数据结构的栈和队列(这不进来看一看)
栈和队列
文章目录
- 栈和队列
-
- 栈
-
- 栈的概念
- 栈的实现
- 栈的面试题
-
- 括号匹配
- 逆波兰表达式求值
- 队列
-
- 队列的概念
- 循环队列
-
- 如何区分循环队列的空与满
- 队列的面试题
-
- 分条件出栈
- 最近的请求次数
栈
栈的概念
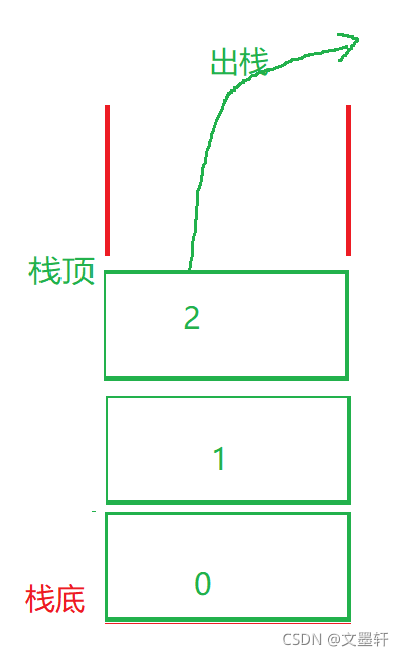
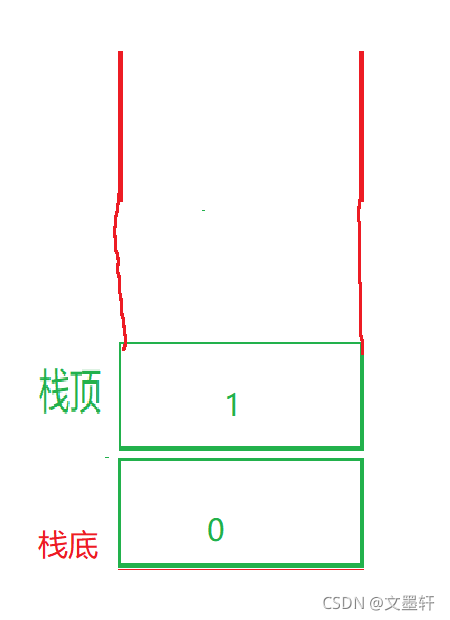
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据在栈顶
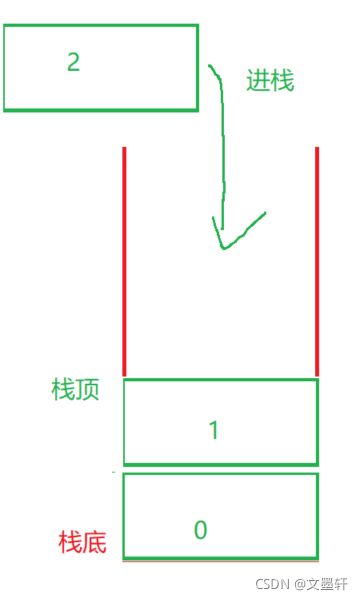
如图:
入栈时:
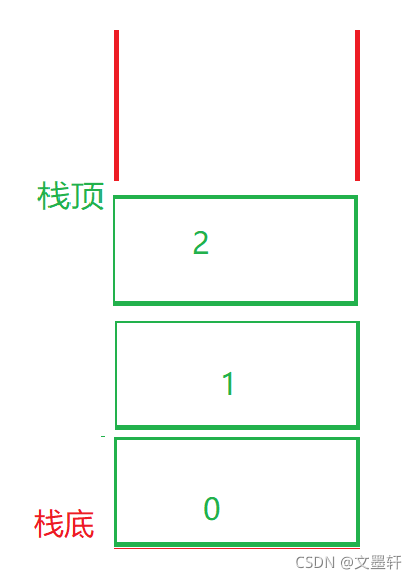
出栈时:
栈的实现
实现栈一般有两种方法一个为利用顺序表实现另一个为链表实现,在实际情况下,我们使用顺序表实现栈
public class MyStack {
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;
public MyStack(){
this.elem=new int[10];
}
//判断栈是否为空
public boolean isFull() {
if(usedSize==this.elem.length){
return true;
}
return false;
}
//将元素插入栈当中
public void push(int item) {
if(isFull()){
//如果栈已经填满,则将栈进行2倍扩容
this.elem= Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,2*this.elem.length);
}
this.elem[this.usedSize]=item;
this.usedSize++;
}
public boolean empty() {
//判断栈是否为空,是则返回true,不是则返回false
return this.usedSize==0;
}
public int pop() throws RuntimeException{
if (empty()){
//如果栈为空则抛出异常
throw new RuntimeException("栈空了");
}
//返回栈顶元素并从栈中删除栈顶元素
return this.elem[--this.usedSize];
}
public int peek() {
if (empty()){
//如果栈为空则抛出异常
throw new RuntimeException("栈空了");
}
//返回栈顶元素但不从栈中删除栈顶元素
return this.elem[this.usedSize-1];
}
}
注意:在java程序中,可以直接使用栈
格式:
Stack 变量名=new Stack<>()
| 方法 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| E push(E item) | 压栈 |
| E pop() | 出栈 |
| E peek() | 查看栈顶元素 |
| boolean empty() | 判断栈是否为空 |
栈的面试题
括号匹配
题解:
该题考查对栈掌握程度,为了匹配有效括号,我们可以使用使用一个栈,将遇到的左括号都放入栈中,遇到右括号就取出栈顶元素进行比较,如果匹配则删除栈顶,如果不匹配则返回false;循环结束后再判断栈是否为空如果为空则返回true,相反则返回false;
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Stack<Character> stack=new Stack<>();
char[] ch=s.toCharArray();
for(char ch1:ch){
switch(ch1){
case '(':
case '{':
case '[':
stack.push(ch1);
break;
case ')':
if(!stack.isEmpty()&&stack.peek()=='('){
stack.pop();
}
else{
return false;
}
break;
case ']':
if(!stack.isEmpty()&&stack.peek()=='['){
stack.pop();
}
else{
return false;
}
break;
case '}':
if(!stack.isEmpty()&&stack.peek()=='{'){
stack.pop();
}
else{
return false;
}
break;
}
}
if(stack.isEmpty()){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
逆波兰表达式求值
该题考查我们对前缀算法和中缀算法的熟悉程度,使用一个栈,将数字放入其中当遇到‘+’,‘-’,‘*’,‘/’,则取出栈顶的两个元素,与相应的运算符进行操作
再将新获得的数放入栈中。
class Solution {
public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int n = tokens.length;
for (String token:tokens) {
if (isNumber(token)) {
stack.push(Integer.parseInt(token));
} else {
int num2 = stack.pop();
int num1 = stack.pop();
switch (token) {
case "+":
stack.push(num1 + num2);
break;
case "-":
stack.push(num1 - num2);
break;
case "*":
stack.push(num1 * num2);
break;
case "/":
stack.push(num1 / num2);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
return stack.pop();
}
public boolean isNumber(String token) {
return !("+".equals(token) || "-".equals(token) || "*".equals(token) || "/".equals(token));
}
}
队列
队列的概念
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出FIFO(First In First Out) 入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾(Tail/Rear) 出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头(Head/Front)
如图:
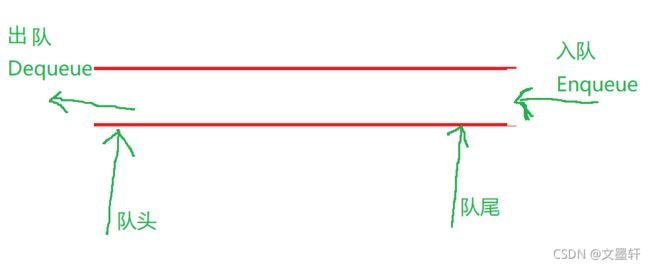
为了实现队列,可以采用数组和链表的结构实现,使用链表的结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构,出队列在数组头上出数据,效率会比较低。
class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
public class MyQueueLinked {
private Node front;
private Node rear;
private int usedSize;
//插入元素进入队列中
public void offer(int val) {
Node node=new Node(val);
if (front==null){
this.front=node;
this.rear=node;
}
else {
this.rear.next=node;
this.rear=node;
}
this.usedSize++;
}
public int size() {
return this.usedSize;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.usedSize == 0;
}
//返回栈头元素,并从队列中删除
public int poll() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空!");
}
int val=this.front.data;
if(this.front.next == null) {
this.front = null;
this.rear = null;
}
else {
this.front=this.front.next;
}
this.usedSize--;
return val;
}
//返回栈头元素,但不从队列中删除
public int peek(){
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空!");
}
return this.front.data;
}
}
循环队列
实际中我们有时还会使用一种队列叫循环队列。如操作系统课程讲解生产者消费者模型时可以就会使用循环队列。环形队列通常使用数组实现。
如何区分循环队列的空与满
循环队列一般会保留一个位置以便于判断是否满了
如图:
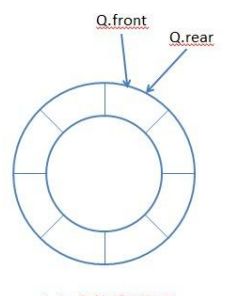
当Q.front==Q.rear时,此时循环队列为空。
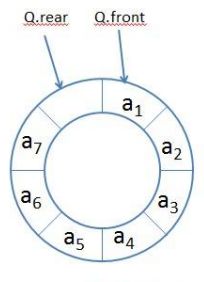
当(Q.rear+1)%数组的长度=Q.front时则循环队列为满
队列的面试题
分条件出栈
由题我们可以创建两个队列a,b,一个队列a用于先放元素,第二个队列b用于存储从a中删除的元素最后返回队列b.
import java.util.*;
public class CatDogAsylum {
public ArrayList<Integer> asylum(int[][] ope) {
// write code here
ArrayList<Integer> one=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> two=new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < ope.length; i++) {
if (ope[i][0]==1){
one.add(ope[i][0]*ope[i][1]);
}
else {
if (ope[i][1]==1){
int size= one.size();
for(int j=0;j<size;j++){
if(one.get(j)>0){
two.add(one.remove(j));
break;
}
}
}
else if(ope[i][1]==0){
two.add(one.remove(0));
}
else {
int size= one.size();
for(int j=0;j<size;j++){
if(one.get(j)<0){
two.add(one.remove(j));
break;
}
}
}
}
}
return two;
}
}
最近的请求次数
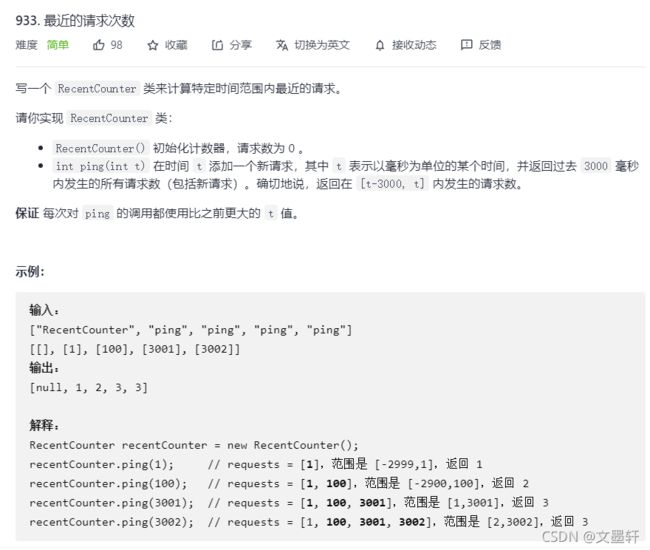
这题考的是我们对题的理解,大概意思就是把t放入队列中,再判断队列中的值是不是在区间[t-3000,t];如果有值不在这个范围则将他从队列中删除,最后返回队列中还有多少个元素。
class RecentCounter {
Queue<Integer> q;
public RecentCounter() {
this.q=new LinkedList<>();
}
public int ping(int t) {
q.add(t);
while(q.peek()<t-3000){
q.poll();
}
return q.size();
}
}