我们今天不探讨框架层面的内容,暂且认为90%的框架不存在无法容忍的性能问题。在做系统调优的过程中,面对随处可见的invoke调用,我的内心其实是比较抵触的,倒不是说反射怎么不好,对于优雅的源码来说,反射必不可少,个人抵触的原因主要是因为反射把真实的方法“隐藏”的很好,面对长长的线程栈比较头大而已。而且我心里一直有个大大的问号,反射到底存在哪些性能问题。
带着这个疑惑,基于java最基本的反射使用,通过查看资料及源码阅读,有如下的总结和分享,欢迎交流和指正。
一、准备
注:本案例针对JDK1.8
测试代码:
【TestRef.java】
public class TestRef {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.allen.commons.entity.CommonTestEntity");
Object refTest = clazz.newInstance();
Method method = clazz.getMethod("defaultMethod");
//Method method1 = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("defaultMethod");
method.invoke(refTest);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException | NoSuchMethodException | InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
【CommonTestEntity.java】
public class CommonTestEntity {
static {
System.out.println("CommonTestEntity执行类加载...");
}
public CommonTestEntity() {
System.out.println(this.getClass() + " | CommonTestEntity实例初始化 | " + this.getClass().getClassLoader());
}
public void defaultMethod() {
System.out.println("执行实例方法:defaultMethod");
}
}
二、反射调用流程
1.反射的使用
- 1)创建
class对象(类加载,使用当前方法所在类的ClassLoader来加载) - 2)获取
Method对象(getMethod和getDeclaredMethod) - 3)调用
invoke方法
2.getMethod 和 getDeclaredMethod区别
getMethod源码如下:
public Method getMethod(String name, Class... parameterTypes)
throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException {
Objects.requireNonNull(name);
SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
// 1. 检查方法权限
checkMemberAccess(sm, Member.PUBLIC, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true);
}
// 2. 获取方法
Method method = getMethod0(name, parameterTypes);
if (method == null) {
throw new NoSuchMethodException(methodToString(name, parameterTypes));
}
// 3. 返回方法
return method;
}
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
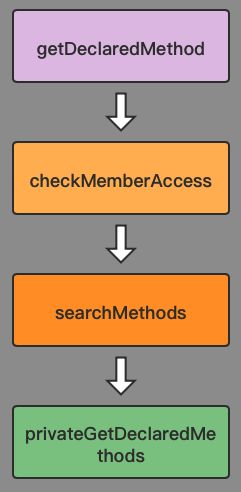
public Method getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class... parameterTypes)
throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException {
Objects.requireNonNull(name);
SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
// 1. 检查方法是权限
checkMemberAccess(sm, Member.DECLARED, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true);
}
// 2. 获取方法
Method method = searchMethods(privateGetDeclaredMethods(false), name, parameterTypes);
if (method == null) {
throw new NoSuchMethodException(methodToString(name, parameterTypes));
}
// 3. 返回方法
return method;
}
获取方法的流程分三步走:
- a.检查方法权限
- b.获取方法
Method对象 - c.返回方法
主要有两个区别:
1.getMethod 中 checkMemberAccess 传入的是 Member.PUBLIC,而 getDeclaredMethod 传入的是 Member.DECLARED 。
代码中的注释:
注释里解释了 PUBLIC 和 DECLARED 的不同,PUBLIC 会包括所有的 public 方法,包括父类的方法,而 DECLARED 会包括所有自己定义的方法,public,protected,private 都在此,但是不包括父类的方法。
2.getMethod 中获取方法调用的是 getMethod0,而 getDeclaredMethod 获取方法调用的是 privateGetDeclaredMethods 。privateGetDeclaredMethods 是获取类自身定义的方法,参数是 boolean publicOnly,表示是否只获取公共方法。
privateGetDeclaredMethods 源码如下:
// Returns an array of "root" methods. These Method objects must NOT
// be propagated to the outside world, but must instead be copied
// via ReflectionFactory.copyMethod.
private Method[] privateGetDeclaredMethods(boolean publicOnly) {
checkInitted();
Method[] res;
ReflectionData rd = reflectionData();
if (rd != null) {
res = publicOnly ? rd.declaredPublicMethods : rd.declaredMethods;
if (res != null) return res;
}
// No cached value available; request value from VM
res = Reflection.filterMethods(this, getDeclaredMethods0(publicOnly));
if (rd != null) {
if (publicOnly) {
rd.declaredPublicMethods = res;
} else {
rd.declaredMethods = res;
}
}
return res;
}
①relectionData 通过缓存获取
②如果缓存没有命中的话,通过 getDeclaredMethods0 获取方法
getMethod0源码如下:
private Method getMethod0(String name, Class[] parameterTypes, boolean includeStaticMethods) {
MethodArray interfaceCandidates = new MethodArray(2);
Method res = privateGetMethodRecursive(name, parameterTypes, includeStaticMethods, interfaceCandidates);
if (res != null)
return res;
// Not found on class or superclass directly
interfaceCandidates.removeLessSpecifics();
return interfaceCandidates.getFirst(); // may be null
}
其中privateGetMethodRecursive方法中也会调用到privateGetDeclaredMethods方法和searchMethods方法
3.getMethod 方法流程
4.getDeclaredMethod方法流程
三、调用反射方法
invoke源码:
class Method {
public Object invoke(Object obj, Object... args)
throws IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException,
InvocationTargetException
{
if (!override) {
Class caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
// 1. 检查权限
checkAccess(caller, clazz,
Modifier.isStatic(modifiers) ? null : obj.getClass(),
modifiers);
}
// 2. 获取 MethodAccessor
MethodAccessor ma = methodAccessor; // read volatile
if (ma == null) {
// 创建 MethodAccessor
ma = acquireMethodAccessor();
}
// 3. 调用 MethodAccessor.invoke
return ma.invoke(obj, args);
}
}
Method.invoke()实际上并不是自己实现的反射调用逻辑,而是委托给sun.reflect.MethodAccessor来处理。
每个实际的Java方法只有一个对应的Method对象作为root(实质上就是Method类的一个成员变量)。每次在通过反射获取Method对象时新创建Method对象把root封装起来。在第一次调用一个实际Java方法对应得Method对象的invoke()方法之前,实现调用逻辑的MethodAccessor对象是第一次调用时才会新建并更新给root,然后调用MethodAccessor.invoke()真正完成反射调用。
MethodAccessor只是单方法接口,其invoke()方法与Method.invoke()的对应。创建MethodAccessor实例的是ReflectionFactory。
MethodAccessor实现有两个版本,一个是Java实现的,另一个是native code实现的。
Java 版本的 MethodAccessorImpl 调用效率比 Native 版本要快 20 倍以上,但是 Java 版本加载时要比 Native 多消耗 3-4 倍资源,所以默认会调用 Native 版本,如果调用次数超过 15 次以后,就会选择运行效率更高的 Java 版本。
Native版本中的阈值(静态常量)
四、反射效率低的原因
1.Method#invoke 方法会对参数做封装和解封操作
我们可以看到,
invoke方法的参数是Object[]类型,也就是说,如果方法参数是简单类型(8中基本数据类型)的话,需要在此转化成 Object 类型,例如 long ,在javac compile的时候 用了Long.valueOf()转型,也就大量了生成了Long的 Object, 同时 传入的参数是Object[]数值,那还需要额外封装object数组。而在上面
MethodAccessorGenerator#emitInvoke方法里我们看到,生成的字节码时,会把参数数组拆解开来,把参数恢复到没有被 Object[] 包装前的样子,同时还要对参数做校验,这里就涉及到了解封操作。因此,在反射调用的时候,因为封装和解封,产生了额外的不必要的内存浪费,当调用次数达到一定量的时候,还会导致 GC。
2.需要检查方法可见性
checkAccess方法
3.需要遍历方法并校验参数
PrivateGetMethodRecursive中的searhMethod
4.JIT 无法优化
在 JavaDoc 中提到:
Because reflection involves types that are dynamically resolved, certain Java virtual machine optimizations can not be performed. Consequently, reflective operations have slower performance than their non-reflective counterparts, and should be avoided in sections of code which are called frequently in performance-sensitive applications.
五、反射优化
1.(网上看到)尽量不要getMethods()后再遍历筛选,而直接用getMethod(methodName)来根据方法名获取方法
但是在源码中获取方法的时候,在searchMethods方法中,其实也是采用遍历所有方法的方式。但是相比getMethod,getDeclaredMethod遍历的方法数量相对较少,因为不包含父类的方法。
2.缓存class对象
a)Class.forName性能比较差
b)如上所述,在获取具体方法时,每次都要调用native方法获取方法列表并遍历列表,判断入参类型和返回类型。将反射得到的method/field/constructor对象做缓存,将极大的提高性能。
3.涉及动态代理的:在实际使用中,CGLIB和Javassist基于动态代码的代理实现,性能要优于JDK自带的动态代理
JDK自带的动态代理是基于接口的动态代理,相比较直接的反射操作,性能还是高很多,因为接口实例相关元数据在静态代码块中创建并且已经缓存在类成员属性中,在运行期间是直接调用,没有额外的反射开销。
4.使用ReflectASM,通过生成字节码的方式加快反射(使用难度大)
到此这篇关于Java反射及性能详细的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java反射及性能内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!