读论文 The Edge of Depth Explicit Constraints between Segmentation and Depth
The Edge of Depth: Explicit Constraints between Segmentation and Depth
一句话总结
明摆着用语义来约束深度估计
相关工作
10,12 自监督;需要事先知道两个相机的位置,把深度估计问题转化为 差异图 估计。
10: Unsupervised cnn for single view depth estimation:
Geometry to the rescue. In Proceedings of the European
Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pages 740–756,
2016.
✅ 12: Unsupervised monocular depth estimation with left
right consistency. ; 2017
29, 39 正则项;
29: Superdepth: Self-supervised, super-resolved monocular depth
estimation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pages 9250–9256,2019
39: Deep virtual stereo odometry: Leveraging deep depth prediction for monocular direct sparse odometry. In Proceedings
of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV),
pages 817–833, 2018
35, 42,45 从视频序列
35: Sfm
net: Learning of structure and motion from video. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1704.07804, 2017.
42: Geonet: Unsupervised learn
ing of dense depth, optical flow and camera pose. In Pro
ceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pages 1983–1992, 2018.
45: Unsupervised learning of depth and ego-motion from
video. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer
Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pages 1851–1858,
2017.
自监督需要一些辅助: 光流 42,表面法线 40;语义分割 3,27,36,44;
光流和相机的自移动,目标移动;表面法线就是3d里面的深度渐变方向??
而语义分割是相当特别的,它看起来跟深度相关,但是很难找到一个它和深度的确定性的关系。
3,36 共同训练了 语义网络 和 深度网络,表明对两者都好。
44 学会了一个转换,语义分割 和 深度特征空间;
本文的思路
本文探索了一个未曾探索的议题: 语义分割 和 深度 的边缘,是共享的;
本文的目标在于: 令单目自监督的深度估计 得到的 结果和 语义分割的副本 更加一致和对齐。
不能把 语义边缘 和 深度边缘的差距 当作 loss ,而是会当作 一个 贪心搜索。
深度图的重建 用 Beier–Neely morphing algorithm
语义标签里面 存在噪声;所以训练过程需要稳定 和 提升。方法是: 参考立体图像的处理方式,对两张图的 里面的 egde 进行 mask, 这就会造成一个 新的 立体 遮挡mask 到 loss 里面。
morphing technique: 变种技术;
总结下我们的贡献:
- 定义 ,并 利用了 边缘约束,在 语义 和 深度 之间,这让深度边界 更加 匹配/一致/对应 语义边界
- 减少了 bleeding artifacts, 提升了在物体边界那里的深度预测效果
- 在自监督方面,实现了 SOTA,在绝对相对误差abs rel 上 达到了和 有监督的方法媲美的
再度回忆相关的工作
光度上的损失loss,主要可以归纳为两原因:
1, 遮挡
2, 纹理不清晰的,天空,路,树叶,窗户,无法受到足够的监督信号
怎么解决:
1, 一个 立体遮挡mask
2. 从语义分割任务里面 提供额外的监督信息
一个有效的 遮挡 mask 基于单张 差异 map 图
额外的modality/形式;
深度预测需要帮助,以前有用 表面 法线的,语义的,光流的,立体匹配的(33,38)
33 : Learning monocular depth estimation infusing traditional stereo knowledge. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR),
pages 9799–9809, 2019
38: . Self-supervised monocular depth
hints. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference
on Computer Vision (ICCV), pages 2162–2171, 2019.
语义和其他形式 对 深度估计的 辅助 不同,因为其他形式 可以 找到 和深度的 数学关系,但是 语义很难找到 跟 深度 有什么 确定 的关系。所以之前的 工作,都是用 语义 当作 一个 暗中帮助的线索,但是我们就是明着用 语义。
我们认为之前的工作,是如何用 语义的呢?有三种方式用:
- 共享 权重的方式 用 语义结果,3, 36
- 混合 深度 和 语义 的 feature;27,36,44;CRF:conditional random field
- 21,31, 用 深度 和 语义 的统计关系,建模两者之间的这种不确定性
明着用 语义 这种形式, 来帮助 深度 估计,需要克服几个问题:
- 语义 和 深度 实际上,仅仅共享 不多 的边缘,部分的边缘
- 写出来一个 可微分的 函数 来连接 【二值的】边界 ,和 连续的语义 ,这挑战很高。
本文的贡献,就在于 克服这俩 问题。
第三节:本文提出的方法
edge edge consistency loss , 但是 这个 loss 不可微分。
circumvent:包围,陷害;得到一个 优化的 深度图
在训练的时候,,需要立体的图片 和 实现计算的 语义 标签。
就是他: 明显的深度 - 语义 的一致性
T 是一个 边缘,定义如下:



大概的意义我猜是这样的: 在左图中,前面的像素 遮挡了 后面的像素,在右图中,这种遮挡就可能不存在,或者存在很少,但是 在 大一统的 计算过程中,算法还是固执地 认为被遮挡的像素,就是原来物体的一部分,于是在最后生成的 disparity图 ,或者说 深度图中,就会出现一个情况:边缘在流血。
bleeding artifact ,原文是这样说的。如何处理这个 问题呢?
使用 一个 遮挡指示矩阵 M

具体的还是没看懂,现在 你可以i知道的 结论是: 但凡被M认定的区域,都是 有可能是 被遮挡的,到时候,计算 loss 的时候,这个区域会被特殊处理;我猜啊,要么是忽略之,要么是什么真的非常奇特的花样去处理它。
3.3 网络 和 loss 函数
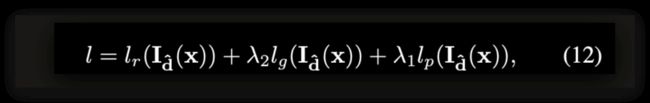
detail的 咱们不看,就看看 每个 项目 是什么 意思吧:
lr 是 一个 光流 的 重建 损失;
lg 是 morph 的loss
lp 是个 立体 代理 loss
然后,咱们再看看 每个 是怎么写的:
另外还说了 一个 fine tuning 的 loss :
第四节:实现的细节
看人家的代码:
http://cvlab.cse.msu.edu/project-edgedepth.html

