MYSQL基础知识总结
自连接查询
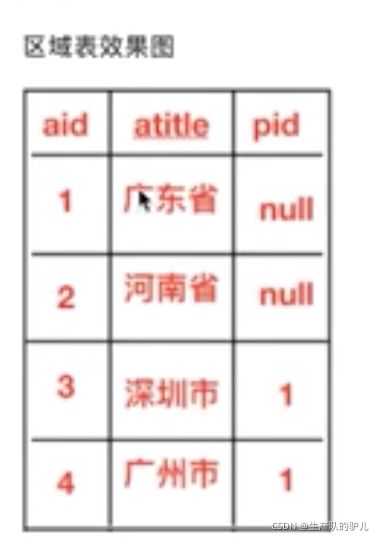
城市表 和 省份表
create table areas(
id varchar(30) not null primary key,
title varchar(30),
pid varchar(30)
);
创建一张表
id 是当前城市id
pid是当前省份id,有的数据pid为空,因为本身就是省份
source 命令执行sql文件,导入
cd Desktop/ # 进入桌面
mysql -uroot -p # 进入mysql
不在当前目录的下,打开启动的mysql,需要 source
source Desktop/areas.sql;
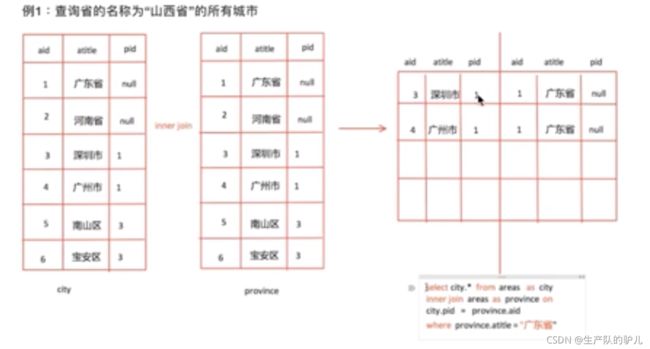
select c.id,c.title,c.pid,p.title from areas c inner join areas p on c.pid = p.id
where p.title = '山西省'
limit 100;
总结:
自连接查询
把一张表 模拟成左右两张表,进行连表查询。
子查询
在一个select中再嵌套一个select语句查询
括号里面是一个完成的查询语句,可以用来单独执行的
案例: 查询出 大于平均值的学生
select avg(age) from students;
select * from students where age >= 30;
合并
select * from students where age > (select avg(age) from students);
案例
查询有学生的班级
select c_id from students where c_id is not null;
select * from classes where id in (select c_id from students where c_id is not null);
查询年龄最大 身高最高 的人
select max(age) from students;
select max(height) from students;
select * from students where age = (select max(age) from students)
and height = (select max(height) from students);
select * from students where (age,height) = (select max(age), max(height) from students);
总结:
子查询是一个完整的查询语句,
执行子查询执行顺序: 先括号内子查询,后主查询根据子查询的结果再进行执行。
小tips:
当select查询的表的内容复杂,输出导致乱码
可以在后面 加上 \t; 让其排列整齐后输出;
例子:查询 mysql本身的user表,
select * from users; 会乱
select * from users \t; 就不乱了.
mysql修改数据
修改字段 类型 名字 和 删除表
alter table 表名 modify/change 列名 新列名/类型 约束;

mysql常用增删查改数据重点
查询

添加

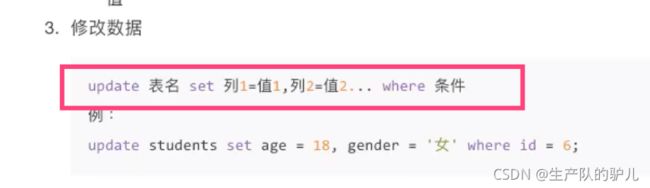
修改数据
update 记得一定要加 where 条件!!!!!
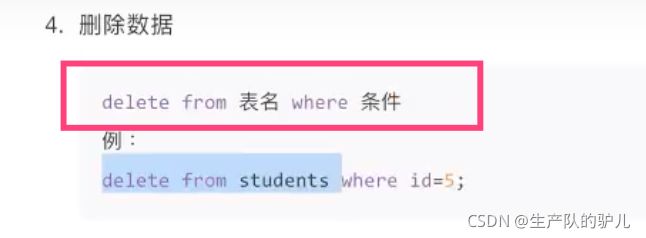
删除数据
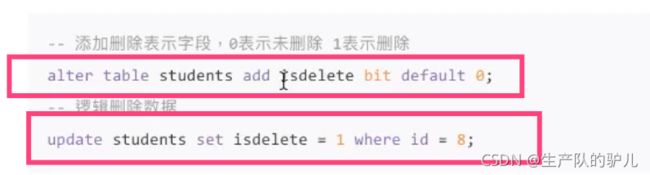
逻辑删除
总结
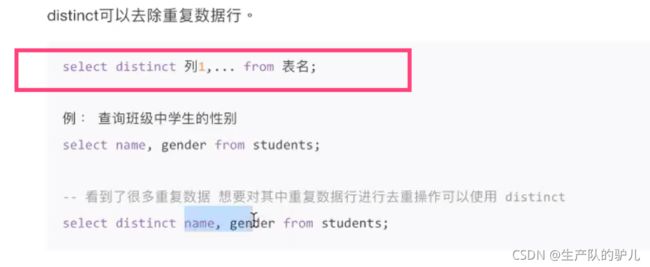
as 和 distinct 去重
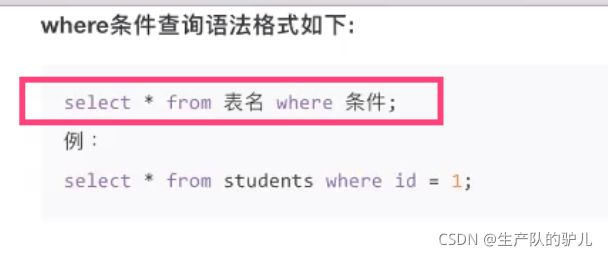
where 条件语法
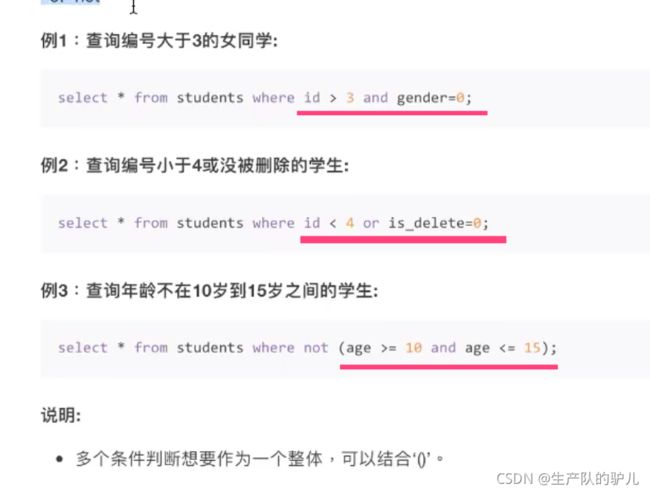
比较运算符
逻辑运算符
模糊查询
范围查询
连续范围 beteween … and …
in 非连续的范围查询

空判断
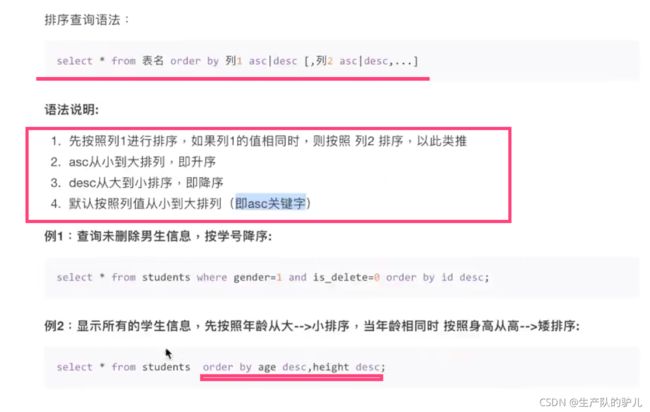
排序 order by
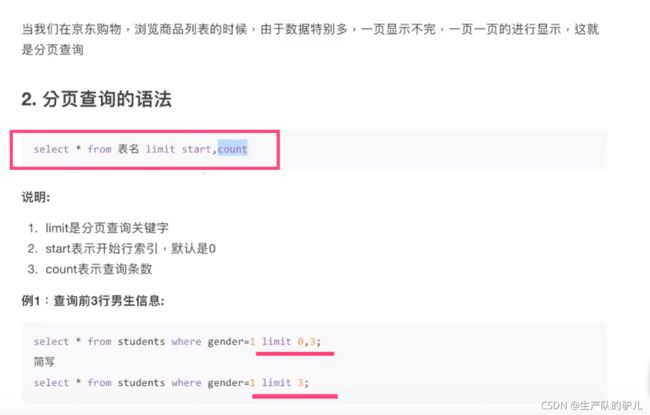
分页查询
聚合函数

例子:

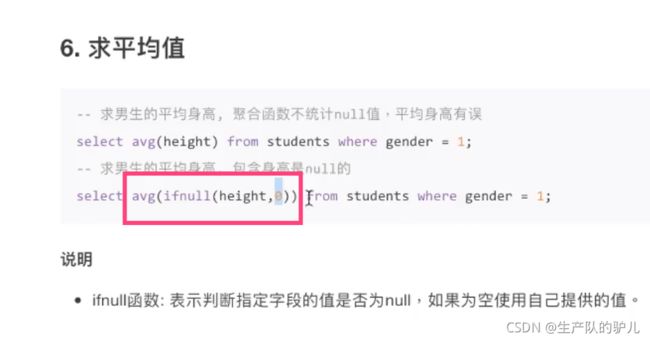
注意 ifnull 函数
可以讲 null 的部分,按照 均值 进行 统计到其中 来显示
这个例子就是统计 身高的平均值, 将 height 为 null的字段中的数据 按照 0来计算