人的一生会遇到三种人,一个惊艳了时光,一个温柔了岁月,一个讲懂了“堆”
这里写目录标题
- 堆的概念
- 堆的操作
-
- 向下调整
- 搞一个大堆
- 向上调整
- 入堆
- 出堆
- 使用Java中的堆
- top-K问题
-
- 分享一个题目
- 数组排序
堆的概念
- 堆在逻辑上是一棵完全二叉树
- 堆在物理上是储存在数组中的
- 进行堆操作时,可以将数组写作完全二叉树,运用双亲的下标操作
双亲下标 parent
左孩子下标 = parent * 2 + 1;
右孩子下标 = parent * 2 + 2;
知道孩子下标(左孩子和右孩子都行)
parent = ( child - 1 ) / 2; - 大根堆
任意节点的值都大于其孩子节点的值(左右孩子值的大小比较无要求)

堆的操作
向下调整
前提:左右子树必须已经是一个堆
如某节点的左右子树都是大堆,将这个树向下调整成大堆
- parent是开始节点的下标,child是其左孩子的下标
- 如果child超过或等于数组长度,说明没有左孩子,因为是完全二叉树,也没有右孩子,即说明这树是大堆喽
- 如果child
- 先判断其有没有右孩子,如果有并且大于左孩子,则child++,成为右孩子下标;如果没有,child依旧是左孩子下标
- 判断parent与child节点的大小,如果parent节点小于child节点,交换值,继续向下调整,parent标记子孩子,child向下标记新的子孩子(因为子树的节点变换了,不一定是大堆了,要继续将其变为大堆);如果parent节点大于child节点,直接break退出循环,此时它就是一个大堆
public void adjustDown(int[] array, int begin, int size) {
int parent = begin;
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < size) {
if (child + 1 < array.length && array[child + 1] > array[child]) {
child++;
}
if (array[parent] < array[child]) {
int temp = array[parent];
array[parent] = array[child];
array[child] = temp;
parent = child;
child = child*2+1;
}else{
break;
}
}
}
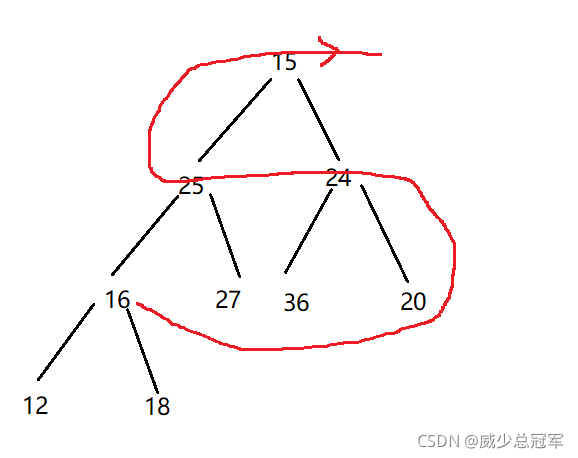
搞一个大堆
- 堆就是一个数组,创建字段
- 找最后的一棵子树,child为最后一个节点的下标,然后找到parent是父亲节点的下标,进行向下调整,调整成大堆
- 对于每一棵子树进行向下调整,直至最后一棵树(parent=0,即parent标记第一个节点)
public class MyHeap {
public int[] elem;
public int useSize;
public MyHeap() {
this.elem = new int[10];
}
//建一个最大堆
public void creatHeap(int[] array){
for (int i = 0 ; i < array.length; i++) {
this.elem[i] = array[i];
this.useSize++;
}
//确定最后一棵子树的父树
int child = this.useSize-1;
int parent = (child-1)/2;
//对于每棵子树进行调换大小的操作
for( ;parent>=0;parent--){
adjustDown(parent,this.useSize);
}
}
//向下调整
public void adjustDown(int parent,int size){
int child = parent*2+1;
while(child < size) {
if (child + 1 < len && this.elem[child + 1] > this.elem[child]) {
child++;
}
if (this.elem[parent] < this.elem[child]) {
int temp = this.elem[parent];
this.elem[parent] = this.elem[child];
this.elem[child] = temp;
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
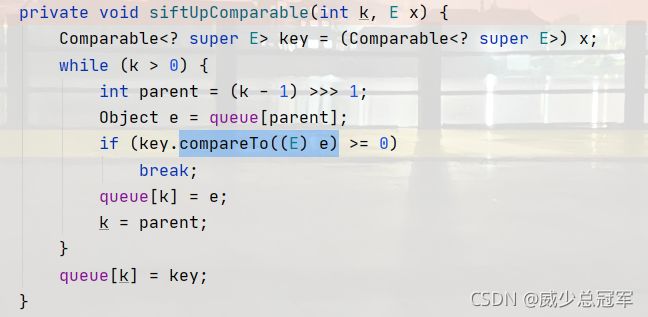
向上调整
前提:这个树已经是一个堆
如某树是一个大堆
向上调整用于 入堆或改变原来堆的叶子节点,再将其变为大堆

- 向上调整的起点child,如果child<=0,说明完成调整了
- 比较孩子节点与父亲节点的大小,如果孩子节点>父亲节点,交换;否则,直接break退出循环
- 交换节点后,新的父亲节点为原parent的父亲节点,新的孩子节点为原parent,进行循环
- 由于原本就是一个大堆,只要孩子节点没交换,一定小于父亲节点,所以不用左右比较
public void adjustUp(int[] arrays, int child){
int parent = (child-1)/2;
while(child > 0){
if(arrays[parent] < arrays[child]){
int temp = arrays[parent];
arrays[parent] = arrays[child];
arrays[child] = temp;
child = parent;
parent = (child-1)/2;
}else{
break;
}
}
}
入堆
数组尾插,不够扩容,向上转型
//this.elem已经是一个大堆啦
public void adjustUp(int child){
int parent = (child-1)/2;
while(child > 0){
if(this.elem[child] > this.elem[parent]){
int temp = this.elem[child];
this.elem[child] = this.elem[parent];
this.elem[parent] = temp;
child = parent;
parent = (child-1)/2;
}else{
break;
}
}
}
public void push(int val){
if(isFull()){
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,2*this.elem.length);
}
this.elem[this.useSize] = val;
this.useSize++;
adjustUp(this.useSize-1);
}
public boolean isFull(){
return this.useSize == this.elem.length;
}
出堆
- 判断堆是否为空
- 交换堆首元素与堆尾的元素,即交换数组第一个元素和最后一个元素
- 堆的长度-1
- 向下调整
//this.elem是一个大堆
public void pop(){
if(isEmpty()){
return;
}
int temp = this.elem[0];
this.elem[0] = this.elem[this.useSize -1];
this.elem[this.useSize -1] = temp;
this.useSize--;
adjustDown(0,this.useSize);
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return this.useSize == 0;
}
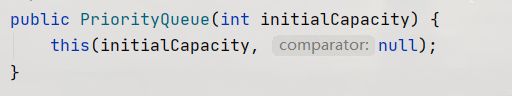
使用Java中的堆
默认是一个小堆
PriorityQueue<Integer> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<>();
如果堆中的元素无法直接比较的话,可以用Java对象比较的两种方法
class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
class AgeComparator implements Comparator<Student>{
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
//o1是前面的,o2是后面的
//从小到大
return o1.getAge()-o2.getAge();
//从大到小
// return o2.getAge()-o1.getAge();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//建最大堆
PriorityQueue<Student> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<>(new AgeComparator());
maxHeap.offer(new Student("dong",18));
maxHeap.offer(new Student("gang",20));
maxHeap.offer(new Student("hui",16));
System.out.println(maxHeap);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<Student> heap = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return o1.getAge()-o2.getAge();
}
});
}
- 重写Comparable的compareTo()方法
class Student implements Comparable<Student>{
private String name;
private int age;
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
//建小堆
return this.getAge()-o.getAge();
//建大堆
return o.getAge()-this.getAge();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student1 = new Student("拉塞尔",29);
Student student2 = new Student("亚历山大",27);
Student[] students = {
student1,student2};
Arrays.sort(students);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(students));
}
top-K问题
一组数据中找前k个最大(最小)的数
- 若找前k个最大的数,建立一个长度为k的最小堆
- 遍历数组,前k个元素建堆
- 堆建好后继续遍历数组,如果元素比堆顶的元素大,出堆顶元素,如该元素,以此循环
- 遍历完成数组,最后的堆中就是所求的元素
public PriorityQueue<Integer> topK(int[] array,int k){
PriorityQueue<Integer> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<>(k, new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2-o1;
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if(maxHeap.size() < k){
maxHeap.offer(array[i]);
}else{
if(maxHeap.peek()>array[i]){
maxHeap.poll();
maxHeap.offer(array[i]);
}
}
}
return maxHeap;
}
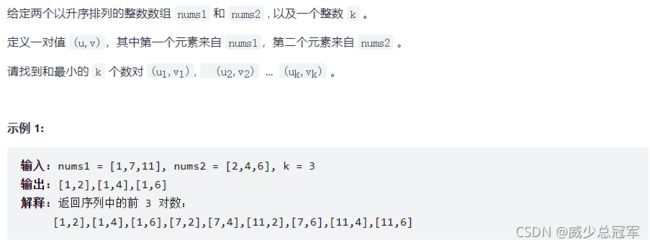
分享一个题目
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-k-pairs-with-smallest-sums/
public List<List<Integer>> kSmallestPairs(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int k){
PriorityQueue<List<Integer>> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<>(k, new Comparator<List<Integer>>() {
@Override
public int compare(List<Integer> o1, List<Integer> o2) {
return (o2.get(0)+o2.get(1)) - (o1.get(0)+o1.get(1));
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < nums1.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < nums2.length; j++) {
if(maxHeap.size() < k){
List<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add(nums1[i]);
list.add(nums2[j]);
maxHeap.offer(list);
}else{
List<Integer> list = maxHeap.peek();
int count = list.get(0) + list.get(1);
if(nums1[i] + nums2[j] < count){
List<Integer> list1 = new LinkedList<>();
list1.add(nums1[i]);
list1.add(nums2[j]);
maxHeap.poll();
maxHeap.offer(list1);
}
}
}
}
List<List<Integer>> list = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < k && !maxHeap.isEmpty(); i++) {
list.add(maxHeap.poll());
}
return list;
}
此时堆顶元素就是这个数组第第k小的元素
数组排序
从小到大排列,此时this.elem是一个大堆了!!!
- 交换 堆顶元素(第一个元素) 和 堆尾(最后一个元素),此时堆尾的元素就是此数组中最大的元素
- 再对堆顶元素进行向下调整(注意范围要-1,最后一个元素不参与此调整)
- end–,再交换第一个元素和倒数第二个元素,此时倒数第二个元素就是第二大
- 依次循环,直到end=0为止
public void sort(){
int end = this.useSize-1;
while(end>0) {
int temp = this.elem[0];
this.elem[0] = this.elem[end];
this.elem[end] = temp;
adjustDown(this.elem, 0, end);
end--;
}
}
认真生活,就能找到生活藏起来的糖果。