基于websocket的跨平台通信——iPhone/iPad/Mac控制树莓派(一):Springboot后端搭建
基于websocket的跨平台通信——iPhone/iPad/Mac控制树莓派(一):后端搭建
- 思路/接口说明
-
- 后端代码参考了这位大佬博主的文章:
- 发送数据到后端的接口
- 后端发送数据格式
- 实现
-
- 工程创建等配置
- Config文件
-
- WebSocketConfig.java
- FJsonConfig.java
- 参数类代码
-
- 后端接收信息参数类
- 后端发送信息参数类
- WebSocket业务处理代码
-
- 成品
- 部署
- 测试
思路/接口说明
后端采用Springboot框架开发;
由于涉及到跨平台、多种语言的开发,为了避免今后对后端频繁的更改导致频繁的部署,以及保证我的1元包年拉跨1核2G服务器不会动不动就跑满CPU,后端我们就设计的简单一些,数据处理统统交给终端和设备来做。
后端代码参考了这位大佬博主的文章:
springboot+websocket构建在线聊天室(群聊+单聊)
发送数据到后端的接口
URL:/websocket/{device}
路径参数device为连接服务器的设备名称
参数:
{
"type": 1,
"toPlatform":["MacBook", "WM7"],
"msgType": "MasterControl",
"msg": "阿巴阿巴"
}
type:数据发送的模式,我预留的一个参数,无需理会,我固定设置为1;
toPlatform:一个String类的数组,为该信息需要发送到的设备名称数组;
msg:某种数据类转换成的json字符串;
msgType:msg原本类的名称,接收到数据的设备用这个名称通过工厂模式来解析msg。
后端发送数据格式
参数:
{
"fromPlatform": "Raspberry Pi",
"msgType": "MasterControl",
"msg": "阿巴阿巴"
}
fromPlatfrom:表示该数据由这个名称的设备发送;
msgType与msg同上。
实现
工程创建等配置
我使用IDEA进行开发。
我采用application.properties进行配置;
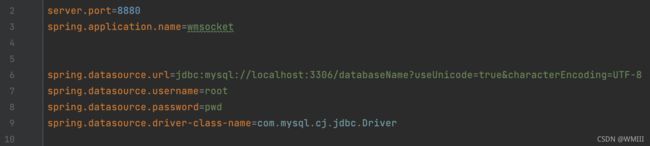
server.port、application.name、url、password等参数根据需要修改;
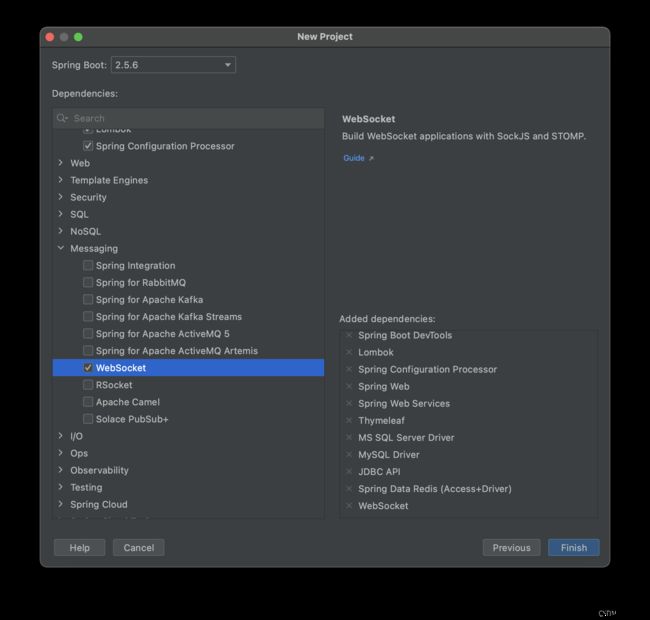
这里我选择了Mysql Server的依赖,必须要配置一个数据库连接,否则无法部署;也便于之后扩展数据库相关功能。
pom.xml导入FastJson:(可以换成别的JSON解析库)
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>fastjsonartifactId>
<version>1.2.76version>
dependency>
Config文件
由于我采用了websocket依赖以及FastJson库(可以换成别的JSON解析库),而这两个库都有比较蛋疼的bug,需要配置两个config文件:
WebSocketConfig.java
// package com.wmiii.wmsocket.config; 改成自己的package路径
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.socket.server.standard.ServerEndpointExporter;
@Configuration
public class WebSocketConfig {
@Bean
public ServerEndpointExporter serverEndpointExporter() {
return new ServerEndpointExporter();
}
}
FJsonConfig.java
// package com.wmiii.wmsocket.config; 改成自己的package路径
import com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.SerializerFeature;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.support.config.FastJsonConfig;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.support.spring.FastJsonHttpMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageConverter;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@Configuration
public class FJsonConfig {
@Bean
public HttpMessageConverter configureMessageConverters() {
FastJsonHttpMessageConverter converter = new FastJsonHttpMessageConverter();
FastJsonConfig config = new FastJsonConfig();
config.setSerializerFeatures(
// 保留map空的字段
SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue,
// 将String类型的null转成""
SerializerFeature.WriteNullStringAsEmpty,
// 将Number类型的null转成0
SerializerFeature.WriteNullNumberAsZero,
// 将List类型的null转成[]
SerializerFeature.WriteNullListAsEmpty,
// 将Boolean类型的null转成false
SerializerFeature.WriteNullBooleanAsFalse,
// 避免循环引用
SerializerFeature.DisableCircularReferenceDetect);
converter.setFastJsonConfig(config);
converter.setDefaultCharset(Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
List<MediaType> mediaTypeList = new ArrayList<>();
// 解决中文乱码问题,相当于在Controller上的@RequestMapping中加了个属性produces = "application/json"
mediaTypeList.add(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);
converter.setSupportedMediaTypes(mediaTypeList);
return converter;
}
}
参数类代码
(类名我乱取的
后端接收信息参数类
BaseMsg.java
// package com.wmiii.wmsocket.msg; 改成自己package的路径
import lombok.Data; // 记得导入lombok依赖
import java.util.ArrayList;
@Data
public class BaseMsg {
Integer type; // 1为指定发送对象,其余暂定为广播test
ArrayList<String> toPlatform;
String msgType;
String msg; // json格式的msg,后端无需关心具体内容
}
后端发送信息参数类
ToMsgParam.java
// package com.wmiii.wmsocket.param; 改成自己package的路径
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class ToMsgParam {
String fromPlatform;
String msgType;
String msg; // JSON格式的数据
}
WebSocket业务处理代码
// 省略import
@ServerEndpoint(value = "/websocket/{device}")
@Component
public class WmWebSocket {
@OnOpen
public void onOpen(Session session, @PathParam("device") String device) {
}
/**
* 连接关闭调用的方法
*/
@OnClose
public void onClose() {
}
/**
* 收到客户端消息后调用的方法
*
* @param message 客户端发送过来的消息*/
@OnMessage
public void onMessage(String message, Session session, @PathParam("device") String device) {
}
/**
* 发生错误时调用
*te
*/
@OnError
public void onError(Session session, Throwable error) {
}
}
对于一个拥有 @ServerEndpoint 注解的类,它就会被当做处理对应url的websocket业务的组件;其中需要实现四个注解的方法:
拥有 @OnOpen 注解的方法:在创建了一个新的websocket连接时调用;
拥有 @OnClose 注解的方法:websocket连接断开时调用;
拥有 @OnMessage 注解的方法:收到消息时调用;
拥有 @OnError 注解的方法:发生错误时调用;
成品
(看注释就好懒得另外打字了
// 省略import
@ServerEndpoint(value = "/websocket/{device}")
@Component
public class WmWebSocket {
//用来存放每个客户端对应的WmWebSocket对象。
private static CopyOnWriteArraySet<WmWebSocket> webSocketSet = new CopyOnWriteArraySet<WmWebSocket>();
//与某个客户端的连接会话,需要通过它来给客户端发送数据
private Session session;
private String device;
//用来记录平台名称和该session进行绑定
private static Map<String,Session> deviceMap = new HashMap<String, Session>();
@OnOpen
public void onOpen(Session session, @PathParam("device") String device) {
this.session = session;
this.device = device;
deviceMap.put(device, session);
webSocketSet.add(this); // 加入set中
System.out.println("设备" + device +"加入, 当前设备数为" + webSocketSet.size());
this.session.getAsyncRemote().sendText(device+"成功连接上WebSocket(sessionId: "+session.getId()+")-->当前在线设备数: "+webSocketSet.size());
}
/**
* 连接关闭调用的方法
*/
@OnClose
public void onClose() {
webSocketSet.remove(this); // 从set中删除
deviceMap.remove(device);
System.out.println("设备" + this.device +"连接关闭!当前在线设备数: " + webSocketSet.size());
}
/**
* 收到客户端消息后调用的方法
*
* @param message 客户端发送过来的消息*/
@OnMessage
public void onMessage(String message, Session session, @PathParam("device") String device) {
System.out.println(device + ": " + message);
BaseMsg baseMsg;
try {
baseMsg = JSON.parseObject(message, BaseMsg.class);
switch (baseMsg.getType()) {
case 1:
ToMsgParam toMsgParam = new ToMsgParam();
toMsgParam.setFromPlatform(device);
toMsgParam.setMsgType(baseMsg.getMsgType());
toMsgParam.setMsg(baseMsg.getMsg());
String toMsg = JSON.toJSONString(toMsgParam);
Session fromSession = deviceMap.get(device);
Session toSession;
// 获取数据目标设备列表
ArrayList<String> toList = baseMsg.getToPlatform();
// 用来存储数据发送失败的目标设备,暂时没用;
ArrayList<String> failed = new ArrayList<>();
// 逐个查询session的map进行数据发送
for(String toPlatform: toList) {
toSession = deviceMap.get(toPlatform);
try {
toSession.getAsyncRemote().sendText(toMsg);
} catch (Exception e) {
// 如果该目标平台的数据发送失败,则加入发送失败列表,暂时没用;
failed.add(toPlatform);
}
}
break;
default:
System.out.println("default");
}
} catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 发生错误时调用
*/
@OnError
public void onError(Session session, Throwable error) {
System.out.println("发生错误");
error.printStackTrace();
}
}
部署
使用宝塔面板部署,jar包部署。
选择IDEA右侧的Maven,运行Lifecycle下的package:
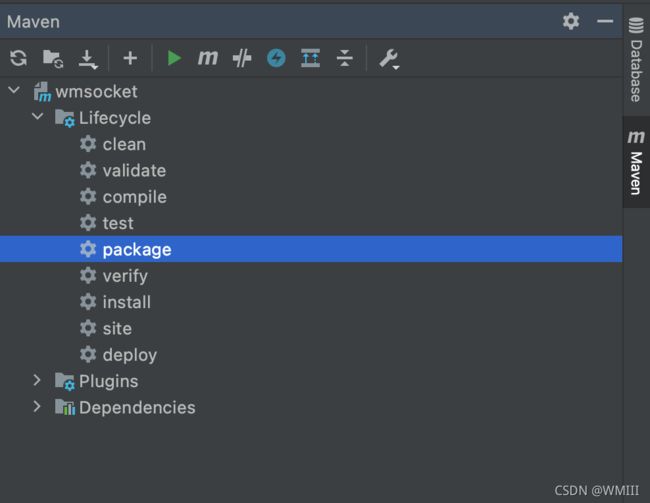
然后在项目根目录下的target文件夹中找到生成的一个.jar文件,上传到云服务器;
记得在服务器上开放设定的项目端口(我的是8880)。
在上传jar包的路径下运行:
nohup java -jar xxx.jar &
这里的xxx是你的jar包名称,就部署完毕了。
测试
最近(指写下这篇文章的时候)postman更新了WebSocket接口的测试;在Workspace右边点击New选择WebSocket Request就可以了。
(终于不用自写HTML测试了)