不用看网课就能学到python的文章(第一天)
为什么要学python?
在大数据时代,抖音快手火爆全球,作业帮小猿搜题的数据库,都离不开大数据,大数据的科学计算,最重要的语言就是python,网络爬虫(网络爬虫 - 搜狗百科)搜索引擎等等也主要是python,包括一些游戏图像等等都缺少不了python,最重要的是如今百度的人工智能技术不断提高,人工智能熊熊崛起,而ai智能的主要语言也是python。最神奇的的python可以混合编程可以用c语言,java等等混合编程,那么我们一起看懂一篇文章,入门python。
环境搭建
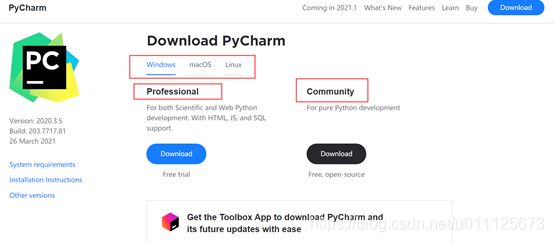
我使用的编译器是pycharm
一般来说下载社区版(免费版)就欧克,一套式服务到位,不用看视频
Download PyCharm: Python IDE for Professional Developers by JetBrains
安装过程的话
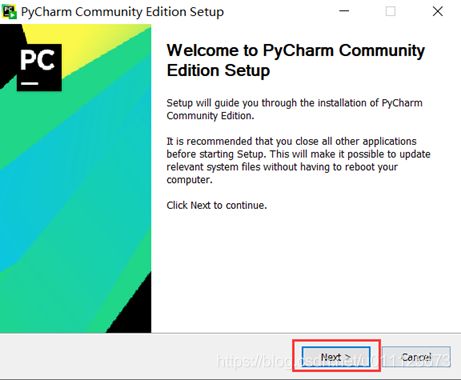
1、双击已下载的PyCharm安装包,出现如下图所示的界面,点击“next”。
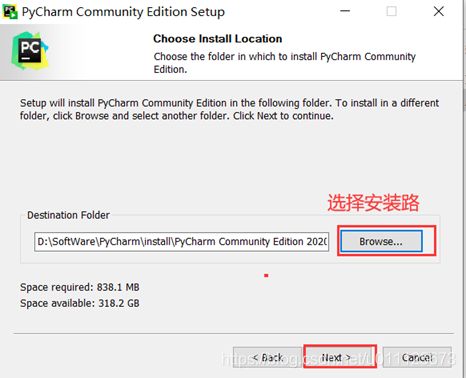
2、选择安装目录,Pycharm需要的内存较多,建议将其安装在D盘或者E盘,不建议放在系统盘C盘。
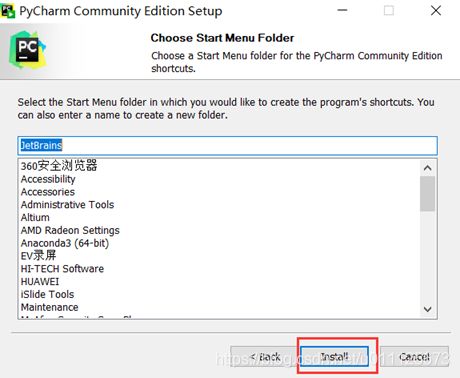
3、进行相关设置,如果你无特殊需要按照图中勾选即可。
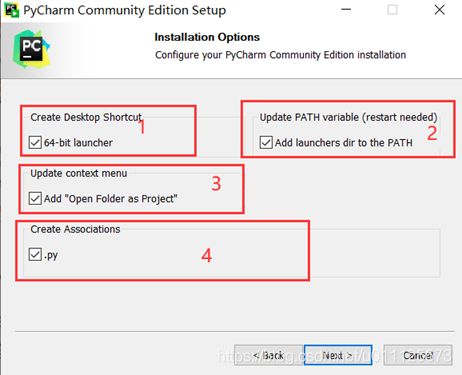
数字1:create desktop shortcut(创建桌面快捷方式),系统32位就选32-bit,系统64位就选64-bit。
笔者的电脑是64位系统,它自动显示64位。
数字2:update path variable(restart needed)更新路径变量(需要重新启动),add launchers dir to the path(将启动器目录添加到路径中)。
数字3:update context menu(更新上下文菜单),add open folder as project(添加打开文件夹作为项目)。添加鼠标右键菜单,使用打开项目的方式打开此文件架。如果你经常需要下载一些别人的代码查看,可以勾选此选项,这会增加鼠标右键菜单的选项。也就是你双击你电脑上的 py 文件,会默认使用 pycharm 打开。
数字4:create associations 创建关联,关联.py文件。将所有py文件关联到pycharm。
4、默认即可,点击install。
安装完成
5、打开PyCharm
五、配置PyCharm
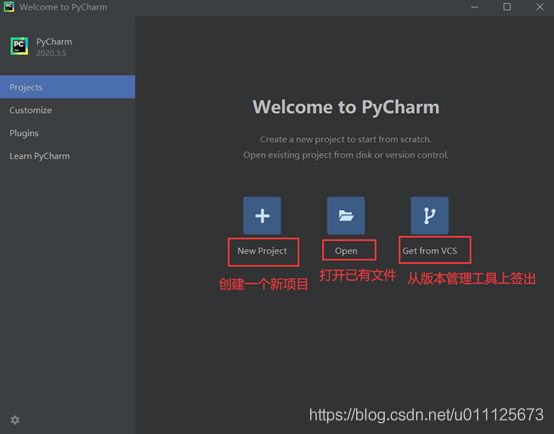
1、点击New Project创建一个新的项目
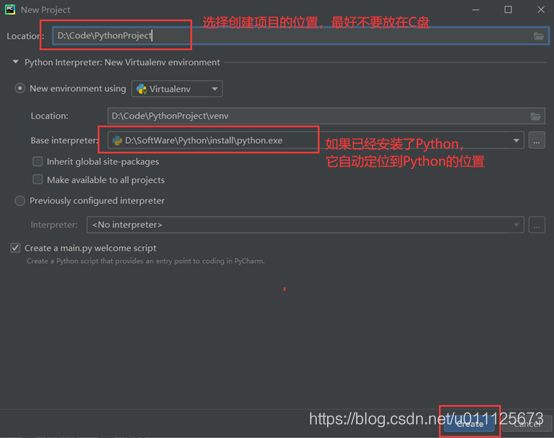
2、项目设置
3、环境配置,需要一定的时间
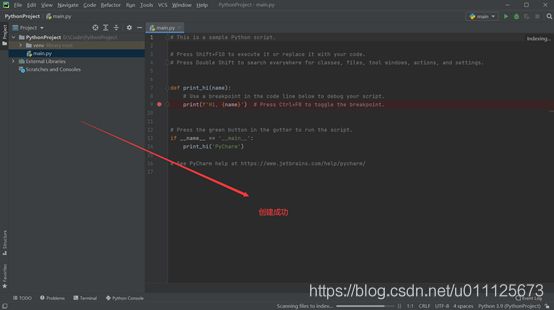
4、创建python文件
先放个烟花检验一下操作是否正确
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import math, random,time
import threading
import tkinter as tk
import re
#import uuid
Fireworks=[]
maxFireworks=8
height,width=600,600
class firework(object):
def __init__(self,color,speed,width,height):
#uid=uuid.uuid1()
self.radius=random.randint(2,4) #粒子半径为2~4像素
self.color=color #粒子颜色
self.speed=speed #speed是1.5-3.5秒
self.status=0 #在烟花未爆炸的情况下,status=0;爆炸后,status>=1;当status>100时,烟花的生命期终止
self.nParticle=random.randint(20,30) #粒子数量
self.center=[random.randint(0,width-1),random.randint(0,height-1)] #烟花随机中心坐标
self.oneParticle=[] #原始粒子坐标(100%状态时)
self.rotTheta=random.uniform(0,2*math.pi) #椭圆平面旋转角
#椭圆参数方程:x=a*cos(theta),y=b*sin(theta)
#ellipsePara=[a,b]
self.ellipsePara=[random.randint(30,40),random.randint(20,30)]
theta=2*math.pi/self.nParticle
for i in range(self.nParticle):
t=random.uniform(-1.0/16,1.0/16) #产生一个 [-1/16,1/16) 的随机数
x,y=self.ellipsePara[0]*math.cos(theta*i+t), self.ellipsePara[1]*math.sin(theta*i+t) #椭圆参数方程
xx,yy=x*math.cos(self.rotTheta)-y*math.sin(self.rotTheta), y*math.cos(self.rotTheta)+x*math.sin(self.rotTheta) #平面旋转方程
self.oneParticle.append([xx,yy])
self.curParticle=self.oneParticle[0:] #当前粒子坐标
self.thread=threading.Thread(target=self.extend) #建立线程对象
def extend(self): #粒子群状态变化函数线程
for i in range(100):
self.status+=1 #更新状态标识
self.curParticle=[[one[0]*self.status/100, one[1]*self.status/100] for one in self.oneParticle] #更新粒子群坐标
time.sleep(self.speed/50)
def explode(self):
self.thread.setDaemon(True) #把现程设为守护线程
self.thread.start() #启动线程
def __repr__(self):
return ('color:{color}\n'
'speed:{speed}\n'
'number of particle: {np}\n'
'center:[{cx} , {cy}]\n'
'ellipse:a={ea} , b={eb}\n'
'particle:\n{p}\n'
).format(color=self.color,speed=self.speed,np=self.nParticle,cx=self.center[0],cy=self.center[1],p=str(self.oneParticle),ea=self.ellipsePara[0],eb=self.ellipsePara[1])
def colorChange(fire):
rgb=re.findall(r'(.{2})',fire.color[1:])
cs=fire.status
f=lambda x,c: hex(int(int(x,16)*(100-c)/30))[2:] #当粒子寿命到70%时,颜色开始线性衰减
if cs>70:
ccr,ccg,ccb=f(rgb[0],cs),f(rgb[1],cs),f(rgb[2],cs)
else:
ccr,ccg,ccb=rgb[0],rgb[1],rgb[2]
return '#{0:0>2}{1:0>2}{2:0>2}'.format(ccr,ccg,ccb)
def appendFirework(n=1): #递归生成烟花对象
if n>maxFireworks or len(Fireworks)>maxFireworks:
pass
elif n==1:
cl='#{0:0>6}'.format(hex(int(random.randint(0,16777215)))[2:]) # 产生一个0~16777215(0xFFFFFF)的随机数,作为随机颜色
a=firework(cl,random.uniform(1.5,3.5),width,height)
Fireworks.append( {'particle':a,'points':[]} ) #建立粒子显示列表,‘particle’为一个烟花对象,‘points’为每一个粒子显示时的对象变量集
a.explode()
else:
appendFirework()
appendFirework(n-1)
def show(c):
for p in Fireworks: #每次刷新显示,先把已有的所以粒子全部删除
for pp in p['points']:
c.delete(pp)
for p in Fireworks: #根据每个烟花对象,计算其中每个粒子的显示对象
oneP=p['particle']
if oneP.status==100: #状态标识为100,说明烟花寿命结束
Fireworks.remove(p) #移出当前烟花
appendFirework() #新增一个烟花
continue
else:
li=[[int(cp[0]*2)+oneP.center[0],int(cp[1]*2)+oneP.center[1]] for cp in oneP.curParticle] #把中心为原点的椭圆平移到随机圆心坐标上
color=colorChange(oneP) #根据烟花当前状态计算当前颜色
for pp in li:
p['points'].append(c.create_oval(pp[0]-oneP.radius, pp[1]-oneP.radius, pp[0]+oneP.radius, pp[1]+oneP.radius, fill=color)) #绘制烟花每个粒子
root.after(50, show,c) #回调,每50ms刷新一次
if __name__=='__main__':
appendFirework(maxFireworks)
root = tk.Tk()
cv = tk.Canvas(root, height=height, width=width)
cv.create_rectangle(0, 0, width, height, fill="black")
cv.pack()
root.after(50, show,cv)
root.mainloop()