FastJson的使用
使用maven导入依赖包
com.alibaba fastjson 1.2.70
常用方法:
1.JSON.toJSONString(obejct) - java对象转JSON字符串,
注意:
默认情况下,如果int类型和boolean类型的属性没赋值的时候 (public boolean a; public int b;),调用 JSON.toJSONString(obejct) 序列化后,a和b不会被过滤掉,而是返回boolean类型和int类型的默认值 false和0。当然其他类型如果没有赋值,序列化时,会被过滤掉。
来看下例子就明白了
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List userList = new ArrayList<>();
User user = new User();
user.setName("123");
userList.add(user);
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(userList));
}
public static class User{
private String name;
private int age;
public boolean health;
public Date time;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
}
先给name赋值,其他的都不赋值,结果time属性被过滤掉了,如下:
再看下都不赋值的情况,结果name和time属性都被过滤掉了,而int类型的age和boolean类型的health属性取得时类型的默认值:
2.JSON.parseObject(string, User.class) - JSON字符串转java对象
(1)List集合转JSON
@RestController
public class Json {
@RequestMapping(value = "/json")
public String json() throws Exception{
List userList = new ArrayList<>();
userList.add(new User("1", "1", 20));
String res = JSON.toJSONString(userList);
return res;
}
}
(2)Map集合转JSON
package com.lxc.Test;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class Json {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map userList = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i ++) {
userList.put("user"+i, new User("name"+i, 20+i));
}
System.out.println("json:"+JSON.toJSONString(userList));
}
public static class User{
private String name;
private int age;
public User(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
}
反序列化
1.JSON转Java对象 - JSON.perseObject()
public class Json {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String json = "{\"age\":20,\"name\":\"name0\"}";
System.out.println(JSON.parseObject(json, User.class)+"");
}
}
2.JSON转Java集合 - JSON.perseArray()
public class Json {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String json = "[{\"age\":20,\"name\":\"name0\"}]";
List userList = JSON.parseArray(json, User.class);
userList.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
JSON.toJSONString() 参数 - SerializerFeature枚举常量
toJSONString 静态方法参数有两个:
参数一:要序列化的对象;
参数二:SerializerFeature 枚举类型的可变参数 ( 我们可以传递多个参数 ),进行序列化时,我们可以定义特殊的需求。
1.SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue
对一个对象或者列表进行序列化时,默认情况下如果属性值为null,序列化后的结果会过滤掉其属性,如果想保留其属性值,可以使用 SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue。
public class Json {
public static void main(String[] args) {
User user = new User();
user.setAge(20);
String res = JSON.toJSONString(user, SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue);
System.out.println(res);
}
public static class User{
private String name = null;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
}
2.SerializerFeature.WriteNullStringAsEmpty
对一个对象或者列表进行序列,把属性值为null的字段进行转化为 "" 双引号。
public class Json {
public static void main(String[] args) {
User user = new User();
user.setAge(20);
String res = JSON.toJSONString(user, SerializerFeature.WriteNullStringAsEmpty);
System.out.println(res);
}
}
3.SerializerFeature.WriteNullNumberAsZero
序列之后, 把属性值为 null 的属性转化为 0,这个前提是此属性是 int 类型的!
public class Json {
public static void main(String[] args) {
User user = new User();
user.setName("测试");
String res = JSON.toJSONString(user, SerializerFeature.WriteNullNumberAsZero);
System.out.println(res);
}
}
4.SerializerFeature.WriteNullBooleanAsFalse
序列之后, 把属性值为 null 的属性转化为 false,这个前提是此属性是 boolean 类型的!
@Data
public class User{
private String name;
private int age;
private boolean health;
}
5.SerializerFeature.WriteDateUseDateFormat
把时间戳序列化为正常的时间,默认输出JSON.toJSONString() 序列之后, 默认输出如下:
添加 SerializerFeature.WriteDateUseDateFormat 之后的效果:
@Data
public class User{
private String name;
private int age;
private Date birthday = new Date();
private boolean health;
}
6.SerializerFeature.PrettyFormat
序列化的数据纵向布局。
@JSonField() 注解
在序列化时,进行个性定制!该注解的作用于方法上,字段上、参数上,可在序列化和反序列化时进行特性功能定制。
1.注解属性 name序列化后的名字(单独序列化,对属性名进行修改)
@JSONField(name="username") private String name;
2.注解属性 ordinal序列化后的顺序(字段的排序)
@JSONField(ordinal = 1) private String name; @JSONField(ordinal = 2) private int age;
3.注解属性 format 序列化后的格式
@JSONField(format = "YYYY-MM-dd") private Date birthday = new Date();
4.注解属性 serialize 是否序列化该字段(默认为true,如果false,当字段值为null时,会被过滤掉)
5.使用serializeUsing来定制属性的序列化类
什么意思呢,类似vue中的过滤器,可以单独订制处理类下的某个属性:
第一步:编写一个类A,实现ObjectSerializer 接口;
第二步:重写write方法;
第三步:在需要定制化的属性上边 添加注解,@JSONField(serializeUsing = A.class)
具体实现如下:
public class Json {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List userList = new ArrayList<>();
User user = new User();
user.setName("测试,");
userList.add(user);
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(userList));
}
public static class SerializeUsingFn implements ObjectSerializer {
@Override
public void write(JSONSerializer jsonSerializer, Object fieldValue, Object fieldName, Type fieldType, int i) throws IOException {
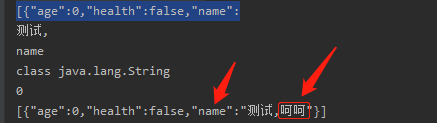
System.out.println(fieldValue); // 测试,
System.out.println(fieldName); // name
System.out.println(fieldType); // String
System.out.println(i); // 0
String name = (String) fieldValue; // 向下转型,获取到age属性值
String filterName = name + "呵呵"; // 这里可以对name属性进行定制化
jsonSerializer.write(filterName); // 调用write方法
}
}
public static class User{
@JSONField(serializeUsing = SerializeUsingFn.class)
private String name;
private int age;
public boolean health;
public Date time;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
}
可以看到name字段值 被修改了后边添加了 "呵呵" 俩字。
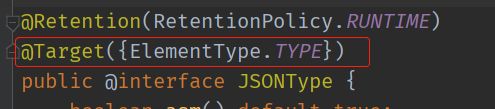
@JSONType() 注解
只能作用在类上,也是对类里边的字段进行序列化
@JSONType()注解中的属性
· includes 要序列化的字段(注意:如果字段上有 @serialize(true),如果没有includes字段也不会被序列化),它是一个数组,源码如下:
@Data
@JSONType(includes = {"name", "age"})
public class User{
private String name;
private int age;
private boolean health;
private Date birthday = new Date();
}
· orders序列化后的字段顺序,也是一个数组,源码如下:
@JSONType(includes = {"name","birthday", "health", "age"}, orders = {"age","name","birthday","health"})
public static class User{
private String name;
private int age;
private boolean health;
private Date birthday = new Date();
}
FastJson属性名过滤器
过滤字段,通过 SimplePropertyPreFilter 过滤器,来过滤指定的属性名,然后在转JSON的时候,带上过滤器参数即可。
例如,把下边属性health 过滤掉:
// userList = [{"age":20,"health":true,"name":"测试,呵呵","time":"2021-06-29 09:40:55"}]
SimplePropertyPreFilter filter = new SimplePropertyPreFilter();
// 下边方法也很好理解:调用过滤器上边的getExcludes排除字段的方法,什么字段需要排除呢:add() 添加需要排除的字段即可
filter.getExcludes().add("health");
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(userList, filter));
![]()
当然,如果需要排除大量的字段,保留一个字段,可以使用:filter.getIncludes() .add("xxx") 方法,意思:只保留xxx属性,其他的都会被过滤。
如果过滤或者添加多个字段,可以使用:addAll() 方法,参数必须是一个集合Collection 。
过滤多个字段:
SimplePropertyPreFilter filter = new SimplePropertyPreFilter(); Listr = new ArrayList<>() { { add("health"); add("name"); } }; filter.getExcludes().addAll(r); System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(userList, filter));
暂时就这么多,项目中用到别的方法在记录!
到此这篇关于浅谈Java中FastJson的使用的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关FastJson的使用内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!