QML定位、布局、输入元素
目录
定位、布局、输入元素以及转换
组件(Compontents)
元素转换(Transformations)
定位元素(Positioning Element)
Row定位器
Column定位器
Grid定位器
Flow定位器
Repeater(重复元素)
布局元素(Layout Element)
输入元素(Input Element)
文本输入(TextInput)
焦点区域(FocusScope)
文本编辑(TextEdit)
按键元素(Key Element)
定位、布局、输入元素以及转换
组件(Compontents)
一个可以重复使用的元素,QML可以自定义元素组件。本文主要介绍以单独文件创建组件。定义一个ClickableImage.qml供下文使用。
ClickableImage.qml实现:
import QtQuick 2.0
Image {
id: root
signal clicked
MouseArea {
anchors.fill: parent
onClicked: root.clicked()
}
}
元素转换(Transformations)
QML元素可以通过平移、旋转、缩放改变对象的几何状态。
平移:通过X、Y坐标完成
旋转:通过rotation(旋转)属性完成(0~360)
缩放:通过scale(比例)完成(小于1缩小,大于1放大)
下面看一个代码案例:
import QtQuick 2.9
import QtGraphicalEffects 1.0
Item {
width: bg.width
height: bg.height
Image {
id: bg
source: "./background.png"
}
MouseArea {
id: backgroundClicker
anchors.fill: parent
onClicked: {
rocket1.x = 20
rocket2.rotation = 0
rocket3.rotation = 0
rocket3.scale = 1.0
}
}
Image {
id: rocket1
x: 20; y: 100
source: "./pole.png"
MouseArea {
anchors.fill: parent
onClicked: {
rocket1.x += 5
}
}
}
ClickableImage {
id: rocket2
x: 140; y: 100
source: "./pole.png"
smooth: true
onClicked: {
rotation += 5
}
}
ClickableImage {
id: rocket3
x: 240; y: 100
source: "./pole.png"
smooth: true
onClicked: {
rotation += 5
scale -= 0.05
}
}
}实现效果:
原图:
点击后效果:
定位元素(Positioning Element)
在QML中定位器用于放置元素对象。QtQuick模块提供Row、Column、Grid、Flow作为定位器。下面分别通过看一下各定位器实现效果:
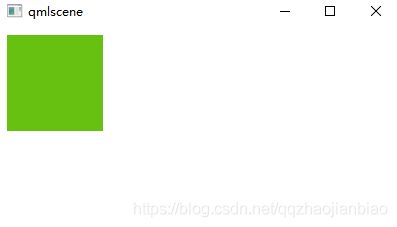
Row定位器
//Row
import QtQuick 2.5
Item {
id: root
width: 400; height: 120
Row {
id: row
anchors.centerIn: parent
spacing: 20
Rectangle {
width: 48
height: 48
color: "#ea7025"
}
Rectangle {
width: 48
height: 48
color: "#67c111"
}
Rectangle {
width: 48
height: 48
color: "#00bde3"
}
}
}效果图:
Column定位器
//Column
import QtQuick 2.5
Item {
id: root
width: 120
height: 240
Column {
id: row
anchors.centerIn: parent
spacing: 20
Rectangle {
width: 48
height: 48
color: "#ea7025"
}
Rectangle {
width: 96
height: 48
color: "#67c111"
}
Rectangle {
width: 48
height: 48
color: "#00bde3"
}
}
}效果图:
Grid定位器
//Grid
import QtQuick 2.5
Item {
id: root
width: 160
height: 160
Grid {
id: grid
rows: 2
columns: 2
anchors.centerIn: parent
spacing: 8
Rectangle {
width: 48
height: 48
color: "#ea7025"
}
Rectangle {
width: 48
height: 48
color: "#67c111"
}
Rectangle {
width: 48
height: 48
color: "#00bde3"
}
Rectangle {
width: 48
height: 48
color: "#3c3c3c"
}
}
}效果图:
Flow定位器
//Flow
import QtQuick 2.5
Item {
id: root
width: 160
height: 160
Flow {
anchors.fill: parent
anchors.margins: 20
spacing: 20
Rectangle {
width: 48
height: 48
color: "#ea7025"
}
Rectangle {
width: 48
height: 48
color: "#67c111"
}
Rectangle {
width: 48
height: 48
color: "#00bde3"
}
Rectangle {
width: 48
height: 48
color: "#3c3c3c"
}
}
}效果图:
默认:
拉伸后:
Repeater(重复元素)
这里介绍一下Repeater(重复元素)与定位器一起使用的例子。Repeater类似于for循环与迭代器的模式一样。
看一段代码:
import QtQuick 2.5
Item {
id: root
width: 252
height: 252
//使用数组定义一组颜色属性
property variant colorArray: ["#00bde3", "#67c111", "#ea7025"]
Grid{
anchors.fill: parent
anchors.margins: 8
spacing: 4
Repeater {
//重复元素创建16个Rectangle
model: 16
Rectangle {
width: 56; height: 56
//使用数学函数随机选择颜色
property int colorIndex: Math.floor(Math.random()*3)
color: root.colorArray[colorIndex]
border.color: Qt.lighter(color)
Text {
anchors.centerIn: parent
color: "#f0f0f0"
//显示index
text: "Cell " + index
}
}
}
}
}
效果图:
布局元素(Layout Element)
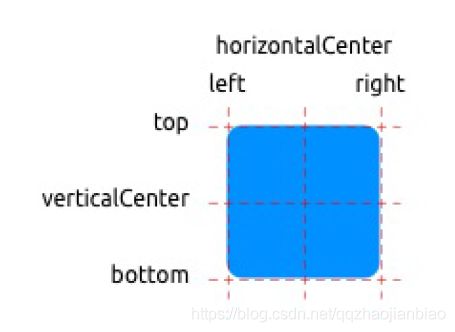
QML中使用anchors(锚)对元素进行布局。anchors是基础元素对象的基本属性,可以被所有可视化QML元素使用。
anchors图:
通过一段代码了解anchors基本使用方法:
import QtQuick 2.5
Item {
id: root
width: 400; height: 240
// M1>>
Rectangle{
id:rect1
width: 96
height: width
anchors.margins: 8
color: "#67c111"
Text {
anchors.centerIn: parent
text: '(1)'
color: "#f0f0f0"
}
}
// M2>>
Rectangle{
id:rect2
width: 96
height: width
anchors.margins: 8
color: "#00bde3"
anchors.left: rect1.right
Text {
anchors.centerIn: parent
text: '(2)'
color: "#f0f0f0"
}
}
// <>
Rectangle{
id:rect4
width: 96
height: width
anchors.margins: 8
color: "#00bde3"
anchors.top: rect2.bottom
anchors.right: parent.right
anchors.topMargin: 10
Text {
anchors.centerIn: parent
text: '(4)'
color: "#f0f0f0"
}
}
}
效果图:
输入元素(Input Element)
本段主要介绍TextInput(文本输入)和TextEdit(文本编辑)两种文本元素
文本输入(TextInput)
文本输入:允许用户输入一行文本。该元素支持使用正则表达式限制输入。
看一段代码示例:
import QtQuick 2.5
Rectangle {
width: 300
height: 80
color: "#f0f0f0"
TextInput {
id: textInput1
x: 8; y: 8
width: 250; height: 20
focus: true //接收光标
text: "please input text to textInput1" //默认text
KeyNavigation.tab: textInput2 //tab键光标切换到textInput2
}
TextInput {
id: textInput2
x: 8; y: 36
width: 250; height: 20
text: "please input text to textInput2"
KeyNavigation.tab: textInput1
}
}效果图:
焦点区域(FocusScope)
焦点区域(focus scope)定义如果该区域接收焦点,它最后一个使用focus:true的子元素接收焦点。
示例代码:
Rectangle {
width: 300
height: 80
FocusScope {
TextInput {
id: textInput1
x: 8; y: 8
width: 250; height: 20
focus: true //接收光标
text: "please input text to FocusScope" //默认text
KeyNavigation.tab: textInput2 //tab键光标切换到textInput2
}
}
FocusScope {
TextInput {
id: textInput2
x: 8; y: 36
width: 250; height: 20
text: "please input text to FocusScope"
KeyNavigation.tab: textInput1
}
}
}
实现效果:
文本编辑(TextEdit)
文本编辑(TextEdit)元素与文本输入(TextInput)元素类似,支持多行文本编辑,但是不支持文本输入限制,提供已输入文本大小的查询功能。
示例代码:
import QtQuick 2.5
Rectangle {
width: 300
height: 80
FocusScope {
TextEdit {
id: textEdit1
x: 8; y: 8
color: "red"
width: 250; height: 100
focus: true //接收光标
text: "textEdit" //默认text
KeyNavigation.tab: textEdit2 //tab键光标切换到textInput2
}
}
}效果图:
按键元素(Key Element)
程序运行中,可以使用按键元素(Key Element)执行某个操作,比如up、down进行移动,tab进行切换焦点等。
示例代码:
import QtQuick 2.5
Rectangle {
width: 400; height: width
Rectangle{
id: square
width: 96
height: width
x: 8; y: 8
color: "#67c111"
}
focus:true
Keys.onLeftPressed: square.x -= 8 //left 向左移动
Keys.onRightPressed: square.x += 8 //right 向右移动
Keys.onUpPressed: square.y -= 8 //up 向上移动
Keys.onDownPressed: square.y += 8 //down 向下移动
Keys.onPressed: {
switch(event.key) {
case Qt.Key_Plus: //+ 放大
square.scale += 0.2
break;
case Qt.Key_Minus: //缩小
square.scale -= 0.2
break;
}
}
}
效果图:
默认:
右移---->下移----->放大: