Yolov3 和 Yolov3-tiny快速实现目标检测(TensorFlow2版)
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、Yolov3 和 Yolov3-tiny
- 1.网络结构
-
-
- yolov3-tiny
- yolov3
-
- 二、配置训练参数
-
- 1.目标检测数据集
- 2.设置anchor box 和classes
- 三、 配置训练过程
- 四、模型预测
- 总结
- 博主的抱怨
前言
上一篇文章 神奇的目标检测 已经介绍了目标检测的基础啦。目标检测呢,就是在图片中定位出目标的位置,把它“框”出来就好了。本篇文章使用Yolov3 和Yolov3-tiny,以训练VOC2007和口罩检测为例。教大家如何快速的搭建自己的目标检测平台。下面是资源链接:
| 内容 | 链接 |
|---|---|
| VOC2007 数据集 | 链接 |
| 戴口罩数据集 | 链接 |
| 权重文件 | 链接 提取码:y32m |
| github项目地址 | 链接 |
| 完整项目地址(包含所有文件) | 链接 提取码 jmpl |
一、Yolov3 和 Yolov3-tiny
2018 年,推出了Yolov3,相比于Yolov2 最主要的改进有,一就是加深了网络,使用53层Darknet,二就是采用了FPN(空间金字塔结构),三是使用了focal loss。对于tiny版本来说,只使用了简单的44层卷积用作普通的特征提取,每个网格点使用两个anchor boxes(Yolov3三个)。所以tiny版本检测速度是很快的哦~,但检测效果就…。
1.网络结构
网络结构中包含了很多基础块,我们先实现这些基本的块,然后像搭积木一样将这些块给组装起来。每个块的用途我已经写在代码注释里了。
#定义的卷积设置初始化方法和卷积步长和填充方式
@wraps(Conv2D)
def DarknetConv2D(*args, **kwargs):
"""Wrapper to set Darknet parameters for Convolution2D."""
#定义卷积块
darknet_conv_kwargs = {
'kernel_regularizer': l2(5e-4)}
darknet_conv_kwargs['padding'] = 'valid' if kwargs.get('strides')==(2,2) else 'same'
darknet_conv_kwargs.update(kwargs)
return Conv2D(*args, **darknet_conv_kwargs)
def DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(*args, **kwargs):
#定义的卷积块包含了BN Leaky 激活函数
"""Darknet Convolution2D followed by BatchNormalization and LeakyReLU."""
no_bias_kwargs = {
'use_bias': False}
no_bias_kwargs.update(kwargs)
return compose(
DarknetConv2D(*args, **no_bias_kwargs),
BatchNormalization(),
LeakyReLU(alpha=0.1))
def resblock_body(x, num_filters, num_blocks):
'''A series of resblocks starting with a downsampling Convolution2D'''
#定义 yolo 主干使用的残差快
# Darknet uses left and top padding instead of 'same' mode
x = ZeroPadding2D(((1,0),(1,0)))(x)
x = DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(num_filters, (3,3), strides=(2,2))(x)
for i in range(num_blocks):
y = compose(
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(num_filters//2, (1,1)),
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(num_filters, (3,3)))(x)
x = Add()([x,y])
return x
def darknet_body(x):
'''Darknent body having 52 Convolution2D layers'''
#darknet 53
#卷积核大小3x3 32 个卷积核
x = DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(32, (3,3))(x)
x = resblock_body(x, 64, 1)
x = resblock_body(x, 128, 2)
x = resblock_body(x, 256, 8)
x = resblock_body(x, 512, 8)
x = resblock_body(x, 1024, 4)
return x
def make_last_layers(x, num_filters, out_filters):
'''6 Conv2D_BN_Leaky layers followed by a Conv2D_linear layer'''
# 这里是输入yolo,制造最后一层的代码 也就是yolo head
x = compose(
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(num_filters, (1,1)),
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(num_filters*2, (3,3)),
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(num_filters, (1,1)),
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(num_filters*2, (3,3)),
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(num_filters, (1,1)))(x)
y = compose(
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(num_filters*2, (3,3)),
DarknetConv2D(out_filters, (1,1)))(x)
return x, y
yolov3-tiny
tiny 版本网络结构比较简单,我们先来看一个图:
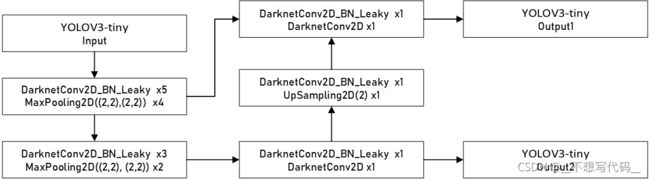
网络中就是普通的卷积核和池化,且网络很浅,网络的计算过程如箭头所示。是不是网络很简单呀~~~~~。
我们接下来看代码如何实现。
def tiny_yolo_body(inputs, num_anchors, num_classes):
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
# inputs 输入向量 num_anchors anchor boxes的数量 num_classes 类别数
#------------------------------------------------------------------
'''Create Tiny YOLO_v3 model CNN body in keras.'''
x1 = compose(
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(16, (3,3)),
MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides=(2,2), padding='same'),
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(32, (3,3)),
MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides=(2,2), padding='same'),
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(64, (3,3)),
MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides=(2,2), padding='same'),
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(128, (3,3)),
MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides=(2,2), padding='same'),
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(256, (3,3)))(inputs)
x2 = compose(
MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides=(2,2), padding='same'),
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(512, (3,3)),
MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides=(1,1), padding='same'),
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(1024, (3,3)),
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(256, (1,1)))(x1)
y1 = compose(
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(512, (3,3)),
DarknetConv2D(num_anchors*(num_classes+5), (1,1)))(x2)
x2 = compose(
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(128, (1,1)),
UpSampling2D(2))(x2)
y2 = compose(
Concatenate(),
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(256, (3,3)),
DarknetConv2D(num_anchors*(num_classes+5), (1,1)))([x2,x1])
return Model(inputs, [y1,y2])
DarknetConv2D DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky 是使用二维卷积定义的块,可以去代码里查看,很好理解的。
yolov3
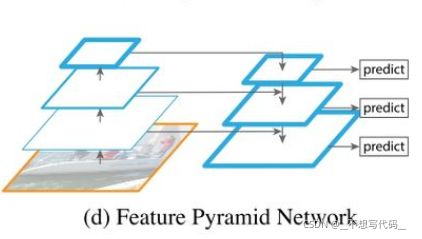
yolov3使用了残差结构和FPN, 网络较深,结构复杂,我们先来看一下他的整体网络结构:
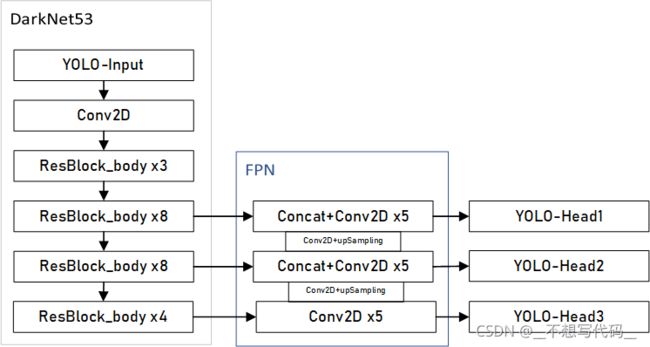
这里使用的FPN(Feature Pyramid Network) 特征金字塔如下图所示:
在目标检测中,往往会包含不用大小的目标,多层卷积后,小目标的语义丢失比较严重,使用FPN 能有效的利用多层特征信息 加强浅层小目标的特征新信息,提升网络的检测能力。
def yolo_body(inputs, num_anchors, num_classes):
"""Create YOLO_V3 model CNN body in Keras."""
#------------------------------------------------------------------
# inputs 输入向量 num_anchors anchor boxes的数量 num_classes 类别数
#------------------------------------------------------------------
darknet = Model(inputs, darknet_body(inputs))
x, y1 = make_last_layers(darknet.output, 512, num_anchors*(num_classes+5))
x = compose(
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(256, (1,1)),
UpSampling2D(2))(x)
x = Concatenate()([x,darknet.layers[152].output])
x, y2 = make_last_layers(x, 256, num_anchors*(num_classes+5))
x = compose(
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(128, (1,1)),
UpSampling2D(2))(x)
x = Concatenate()([x,darknet.layers[92].output])
x, y3 = make_last_layers(x, 128, num_anchors*(num_classes+5))
# yolo head的输出。
return Model(inputs, [y1,y2,y3])
代码中的 make_last_layers 是产生YOLO的输出层,对于参数 :
num_anchors*(num_classes+5)
yolo3 每个网格点有3个anchor boxes,num_achors=3 ,每个anchor box都要预测所有的类别,假设我们使用的是Voc2007 有20类别,num_classes=20, 5代表框的p(框中有目标的概率),x_offset、y_offset、h和w 4个值。yolo head 中的输出维度就为 [batch_size,w,h,3x(20+5)]。
到这里YOLO的主干网络解介绍完了。
二、配置训练参数
1.目标检测数据集
以VOC 2007 数据集为例,首先来看一下文件树:
─VOC2007
├─Annotations
│ └─000005.xml
│ └─000006.xml
│ └─xxxx.xml
├─ImageSets
│ └─Main
└─JPEGImages
│ └─000005.jpg
│ └─000006.jpg
│ └─xxxx.jpg
每一个xml 包含同名jpg 中目标的位置以及类别,在训练时,首先要将数据 通过 voc_annotation.py 转换到记事本中,方便训练时读取。记事本形式如下:
VOC2007/JPEGImages/000005.jpg(图片路径)98,267,194,383(框的位置) ,1(框中目标的类别)
VOC2007/JPEGImages/000006.jpg(图片路径)99,205,198,318(框的位置) ,1(框中目标的类别)
这样的数据是无法直接和YOLO的输出进行计算的,那么我们还需要将,这种数据编码成和yolo head 的格式一样,才能去计算loss,反向传播调整参数
通过如下函数将y_ture,转换成和y_predict 一样的形式:
def preprocess_true_boxes(true_boxes, input_shape, anchors, num_classes):
'''Preprocess true boxes to training input format
Parameters
----------
true_boxes: array, shape=(m, T, 5)
Absolute x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max, class_id relative to input_shape.
input_shape: array-like, hw, multiples of 32
anchors: array, shape=(N, 2), wh
num_classes: integer
Returns
-------
y_true: list of array, shape like yolo_outputs, xywh are reletive value
'''
assert (true_boxes[..., 4]<num_classes).all(), 'class id must be less than num_classes'
num_layers = len(anchors)//3 # default setting
anchor_mask = [[6,7,8], [3,4,5], [0,1,2]] if num_layers==3 else [[3,4,5], [1,2,3]]
true_boxes = np.array(true_boxes, dtype='float32')
input_shape = np.array(input_shape, dtype='int32')
boxes_xy = (true_boxes[..., 0:2] + true_boxes[..., 2:4]) // 2
boxes_wh = true_boxes[..., 2:4] - true_boxes[..., 0:2]
true_boxes[..., 0:2] = boxes_xy/input_shape[::-1]
true_boxes[..., 2:4] = boxes_wh/input_shape[::-1]
m = true_boxes.shape[0]
grid_shapes = [input_shape//{
0:32, 1:16, 2:8}[l] for l in range(num_layers)]
y_true = [np.zeros((m,grid_shapes[l][0],grid_shapes[l][1],len(anchor_mask[l]),5+num_classes),
dtype='float32') for l in range(num_layers)]
# Expand dim to apply broadcasting.
anchors = np.expand_dims(anchors, 0)
anchor_maxes = anchors / 2.
anchor_mins = -anchor_maxes
valid_mask = boxes_wh[..., 0]>0
for b in range(m):
# Discard zero rows.
wh = boxes_wh[b, valid_mask[b]]
if len(wh)==0: continue
# Expand dim to apply broadcasting.
wh = np.expand_dims(wh, -2)
box_maxes = wh / 2.
box_mins = -box_maxes
intersect_mins = np.maximum(box_mins, anchor_mins)
intersect_maxes = np.minimum(box_maxes, anchor_maxes)
intersect_wh = np.maximum(intersect_maxes - intersect_mins, 0.)
intersect_area = intersect_wh[..., 0] * intersect_wh[..., 1]
box_area = wh[..., 0] * wh[..., 1]
anchor_area = anchors[..., 0] * anchors[..., 1]
iou = intersect_area / (box_area + anchor_area - intersect_area)
# Find best anchor for each true box
best_anchor = np.argmax(iou, axis=-1)
for t, n in enumerate(best_anchor):
for l in range(num_layers):
if n in anchor_mask[l]:
i = np.floor(true_boxes[b,t,0]*grid_shapes[l][1]).astype('int32')
j = np.floor(true_boxes[b,t,1]*grid_shapes[l][0]).astype('int32')
k = anchor_mask[l].index(n)
c = true_boxes[b,t, 4].astype('int32')
y_true[l][b, j, i, k, 0:4] = true_boxes[b,t, 0:4]
y_true[l][b, j, i, k, 4] = 1
y_true[l][b, j, i, k, 5+c] = 1
#print(y_true.shape)
return y_true
2.设置anchor box 和classes
Yolo 中的anchor boxes 是通过数据集中框的大小通过kmeans聚类而来,yolov3 有三个输出,每个网格预测3个,所以 Kmeans中的K设置9,如果是tiny版本的话,就设置为6。代码如下:
import numpy as np
"""
Kmeans 聚类算法, 根据 数据集中的xml 文件 聚类出是和目标的anchor boxes
"""
class YOLO_Kmeans:
def __init__(self, cluster_number, filename):
self.cluster_number = cluster_number
self.filename =filename
def iou(self, boxes, clusters): # 1 box -> k clusters
n = boxes.shape[0]
k = self.cluster_number
box_area = boxes[:, 0] * boxes[:, 1]
box_area = box_area.repeat(k)
box_area = np.reshape(box_area, (n, k))
cluster_area = clusters[:, 0] * clusters[:, 1]
cluster_area = np.tile(cluster_area, [1, n])
cluster_area = np.reshape(cluster_area, (n, k))
box_w_matrix = np.reshape(boxes[:, 0].repeat(k), (n, k))
cluster_w_matrix = np.reshape(np.tile(clusters[:, 0], (1, n)), (n, k))
min_w_matrix = np.minimum(cluster_w_matrix, box_w_matrix)
box_h_matrix = np.reshape(boxes[:, 1].repeat(k), (n, k))
cluster_h_matrix = np.reshape(np.tile(clusters[:, 1], (1, n)), (n, k))
min_h_matrix = np.minimum(cluster_h_matrix, box_h_matrix)
inter_area = np.multiply(min_w_matrix, min_h_matrix)
result = inter_area / (box_area + cluster_area - inter_area)
return result
def avg_iou(self, boxes, clusters):
accuracy = np.mean([np.max(self.iou(boxes, clusters), axis=1)])
return accuracy
def kmeans(self, boxes, k, dist=np.median):
box_number = boxes.shape[0]
distances = np.empty((box_number, k))
last_nearest = np.zeros((box_number,))
np.random.seed()
clusters = boxes[np.random.choice(
box_number, k, replace=False)] # init k clusters
while True:
distances = 1 - self.iou(boxes, clusters)
current_nearest = np.argmin(distances, axis=1)
if (last_nearest == current_nearest).all():
break # clusters won't change
for cluster in range(k):
clusters[cluster] = dist( # update clusters
boxes[current_nearest == cluster], axis=0)
last_nearest = current_nearest
return clusters
def result2txt(self, data):
f = open("yolo_anchors1.txt", 'w') # 这里是生存achor后保存的路径
row = np.shape(data)[0]
for i in range(row):
if i == 0:
x_y = "%d,%d" % (data[i][0], data[i][1])
else:
x_y = ", %d,%d" % (data[i][0], data[i][1])
f.write(x_y)
f.close()
def txt2boxes(self):
f = open(self.filename, 'r')
dataSet = []
for line in f:
infos = line.split(" ")
length = len(infos)
for i in range(1, length):
width = int(infos[i].split(",")[2]) - \
int(infos[i].split(",")[0])
height = int(infos[i].split(",")[3]) - \
int(infos[i].split(",")[1])
dataSet.append([width, height])
result = np.array(dataSet)
f.close()
return result
def txt2clusters(self):
all_boxes = self.txt2boxes()
result = self.kmeans(all_boxes, k=self.cluster_number)
result = result[np.lexsort(result.T[0, None])]
self.result2txt(result)
print("K anchors:\n {}".format(result))
print("Accuracy: {:.2f}%".format(
self.avg_iou(all_boxes, result) * 100))
#通过聚类方法设置数据集中合适的框
if __name__ == "__main__":
cluster_number =9 #聚类框的个数 6 或者 9
filename = r"2007_train.txt" # 指定train.txt的路劲
kmeans = YOLO_Kmeans(cluster_number, filename)
kmeans.txt2clusters()
当然也可以使用yolo中默认的achor box的大小。
classes.txt 是声明 你目标中所有的类别,以戴口罩数据集为例
without_mask
with_mask
mask_weared_incorrect
文本中书写的类别要和你xml 文件中所写类别保持一致,才能正确索引。
三、 配置训练过程
训练过程需要配置的东西,就是之前的数据准备。输入模型即可。
训练过错内存溢出,记得吧batch_size 改小一点,yolo完整版的话一般设置为8比较好
代码:
def train():
# 你的 数据集文件路劲
train_annotation_path = r"2007_train.txt" # 生存的数据索引txt文本
val_annotation_path = r"2007_val.txt"
anchors_path = r"model_data\mask_anchor.txt" # 生成的anchor
classes_path = r"model_data\mask_classes.txt" #自己数据集的类别
log_dir = "logs/tiny_log/"
weights_dir = "weights/"
class_names = get_classes(classes_path)
num_classes = len(class_names)
anchors = get_anchors(anchors_path)
input_shape = (416, 416) # 必须是32的 倍数 yolo 的设定
# tiny 版本
model = create_tiny_model(
input_shape=input_shape,
anchors=anchors,
num_classes=num_classes,
freeze_body=2,
weights_path="model_data\yolov3-tiny.h5",
)
''''
# yolo v3 的完整版本 ,
model = create_model(
input_shape=input_shape,
anchors=anchors,
num_classes=num_classes,
# freeze_body=0,
weights_path="model_data\yolov3.h5",
)
'''
print(len(model.layers))
logging = TensorBoard(log_dir=log_dir)
checkpoint = ModelCheckpoint(
weights_dir + "ep{epoch:03d}-loss{loss:.3f}-val_loss{val_loss:.3f}.h5",
monitor="val_loss",
save_weights_only=True,
save_best_only=True,
period=3,
)
reduce_lr = ReduceLROnPlateau(monitor="val_loss", factor=0.1, patience=3, verbose=1)
early_stopping = EarlyStopping(
monitor="val_loss", min_delta=0, patience=10, verbose=1
)
# 读取数据集对应的 .txt 文件
with open(train_annotation_path) as f:
train_lines = f.readlines()
with open(val_annotation_path) as f:
val_lines = f.readlines()
num_train = len(train_lines)
num_val = len(val_lines)
# 配置训练参数
Freeze_Train = True
# ------------------------------------------------------------
# 先冻结一定网络层进行训练,这样训练比较快 ,得到一个loss稳定的model
# -------------------------------------------------------------
if Freeze_Train:
batch_size = 32
model.compile(
optimizer=Adam(1e-3),
loss={
# use custom yolo_loss Lambda layer.
"yolo_loss": lambda y_true, y_pred: y_pred}
)
print("Train on {} samples, val on {} samples, with batch size {}.".format(num_train, num_val, batch_size))
model.fit(
data_generator_wrapper(train_lines,batch_size,input_shape,anchors,num_classes),
steps_per_epoch=max(1,num_train//batch_size),
validation_data=data_generator_wrapper(val_lines,batch_size,input_shape,anchors,num_classes),
validation_steps=max(1,num_val//batch_size),
epochs=50,
initial_epoch=0,
callbacks=[logging,checkpoint]
)
model.save_weights(weights_dir+'trained_weights_stage_1.h5')
#-----------------------------------------------------------------
# 解冻所有层,并调小学习率训练
#-----------------------------------------------------------------
if True:
for i in range(len(model.layers)): model.layers[i].trainable = True
model.compile(optimizer=Adam(lr=1e-4), loss={
'yolo_loss': lambda y_true, y_pred: y_pred}) # recompile to apply the change
print('Unfreeze all of the layers.')
batch_size = 32 # note that more GPU memory is required after unfreezing the body
print('Train on {} samples, val on {} samples, with batch size {}.'.format(num_train, num_val, batch_size))
model.fit_generator(data_generator_wrapper(train_lines, batch_size, input_shape, anchors, num_classes),
steps_per_epoch=max(1, num_train//batch_size),
validation_data=data_generator_wrapper(val_lines, batch_size, input_shape, anchors, num_classes),
validation_steps=max(1, num_val//batch_size),
epochs=100,
initial_epoch=50,
callbacks=[logging, checkpoint, reduce_lr, early_stopping])
model.save_weights(log_dir + 'trained_weights_final.h5')
if __name__=='__main__':
train()
上述就是训练过程了,训练时,
注意:
使用model 时,tiny 和YOLOv3 achor 不一样,一个是6 类 一个是9类 ,记得更换。
tips:训练过错先冻结一部分层去训练,这样训练比较快,当损失稳定之后,使用更小的学习率去,趋势模型收敛更好。
训练结果如下:
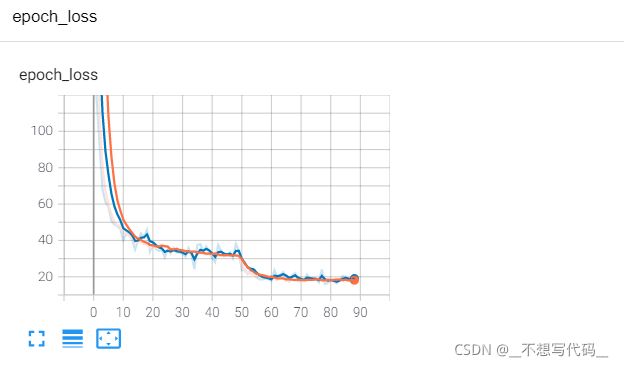
可以看出收敛效果还是相当不错的。。。。
四、模型预测
模型预测,将图片输入到保存的模型当中,如果输出一个跟yolo head 一样的维度,很显然这个时候我们是无法获图片的类别还有框的,那么需要通过解码,拿到我们有用的数据。这个工作在项目中的yolo.py 中实现。
#这里不给出全部代码了,但在预测是,网络的权重文件 achor boxes 和classes 要保持一直,在文件中这个位置配置
_defaults = {
# ----------------------------------
# 模型路径, anchor路径,class 路径,
# sorce 一本设为0.5 置信度阈值 iou
# 输入图片大小 一般是13 的倍数
# gpu 1
# 遇上维度 不匹配问题 可能是训练时 忘记让model_path 和class_path 对应
# -----------------------------------
"model_path": r"logs\yolov3_log\trained_weights_final.h5",
"anchors_path": "model_data\mask_anchor.txt",
"classes_path": "model_data\mask_classes.txt",
"score": 0.3,
"iou": 0.3,
"model_image_size": (416, 416),
"gpu_num": 1, # 这里使用1 ,多gpu 由于TensorFlow 版本问题 我给注解掉了
}
模型预测完整代码:
import time
import cv2
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from PIL import Image
from yolo import YOLO,detect_video
import os
from tqdm import tqdm
def predict():
#-------------------------------------------------------------
# 新建 yolo 对象,使用模型权重路径,以及其他参数,到yolo.py 中更改
# predict_model 为 img 预测图片, video 输入为视频,记得更改视频路劲 video_path 为 0 时调用摄像头 为视频路径时 读取视频
# predict_model 为 dir_predict 时输入为存放图片的路径 ,预测完成后 放入out_img 使用时记得修改路劲
# 要预测 指定类别是 ,可以设置好重新训练模型,或者进入detect_image 修改参数 if predicted_classes='car'
#--------------------------------------------------------------
yolo=YOLO()
predict_model='dir_predict'
video_path= 0
video_save_path=""
dir_img_input='img/'
dir_save_path='out_img/'
if predict_model=='img':
while(True):
img=input('Input image filename:')
try:
image=Image.open(img)
except:
print('Open Image Error! Please Try Again')
continue
else:
out_image=yolo.detect_image(image)
out_image.show()
elif predict_model=='video':
detect_video(yolo,video_path,video_save_path) # 可以获取fps
elif predict_model=='dir_predict':
#---------------------------------
#拿到所有图片 通过detect image 检测
#-------------------------------
imgs=os.listdir(dir_img_input)
for img_name in tqdm(imgs):
if img_name.lower().endswith(('.bmp', '.dib', '.png', '.jpg', '.jpeg', '.pbm', '.pgm', '.ppm', '.tif', '.tiff')):
image_path = os.path.join(dir_img_input, img_name)
image = Image.open(image_path)
r_image = yolo.detect_image(image)
if not os.path.exists(dir_save_path):
os.makedirs(dir_save_path)
r_image.save(os.path.join(dir_save_path, img_name))
else:
raise AssertionError("Please specify the correct mode: 'img', 'video', 'dir_predict'.")
if __name__=='__main__':
predict()
总结
目标检测网络结构,其实跟图像分类差不多,但对数据读取过程,编码解码过程比较复杂,对于这个过程,我掌握不是很多,所以就不在这里讲解了。
目标检测训练比较难,数据标注比较麻烦。后面可能会出一期视频,教大家如何配置。所有代码和资源均会上传,写代码不易,欢迎点赞~
博主的抱怨
哎,太难了,哎~ cv 太卷了。