Java并发——ThreadPoolExecutor详解(二)
工厂ThreadFactory+execute()+UncaughtExceptionHandler处理异常
public class Run4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 99999, 9999L,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingDeque<Runnable>());
pool.setThreadFactory(new MyThreadFactory());
pool.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + System.currentTimeMillis());
String abc = null;
abc.indexOf(0);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + System.currentTimeMillis());
});
}
}
class MyThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory{
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread thread = new Thread(r);
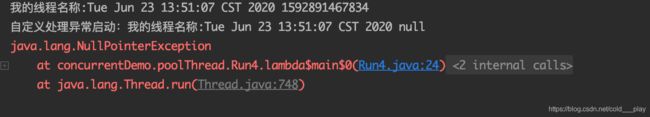
thread.setName("我的线程名称:" + new Date());
thread.setUncaughtExceptionHandler(new Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler() {
@Override
public void uncaughtException(Thread t, Throwable e) {
System.out.println("自定义处理异常启动:" + t.getName() + " " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
return thread;
}
}
set/getRejectedExecutionHandler()
方法setRejectedExecutionHandler()和getRejectedExecutionHandler()的作用是可以处理任务被拒绝执行时的行为。
public class MyRunnable3 implements Runnable {
private String username;
public MyRunnable3(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + System.currentTimeMillis());
Thread.sleep(4000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + System.currentTimeMillis());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyRunnable3 r1 = new MyRunnable3("111");
MyRunnable3 r2 = new MyRunnable3("222");
MyRunnable3 r3 = new MyRunnable3("333");
MyRunnable3 r4 = new MyRunnable3("444");
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 3, 999L,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
pool.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new RejectedExecutionHandler() {
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
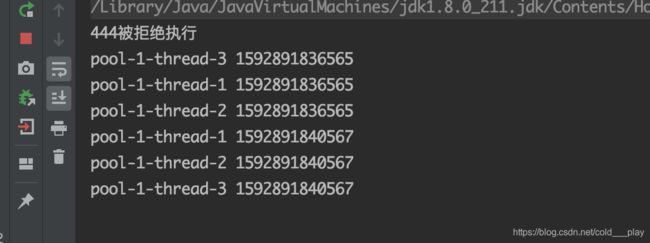
System.out.println(((MyRunnable3)r).username + "被拒绝执行");
}
});
pool.execute(r1);
pool.execute(r2);
pool.execute(r3);
pool.execute(r4);
}
}
allowsCoreThreadTimeOut()/(boolean)
方法allowsCoreThreadTimeOut()和allowsCoreThreadTimeOut(boolean value) 的作用是配置核心线程是否有超时的效果。
public class Run5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(4, 5, 5,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
System.out.println(pool.allowsCoreThreadTimeOut());
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
pool.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "begin " + System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "end " + System.currentTimeMillis());
});
}
Thread.sleep(4000);
System.out.println(pool.getPoolSize());
}
}
public class Run5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(4, 5, 5,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
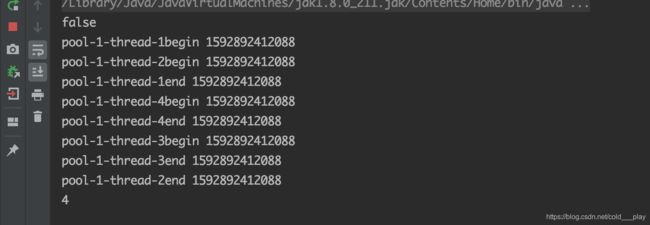
pool.allowCoreThreadTimeOut(true);
System.out.println(pool.allowsCoreThreadTimeOut());
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
pool.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "begin " + System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "end " + System.currentTimeMillis());
});
}
Thread.sleep(4000);
System.out.println(pool.getPoolSize());
}
}
prestartCoreThread()和prestartAllCoreThreads()
方法 prestartCoreThread每调用一次就创建一个核心线程,返回值为 boolean,含义是是否启动了
public class Run6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("打印了!begin " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
Thread.sleep(4000);
System.out.println("打印了!end " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 2, 5,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingDeque<Runnable>());
System.out.println("线程池中的线程数A:" + pool.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("Z1=" + pool.prestartCoreThread());
System.out.println("线程池中的线程数B:" + pool.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("Z2=" + pool.prestartCoreThread());
System.out.println("线程池中的线程数C:" + pool.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("Z3=" + pool.prestartCoreThread());//无效代码
System.out.println("Z4=" + pool.prestartCoreThread());//无效代码
System.out.println("Z5=" + pool.prestartCoreThread());//无效代码
System.out.println("Z6=" + pool.prestartCoreThread());//无效代码
System.out.println("线程池中的线程数D:" + pool.getPoolSize());
}
}

方法 prestartAllCoreThreads的作用是启动全部核心线程,返回值是启动核心线程的数量。
public class Run6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("打印了!begin " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
Thread.sleep(4000);
System.out.println("打印了!end " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 2, 5,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingDeque<Runnable>());
System.out.println("线程池中的线程数A:" + pool.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("启动核心线程数量为:" + pool.prestartAllCoreThreads());
System.out.println("线程池中的线程数B:" + pool.getPoolSize());
}
}
getCompletedTaskCount()
取得已经执行完成的任务数。
ThreadPoolExecutor的拒绝策略
线程池中的资源全部被占用的时候,对新添加的Task任务有不同的处理策略,在默认的情况下, ThreadPoolExecutor类中有4种不同的处理方式:
AbortPolicy:当任务添加到线程池中被拒绝时,它将抛出 RejectedExecution Exception异常。CallerrunsPolicy:当任务添加到线程池中被拒绝时,会使用调用线程池的 Thread线程对象处理被拒绝的任务。DiscardOldestPolicy:当任务添加到线程池中被拒绝时,线程池会放弃等待队列中最旧的未处理任务,然后将被拒绝的任务添加到等待队列中。DiscardPolicy:当任务添加到线程池中被拒绝时,线程池将丢弃被拒绝的任务。
AbortPolicy:
AbortPolicy策略是当任务添加到线程池中被拒绝时,它将抛出 RejectedExecutionException异常。
public class AbortDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " run end!");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 3, 5,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(2), new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
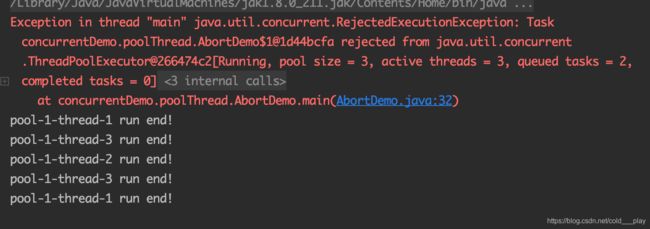
pool.execute(runnable);//不报错 立即在核心线程运行
pool.execute(runnable);//不报错 立即在核心线程运行
pool.execute(runnable);//不报错 未超过最大线程数,创建一个新线程运行
pool.execute(runnable);//不报错 放入队列
pool.execute(runnable);//不报错 放入队列
pool.execute(runnable);//队列满了,报错
}
}
CallerRunsPolicy:
Caller Runs Policy策略是当任务添加到线程池中被拒绝时,会使用调用线程池的 Thread线程对象处理被拒绝的任务。
public class CallerRunsDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThreadA a = new MyThreadA();
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 3, 5,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(2), new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
System.out.println("a begin " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + System.currentTimeMillis());
pool.execute(a);
pool.execute(a);
pool.execute(a);
pool.execute(a);
pool.execute(a);
pool.execute(a);
System.out.println("a end " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
class MyThreadA extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println("end" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + System.currentTimeMillis());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
在上面的实验中,线程main被阻塞,严重影响程序
的运行效率,所以并不建议这样做.
DiscardOldestPolicy:
DiscardOldestPolicy策略是当任务添加到线程池中被
拒绝时,线程池会放弃等待队列中最旧的未处理任务,然
后将被拒绝的任务添加到等待队列中。
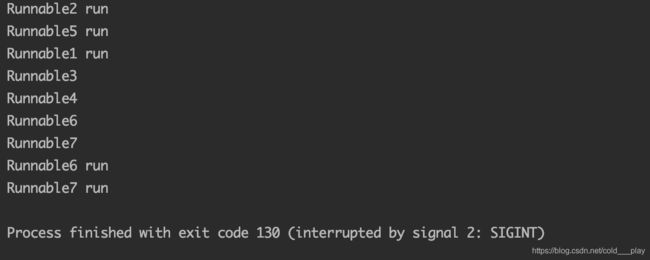
public class DiscardOldestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ArrayBlockingQueue queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue(2);
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 3, 5,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, queue, new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy());
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
MyThreadD r = new MyThreadD("Runnable" + (i + 1));
executor.execute(r);
}
Thread.sleep(50);
Iterator iterator = queue.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object next = iterator.next();
System.out.println(((MyThreadD)next).getUsername());
}
executor.execute(new MyThreadD("Runnable6"));
executor.execute(new MyThreadD("Runnable7"));
iterator = queue.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object next = iterator.next();
System.out.println(((MyThreadD)next).getUsername());
}
}
}
class MyThreadD extends Thread {
private String username;
public MyThreadD(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(username + " run");
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
DiscardPolicy:
DiscardPolicy策略是当任务添加到线程池中被拒绝时,线程池将丢弃被拒绝的任务。
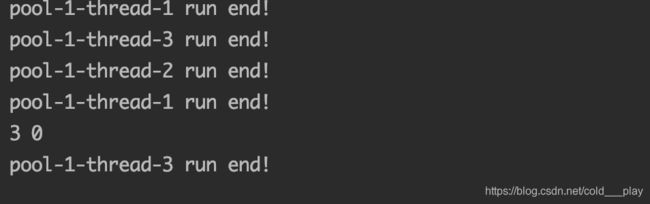
public class DiscardDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " run end!");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
ArrayBlockingQueue queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue(2);
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 3, 5,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, queue, new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy());
executor.execute(runnable);
executor.execute(runnable);
executor.execute(runnable);
executor.execute(runnable);
executor.execute(runnable);
executor.execute(runnable);
executor.execute(runnable);
executor.execute(runnable);
Thread.sleep(10000);
System.out.println(executor.getPoolSize() + " " + queue.size());
}
}
afterExecute()和beforeExecute()
在线程池 ThreadPoolExecutor类中重写这两个方法可以
对线程池中执行的线程对象实现监控。
public class MyPool extends ThreadPoolExecutor {
public MyPool(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
super(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue, handler);
}
@Override
protected void afterExecute(Runnable r, Throwable t) {
super.afterExecute(r, t);
System.out.println("执行完毕...");
}
@Override
protected void beforeExecute(Thread t, Runnable r) {
super.beforeExecute(t, r);
System.out.println("准备执行...");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyPool pool = new MyPool(2, 2, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(), new AbortPolicy());
pool.execute(() -> {
System.out.println("执行中...");
});
}
}
remove(Runnable)
方法 remove( Runnable)可以删除尚未被执行的Runnable任务。
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " begin");
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " end");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 10,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingDeque<>());
executor.execute(runnable);
Thread.sleep(1000);
executor.remove(runnable);
System.out.println("任务正在运行不能删除...");
}
}
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " begin");
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " end");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
Runnable runnable2 = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " begin");
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " end");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 10,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingDeque<>());
executor.execute(runnable);
executor.execute(runnable2);
Thread.sleep(1000);
executor.remove(runnable2);
}
}
executor()方法提交的且并未执行的任务可以删除。

注意:submit()方法提交的任务,无论是否正在执行,都不可以删除!!!!
多个get方法
getActiveCount():
方法 getActive Counto的作用是取得有多少个线程正在执行任务。
getCompletedTaskCount():
方法 getCompleted Task Count0的作用是取得有多少个线程已经执行完任务了。
getCorePoolSize():
方法 getCorePoolSize的作用是取得构造方法传入的 core Poolsize参数值。
getMaximumPoolSize():
方法 getMaximum PoolSize O的作用是取得构造方法传入的 maximum PoolSize参数值。
getPoolSize():
方法 getPoolSize O的作用是取得池中有多少个线程。
getTaskCount():
方法 getTask Count0的作用是取得有多少个任务发送给了线程池。
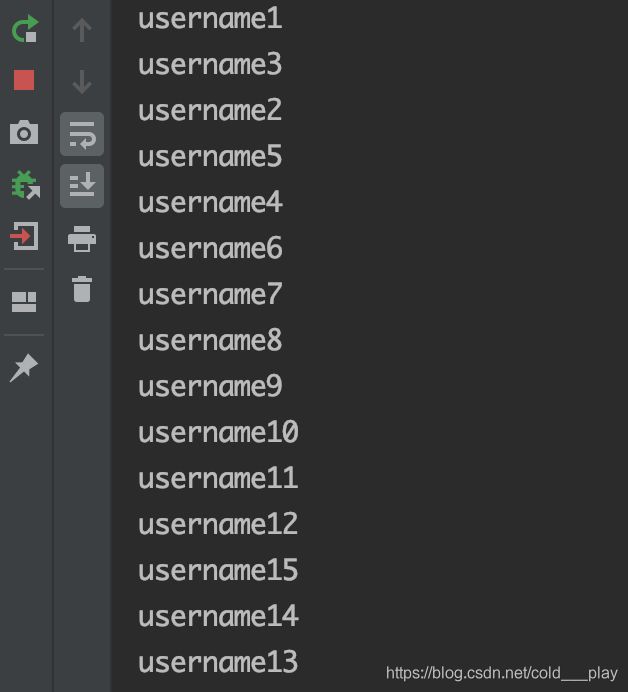
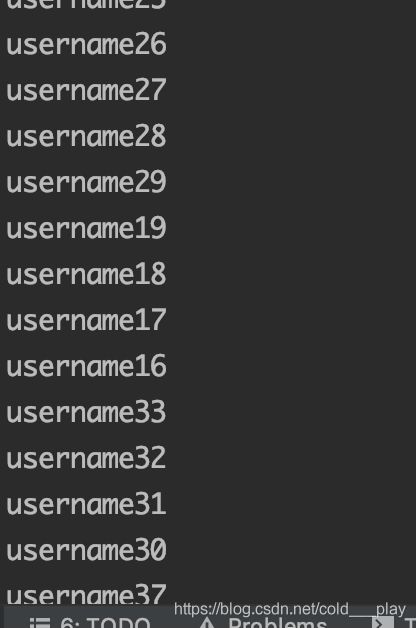
ThreadPoolExecutor与Runnable执行为乱序特性
接口 Runnable在 Thread PoolExecutor的队列中是按顺序取出,执行却是乱序的。
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5, 10, 10,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingDeque<>());
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
MyThreadE t = new MyThreadE("username" + (i + 1));
executor.execute(t);
}
}
}
class MyThreadE extends Thread {
private String username;
public MyThreadE(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(username);
}
}