Qt Quick QML 实例之疯狂数字游戏(QML C++混合编程、翻译、QSetting )【建议收藏】
文章目录
- 一、开门见山
- 二、最基本的框架(v0.1)
-
- 1. 后端数据处理
- 2. 导出 C++ 对象的 QML 的属性
- 3. 前台 UI 数据
- 三、完善执行逻辑(v0.2)
- 四、发布版本(v1.0)
-
- 1. 翻译
- 2. QSetting 数据保存
GitHub 源码: QmlLearningPro ,选择子工程 CrazyMath.pro
QML 其它文章请点击这里: QT QUICK QML 学习笔记
一、开门见山
● Windows 下运行效果:
● Android 下运行效果:
此实例,参考了安老师 的 Qt Quick实现的疯狂算数游戏,在此基础上一步步深入学习和完善,非常适合 Qt QML 和 C++ 学习入门。
● 可供学习的点:
1)跨平台程序,Windows 和 Android 下都能运行;
2)C++ 与 QML 相结合,在 QML 文件中使用了两种方法调用 C++ 类;
3)自定义不同的基础控件,如悬浮按钮CCHoverHorzButton、文本CCLabel,方便移植;
4)QML 中不同控件的使用,column、SpringAnimation、transitions、State 等等;
5)数据可持久化,利用 QSettings 可以把内存中的数据保存到地电脑的磁盘中;
6)加入国际化翻译机制
二、最基本的框架(v0.1)
最简单的 UI 和 最基本的框架,先实现核心功能:

● 先实现以下部分:
1)基本的框架
2)增加**开始键**,开始游戏
3)增加**确认(√)按键**,确定下一组的算术题目
1. 后端数据处理
MathProblem.cpp
#include "MathProblem.h"
const char *MathProblem::_problems[] = {
"1 + 2 = ", "2 + 3 = ", "2 + 2 = ","1 + 4 = ", "2 + 5 = " };
const int MathProblem::_answers[] = {
3, 5, 4, 5, 7 };
MathProblem::MathProblem(QObject *parent)
: QObject(parent)
, newIdx(0)
{
}
MathProblem::~MathProblem() {
}
//返回下一组算术
QString MathProblem::nextMath()
{
newIdx = qrand() % 5;
//随机的答案
int randAnswer = _answers[newIdx] + (qrand() % 7 - 3); // 取 -3~3 的随机数
return QString("%1%2").arg(_problems[newIdx]).arg(randAnswer);
}
MathProblem.h
#ifndef MATH_PROBLEM_H
#define MATH_PROBLEM_H
#include 2. 导出 C++ 对象的 QML 的属性
#include 主要在默认的 main.cpp 中增加上述 [flag] 三处
3. 前台 UI 数据
import QtQuick 2.12
import QtQuick.Window 2.12
import QtQuick.Controls 2.5
Window {
visible: true
width: 640
height: 480
title: qsTr("疯狂算术")
color: "#84C1FF"
Button {
id: startBtn
anchors.centerIn: parent
text: "开始"
onClicked: {
startBtn.visible = false
columnRoot.visible = true
mathText.text = MathProblem.nextMath();
}
}
Column {
id: columnRoot
visible: false
anchors.top: parent.top
anchors.topMargin: parent.width*0.1
anchors.horizontalCenter: parent.horizontalCenter
spacing: 20
Text {
id: mathText;
color: "white"
font.pointSize: 28
font.bold: true
anchors.horizontalCenter: parent.horizontalCenter
}
Row {
spacing: 10
anchors.horizontalCenter: parent.horizontalCenter
Button {
text: "√"
onClicked:
mathText.text = MathProblem.nextMath();
}
Button {
text: "X"
}
}
}
}
三、完善执行逻辑(v0.2)
● 增加功能:
1)增加游戏结束界面
2)判断回答是否正确,回答正确进入下一题,回答错误进入结束界面
3)增加到60个算术题
4)增加计时功能,设定为 4s,超时则进入结束界面
5)增加积分:答对1题 +10,再加上 剩余的时间 *5,如剩余的时候为 2s 时候,积分:10 + 2 * 5 = 20
● 主要 UI 代码结构如下:
main.qml :

可以下载源码,参考第二个版本 v0.2, C++ 后台数据中基本不变
四、发布版本(v1.0)
● 增加功能:
1)美化界面
2)整理结构
3)跨平台程序,**Windows** 和 **Android** 下都能运行;
4)C++ 与 QML 相结合,在 QML 文件中使用了两种方法调用 C++ 类;
5)自定义不同的基础控件,如悬浮按钮CCHoverHorzButton、文本CCLabel,方便移植;
6)数据可持久化,利用 QSettings 可以把内存中的数据保存到地电脑的磁盘中;
7)加入国际化翻译机制;
● 目录结构:

源码更新了很多,包括执行的逻辑,具体看源码,再这里展开说下 国际化翻译机制 和QSettings 数据可持久化
1. 翻译
参考:Qt 本地化(翻译)
1)准备要翻译的源代码
在 QML 中使用 qsTr() 来包裹,在 cpp 中使用 tr() 来包裹。用它包裹的文本会被 Qt Linguist(Qt 语言家)捕捉到从而进行翻译工作。
//main.qml
text: qsTr("Correct")
2)生成 xxx.ts 文件
先在 CrazyMath.pro 文件中添加如下代码:
TRANSLATIONS += $$PWD/Translations/zh_CN.ts
可以使用两种方法生成:
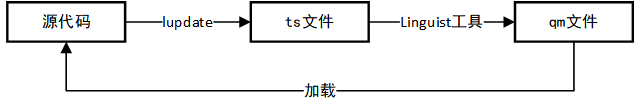
① 在 Qt Creator 的菜单栏中依次点击 工具->外部->Qt语言家->发布更新翻译(lrelease)(lupdate),就会在源代码文件所在的目录生成 ts 文件。

② 使用 CMD 命令生成:
使用 lupdate CrazyMath.pro

3)翻译并生成 qm 文件
方法一: 右键打开翻译文件 zh_CN.ts
翻译后发布:
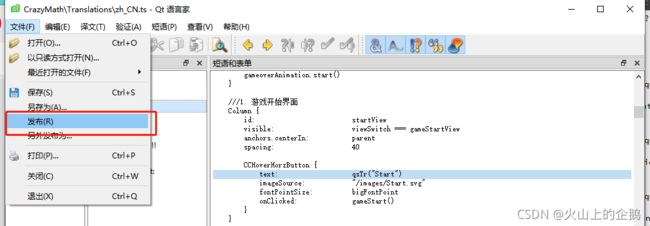
方法二,执行指令:
lrelease -verbose zh_CN.ts
4)加载 qm 翻译文件
在 main.cpp 中加载生成的 qm 文件
void setLanguage(QGuiApplication *app) {
QLocale locale = QLocale::system();
if(locale.language() == QLocale::Chinese)
{
QTranslator *translator = new QTranslator(app);
///--以下三种方法都可以加载翻译文件
if(translator->load(":/translations/zh_CN.qm"))
// if(translator->load(locale, ":/translations/zh_CN.qm", "", ":/i18n"))
// if (translator->load(locale, "zh_CN", ".", ":/translations", ".qm"))
{
app->installTranslator(translator);
}
else {
qDebug() << "Error loading source localization ";
}
}
}
最后编译即可。
2. QSetting 数据保存
纯 QML 软件状态的保存可以参考这个:QT Quick QML 之Setting状态保存
本文设定了 bestScore 变量来保存历史最好成绩 ,在软件关闭后能保存到注册表中。

如果指定了名字,公司等,就不需要手动创建.ini配置文件了, 会自动创建ini文件,且保存到注册表中:
main.cpp:
void setOrganization(void) {
QCoreApplication::setOrganizationName("CrazyMath");
QCoreApplication::setOrganizationDomain("CrazyMath.com");
QCoreApplication::setApplicationName("CrazyMath");
}
//注册:
qmlRegisterType<Values> ("cc.Values", 1, 0, "Values");
cpp 源文件:
//Values.cc
#include "Values.h"
#include 打印的路径:
![]()
.h 头文件:
//Values.h:
#ifndef Values_H
#define Values_H
#include QML 中调用
//main.qml
import cc.Values 1.0
Values {
id: values
}
function gameOver() {
values.bestScore = Math.max(values.bestScore, currentScore)
...
}
GitHub 地址: QmlLearningPro ,选择子工程 CrazyMath.pro
QML 其它文章请点击这里: QT QUICK QML 学习笔记