现在以一个例子来介绍mybatis的动态SQL和模糊查询:通过多条件查询用户记录,条件为姓名模糊匹配,并且年龄在某两个值之间。
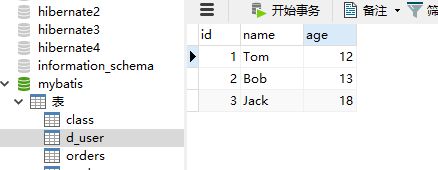
新建表d_user:
create table d_user(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(10),
age int(3)
);
insert into d_user(name,age) values('Tom',12);
insert into d_user(name,age) values('Bob',13);
insert into d_user(name,age) values('Jack',18);
建表成功:
新建实体类User:
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
//getters and setters
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
public User(Integer id, String name, Integer age) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public User() {
super();
}
}
创建查询条件实体类ConditionUser:
public class ConditionUser {
private String name;
private int minAge;
private int maxAge;
//getters and setters
public ConditionUser(String name, int minAge, int maxAge) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.minAge = minAge;
this.maxAge = maxAge;
}
public ConditionUser() {
super();
}
}
新建映射文件userMapper.xml:
编写测试类:
public class Test {
private SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory;
private SqlSession session;
@Before
public void init(){
//读取配置文件
String resource = "conf.xml";
InputStream is = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(resource);
//创建SqlSessionFactory和SqlSession
sessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);
session = sessionFactory.openSession();
}
@After
public void free(){
session.commit();
session.close();
}
@org.junit.Test
public void getUser() {
String statement = "com.mybatis.test7.userMapper"+".getUser";
ConditionUser conditionUser = new ConditionUser("o", 13, 18);
List list = session.selectList(statement, conditionUser);
System.out.println(list);
}
}
运行结果:
注意:
1. 在配置文件中编写sql语句时,为防止大于号和小于号在表示大小关系和表示标签符号之间产生混淆,所以通常用>;和<;来代替sql语句中大于号和小于号。
2. 在SQL语句中添加动态SQL标签if的原因是,当在后台获取的name属性值为null时,防止生成where name like %null%的条件判断语句,正确的逻辑应该是,当传来的name属性值为null时,取消此筛选条件,即不使用where name like ?的判断条件。在mybatis中,可用的动态SQL标签有:if,choose(when,otherwise),trim(where,set),foreach。
3. 在使用模糊查询时,拼接%+#{name}+%的方法有如下几种:
(1).像上述例子中一样,在SQL语句中使用CONCAT关键字。
(2).使用${}代替#{}:
注意,默认情况下,使用#{}语法,MyBatis会产生PreparedStatement语句,并且安全地设置PreparedStatement参数,这个过程中MyBatis会进行必要的安全检查和转义。例如:
执行SQL:select * from emp where name = #{employeeName}
参数:employeeName=>Smith
解析后执行的SQL:select * from emp where name = ?
执行SQL:Select * from emp where name = ${employeeName}
参数:employeeName传入值为:Smith
解析后执行的SQL:Select * from emp where name =Smith
综上所述,${}方式可能会引发SQL注入的问题,同时也会影响SQL语句的预编译,所以从安全性和性能的角度出发,应尽量使用#{}。当需要直接插入一个不做任何修改的字符串到SQL语句中,例如在ORDER BY后接一个不添加引号的值作为列名,这时候就需要使用${}。
(3).在程序中拼接。
总结
到此这篇关于mybatis的动态SQL和模糊查询的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关mybatis动态SQL模糊查询内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!