1.介绍
Nginx(发音同“engine X”)是异步框架的web服务器,也可以用作反向代理、负载平衡器和HTTP缓存。
特点:和node类似,Nginx使用异步事件驱动的方法来处理请求,适合处理io密集型场景
前端为什么要学:
-
- 测试环境需要自己部署
-
- 遇到网络问题,我们要会排查问题,要有独立解决的能力
-
- 性能优化
-
- 上线的时候指导ops部署
2.安装
推荐还是通过yum一键安装(centos)
一般需要知道两个地址,
- 执行地址 /usr/local/bin 这里存放着可以直接执行的二进制文件,用来启动或者重启nginx
(which nginx查询) - 配置地址
一般在 /usr/local/etc/nginx,不同的安装方式可能有差异,但是安装的时候一定会有信息显示(nginx -t查询)
执行地址(启动,重启)
启动nginx
cd /use/local/sbin
./nginx重启nginx
cd /usr/sbin
nginx -s reload
或者直接/usr/sbin/nginx -s reload配置地址
nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
在/etc/nginx里面 我们可以看到有个文件叫nginx.conf,这个就是基础配置文件,也可以说是大配置文件.
里面写了一句话include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
这就是说nginx会读conf.d里面的.conf当做小配置文件 对于不同的项目我们可以单独在小配置文件里面进行配置,这样结构更清晰,更易维护。
编译参数
我们还可以用nginx -V 来查一下所有的相关路径。这些不是固定的,我们可以在安装的时候指定这些参数进行编译安装。具体的可以网上查一下。
3.日志
资源的访问,是会产生日志的,日志分两种,成功访问日志和失败日志
access_.log 访问日志
error.log 错误日志
我们在nginx.conf里面可以看到access日志的目录,以及日志的格式
我们在/var/log/nginx/access里面看一下,确实是按设定的格式返的
[roo@centos]# cat access.log
[roo@centos]# 111.206.87.56 - - [18/Aug/2021:17:42:47 +0800] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 4833 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/92.0.4515.131 Safari/537.36" "-"
tail -f /var/log/nginx/access.log //实时更新内置变量
上面的log_format里面 有一些$xxx 这玩意是nginx的内置变量,更详细的可以网上查一下
| 名称 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| $remote_addr | 客户端地址 |
| $remote_user | 客户端用户名称 |
| $time_local | 访问时间和时区 |
| $request | 请求的URI和HTTP协议 |
| $http_host | 请求地址,即浏览器中你输入的地址(IP或域名) |
| $status | HTTP请求状态 |
| $body_bytes_sent | 发送给客户端文件内容大小 |
| $http_user_agent | 用户代理 |
4.静态页面
解读下初始配置
/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
# For more information on configuration, see:
# * Official English Documentation: http://nginx.org/en/docs/
# * Official Russian Documentation: http://nginx.org/ru/docs/
user root; #设置nginx服务的系统使用用户
worker_processes auto; #工作进程数,一般和CPU数量相同
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log; #错误日志地址
pid /run/nginx.pid; #错误日志地址
# Load dynamic modules. See /usr/share/doc/nginx/README.dynamic.
include /usr/share/nginx/modules/*.conf; # 模块化开发
events {
worker_connections 1024; #每个进程允许的最大连接数
}
http {
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main; # main日志
sendfile on; # 不经过用户内核
tcp_nopush on; # 攒一波再发
# tcp_nodelay on; # 不延迟
keepalive_timeout 65; # 超时时间
types_hash_max_size 4096;
gzip on; #决定是否开启gzip模块,on表示开启,off表示关闭;
gzip_min_length 1k; #设置允许压缩的页面最小字节(从header头的Content-Length中获取) ,当返回内容大于此值时才会使用gzip进行压缩,以K为单位,当值为0时,所有页面都进行压缩。建议大于1k
gzip_buffers 4 16k; #设置gzip申请内存的大小,其作用是按块大小的倍数申请内存空间,param2:int(k) 后面单位是k。这里设置以16k为单位,按照原始数据大小以16k为单位的4倍申请内存
gzip_http_version 1.1; #识别http协议的版本,早起浏览器可能不支持gzip自解压,用户会看到乱码
gzip_comp_level 2; #设置gzip压缩等级,等级越底压缩速度越快文件压缩比越小,反之速度越慢文件压缩比越大;等级1-9,最小的压缩最快 但是消耗cpu
gzip_types text/plain application/x-javascript text/css application/xml; #设置需要压缩的MIME类型,非设置值不进行压缩,即匹配压缩类型
gzip_vary on;
include /etc/nginx/mime.types; # 文件扩展名与类型映射表
default_type application/octet-stream;
# Load modular configuration files from the /etc/nginx/conf.d directory.
# See http://nginx.org/en/docs/ngx_core_module.html#include
# for more information.
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf; # 子配置
server {
listen 80; #端口
listen [::]:80; # It is for the IPv6 configs
server_name _;
root /usr/share/nginx/html; #根目录
# Load configuration files for the default server block.
include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
error_page 404 /404.html;
location = /404.html {
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
}
}
# Settings for a TLS enabled server. ## 配置https的
#
# server {
# listen 443 ssl http2;
# listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
# server_name _;
# root /usr/share/nginx/html;
#
# ssl_certificate "/etc/pki/nginx/server.crt";
# ssl_certificate_key "/etc/pki/nginx/private/server.key";
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 10m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
#
# # Load configuration files for the default server block.
# include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
#
# error_page 404 /404.html;
# location = /40x.html {
# }
#
# error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
# location = /50x.html {
# }
# }
}
5.具体应用
5.1 跨域(反向代理)
location ~ /api {
proxy_pass http://l-test9.dev.cn2.corp.xxx.cn:8080
}5.2 性能优化
- 缓存 expiress
location ~ .*\.(jpg|png|gif)$ {
expires 24h;
gzip on ;
}- 压缩 gzip
gzip开启后的标志,响应头里面:
Content-Encoding: gzip1.3 防盗链
location ~ .*\.(jpg|png|gif)$ {
expires 1h;
gzip off;
gzip_http_version 1.1;
gzip_comp_level 3;
gzip_types image/jpeg image/png image/gif;
# none没有refer blocked非正式HTTP请求 特定IP
+ valid_referers none blocked 47.104.184.134;
+ if ($invalid_referer) { # 验证通过为0,不通过为1
+ return 403;
+ }
root /data/images;
}
1.4 负载均衡
var http = require( 'http' );
var server =http.createServer( function ( request ,response ){
response.end('server3 000');
} );
server.listen( 3000 ,function(){
console.log( 'HTTP服务器启动中,端口:3000' );
});
var server =http.createServer( function ( request ,response ){
response.end('server4 000');
} );
server.listen( 4000 ,function(){
console.log( 'HTTP服务器启动中,端口:4000' );
});
var server =http.createServer( function ( request ,response ){
response.end('server5 000');
} );
server.listen( 5000 ,function(){
console.log( 'HTTP服务器启动中,端口:5000' );
});
upstream fyy {
server 127.0.0.1:3000 weight=10;
server 127.0.0.1:4000;
server 127.0.0.1:5000;
}
server {
location / {
proxy_pass http://fyy;
}负载均衡策略
| 类型 | 种类 |
|---|---|
| 轮询(默认) | 每个请求按时间顺序逐一分配到不同的后端服务器,如果后端服务器down掉,能自动剔除 |
| weight(加权轮询) | 指定轮询几率,weight和访问比率成正比,用于后端服务器性能不均的情况 |
| ip_hash | 每个请求按访问ip的hash结果分配,这样每个访客固定访问一个后端服务器,可以解决session的问题 |
| least_conn | 哪个机器上连接数少就分发给谁 |
| url_hash(第三方) | 按访问的URL地址来分配 请求,每个URL都定向到同一个后端 服务器上(缓存) |
| fair(第三方) | 按后端服务器的响应时间来分配请求,响应时间短的优先分配 |
| 正定义hash | hash自定义key |
1.5 rewrite
Port:9003 9004
- 可以实现url重写及重定向
使用场景: url页面跳转,维护,转发
比如手机PC的一个重定向
server {
listen 9003; # 这个是pc网页,但是如果用户代理是手机即使访问pc站也会重定向到移动端
location / {
if ($http_user_agent ~* '(Android|webOS|iPhone)') {
rewrite ^(.*)$ http://localhost:9004 break;
}
root /Users/fengyangyang/Desktop/nginx/pc;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
server {
listen 9004; # 这个是手机网页
location / {
root /Users/fengyangyang/Desktop/nginx/mobile;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}6.可视化配置
传统的书写Nginx配置 学习操作成本比较高
可视化配置:根据你的交互,选择一些条件,动态生成nginx配置文件
比如我选择的这个基础配置
nignxConfig
好处:比较全,对前端暴露的东西比较少(高度封装),学习成本低一点
坏处:太全了,不灵活
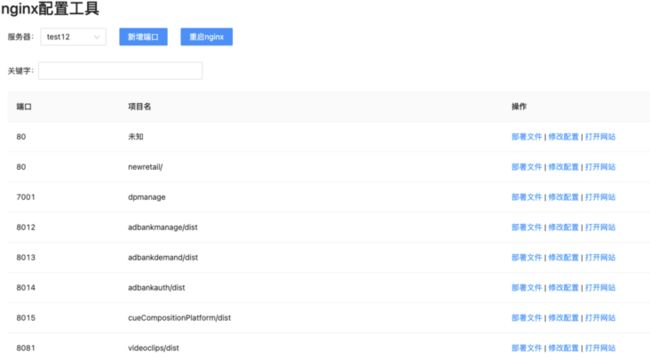
7.自己实现的一个可视化的工具
7.1 目前项目中存在的问题
测试环境
1.测试服务器上项目太多,端口管理混轮:
- 项目和端口的映射混乱 ---->找不到对应的端口 (几十个项目谁能记住响应端口)
- 项目和配置文件映射混乱 ---->找不到配置的地方(比如A项目的配置写到B项目配置里)
2.服务器上完成各种操作比较繁琐(新建修改项目配置)对前端水平也有一定要求
7.2 解决方案
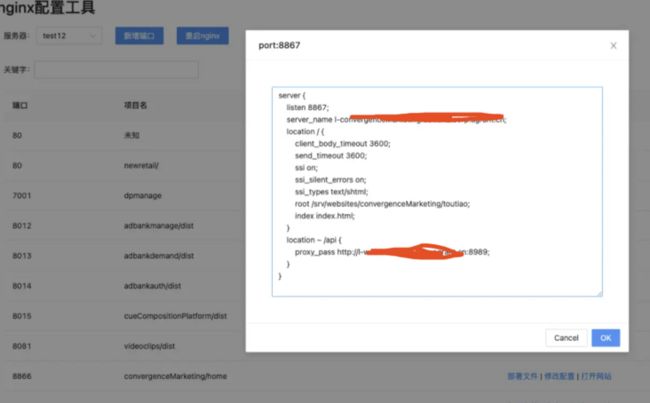
做了一个线上编辑nginx的工具
支持以下功能
- 新建项目 输入项目名和端口 自动在服务器上生成相关配置并完成nginx重启
- 支持在线修改服务器上的配置,改完自动重启nginx
- 实时读取服务器你上配置,生成项目名与端口的映射
- 支持自动部署