反转问题
2021.02.11
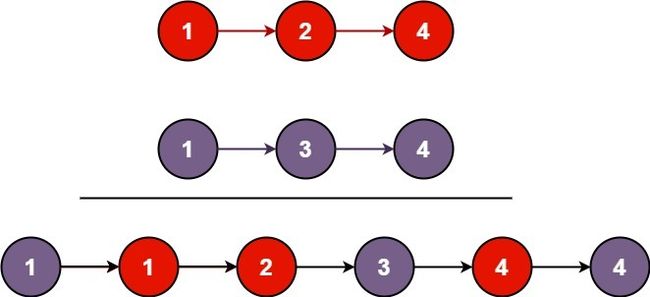
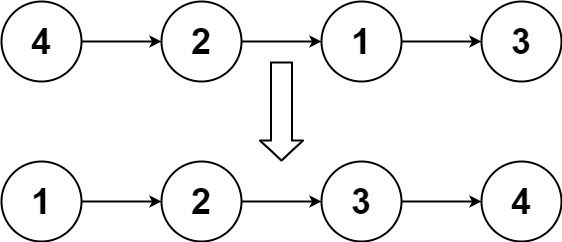
No.25 K个一组翻转链表
给你一个链表,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回翻转后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。
如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
示例:
给你这个链表:1->2->3->4->5
当 k = 2 时,应当返回: 2->1->4->3->5
当 k = 3 时,应当返回: 3->2->1->4->5
说明:
你的算法只能使用常数的额外空间。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际进行节点交换。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-nodes-in-k-group
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=25 lang=javascript
*
* [25] K 个一组翻转链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} k
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var reverseKGroup = function(head, k) {
// 链表转数组
const list2Arr = head => {
const a = [head.val];
while(head.next) {a.push(head.next.val);head = head.next;}
return a;
}
// 数组转链表
const arr2List = arr => {
let head = new ListNode(arr[0]);
let cur = head;
for(let i=1; i < arr.length; i++) {
cur.next = new ListNode(arr[i]);
cur = cur.next;
};
return head;
};
// 对k个节点进行数组切割即可
const kReverse = (a,k) => {
const r = [];
let cnt = 0;
while(a.length >= k + cnt)
{
let tmp = a.slice(cnt, cnt+k);
tmp.reverse();
tmp.map( (x)=> r.push(x));
cnt += k;
}
a.slice(cnt).map( (x)=> r.push(x));
return r;
}
return arr2List(kReverse(list2Arr(head), k));
};方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=25 lang=javascript
*
* [25] K 个一组翻转链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} k
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var reverseKGroup = function(head, k) {
let cur = head;
let count = 0;
// 求k个待反转元素的首节点和尾节点
while(cur != null && count != k){
cur = cur.next;
count++;
}
// 足够k个节点,去反转
if(count == k){
// 递归链接后续k个反转的链表头节点
cur = reverseKGroup(cur,k);
while(count != 0){
count--;
// 反转链表
let tmp = head.next;
head.next = cur;
cur = head;
head = tmp;
}
head = cur;
}
return head;
};方案三:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=25 lang=javascript
*
* [25] K 个一组翻转链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} k
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var reverseKGroup = function(head, k) {
if(!head) return null;
// 反转链表
let reverse = (a,b) => {
let pre;
let cur = a;
let next = b;
while(cur != b){
next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
// 反转区间a-b的k个待反转的元素
let a = head;
let b = head;
for(let i = 0;i < k;i++){
// 不足k个,不需要反转
if(!b) return head;
b = b.next;
}
// 反转前k个元素
let newHead = reverse(a,b);
// 递归链接后续反转链表
a.next = reverseKGroup(b,k);
return newHead;
};方案四:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=25 lang=javascript
*
* [25] K 个一组翻转链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} k
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var reverseKGroup = function(head, k) {
let stack = [];
let preHead = new ListNode(0);
let pre = preHead;
// 循环链接后续反转链表
while(true){
let count = 0;
let tmp = head;
while(tmp && count < k){
stack.push(tmp);
tmp = tmp.next;
count++;
}
// 不够k个,直接链接剩下链表返回
if(count != k){
pre.next = head;
break;
}
// 出栈即是反转
while(stack.length > 0){
pre.next = stack.pop();
pre = pre.next;
}
pre.next = tmp;
head = tmp;
}
return preHead.next;
};方案五:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=25 lang=javascript
*
* [25] K 个一组翻转链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} k
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var reverseKGroup = function(head, k) {
const myReverse = (head, tail) => {
let prev = tail.next;
let p = head;
while (prev !== tail) {
const nex = p.next;
p.next = prev;
prev = p;
p = nex;
}
return [tail, head];
}
const hair = new ListNode(0);
hair.next = head;
let pre = hair;
while (head) {
let tail = pre;
// 查看剩余部分长度是否大于等于 k
for (let i = 0; i < k; ++i) {
tail = tail.next;
if (!tail) {
return hair.next;
}
}
const nex = tail.next;
[head, tail] = myReverse(head, tail);
// 把子链表重新接回原链表
pre.next = head;
tail.next = nex;
pre = tail;
head = tail.next;
}
return hair.next;
};有五种解法:1、利用数组求解,比较笨重,需要切换成数组再切回来;2、递归相关方案,利用栈、迭代等进行解析;3、利用虚置前节点,将复杂度降到常数级别,很巧妙
2021.02.12
No.61 旋转链表
给定一个链表,旋转链表,将链表每个节点向右移动 k 个位置,其中 k 是非负数。
示例 1:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, k = 2
输出: 4->5->1->2->3->NULL
解释:
向右旋转 1 步: 5->1->2->3->4->NULL
向右旋转 2 步: 4->5->1->2->3->NULL
示例 2:
输入: 0->1->2->NULL, k = 4
输出: 2->0->1->NULL
解释:
向右旋转 1 步: 2->0->1->NULL
向右旋转 2 步: 1->2->0->NULL
向右旋转 3 步: 0->1->2->NULL
向右旋转 4 步: 2->0->1->NULL
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/rotate-list
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=61 lang=javascript
*
* [61] 旋转链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} k
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var rotateRight = function(head, k) {
// 链表转数组
const list2Arr = head => {
if(!head) return [];
const a = [head.val];
while(head.next) {a.push(head.next.val);head = head.next;}
return a;
}
// 数组转链表
const arr2List = arr => {
if(arr.length == 0) return null;
let head = new ListNode(arr[0]);
let cur = head;
for(let i=1; i < arr.length; i++) {
cur.next = new ListNode(arr[i]);
cur = cur.next;
};
return head;
};
// 数组位置变化
const arrRotate = (a, k) => {
const len = a.length;
const hashTable = {};
for(let i=0; i< a.length; i++) {
hashTable[(i+k) % len] = a[i]
};
return Object.values(hashTable)
};
return arr2List(arrRotate(list2Arr(head), k));
};方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=61 lang=javascript
*
* [61] 旋转链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} k
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var rotateRight = function (head, k) {
if (!head || k === 0) return head; // 特判
let p = head, len = 1;
while (p.next) {
p = p.next;
len++;
}
p.next = head; // 首尾相接
k = len - k % len; // 处理要移动的距离
while (k--) p = p.next;
head = p.next; // head 指向第 len - k + 1 个节点,即答案
p.next = null; // 切断 len - k 与 len - k + 1 的关系
return head;
}方案三:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=61 lang=javascript
*
* [61] 旋转链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} k
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var rotateRight = function(head, k) {
if(head===null||head.next===null)return head;
let len = 0;//链表长度
let p = head;
let first = head;//第一个结点
let stack = [];//辅助栈
while(p){
stack.push(p);
p = p.next;
len++;
}
p = stack.pop();
for(let i = 1;i<=k%len;i++){
p.next = first;
stack.unshift(p);
first = p;
p = stack.pop();
p.next = null;
}
return first;
};方案四:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=61 lang=javascript
*
* [61] 旋转链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} k
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var rotateRight = function(head, k) {
var order = new ListNode(0,head); // head链表的copy
var fast = new ListNode(0,head); // 快指针
var slow = new ListNode(0,head); // 慢指针
var count = 0; // 链表长度
while(order && order.next){ // 循环求链表长度
order = order.next;
count ++;
}
var n = k % count; // 因为 k > 链表长度 时,出现重复操作。对 k 求余,去除重复
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++){ // 快指针先走 n 步
fast = fast.next;
}
while(fast && fast.next){ // 链表的快指针、慢指针操作
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
// 两步操作
// 第一、将倒数第 k%count 元素 与 倒数第 (k%count-1) 元素 断开
var resultPre = slow.next; // 序号2 返回结果集的 起始位置
var result = resultPre; // 序号3 最后return的结果集
slow.next = null; // 将链表断开
// 第二、再讲链表的尾部与头部链接
while(resultPre && resultPre.next) {
resultPre = resultPre.next
}
if (resultPre){
resultPre.next = head; // 情况1:旋转链表后有改变,将链表拼接起来
}
else {
result = head; // 情况2: 旋转链表后没有改变,返回原始链表
}
return result;
};方案五:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=61 lang=javascript
*
* [61] 旋转链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} k
* @return {ListNode}
*/
const rotateRight = (head, k) => {
if (!head || !head.next) return head
let curr = head, n = 0
// 遍历链表计算其长度
while (++n && curr.next) curr = curr.next
k = k % n // 去重
// 链表右移
while (k--) {
curr = head
while (curr.next.next) curr = curr.next
// 这里curr是链表的打断位置,即倒数第二项
curr.next.next = head // 链表最后一项指向头部形成环
head = curr.next // 定位新的头节点
curr.next = null // 打断链表环
}
return head
}本题有五种思路:1、hash表存储,利用数组的位置排序进行hash敛散生成新的链表;2、链表成环,对应位置剪开;3、堆栈辅助处理循环剪断位置;4、快慢指针,根据双指针的位置间距进行处理,对新剪开位置使用另外两个指针记录处理;5、常规穷举,一步一步进行
2021.02.13
No.92 翻转链表-ii
反转从位置 m 到 n 的链表。请使用一趟扫描完成反转。
说明:
1 ≤ m ≤ n ≤ 链表长度。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, m = 2, n = 4
输出: 1->4->3->2->5->NULL
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list-ii
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=92 lang=javascript
*
* [92] 反转链表 II
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} m
* @param {number} n
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var reverseBetween = function(head, m, n) {
// 链表转数组
const list2Arr = head => {
if(!head) return [];
const a = [head.val];
while(head.next) {a.push(head.next.val);head = head.next;}
return a;
}
// 数组转链表
const arr2List = arr => {
if(arr.length == 0) return null;
let head = new ListNode(arr[0]);
let cur = head;
for(let i=1; i < arr.length; i++) {
cur.next = new ListNode(arr[i]);
cur = cur.next;
};
return head;
};
// 数组 m => n 翻转
const reversePosition = (a, m, n) => {
return [...a.slice(0,m-1), ...a.slice(m-1,n).reverse(), ...a.slice(n)]
};
return arr2List(reversePosition(list2Arr(head),m,n));
};方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=92 lang=javascript
*
* [92] 反转链表 II
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} m
* @param {number} n
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var reverseBetween = function(head, m, n) {
// step1 => 双指针p1,p2保持固定间距
const dummyHead = new ListNode(0, head);
let p1 = p2 = head;
let step2 = n - m;
while (step2-- > 0) {
p2 = p2.next;
}
let step1 = m - 1;
let tmpHead = p1;
while (step1-- > 0) {
tmpHead = p1;
p1 = p1.next;
p2 = p2.next;
}
// step2 => 极其重要的测试case:p1指针压根没动【dummyHead就起作用了】
if (p1 == head) {
tmpHead = dummyHead;
}
// step3 => 尾插法
let tmp = p1;
while (tmp != p2) {
tmp = p1.next;
p1.next = tmp.next;
tmp.next = tmpHead.next;
tmpHead.next = tmp;
}
return dummyHead.next;
};两种解法:1、转成数组,利用数组的slice及reverse拼接;2、双指针+尾插法,利用头尾指针的交换
2021.02.14
No.206 反转链表
反转一个单链表。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=206 lang=javascript
*
* [206] 反转链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var reverseList = function(head) {
// 链表转数组
const list2Arr = head => {
if(!head) return [];
const a = [head.val];
while(head.next) {a.push(head.next.val);head = head.next;}
return a;
}
// 数组转链表
const arr2List = arr => {
if(arr.length == 0) return null;
let head = new ListNode(arr[0]);
let cur = head;
for(let i=1; i < arr.length; i++) {
cur.next = new ListNode(arr[i]);
cur = cur.next;
};
return head;
};
// 数组 m => n 翻转
const reverseList = (a) => {
return a.reverse()
};
return arr2List(reverseList(list2Arr(head)));
};方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=206 lang=javascript
*
* [206] 反转链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var reverseList = function(head) {
let prev = null;
let curr = head;
while (curr) {
const next = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
};方案三:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=206 lang=javascript
*
* [206] 反转链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var reverseList = function(head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
const newHead = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return newHead;
};三种方法:1、转成数组,利用数组的reverse;2、迭代;3.递归
总结:
- 反转链表问题常见的利用链表的三指针进行相关的反转,常见的为头指针、尾指针及替换指针的相关变形,可以利用栈等数据结构进行迭代或递归;
- 对于反转问题有一个取巧的办法就是将其转成数组后利用数组的相关api进行处理,再将数组转为链表
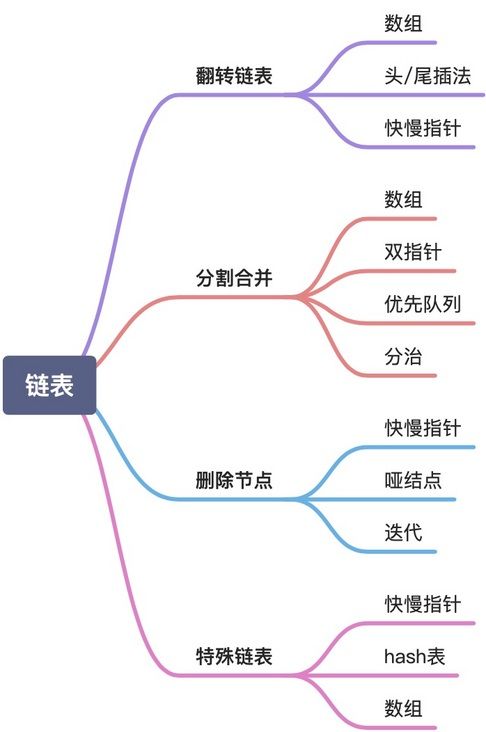
分隔合并
2021.02.18
No.21 合并两个有序链表
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例 1:
输入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
示例 2:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = [0]
输出:[0]
提示:
两个链表的节点数目范围是 [0, 50]
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
l1 和 l2 均按 非递减顺序 排列
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=21 lang=javascript
*
* [21] 合并两个有序链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} l1
* @param {ListNode} l2
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var mergeTwoLists = function(l1, l2) {
if(!l1) return l2;
if(!l2) return l1;
while(l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if(l1.val <= l2.val) {
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
return l1;
} else {
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next);
return l2;
}
}
};方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=21 lang=javascript
*
* [21] 合并两个有序链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} l1
* @param {ListNode} l2
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var mergeTwoLists = function(l1, l2) {
let prev = new ListNode(-1),
head = prev;
while(l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if(l1.val <= l2.val) {
head.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
head.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
head = head.next;
}
head.next = l1 === null ? l2 : l1;
return prev.next;
};方案三:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=21 lang=javascript
*
* [21] 合并两个有序链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} l1
* @param {ListNode} l2
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var mergeTwoLists = function(l1, l2) {
// 链表转数组
const list2Arr = head => {
if(!head) return [];
const a = [head.val];
while(head.next) {a.push(head.next.val);head = head.next;}
return a;
}
// 数组转链表
const arr2List = arr => {
if(arr.length == 0) return null;
let head = new ListNode(arr[0]);
let cur = head;
for(let i=1; i < arr.length; i++) {
cur.next = new ListNode(arr[i]);
cur = cur.next;
};
return head;
};
// 两个数组合并排序
const mergeArr = (a1,a2) => {
return [...a1,...a2].sort((a,b) => a-b);
}
return arr2List(mergeArr(list2Arr(l1), list2Arr(l2)));
};有三种方案:1、递归,利用隐式栈进行链表的合并;2、迭代,使用双指针进行迭代判断;3、转化成数组合并升序排列
2021.02.21
No.23 合并k个升序链表
给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
示例 1:
输入:lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6]
解释:链表数组如下:
[
1->4->5,
1->3->4,
2->6
]
将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。
1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
示例 2:
输入:lists = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:lists = [[]]
输出:[]
提示:
k == lists.length
0 <= k <= 10^4
0 <= lists[i].length <= 500
-10^4 <= listsi <= 10^4
lists[i] 按 升序 排列
lists[i].length 的总和不超过 10^4
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-k-sorted-lists
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=23 lang=javascript
*
* [23] 合并K个升序链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode[]} lists
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var mergeKLists = function(lists) {
// 链表转数组
const list2Arr = head => {
if(!head) return [];
const a = [head.val];
while(head.next) {a.push(head.next.val);head = head.next;}
return a;
}
// 数组转链表
const arr2List = arr => {
if(arr.length == 0) return null;
let head = new ListNode(arr[0]);
let cur = head;
for(let i=1; i < arr.length; i++) {
cur.next = new ListNode(arr[i]);
cur = cur.next;
};
return head;
};
// 对k个节点进行数组切割即可
const mergeArr = lists => {
const r = [];
lists.forEach(list => r.push(...list2Arr(list)))
return r.sort((a,b) => a-b);
}
return arr2List(mergeArr(lists));
};方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=23 lang=javascript
*
* [23] 合并K个升序链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode[]} lists
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var mergeKLists = function(lists) {
// 合并两个链表
const mergeTwoLists = function(l1, l2) {
let prev = new ListNode(-1),
head = prev;
while(l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if(l1.val <= l2.val) {
head.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
head.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
head = head.next;
}
head.next = l1 === null ? l2 : l1;
return prev.next;
};
// 分治
const merge = (lists, l, r) => {
if (l == r) return lists[l];
if (l > r) return null;
const mid = (l + r) >> 1;
return mergeTwoLists(merge(lists, l, mid), merge(lists, mid + 1, r));
};
return merge(lists, 0, lists.length - 1);
};方案三:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=23 lang=javascript
*
* [23] 合并K个升序链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode[]} lists
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var mergeKLists = function(lists) {
let queue = new PriorityQueue();
lists.forEach(list => {
if(list) queue.enqueue(list, list.val)
});
let res = new ListNode(-1);
let cur = res;
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
cur.next = queue.dequeue();
cur = cur.next;
if(cur.next) queue.enqueue(cur.next, cur.next.val);
}
return res.next;
}
class Node {
constructor(val, priority) {
this.val = val;
this.priority = priority;
}
}
class PriorityQueue {
constructor() {
this.values = [];
}
enqueue(val, priority) {
let node = new Node(val, priority);
this.values.push(node);
this.bubbleUp();
}
dequeue() {
let max = this.values[0];
let end = this.values.pop();
if(this.values.length) {
this.values[0] = end;
this.bubbleDown();
}
return max.val;
}
isEmpty() {
return !this.values.length;
}
bubbleUp(index = this.values.length - 1) {
if(index <= 0) return;
let parentIndex = Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);
if(this.values[index].priority <= this.values[parentIndex].priority) {
[this.values[index], this.values[parentIndex]] = [this.values[parentIndex], this.values[index]];
this.bubbleUp(parentIndex);
}
}
bubbleDown(index = 0, swapIndex = null) {
let leftIndex = index * 2 + 1,
rightIndex = index * 2 + 2,
length = this.values.length;
if(leftIndex < length) {
if(this.values[leftIndex].priority <= this.values[index].priority) {
swapIndex = leftIndex;
}
}
if(rightIndex < length) {
if((swapIndex === null && this.values[rightIndex].priority <= this.values[index].priority) || (swapIndex !== null && this.values[rightIndex].priority <= this.values[leftIndex].priority)) {
swapIndex = rightIndex;
}
}
if(swapIndex !== null) {
[this.values[index], this.values[swapIndex]] = [this.values[swapIndex], this.values[index]];
this.bubbleDown(swapIndex, null);
}
}
};有三种解法:1、利用数组解决,最后将数组转为链表;2、结合合并两个链表方案,利用分治算法优化;3、构造优先队列进行优化,利用空间换时间
2021.02.22
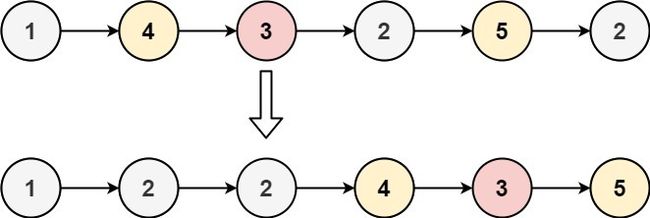
No.86 分隔链表
给你一个链表的头节点 head 和一个特定值 x ,请你对链表进行分隔,使得所有 小于 x 的节点都出现在 大于或等于 x 的节点之前。
你应当 保留 两个分区中每个节点的初始相对位置。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,4,3,2,5,2], x = 3
输出:[1,2,2,4,3,5]
示例 2:
输入:head = [2,1], x = 2
输出:[1,2]
提示:
链表中节点的数目在范围 [0, 200] 内
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
-200 <= x <= 200
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/partition-list
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=86 lang=javascript
*
* [86] 分隔链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} x
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var partition = function(head, x) {
let a = new ListNode(0),
b = new ListNode(0);
const ahead = a,
bhead = b;
while(head) {
if(head.val < x) {
a.next = head;
a = a.next;
} else {
b.next = head;
b = b.next;
}
head = head.next;
}
a.next = bhead.next;
b.next = null;
return ahead.next;
};方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=86 lang=javascript
*
* [86] 分隔链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} x
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var partition = function(head, x) {
// 链表转数组
const list2Arr = head => {
if(!head) return [];
const a = [head.val];
while(head.next) {a.push(head.next.val);head = head.next;}
return a;
}
// 数组转链表
const arr2List = arr => {
if(arr.length == 0) return null;
let head = new ListNode(arr[0]);
let cur = head;
for(let i=1; i < arr.length; i++) {
cur.next = new ListNode(arr[i]);
cur = cur.next;
};
return head;
};
// 数组排序
const arrSort = (arr, x) => {
return [...arr.filter(a => a < x), ...arr.filter(a => a >= x)];
};
return arr2List(arrSort(list2Arr(head), x))
};有两种解法:1、分成大小链表后合并;2、利用数组api排序
2021.03.02
No.725 分隔链表
给定一个头结点为 root 的链表, 编写一个函数以将链表分隔为 k 个连续的部分。
每部分的长度应该尽可能的相等: 任意两部分的长度差距不能超过 1,也就是说可能有些部分为 null。
这k个部分应该按照在链表中出现的顺序进行输出,并且排在前面的部分的长度应该大于或等于后面的长度。
返回一个符合上述规则的链表的列表。
举例: 1->2->3->4, k = 5 // 5 结果 [ [1], [2], [3], [4], null ]
示例 1:
输入:
root = [1, 2, 3], k = 5
输出: [[1],[2],[3],[],[]]
解释:
输入输出各部分都应该是链表,而不是数组。
例如, 输入的结点 root 的 val= 1, root.next.val = 2, oot.next.next.val = 3, 且 root.next.next.next = null。
第一个输出 output[0] 是 output[0].val = 1, output[0].next = null。
最后一个元素 output[4] 为 null, 它代表了最后一个部分为空链表。
示例 2:
输入:
root = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10], k = 3
输出: [[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7], [8, 9, 10]]
解释:
输入被分成了几个连续的部分,并且每部分的长度相差不超过1.前面部分的长度大于等于后面部分的长度。
提示:
root 的长度范围: [0, 1000].
输入的每个节点的大小范围:[0, 999].
k 的取值范围: [1, 50].
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/split-linked-list-in-parts
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=725 lang=javascript
*
* [725] 分隔链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} root
* @param {number} k
* @return {ListNode[]}
*/
var splitListToParts = function (root, k) {
// 1. 获取链表的长度
const getRootLength = root => {
let n = 0;
while (root) {
n++;
root = root.next;
};
return n;
};
// 2. 分析链表的分割方式
// b项是 a+1;k-b项是 a
const len = getRootLength(root),
a = ~~(len / k),
b = len % k;
// 3. 分割链表
const r = []; // 返回的链表数组
// 循环链表
for(let m = 1;m<=k;m++) {
if(!root) {
r.push(null);
continue;
}
let p1 = root,
p2 = root,
num = a;
if(m<=b) {
while(num-->0) p2 = p2.next;
} else {
num -=1;
while(num-->0) p2 = p2.next;
};
// 处理p2为null
if(!p2) {
r.push(p1);
root = null;
continue;
}
root = p2.next;
p2.next = null;
r.push(p1);
}
return r;
};关键在于对k的分离,判断不同的分割长度,对边界条件处理需要注意
总结:
- 链表的合并与分割主要新链表的构造,需要根据要求进行拆分与组合,常见的构造链表有双指针法及堆栈法
- 特殊的,由于js没有自己的链表结构,因而可以将链表转为数组,利用相关api去处理
删除节点
2021.03.04
No.203 移除链表元素
删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点。
示例:
输入: 1->2->6->3->4->5->6, val = 6
输出: 1->2->3->4->5
方案:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=203 lang=javascript
*
* [203] 移除链表元素
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} val
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var removeElements = function(head, val) {
if(!head) return null;
let p = phead = new ListNode(null);
p.next = head;
while(p.next) {
if(p.next.val == val) {
p.next = p.next.next;
} else {
p = p.next;
}
}
return phead.next;
};链表的构造,使用哑节点构造头指针进行双指针遍历
2021.03.06
No.19 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
进阶:你能尝试使用一趟扫描实现吗?
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2
输出:[1,2,3,5]
示例 2:
输入:head = [1], n = 1
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:head = [1,2], n = 1
输出:[1]
提示:
链表中结点的数目为 sz
1 <= sz <= 30
0 <= Node.val <= 100
1 <= n <= sz
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=19 lang=javascript
*
* [19] 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} n
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var removeNthFromEnd = function(head, n) {
let p = head, q = head, m = phead = new ListNode(head);
m.next = head;
// 将q指针变为 q = head.next···next 有n个next
for( let _n = n; _n > 0; _n-- ) {
q = head.next;
head = head.next;
};
// 当q为null时 停止遍历
while(q) {
p = p.next;
q = q.next;
m = m.next;
};
// 删除此时q的节点
p = p.next;
m.next = p;
return phead.next;
};方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=19 lang=javascript
*
* [19] 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} n
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var removeNthFromEnd = function(head, n) {
let lastN = 0;
const recursion = (head) => {
if (!head) {
return null;
}
const next = recursion(head.next);
lastN++;
if (lastN === n) {
head = next;
}
if (lastN === n + 1) {
head.next = next;
}
return head;
};
return recursion(head);
};方案三:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=19 lang=javascript
*
* [19] 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} n
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var removeNthFromEnd = function(head, n) {
const nowHead = [head];
let tempHead = head;
while (tempHead.next) {
nowHead.push(tempHead.next);
tempHead = tempHead.next;
}
let lastN = 0;
let isHead = true;
while (nowHead.length) {
lastN++;
const now = nowHead.pop();
if (lastN - 1 === n) {
isHead = false;
now.next = now.next.next;
}
}
if (isHead) {
head = head.next;
}
return head;
};有三种方案:1、快慢指针,设置快慢指针间距为n,进行遍历;2、递归;3、迭代
2021.03.09
No.82 删除排序链表中的重复元素 ii
给定一个排序链表,删除所有含有重复数字的节点,只保留原始链表中 没有重复出现 的数字。
示例 1:
输入: 1->2->3->3->4->4->5
输出: 1->2->5
示例 2:
输入: 1->1->1->2->3
输出: 2->3
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list-ii
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=82 lang=javascript
*
* [82] 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var deleteDuplicates = function (head) {
if (!head) return null;
let h = p = new ListNode(head),
q = head;
h.next = head;
p.next = head
while (q && q.next) {
if ( q.val == q.next.val) {
while(q.next && q.val == q.next.val) q = q.next;
p.next = q.next;
} else {
p = p.next;
}
q = q.next;
}
return h.next;
};双指针处理,需要注意边界处理
2021.03.10
No.83 删除排序链表中的重复元素
给定一个排序链表,删除所有重复的元素,使得每个元素只出现一次。
示例 1:
输入: 1->1->2
输出: 1->2
示例 2:
输入: 1->1->2->3->3
输出: 1->2->3
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=83 lang=javascript
*
* [83] 删除排序链表中的重复元素
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var deleteDuplicates = function(head) {
if(!head) return null;
let h = p = new ListNode(head),
q = head;
h.next = head;
p.next = head;
while(q && q.next) {
if(q.next.val == q.val) {
while(q.next && q.next.val == q.val) {
q = q.next;
}
p.next = q;
}
p = p.next;
q = q.next;
};
return h.next;
};方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=83 lang=javascript
*
* [83] 删除排序链表中的重复元素
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var deleteDuplicates = function(head) {
if(!head || !head.next) return head;
head.next = deleteDuplicates(head.next);
if(head.next.val == head.val) {
head.next = head.next.next;
}
return head;
};同82题,有两种方案:1、快慢指针,也可以使用单指针遍历;2、递归
2021.03.11
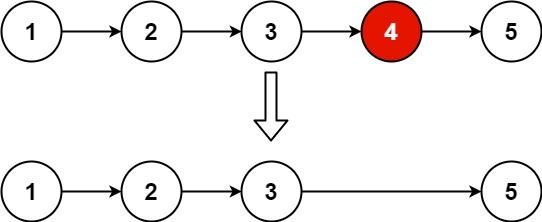
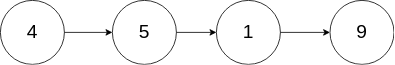
No.237 删除链表中的节点
请编写一个函数,使其可以删除某个链表中给定的(非末尾)节点。传入函数的唯一参数为 要被删除的节点 。
现有一个链表 -- head = [4,5,1,9],它可以表示为:
示例 1:
输入:head = [4,5,1,9], node = 5
输出:[4,1,9]
解释:给定你链表中值为 5 的第二个节点,那么在调用了你的函数之后,该链表应变为 4 -> 1 -> 9.
示例 2:
输入:head = [4,5,1,9], node = 1
输出:[4,5,9]
解释:给定你链表中值为 1 的第三个节点,那么在调用了你的函数之后,该链表应变为 4 -> 5 -> 9.
提示:
链表至少包含两个节点。
链表中所有节点的值都是唯一的。
给定的节点为非末尾节点并且一定是链表中的一个有效节点。
不要从你的函数中返回任何结果。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/delete-node-in-a-linked-list
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=237 lang=javascript
*
* [237] 删除链表中的节点
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} node
* @return {void} Do not return anything, modify node in-place instead.
*/
var deleteNode = function(node) {
if(!node) return null;
node.val = node.next.val;
node.next = node.next.next;
};没有头结点删除节点的方案,移花接木,需要替换当前值,然后删除下一个节点值
总结:
- 删除节点最常见的方案是快慢指针的遍历删除,快指针探索,慢指针作为最后需要返回的链表路径对节点进行相应的控制;
- 也可以使用递归、迭代、栈等额外的空间来换取相应的时间效率
特殊链表
2021.03.15
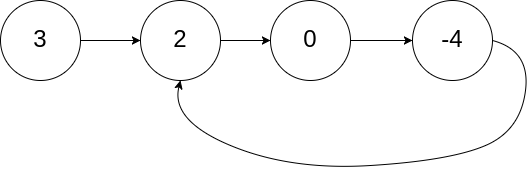
No.141 环形链表
给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
如果链表中存在环,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
进阶:
你能用 O(1)(即,常量)内存解决此问题吗?
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2: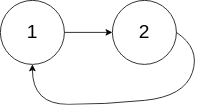
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:
输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:false
解释:链表中没有环。
提示:
链表中节点的数目范围是 [0, 104]
-105 <= Node.val <= 105
pos 为 -1 或者链表中的一个 有效索引 。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=141 lang=javascript
*
* [141] 环形链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {boolean}
*/
var hasCycle = function(head) {
if(!head) return false;
let hash = new Map();
while(head) {
if(hash.has(head)) return true;
hash.set(head, true);
head = head.next;
}
return false;
};方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=141 lang=javascript
*
* [141] 环形链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {boolean}
*/
var hasCycle = function(head) {
let fast = head;
let slow = head;
while (fast) {
if (fast.next == null) return false;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) return true;
}
return false;
};方案三:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=141 lang=javascript
*
* [141] 环形链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {boolean}
*/
var hasCycle = function(head) {
try {
JSON.stringify(head)
return false
} catch {
return true
}
};有三种解法:1、构造hash表;2、快慢指针判断;3、取巧,利用JSON.stringify的不能循环引用
2021.04.26
No.160 相交链表
编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
如下面的两个链表: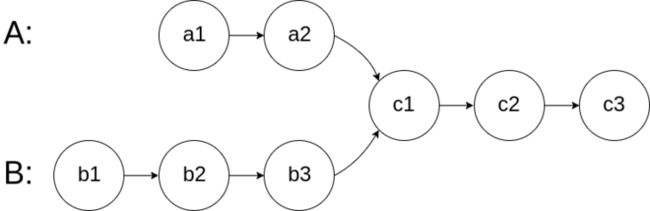
在节点 c1 开始相交。
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Reference of the node with value = 8
输入解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
输出:Reference of the node with value = 2
输入解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [0,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
输出:null
输入解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
解释:这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null。
注意:
如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null.
在返回结果后,两个链表仍须保持原有的结构。
可假定整个链表结构中没有循环。
程序尽量满足 O(n) 时间复杂度,且仅用 O(1) 内存。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=160 lang=javascript
*
* [160] 相交链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} headA
* @param {ListNode} headB
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var getIntersectionNode = function (headA, headB) {
if (!headA || !headB) return null;
let pA = headA;
while (pA) {
let pB = headB;
while (pB) {
if (pA === pB) return pA;
pB = pB.next;
}
pA = pA.next;
}
};方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=160 lang=javascript
*
* [160] 相交链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} headA
* @param {ListNode} headB
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var getIntersectionNode = function (headA, headB) {
if (!headA || !headB) return null;
const hashmap = new Map();
let pA = headA;
while (pA) {
hashmap.set(pA, 1);
pA = pA.next;
}
let pB = headB;
while (pB) {
if (hashmap.has(pB)) return pB;
pB = pB.next;
}
};方案三:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=160 lang=javascript
*
* [160] 相交链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} headA
* @param {ListNode} headB
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var getIntersectionNode = function (headA, headB) {
if (!headA || !headB) return null;
let pA = headA,
pB = headB;
while(pA != pB) {
pA = pA === null ? headB : pA.next;
pB = pB === null ? headA : pB.next;
}
return pA;
};方案四:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=160 lang=javascript
*
* [160] 相交链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} headA
* @param {ListNode} headB
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var getIntersectionNode = function (headA, headB) {
let aNum = 0
let bNum = 0
let short = headA
let long = headB
let tempA = headA
let tempB = headB
while (short) {
aNum += 1
short = short.next
}
while (long) {
bNum += 1
long = long.next
}
if (aNum > bNum) {
let dig = aNum - bNum
for (let i = 0; i < dig; i++) {
tempA = tempA.next
}
while (tempA) {
if(tempA == tempB) {
return tempA
} else {
tempA = tempA.next
tempB = tempB.next
}
}
}
if (aNum < bNum) {
let dig = bNum - aNum
for (let i = 0; i < dig; i++) {
tempB = tempB.next
}
while (tempA) {
if(tempA == tempB) {
return tempA
} else {
tempA = tempA.next
tempB = tempB.next
}
}
}
if (aNum = bNum) {
while (tempA) {
if(tempA == tempB) {
return tempA
} else {
tempA = tempA.next
tempB = tempB.next
}
}
}
};有四种方案:1、暴解,让A去找B;2、先遍历一遍生成hash表,然后判断;3、形成交叉的环形链表,交叉遍历;4、先遍历算出最长表,让最长表先走然后同步判断
2021.04.27
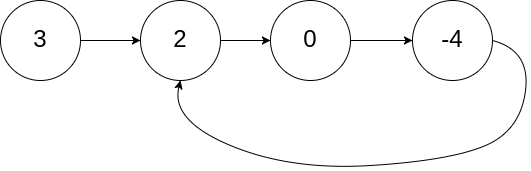
No.142 环形链表 ii
给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意,pos 仅仅是用于标识环的情况,并不会作为参数传递到函数中。
说明:不允许修改给定的链表。
进阶:
你是否可以使用 O(1) 空间解决此题?
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:返回索引为 1 的链表节点
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2: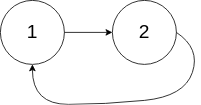
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:返回索引为 0 的链表节点
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:
输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:返回 null
解释:链表中没有环。
提示:
链表中节点的数目范围在范围 [0, 104] 内
-105 <= Node.val <= 105
pos 的值为 -1 或者链表中的一个有效索引
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=142 lang=javascript
*
* [142] 环形链表 II
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var detectCycle = function(head) {
if(!head) return null;
let hash = new Map();
while(head) {
if(hash.has(head)) return head;
hash.set(head);
head = head.next;
}
return null;
};方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=142 lang=javascript
*
* [142] 环形链表 II
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var detectCycle = function(head) {
if (head === null) {
return null;
}
let slow = head, fast = head;
while (fast !== null) {
slow = slow.next;
if (fast.next !== null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
} else {
return null;
}
if (fast === slow) {
let ptr = head;
while (ptr !== slow) {
ptr = ptr.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return ptr;
}
}
return null;
};有两种方案:1、利用map或set数据结构进行链表的记录,空间复杂度为O(N);2、利用快慢指针,计算相遇的距离,省去了数据结构的存储空间,空间复杂度为O(1)
2021.05.10
No.143 重排链表
给定一个单链表 L:L0→L1→…→Ln-1→Ln ,将其重新排列后变为: L0→Ln→L1→Ln-1→L2→Ln-2→…
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
示例 1:
给定链表 1->2->3->4, 重新排列为 1->4->2->3.
示例 2:
给定链表 1->2->3->4->5, 重新排列为 1->5->2->4->3.
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reorder-list
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=143 lang=javascript
*
* [143] 重排链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {void} Do not return anything, modify head in-place instead.
*/
var reorderList = function(head) {
// 翻转链表
const reverseList = head => {
let cur = head;
let pre = null;
while(cur !== null){
let temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return pre;
}
// 分割链表
const spliceList = head => {
let dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
let slow = dummy;
let quick = dummy;
while (quick && quick.next) {
slow = slow.next;
quick = quick.next;
quick = quick.next;
}
let right = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
let left = dummy.next;
return {
left,
right,
dummy
}
}
let { left, right, dummy } = spliceList(head);
right = reverseList(right);
while (left && right) {
let lNext = left.next;
let rNext = right.next;
right.next = left.next;
left.next = right;
left = lNext;
right = rNext;
}
return dummy.next
};方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=143 lang=javascript
*
* [143] 重排链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {void} Do not return anything, modify head in-place instead.
*/
var reorderList = function(head) {
let list = []; // 使用数组存储链表
let node = head; // 使用node遍历链表
// 遍历链表,将每个元素依次存入数组
while (node) {
list.push(node);
node = node.next;
}
let i = 0; // 使用i指针从头往后遍历list
let j = list.length - 1; // 使用j指针从后往前遍历list
// 两个指针向中间推进,直到相遇
while (i < j) {
// 将i指向j,并将i向后移动一位
list[i++].next = list[j];
// 将j指向i,并将j向前移动一位
list[j--].next = list[i];
}
// list[i].next需要设置为null,否则链表会成环
list[i].next = null;
// head也是新链表的头结点
return head;
};有两种方案:1、快慢指针分割左右链表,利用左右链表的插入合成新链表;2、利用数组的位置进行合并处理
2021.05.11
No.148 排序链表
给你链表的头结点 head ,请将其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的链表 。
进阶:
你可以在 O(n log n) 时间复杂度和常数级空间复杂度下,对链表进行排序吗?
输入:head = [4,2,1,3]
输出:[1,2,3,4]
示例 2: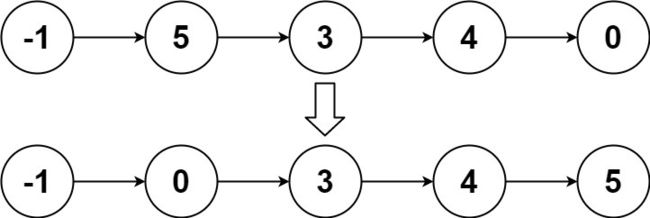
输入:head = [-1,5,3,4,0]
输出:[-1,0,3,4,5]
示例 3:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
提示:
链表中节点的数目在范围 [0, 5 * 104] 内
-105 <= Node.val <= 105
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sort-list
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=148 lang=javascript
*
* [148] 排序链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var sortList = function(head) {
// 链表转数组
const list2Arr = head => {
if(!head) return [];
const a = [head.val];
while(head.next) {a.push(head.next.val);head = head.next;}
return a;
}
// 数组转链表
const arr2List = arr => {
if(arr.length == 0) return null;
let head = new ListNode(arr[0]);
let cur = head;
for(let i=1; i < arr.length; i++) {
cur.next = new ListNode(arr[i]);
cur = cur.next;
};
return head;
};
// 对数组重新排序
const sortArr = arr => {
return arr.sort((a,b) => a-b)
}
return arr2List(sortArr(list2Arr(head)))
};方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=148 lang=javascript
*
* [148] 排序链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var sortList = function(head) {
if (!head || !head.next) return head;
let slow = head, fast = head;
let preSlow = null;
while (fast && fast.next) {
preSlow = slow;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
preSlow.next = null;
const l = sortList(head);
const r = sortList(slow);
// 合并链表函数
const merge = (l1, l2) => {
const dummy = new ListNode(0);
let prev = dummy;
while (l1 && l2) {
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
prev.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
prev.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
prev = prev.next;
}
if (l1) prev.next = l1;
if (l2) prev.next = l2;
return dummy.next;
};
return merge(l, r);
};有两种方案:1、数组操作,利用自带的sort排序;2、归并排序,快慢指针实现
2021.05.12
No.234 回文链表
请判断一个链表是否为回文链表。
示例 1:
输入: 1->2
输出: false
示例 2:
输入: 1->2->2->1
输出: true
进阶:
你能否用 O(n) 时间复杂度和 O(1) 空间复杂度解决此题?
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/palindrome-linked-list
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案一:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=234 lang=javascript
*
* [234] 回文链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {boolean}
*/
var isPalindrome = function(head) {
// 翻转链表
const reverseList = head => {
let cur=head;
let pre=null;
while(cur !== null){
let temp=cur.next;
cur.next=pre;
pre=cur;
cur=temp;
}
return pre;
}
// 分割链表
const splitList = head => {
let fast = head;
let slow = head;
while (fast.next !== null && fast.next.next !== null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
if (head == null) return true;
let l = head;
let _l = reverseList(splitList(head).next);
while( l !== null && _l !== null ) {
if(l.val !== _l.val) {
return false;
}
l = l.next;
_l = _l.next;
}
return true;
};方案二:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=234 lang=javascript
*
* [234] 回文链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {boolean}
*/
var isPalindrome = function(head) {
let a='',b='';
while(head!=null){
a=a+head.val;
b=head.val+b;
head=head.next;
}
return a===b;
};方案三:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=234 lang=javascript
*
* [234] 回文链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {boolean}
*/
var isPalindrome = function(head) {
const vals = [];
while (head !== null) {
vals.push(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
for (let i = 0, j = vals.length - 1; i < j; ++i, --j) {
if (vals[i] !== vals[j]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
};有三种方案:1、利用快慢指针拿到后半段链表进行翻转比较;2、利用js的加号特性,实现了一个类似栈型的操作;3、利用数组实现翻转数组的比较
2021.05.13
No.328 奇偶链表
给定一个单链表,把所有的奇数节点和偶数节点分别排在一起。请注意,这里的奇数节点和偶数节点指的是节点编号的奇偶性,而不是节点的值的奇偶性。
请尝试使用原地算法完成。你的算法的空间复杂度应为 O(1),时间复杂度应为 O(nodes),nodes 为节点总数。
示例 1:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 1->3->5->2->4->NULL
示例 2:
输入: 2->1->3->5->6->4->7->NULL
输出: 2->3->6->7->1->5->4->NULL
说明:
应当保持奇数节点和偶数节点的相对顺序。
链表的第一个节点视为奇数节点,第二个节点视为偶数节点,以此类推。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/odd-even-linked-list
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方案:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=328 lang=javascript
*
* [328] 奇偶链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var oddEvenList = function(head) {
if(!head) return null;
let p = head,
q = head.next,
tmp = q;
while(q && q.next) {
p.next = p.next.next;
q.next = q.next.next;
p = p.next;
q = q.next;
}
p.next = tmp;
return head;
};利用双指针进行分割处理
总结:
- 特殊链表最常见的方案是快慢指针的进行相关的链表查找及处理,然后根据特殊链表的形式要求进行拆分及组合等;
- 也可以使用额外的数据结构如栈及hash表等进行处理