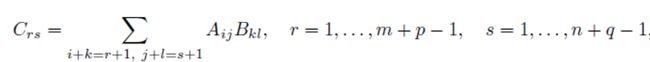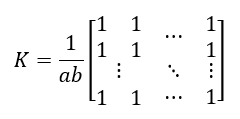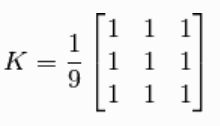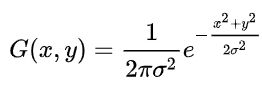模糊图像处理 去除模糊
定义 (Definition)
Roughly speaking, blurring an image is make the image less sharp. This can be done by smoothing the color transition between the pixels.
粗略地说,模糊图像会使图像清晰度降低。 这可以通过平滑像素之间的颜色过渡来完成。
To accomplish this target, we need to apply a convolution operation of a specialized matrix, called kernel, to the image’s matrix.
为了实现这个目标,我们需要对图像的矩阵应用称为内核的专用矩阵的卷积运算。
What is convolution?
什么是卷积?
Mathematically speaking, a convolution of two matrix, A with size m x n, and B with size p x q, is a (m + p -1) x (n+q-1) matrix C with entries:
从数学上讲,两个矩阵(卷积为mxn的A和卷积为pxq的B)的卷积是一个(m + p -1)x(n + q-1)矩阵C,其条目为:
Convolution in matrices 矩阵卷积Casually speaking, convolution is just forming a new matrix in which the entries are the sums of product of the entries of one matrix with the corresponding entry of another matrix. All of these products could be calculated along the rows and columns.
随意地说,卷积只是形成一个新矩阵,其中项是一个矩阵的项与另一矩阵的相应项的乘积之和。 所有这些乘积都可以沿着行和列进行计算。
What is kernel?
什么是内核?
Kernel is a matrix that has purpose to transform an image. It is not exclusive to image blurring. It can also be used to detect edges, sharpening edges, and others kind of image transformation. Kernel that used in blurring image is a low-pass filter kernel. It allows low frequency to enter and stop the higher frequency.
内核是旨在转换图像的矩阵。 它并非仅用于图像模糊。 它还可以用于检测边缘,锐化边缘和其他类型的图像转换。 用于模糊图像的内核是低通滤波器内核。 它允许低频进入并停止更高的频率。
应用 (Application)
Why do we even need to blur an image in the first place? After all, doesn’t it make the image become less visible?
为什么我们甚至首先需要模糊图像? 毕竟,这是否会使图像的可见度降低?
It turns out that blurring an image has several purpose.
事实证明,使图像模糊有几个目的。
Firstly, it reduce the noises in the image. A random brightness spot or incorrect color spot, depends on the type of noise, could be reduced by blurring the image with suitable type of blur.
首先,它减少了图像中的噪点。 根据噪声的类型,可以通过使用适当的模糊类型对图像进行模糊处理来减少随机的亮点或不正确的色点。
Blurring an image also reduces the size of image. With appropriate blurring function, we can deblurring the blurred image into the original image. This can be very helpful in transferring a vast size of images.
模糊图像也会缩小图像的尺寸。 使用适当的模糊功能,我们可以将模糊图像去模糊为原始图像。 这对于传输大量图像非常有帮助。
Blurring also used in media. For example, when the news’ picture is not appropriate or explicit. Another use is to hide the face, name, and all private data of people that happens to be included in the image accidentally.
模糊还用于媒体中。 例如,当新闻的图片不合适或不明确时。 另一个用途是隐藏恰好包含在图像中的人的面部,名字和所有私人数据。
Lastly, for entertainment purpose. For instance, in movies and digital artworks. The blurring effect may enhance the feels of lovely citylights scene. Or it may helps movie audience knows this particular scene occurs in past.
最后,出于娱乐目的。 例如,在电影和数字艺术品中。 模糊效果可以增强可爱的城市灯光场景的感觉。 或者它可以帮助电影观众知道这个特定场景过去发生的情况。
模糊类型 (Types of Blurring)
There are a number of blurring filter type that can be used. All has its own characteristics. In this section, I explain two of them: Mean/Box/Average filter and Gaussian filter. In Python, these blur filter is contained in OpenCV package. In all of these section, the module I used is
可以使用多种模糊滤波器类型。 都有自己的特点。 在本节中,我将解释其中的两个:均值/框/平均滤波器和高斯滤波器。 在Python中,这些模糊过滤器包含在OpenCV软件包中。 在所有这些部分中,我使用的模块是
# For blur and convolution
import cv2# For creating matrix
import numpy as np# From showing images
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt1.均值过滤器(平均过滤器/箱式过滤器) (1. Mean Filter (Average Filter/Box Filter))
This filter takes the average of pixels in kernel and replace the central pixel with this average. This kernel has all of its elements same and sums up to 1. The kernel must be odd-sized. Hence, if the size of the kernel is a x b, the mean filter kernel is
该滤镜获取内核中像素的平均值,然后用该平均值替换中心像素。 该内核的所有元素相同,总和为1。内核必须为奇数大小。 因此,如果内核的大小为axb,则平均滤波器内核为
The general form of mean filter kernel 均值滤波核的一般形式For example, when a = 3 and b = 3, the kernel is
例如,当a = 3且b = 3时,内核为
The greater value of kernel size, the greater blurring effect because the number of pixels involved is greater and the transition of colors become smoother.
内核大小的值越大,模糊效果越大,这是因为所涉及的像素数更大并且颜色的过渡变得更平滑。
# Import the image
img = cv2.imread('103057.jpg')# Show the original image
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()# Creating a mean filter kernel
def meankernel(size):
mk = np.ones((size, size), np.float32)/(size ** 2)
return mk# Convolute the kernel with image
for size in range(3, 14, 2):
blurImg = cv2.filter2D(img, -1, meankernel(size))
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(blurImg)
plt.show()The OpenCV module has given a function for mean filter: cv2.blur(). Here is the sample code for mean filter with different size of kernel:
OpenCV模块提供了均值过滤器功能:cv2.blur()。 以下是具有不同内核大小的均值过滤器的示例代码:
# Import the image
img = cv2.imread('103057.jpg')# Show the original image
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()# Show the blurred image with different size of kernel
for size in range(3, 14, 2):
blurImg = cv2.blur(img,(size,size))
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(blurImg)
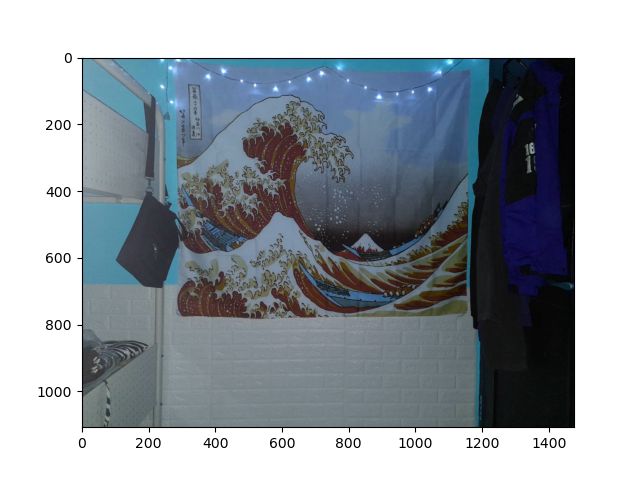
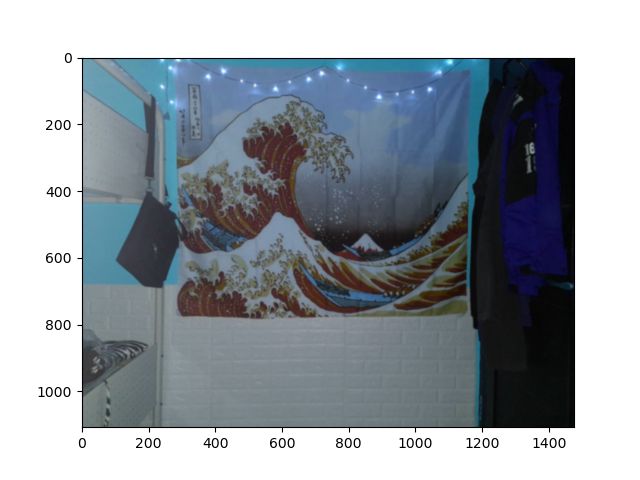
plt.show()The original image is:
原始图像是:
Original image. 原始图像。And the blurred images are
而且模糊的图像是
2.高斯滤波器 (2. Gaussian Filter)
This filter gives different weight to each entries in matrix as entries in kernel. The closer pixel to the selected pixel has greater weight while the further pixel has lower weight. In theory, all pixel in matrix contributes to the value of the entry in final matrix. In fact, the complete (or theoretical) formula for this filter is
该过滤器为矩阵中的每个条目赋予不同的权重,作为内核中的条目。 距所选像素最近的像素具有较大的权重,而另一个像素具有较低的权重。 从理论上讲,矩阵中的所有像素都有助于最终矩阵中条目的值。 实际上,此过滤器的完整(或理论上)公式为
Gaussian function 高斯函数where x and y is the horizontal and vertical distance. σ stands for the standard deviation. The higher value of σ, the greater blurring effect.
其中x和y是水平和垂直距离。 σ表示标准偏差。 σ值越高,模糊效果越大。
In practice, we estimate the Gaussian function by an odd-sized kernel whose entries are the estimation of the Gaussian function at that pixel. Moreover, this kernel cannot be sufficiently large because the further pixel give smaller contribution to the value of kernel. Often, we ignore the σ and just give it to the program to determine the suitable value for the given size kernel. For example, the approximation of 3 x 3 Gaussian kernel is
在实践中,我们通过一个奇数大小的内核来估计高斯函数,其条目是该像素处的高斯函数的估计。 而且,该内核不能足够大,因为另外的像素对内核的值贡献较小。 通常,我们会忽略σ,而只是将其提供给程序以确定给定大小内核的合适值。 例如,3 x 3高斯核的近似值为
Approximation for 3 x 3 Gaussian kernel. Source: Wikipedia 3 x 3高斯核的近似值。 资料来源:维基百科To calculate the Gaussian kernel, we can use the OpenCV function of cv2.GaussianBlur(). Here is the sample code for Gaussian filter with different size of kernel:
要计算高斯内核,我们可以使用cv2.GaussianBlur()的OpenCV函数。 以下是具有不同内核大小的高斯滤波器的示例代码:
# Import the image
img = cv2.imread('103057.jpg')# Show the original image
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()# Show the blurred image with different size of kernel
for size in range(3, 14, 2):
blurImg = cv2.GaussianBlur(img,(size,size), 0)
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(blurImg)
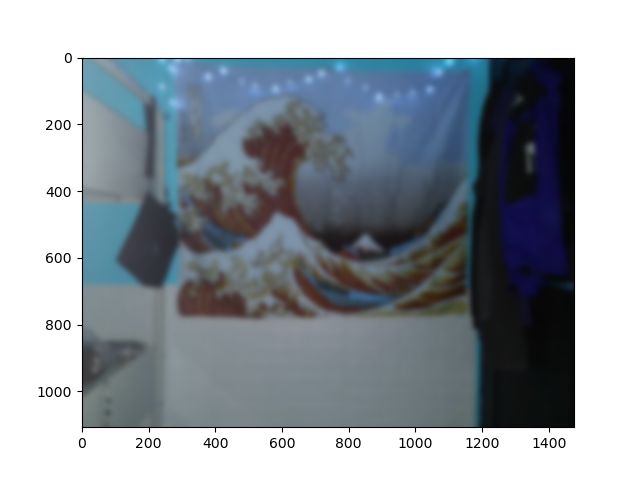
plt.show()The original image is:
原始图像是:
Original image. 原始图像。And the blurred images are
而且模糊的图像是
比较方式 (Comparison)
The Gaussian kernel gives better result in separating frequencies. But, it is slow because of all the calculation involved. On the other hand, mean kernel works in reducing random noise in image space and it is fast. But, it gives worse performance in separating frequency.
高斯核在分离频率方面给出了更好的结果。 但是,由于涉及所有计算,所以速度很慢。 另一方面,均值内核可以减少图像空间中的随机噪声,而且速度很快。 但是,它在分离频率方面的性能较差。
We can compromise both kernel by apply mean kernel 4 times on the image. The blurred image would look like the Gaussian kernel.
我们可以通过在映像上应用平均4次内核来破坏两个内核。 模糊的图像看起来像是高斯核。
Here is some blurred images with different kernel size
这是一些具有不同内核大小的模糊图像
翻译自: https://medium.com/@akeylanaufal/how-image-blurring-works-652051aee2d1
模糊图像处理 去除模糊