零基础JAVA——黑马程序员课程笔记
视频地址:点击访问
文章目录
- JAVA语言发展史
- JAVA跨平台原理
- JRE和JDK
-
- JRE (Java Runtime Environment)
- JDK (Java Development Kit)
- JDK安装目录
- 为什么要配置Path环境变量
- Java程序开发运行流程
- dos命令
- 数据类型
- 变量使用的注意事项:
- 标识符定义规则
- 常见命名约定
- 类型转换
-
- 自动类型转换
- 强制类型转换
- 运算符
-
- 算术运算符
-
- 字符的+操作
- 字符串的+操作
- 赋值运算符
- 自增自减运算符
- 关系运算符
- 逻辑运算符
-
- 短路逻辑运算符
- 三元运算符
- 数据输入
-
- Scanner使用的基本步骤
- 流程控制
-
- 分支结构
-
- if语句
- switch语句
- 循环结构
-
- for语句
-
- 经典案例:
- while语句
- 三种循环的区别
- Random作用和使用步骤
-
- 猜数字案例 
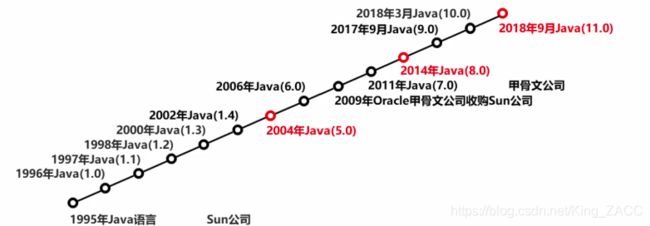
JAVA语言发展史
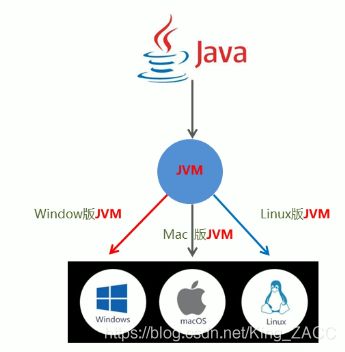
JAVA跨平台原理
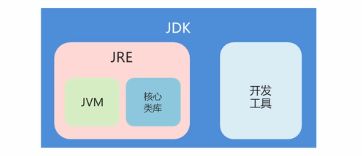
JRE和JDK
JRE (Java Runtime Environment)
是Java程序的运行时环境,包含JVM和运行时所需要的核心类库。
我们想要运行一个已有的Java程序, 那么只需安装JRE即可。
JDK (Java Development Kit)
是Java程序开发工具包,包含JRE和开发人员使用的工具。
其中的开发工具:编译工具(javac.exe)和运行工具(java.exe) 。
我们想要开发一个全新的Java程序,那么必须安装JDK。
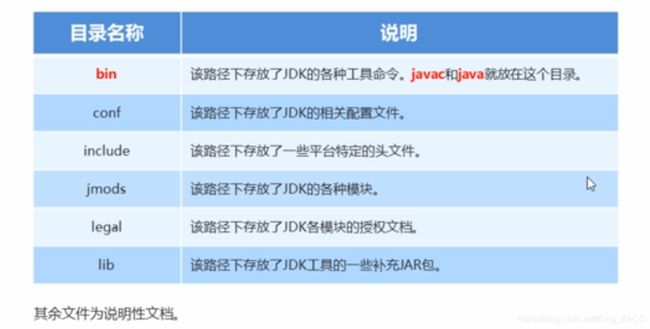
JDK安装目录
为什么要配置Path环境变量
开发Java程序,需要使用JDK提供的开发工具,而这些工具在JDK的安装目录的bin目录下。
为了在开发Java程序的时候,能够方便的使用javac和java这些命令,我们需要配置Path环境变量。
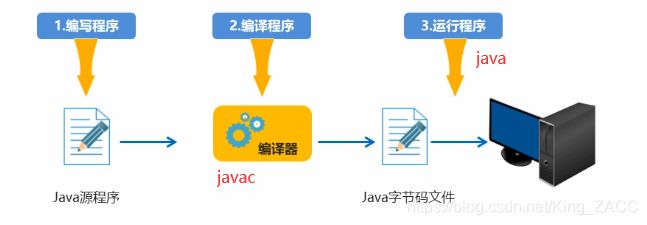
Java程序开发运行流程
开发Java程序,需要三个步骤:编写程序,编译程序,运行程序
空常量不能直接输出
dos命令
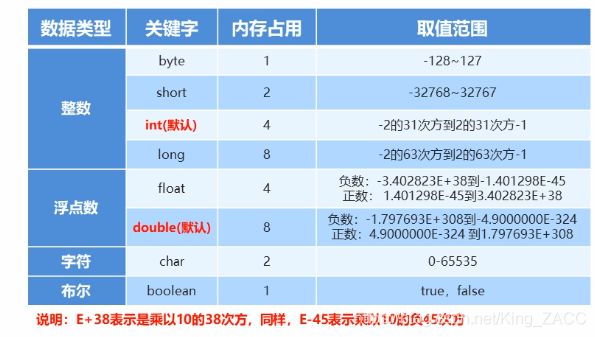
数据类型
变量使用的注意事项:
名字不能重复
变量未赋值,不能使用
long类型的变量定义的时候,为了防止整数过大,后面要加L
float类型的变量定义的时候,为了防止类型不兼容,后面要加F
标识符定义规则
●由数字、字母、下划线( )和美元符($)组成
●不能以数字开头
●不能是关键字
●区分大小写
常见命名约定
小驼峰命名法:方法、变量
●约定1:标识符是一个单词的时候,首字母小写
●范例1:name
●约定2: 标识符由多个单词组成的时候,第一个单词首字母小写,其他单词首字母大写
●范例2: firstName
大驼峰命名法:类
●约定1: 标识符是一个单词的时候,首字母大写
●范例1: Student
●约定2: 标识符由多个单词组成的时候,每个单词的首字母大写
●范例2: GoodStudent
类型转换
自动类型转换
把一个表示数据范围小的数值或者变量赋值给另-个表示数据范围大的变量
范例: doubled = 10;

强制类型转换
把一个表示数据范围大的数值或者变量赋值给另-个表示数据范围小的变量
●格式:目标数据类型变量名= (目标数据类型)值或者变量;
●范例: intk = (int)88.88;
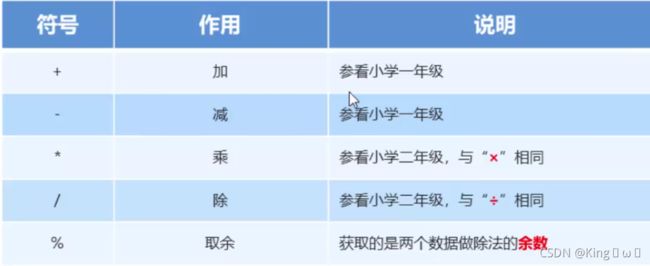
运算符
算术运算符
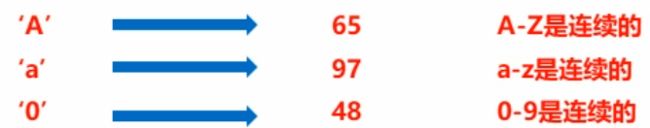
字符的+操作
package test;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 0;
char c = 'A';//'A'的值是65
System.out.println(i + c);
}
}
提升规则:
- byte类型, short类型和char类型将被提升到int类型
- 整个表达式的类型自动提升到表达式中最等级操作数同样的类型
- 等级顺序: bvte. short.char->int-> lona-> float > double
字符串的+操作
package test;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("hello"+"earth");
System.out.println("hello"+ 6666);
System.out.println(6666+ "hello");
System.out.println("hello"+6+666);
System.out.println(6+666+"hello");
}
}
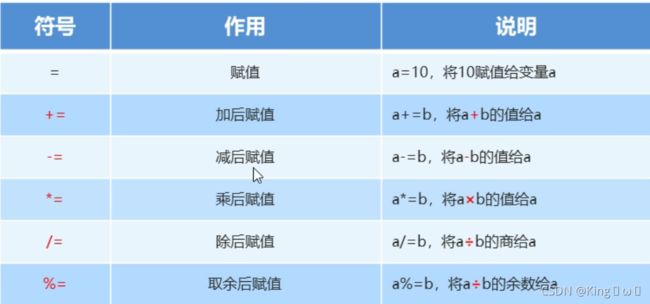
赋值运算符
自增自减运算符
package test;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//单独使用
int i = 1;
System.out.println("i="+i);
i++;
System.out.println("i="+i);
++i;
System.out.println("i="+i);
}
}
package test;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 1;
System.out.println("i="+i);
//参与操作使用
int j = i++;
System.out.println("i="+i);
System.out.println("j="+j);
}
}
package test;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 1;
System.out.println("i="+i);
//参与操作使用
int j = ++i;
System.out.println("i="+i);
System.out.println("j="+j);
}
}
- 参与操作的时候,如果放在变量的后边,先拿变量参与操作,后拿变量做++或者–参与操作的时候,如果放在变量的前边,先拿变量做++或者–,后拿变量参与操作。
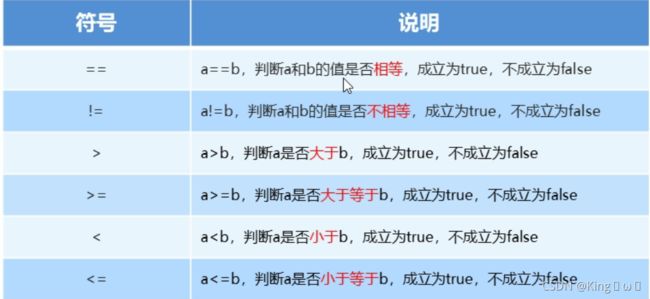
关系运算符
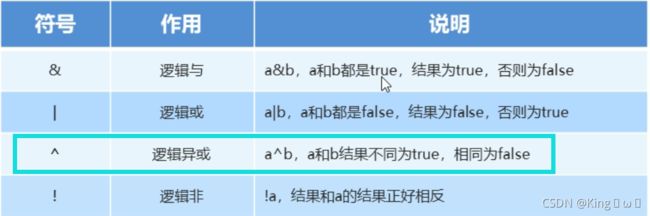
逻辑运算符
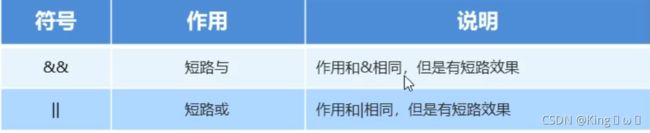
短路逻辑运算符
区别:




注意事项:
逻辑与&,无论左边真假,右边都要执行。
短路与&&,如果左边为真,右边执行;如果左边为假,右边不执行。
逻辑或|,无论左边真假,右边都要执行。
短路或||,如果左边为假,右边执行;如果左边为真,右边不执行。
三元运算符

计算规则:
首先计算关系表达式的值
如果值为true,表达式1的值就是运算结果如果值为false,表达式2的值就是运算结果
数据输入
Scanner使用的基本步骤
package test;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int i = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("i="+i);
sc.close();//关闭sc接口
}
}
流程控制
分支结构
if语句
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = sc.nextInt();
if (a % 2 == 0)
System.out.println("a是偶数");
else
System.out.println("a是奇数");
sc.close();
}
}
switch语句
输入一个数字判断是什么季节
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int i = sc.nextInt();
switch (i) {
case 1:
System.out.println("春季");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("春季");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("春季");
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("夏季");
break;
case 5:
System.out.println("夏季");
break;
case 6:
System.out.println("夏季");
break;
case 7:
System.out.println("秋季");
break;
case 8:
System.out.println("秋季");
break;
case 9:
System.out.println("秋季");
break;
case 10:
System.out.println("冬季");
break;
case 11:
System.out.println("冬季");
break;
case 12:
System.out.println("冬季");
break;
default:
System.out.println("输入不合法");
break;
}
sc.close();
}
}
利用case穿透性
//case穿透
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int i = sc.nextInt();
switch (i) {
case 1:
case 2:
case 3:
System.out.println("春季");
break;
case 4:
case 5:
case 6:
System.out.println("夏季");
break;
case 7:
case 8:
case 9:
System.out.println("秋季");
break;
case 10:
case 11:
case 12:
System.out.println("冬季");
break;
default:
System.out.println("输入不合法");
}
sc.close();
}
}
循环结构
for语句
经典案例:
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//先找到100——999
for(int i = 100;i < 1000;i++) {
//判断条件
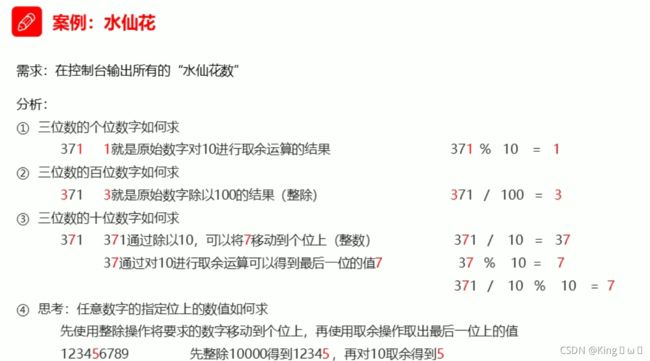
int a = i % 10;
int b = i / 10 % 10;
int c = i / 100 % 10;
if(a*a*a+b*b*b+c*c*c == i) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
}
while语句
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 0;
double hou = 0.1;
while(hou <=8844430) {
i++;
hou = hou*2;
}
System.out.println(i);
}
}
三种循环的区别
Random作用和使用步骤
猜数字案例 
package test;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.*;
public class test1 {
public static void main(String []args ) {
Random r = new Random();
int num = r.nextInt(100)+1;
System.out.println(num);
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true) {
int num1 = sc.nextInt();
if(num > num1) {
System.out.println("需要猜大一点");
}else if(num < num1) {
System.out.println("需要猜小一点");
}else {
System.out.println("猜对了,你真厉害");
break;
}
}
}
}
随着我的学习更新