occupation]];
//模型转字典
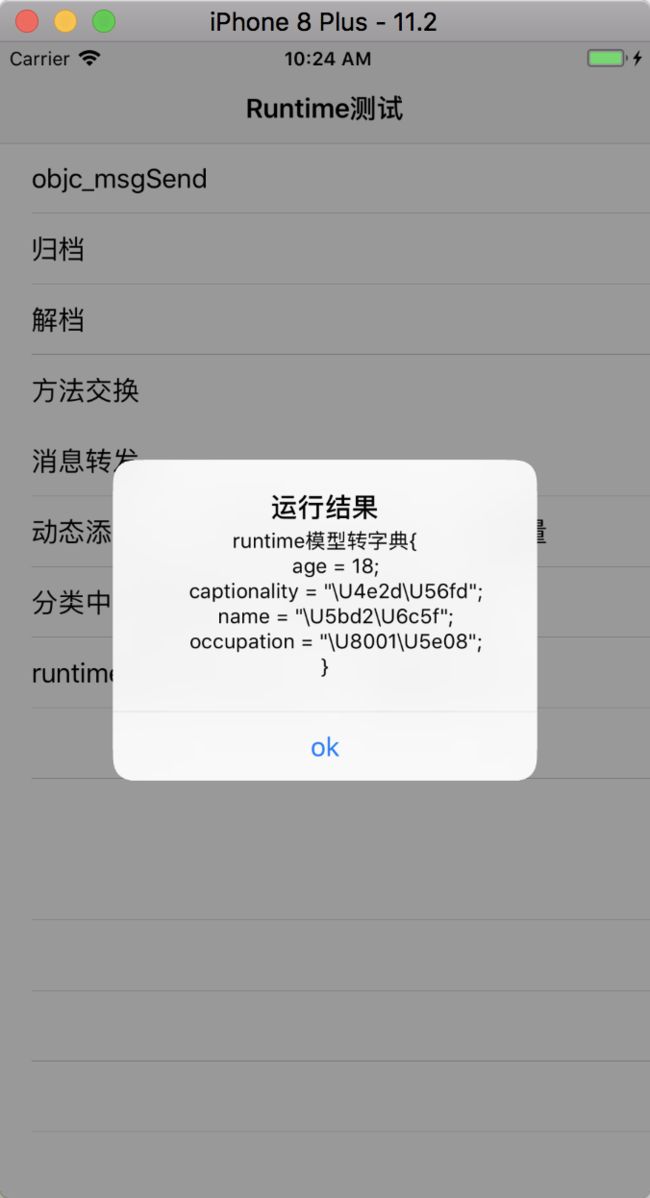
NSDictionary *newDic = [dp convertToDictionary];
[self alertView:[NSString stringWithFormat:@"runtime模型转字典%@", newDic]];
结果: