【OpenCV应用】python处理行李图像匹配项目——图像特征点
OpenCV——图像角点检测应用记录
- 图像特征
-
- Harris角点检测
- Shi-Tomasi 角点检测
- SIFT (尺度不变特征变换)原理
- SURF (加速鲁棒性特征)原理
- FAST角点检测
- BRIEF 特征描述子
图像特征
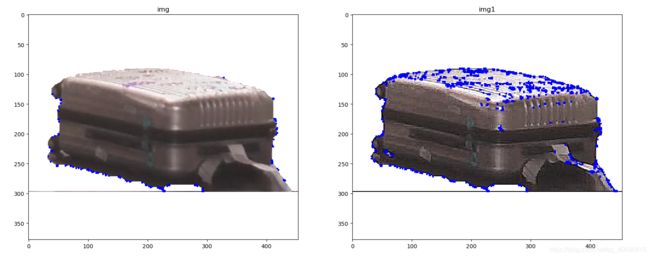
Harris角点检测
Harris Corner Detection: https://docs.opencv.org/master/dc/d0d/tutorial_py_features_harris.html
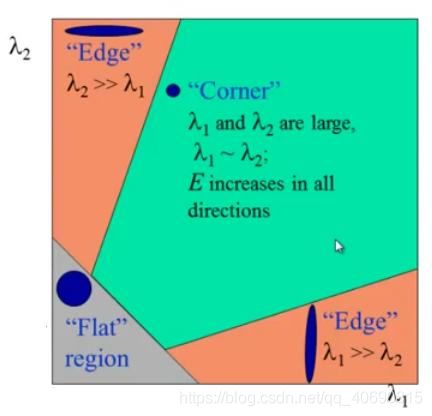
Harris角点检测的结果是一个带着这些分数的灰度图。图像角点检测需要一个合适的阈值
gray = np.float32(gray)
dst = cv.cornerHarris(gray,2,3,0.04)
#result is dilated for marking the corners, not important
dst = cv.dilate(dst,None)
# Threshold for an optimal value, it may vary depending on the image.
img[dst>0.01*dst.max()]=[0,0,255]
稍微使用一点图像锐化
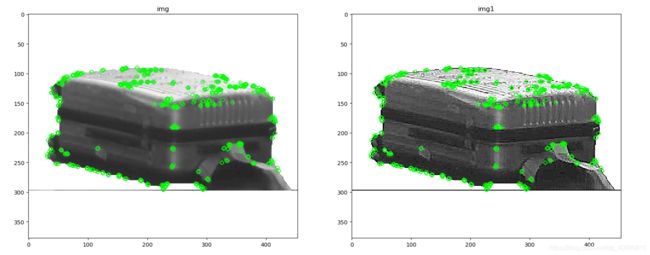
Shi-Tomasi 角点检测
Shi-Tomasi Corner Detector & Good Features to Track:
https://docs.opencv.org/master/d4/d8c/tutorial_py_shi_tomasi.html
https://blog.csdn.net/xiaowei_cqu/article/details/7805206
Shi-Tomasi 算法是Harris 算法的改进。Harris 算法最原始的定义是将矩阵 M 的行列式值与 M 的迹相减,再将差值同预先给定的阈值进行比较。后来Shi 和Tomasi 提出改进的方法,若两个特征值中较小的一个大于最小阈值,则会得到强角点。
gray = cv.cvtColor(img,cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
corners = cv.goodFeaturesToTrack(gray,25,0.01,10)
corners = np.int0(corners)
for i in corners:
x,y = i.ravel()
cv.circle(img,(x,y),3,255,-1)
SIFT (尺度不变特征变换)原理
Introduction to SIFT (Scale-Invariant Feature Transform)
https://docs.opencv.org/master/da/df5/tutorial_py_sift_intro.html
https://www.jianshu.com/p/95c4890c486b?utm_source=oschina-app
SIFT特征以其对旋转、尺度缩放、亮度等保持不变性,是一种非常稳定的局部特征,在图像处理和计算机视觉领域有着很重要的作用,其本身也是非常复杂的,下面对其计算过程做一个粗略总结。
- DoG尺度空间的极值检测。 首先是构造DoG尺度空间,在SIFT中使用不同参数的高斯模糊来表示不同的尺度空间。而构造尺度空间是为了检测在不同尺度下都存在的特征点,特征点的检测比较常用的方法是Δ2G(高斯拉普拉斯LoG),但是LoG的运算量是比较大的,Marr和Hidreth曾指出,可以使用DoG(差分高斯)来近似计算LoG,所以在DoG的尺度空间下检测极值点。
- 删除不稳定的极值点。 主要删除两类:低对比度的极值点以及不稳定的边缘响应点。
- 确定特征点的主方向。以特征点的为中心、以3×1.5σ为半径的领域内计算各个像素点的梯度的幅角和幅值,然后使用直方图对梯度的幅角进行统计。直方图的横轴是梯度的方向,纵轴为梯度方向对应梯度幅值的累加值,直方图中最高峰所对应的方向即为特征点的方向。
- 生成特征点的描述子。 首先将坐标轴旋转为特征点的方向,以特征点为中心的16×16的窗口的像素的梯度幅值和方向,将窗口内的像素分成16块,每块是其像素内8个方向的直方图统计,共可形成128维的特征向量。
gray= cv.cvtColor(img,cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
sift = cv.xfeatures2d.SIFT_create()
kp = sift.detect(gray,None)
# kp, des = sift.detectAndCompute(gray,None)
img=cv.drawKeypoints(gray,kp,img)
SURF (加速鲁棒性特征)原理
Introduction to SURF (Speeded-Up Robust Features)
https://docs.opencv.org/master/df/dd2/tutorial_py_surf_intro.html
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_37764129/article/details/80969515
SURF是SIFT的加速版,它善于处理具有模糊和旋转的图像,但是不善于处理视角变化和光照变化。在SIFT中使用DoG对LoG进行近似,而在SURF中使用盒子滤波器对LoG进行近似,这样就可以使用积分图像了(计算图像中某个窗口内所有像素和时,计算量的大小与窗口大小无关)。总之,SURF最大的特点在于采用了Haar特征以及积分图像的概念,大大加快了程序的运行效率。
#参数为hessian矩阵的阈值
surf = cv2.xfeatures2d.SURF_create(400)
#找到关键点和描述符
key_query,desc_query = surf.detectAndCompute(img,None)
#把特征点标记到图片上
img=cv2.drawKeypoints(img,key_query,img)
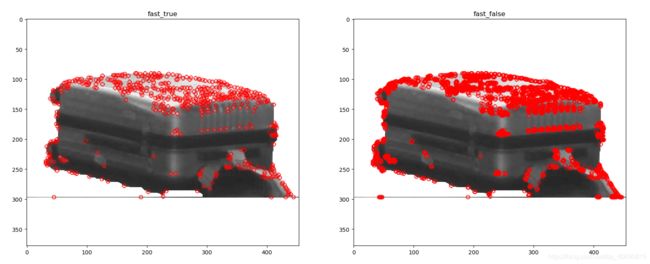
FAST角点检测
FAST Algorithm for Corner Detection (Features from Accelerated Segment Test)
FAST 全称 Features from accelerated segment test,一种用于角点检测的算法,该算法的原理是取图像中检测点,以该点为圆心的周围的16个像素点判断检测点是否为角点,通俗的讲就是中心的的像素值比大部分周围的像素值要亮一个阈值或者暗一个阈值则为角点。
# Initiate FAST object with default values
fast = cv.FastFeatureDetector_create()
# find and draw the keypoints
kp = fast.detect(img,None)
img2 = cv.drawKeypoints(img, kp, None, color=(255,0,0))
# Disable nonmaxSuppression
fast.setNonmaxSuppression(0)
kp = fast.detect(img,None)
print( "Total Keypoints without nonmaxSuppression: {}".format(len(kp)) )
img3 = cv.drawKeypoints(img, kp, None, color=(255,0,0))
Threshold: 10
nonmaxSuppression:True
neighborhood: 2
Total Keypoints with nonmaxSuppression: 528
Total Keypoints without nonmaxSuppression: 2607
BRIEF 特征描述子
Binary Robust Independent Elementary Features
https://docs.opencv.org/master/dc/d7d/tutorial_py_brief.html
# Initiate FAST detector
star = cv.xfeatures2d.StarDetector_create()
# Initiate BRIEF extractor
brief = cv.xfeatures2d.BriefDescriptorExtractor_create()
# find the keypoints with STAR
kp = star.detect(img,None)
# compute the descriptors with BRIEF
kp, des = brief.compute(img, kp)
ORB 特征提取
Oriented FAST and Rotated BRIEF
https://docs.opencv.org/master/d1/d89/tutorial_py_orb.html
orb = cv.ORB_create()
# find the keypoints with ORB
kp = orb.detect(img,None)
# compute the descriptors with ORB
kp, des = orb.compute(img, kp)