小白入门之SpringMVC
文章目录
-
- SpringMVC 框架介绍
-
- 概述
- MVC模型
- 性能超群
- 工作原理
- 案例:展示汽车数据
-
- 需求
- 创建Maven module
- 创建RunApp.java
- Car.java
- CarController.java
- 测试
- 处理请求参数
-
- 概述
- GET方式
- POST方式
- RESTFul方式(推荐)
- 处理Get请求的参数
-
- 编写后端程序
- 编写前端程序
- 处理Post请求的参数
-
- 架构图
- 项目结构
- 接收参数
- 准备stuform.html
- 准备Student.java
- 准备StuController.java
- 日期数据的处理
- 改造成Ajax访问
- 总结
-
- springmvc和struts2比较
- MVC和SSM的关系
- SpringMVC常用的注解
SpringMVC 框架介绍
概述
Spring MVC属于SpringFrameWork的后续产品,已经融合在Spring Web Flow里面。Spring 框架提供了构建 Web 应用程序的全功能 MVC 模块。使用 Spring 可插入的 MVC 架构,从而在使用Spring进行WEB开发时,可以选择使用Spring的SpringMVC框架或集成其他MVC开发框架,如Struts1(现在一 般不用),Struts2(一般老项目使用)等。
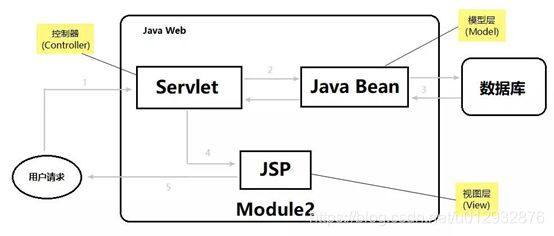
SpringMVC就是基于MVC设计模式来实现的。
我们的POJO就是Model层,我们的JSP就是视图层,我们的Controller就是控制层。
现在主流基于SSM三大框架开发都是在MVC上继续演化,又分为持久层DAO,业务层Service,控制层Controller。持久层用来和数据库读写ORM,业务层用来处理复杂的业务逻辑,控制层用来处理MVC的控制。
MVC模型
用来进行分层的结构,这样代码分离结构清晰,各层代码,各司其职,易于开发大型项目。
MVC(Model模型、View视图、Control控制层),将软件进行分层达到松耦合的效果。
通用的软件编程思想, 在MVC设计模式中认为, 任何软件都可以分三层:控制层(Controller)、数据处理模型(Model)、负责展示数据的视图(View)。
在MVC设计思想中要求一个符合MVC设计思想的软件应该保证上面这三部分相互独立,互不干扰,每一个部分只负责自己擅长的部分。如果某一个模块发生变化,应该尽量做到不影响其他两个模块。提高代码的可读性,实现程序间的松耦合、提高代码复用性。
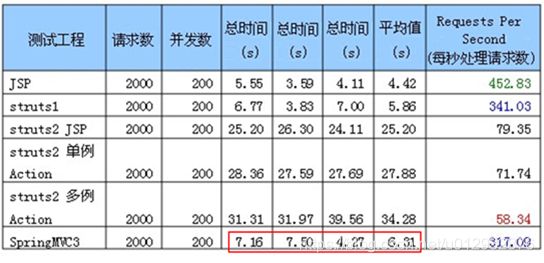
性能超群
简单易用性能佳
工作原理
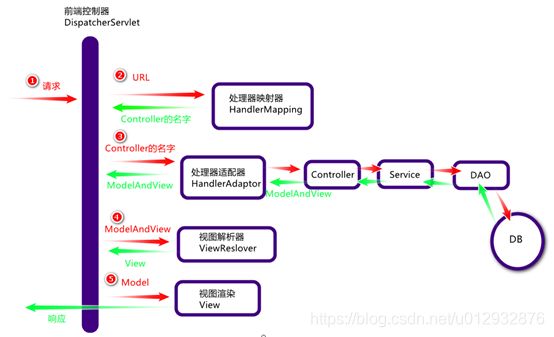
过程简单描述** *
客户端发送请求-> 前端控制器 DispatcherServlet 接受客户端请求 -> 找到处理器映射 HandlerMapping 解析请求对应的 Handler-> HandlerAdapter 会根据 Handler 来调用真正的处理器开处理请求,并处理相应的业务逻辑 -> 处理器返回一个模型视图 ModelAndView -> 视图解析器进行解析 -> 返回一个视图对象->前端控制器 DispatcherServlet 渲染数据(Moder)->将得到视图对象返回给用户.
更具体一些的描述** *
1、用户发送请求至前端控制器DispatcherServlet。
2、DispatcherServlet收到请求调用HandlerMapping处理器映射器。
3、处理器映射器找到具体的处理器(可以根据xml配置、注解进行查找),生成处理器对象及处理器拦截器(如果有则生成)一并返回给DispatcherServlet。
4、DispatcherServlet调用HandlerAdapter处理器适配器。
5、HandlerAdapter经过适配调用具体的处理器(Controller,也叫后端控制器)。
6、Controller执行完成返回ModelAndView。
7、HandlerAdapter将controller执行结果ModelAndView返回给DispatcherServlet。
8、DispatcherServlet将ModelAndView传给ViewReslover视图解析器。
9、ViewReslover解析后返回具体View。
10、DispatcherServlet根据View进行渲染视图(即将模型数据填充至视图中)。
11、DispatcherServlet响应用户。
案例:展示汽车数据
从springmvc2.5开始引入注解方式,特别到了3.0就全面引入注解方式,号称xml零配置。spring3.0配置注解引入后也就是这个点成为了它和struts2的分水岭。随着springmvc的成熟,struts2开始落幕,趋于被市场淘汰。
那下面我们就来体验下:
需求
访问链接: http://localhost:8080/car/get
得到JSON数据: {"id":718,"name":"保时捷","type":"Cayman T","color":"红色","price":641000.0}
创建Maven module
创建RunApp.java
```java
package cn.tedu;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
@SpringBootApplication
@Controller
public class RunApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(RunApp.class);
}
}
Car.java
package cn.tedu.pojo;
//Model对象,也称为POJO
//保时捷718 Cayman T,红色,641000元起
public class Car {
private Integer id; //718
private String name; //保时捷
private String type; //Cayman T
private String color; //红色
private Double price; //641000
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public Double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(Double price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", type=" + type + ", color=" + color + ", price=" + price + "]";
}
}
CarController.java
package cn.tedu.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import cn.tedu.pojo.Car;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/car")
public class CarController {
@RequestMapping("/get")
public Car get() {
//保时捷718 Cayman T,红色,641000元起
Car car = new Car();
car.setId(718);
car.setName("保时捷");
car.setType("Cayman T");
car.setColor("红色");
car.setPrice(641000.0);
return car;
}
}
测试
访问:http://localhost:8080/car/get
执行结果:
{
"id":718,"name":"保时捷","type":"Cayman T","color":"红色","price":641000.0}
处理请求参数
概述
当客户端打开浏览器要访问服务器时,可能会带着一些http请求参数过来.
这时,服务器需要获取http参数进行业务处理,如何处理http请求并获取参数呢?
总共有8种,重点时两种方式:GET方式和POST方式.
GET方式
向特定的资源发出请求,并返回实体.有固定的写法.而且数据有最大长度,超出就不行
例如:
http://localhost:8080/car/insert?id=1&name=张三&age=18
POST方式
向指定资源提交数据进行处理请求(例如提交表单或者上传文件)。数据被包含在请求体中。POST请求可能会导致新的资源的建立和/或已有资源的修改。
RESTFul方式(推荐)
为了简化GET请求的写法,可以使用RESTFul方式,用法:
1、需要使用注解@PathVariable来获取请求路径中的参数值,@PathVariable用来绑定值
2、通过{???}获取路径中传递来的值
3、以前GET的访问方式即将被简化成:
http://localhost:8080/car/insert/1/张三/18
处理Get请求的参数
编写后端程序
如果页面的名称和后台形参的名称不一致,可以使用@RequestParam(“页面名称”),就必须指定值.
package cn.tedu.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import cn.tedu.pojo.Car;
@RestController//接受请求,返回json数据
@RequestMapping("/car/")
public class CarController {
//2,通过GET请求,传入参数并接收处理
//访问 http://localhost:8080/car/add?id=10,必须设置id的值否则报错,?拼接是固定语法
@RequestMapping("add")
public void add(int id) {
System.out.println("数据添加成功,id="+id);
}
//访问 http://localhost:8080/car/save?id=90&name=tony ,设置多个参数值时用&连接
@RequestMapping("save")
public void save(int id,String name) {
System.out.println("数据保存成功,id="+id+",name="+name);
}
//访问 http://localhost:8080/car/obj?id=100&name=BMW&color=red
@RequestMapping("obj")
public void obj(Car c) {
//处理一个对象的参数
System.out.println(c);
}
//3,优化GET传参的restful方式
//GET方式访问: http://localhost:8080/car/insert?id=1&name=张三&age=18
//restful方式访问: http://localhost:8080/car/insert/1/张三/18
@RequestMapping("insert/{x}/{y}/{z}")
//restful配合@PathVariable注解一起用,使用{资源名}获取传过来的值
public void insert(@PathVariable int x,
@PathVariable String y,
@PathVariable int z) {
System.out.println("数据插入成功,id="+x+",name="+y+",age="+z);
}
@RequestMapping("g2/{name}/{age}/{sex}")
//restful获取地址栏中的参数值,并自动封装给了User对应的属性
public String get2(User u){
return ""+u;
}
}
编写前端程序
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>前后端关联title>
head>
<body>
<a href="http://localhost:8080/car/restful/3/1">点我a>
body>
html>
处理Post请求的参数
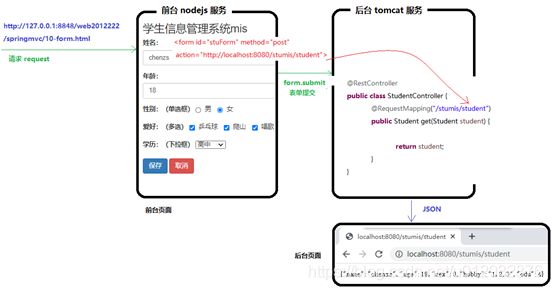
架构图
激动吧,前行吧,终于我们要学一种常规的方式,和ajax不同,它是表单自身提供的一种方式,可以实现前台请求提交给后台系统,经过后台系统处理后,进行展现。
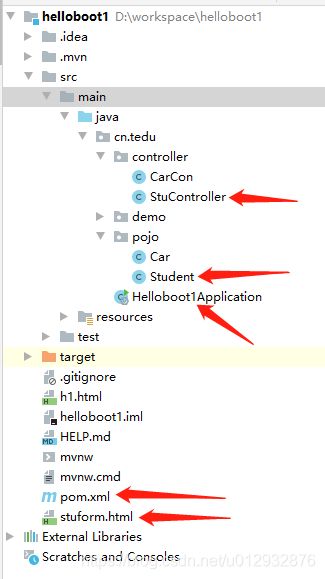
项目结构
接收参数
- 处理一个参数,比如:id
- 处理多个参数,比如:id,name,hobby
- 处理对象,比如:Student数据
- url的RESTFul形式
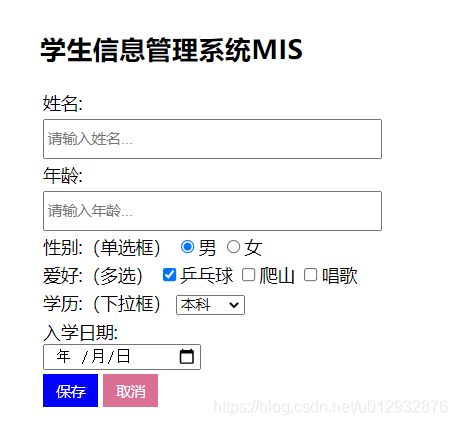
准备stuform.html
DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>stuformtitle>
<style>
input[type='text']{
width: 300px;
height: 20px;
}
style>
head>
<body style="padding-left: 50px;font-size: 15px;font-weight: bold;">
<form action="http://localhost:8080/stu/add" method="post">
<table style="margin: 30px;">
<h2 style="padding-left: 100px;">学生管理系统h2>
<tr>
<td>姓名:td>
tr>
<tr>
<td>
<input type="text" name="name" placeholder="请输入姓名..."/>
td>
tr>
<tr>
<td>年龄:td>
tr>
<tr>
<td>
<input type="text" name="age" placeholder="请输入年龄..." />
td>
tr>
<tr>
<td>
性别:(单选框)
<input type="radio" name="sex" checked="checked" value="0"/>男
<input type="radio" name="sex" value="1" />女
td>
tr>
<tr>
<td>
爱好:(多选)
<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" checked="checked" value="ppq"/>乒乓球
<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="ps"/>爬山
<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="cg"/>唱歌
td>
tr>
<tr>
<td>
学历:(下拉框)
<select name="edu">
<option value ="1">本科option>
<option value ="2">专科option>
<option value ="3">研究生option>
select>
td>
tr>
<tr>
<td>
入学日期:
td>
tr>
<tr>
<td>
<input type="date" name="intime"/>
td>
tr>
<tr>
<td>
<input type="submit" value="保存" />
<input type="reset" value="取消" />
td>
tr>
table>
form>
body>
html>
准备Student.java
注意:: 日期属性要加注解,@DateTimeFormat(pattern="yyyy-MM-dd"),否则400错误
package cn.tedu.pojo;
import org.springframework.format.annotation.DateTimeFormat;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Date;
public class Student {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String sex;
private String[] hobby;
private String edu;
@DateTimeFormat(pattern="yyyy-MM-dd")
//网页上的日期是string,注解用来转换格式,不然400错误
private Date intime;
public Date getIntime() {
return intime;
}
public void setIntime(Date intime) {
this.intime = intime;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public String[] getHobby() {
return hobby;
}
public void setHobby(String[] hobby) {
this.hobby = hobby;
}
public String getEdu() {
return edu;
}
public void setEdu(String edu) {
this.edu = edu;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", sex='" + sex + '\'' +
", hobby=" + Arrays.toString(hobby) +
", edu='" + edu + '\'' +
", intime=" + intime +
'}';
}
}
准备StuController.java
package cn.tedu.controller;
import cn.tedu.pojo.Student;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/stu/")
public class StuController {
//stuform.html的提交路径,会执行此方法的业务
@RequestMapping("add")
public void add(Student s){
System.out.println(s);
}
}
日期数据的处理
把页面上的intime日期数据,交给后台处理.由于页面的数据都当做String类型处理,所以交给后台处理时,会抛出400错误.需要使用注解进行类型转换.并指定日期格式:
//页面报400 IllegalArgumentException: String->Date
@DateTimeFormat(pattern="yyyy-MM-dd";)
private java.util.Date intime;
public Date getIntime() {
return intime;
}
public void setIntime(Date intime) {
this.intime= intime;
}
改造成Ajax访问
–1,把form标签的内容改成:
–2,把提交按钮的内容改成:
–3,添加ajax代码:
<script src="jquery-1.8.3.min.js">script>
<script>
function fun(){
$.ajax({
url:"http://localhost:8080/stu/add",
data:$("#f1").serialize(),
success:function(data){
console.log(data);
}
})
}
script>
–4,修改Controller代码并添加@CrossOrigin注解
总结
springmvc和struts2比较
| 技术 | 核心分发器 | 拦截级别 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Struts1 | DispatcherServlet | 类级别 | 基于Servlet实现企业中很多旧项目采用的框架action是单例模式,线程不安全的。Struts1使用JSTL EL表达式,但是对集合和索引属性的支持很弱。 |
| Struts2 | DispatcherFilter | 类级别一个类对应一个request上下文 | 基于Filter实现Struts2 action是原型模式 prototype,每次访问对象都会创建新的实例,保证线程安全性;采用 OGNL解析页面标签。Struts2是基于松耦合,和web容器脱钩ValueStack复杂值栈、多例、OGNL导致性能低安全漏洞频繁,不安全 |
| SpringMVC | DispatcherServlet | 方法级别一个方法对应一个request上下文,而方法同时又跟一个url对应。 | 基于Servlet实现Springmvc controller是单例模式,整个程序只有一个对象实例。Spring的安全性是通过绑定threadlocal实现Spring3 mvc可以认为已经99.9%零配置了。采用JSTL解析页面标签 |
| 基于web容器、单例、JSTL导致性能高 |
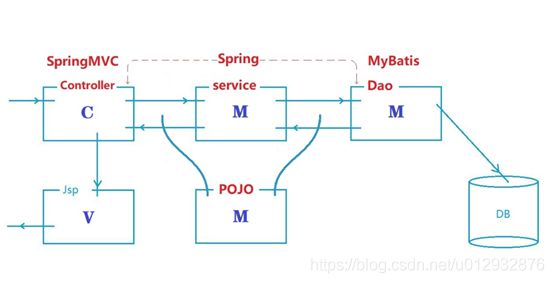
MVC和SSM的关系
SpringMVC常用的注解
@Controller 标识是一个Controller,Spring包扫描创建实例
@RequestMapping 请求后的映射路径
@PathVariable 标识接收单个参数
@ResponseBody 返回对象利用jackson工具类转换为json字符串
@RequestParam 参数名和请求参数名称不同时使用,可以设置默认值