Swin Transformer原文及其代码的理解
Swin Transformer原文及其代码的理解
第一版
更好的排版笔记:Notion
名词解释
基础知识:
搞懂Vision Transformer 原理和代码,看这篇技术综述就够了(三)
token:分词,cv中一般是patch
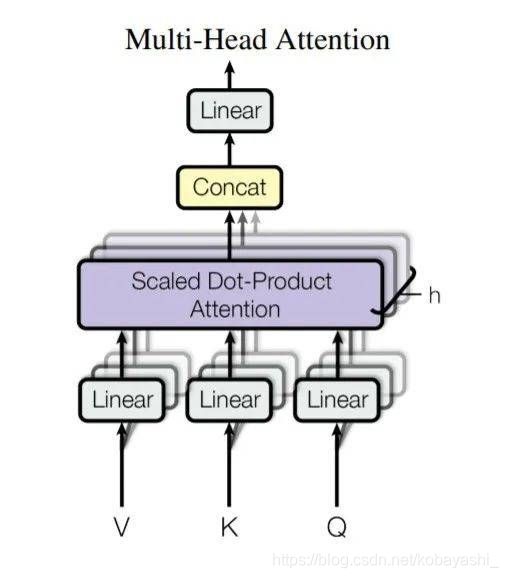
MSA:Multi-head Self Attention
导论(力推)
图解Swin Transformer
official repo:
microsoft/Swin-Transformer
实现
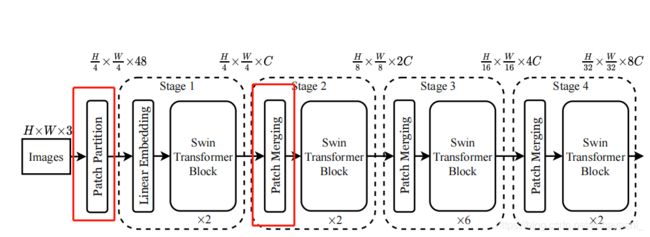
接下来跟着paper中的Architecture图结合原论文来讨论如何具体实现Swin Transformer。
Q1:原论文中Architecture中的Patch Partition和Patch Merging
该结构抽象为一个SwinTransformer 类(省略掉了一些代码)
class SwinTransformer(nn.Module):
r""" Swin Transformer
A PyTorch impl of : `Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows` -
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2103.14030
Args:
img_size (int | tuple(int)): Input image size. Default 224
patch_size (int | tuple(int)): Patch size. Default: 4
in_chans (int): Number of input image channels. Default: 3
num_classes (int): Number of classes for classification head. Default: 1000
embed_dim (int): Patch embedding dimension. Default: 96
depths (tuple(int)): Depth of each Swin Transformer layer.
num_heads (tuple(int)): Number of attention heads in different layers.
window_size (int): Window size. Default: 7
mlp_ratio (float): Ratio of mlp hidden dim to embedding dim. Default: 4
qkv_bias (bool): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key, value. Default: True
qk_scale (float): Override default qk scale of head_dim ** -0.5 if set. Default: None
drop_rate (float): Dropout rate. Default: 0
attn_drop_rate (float): Attention dropout rate. Default: 0
drop_path_rate (float): Stochastic depth rate. Default: 0.1
norm_layer (nn.Module): Normalization layer. Default: nn.LayerNorm.
ape (bool): If True, add absolute position embedding to the patch embedding. Default: False
patch_norm (bool): If True, add normalization after patch embedding. Default: True
use_checkpoint (bool): Whether to use checkpointing to save memory. Default: False
"""
def __init__(self, img_size=224, patch_size=4, in_chans=3, num_classes=1000,
embed_dim=96, depths=[2, 2, 6, 2], num_heads=[3, 6, 12, 24],
window_size=7, mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None,
drop_rate=0., attn_drop_rate=0., drop_path_rate=0.1,
norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm, ape=False, patch_norm=True,
use_checkpoint=False, **kwargs):
super().__init__()
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.num_layers = len(depths)
self.embed_dim = embed_dim
self.ape = ape
self.patch_norm = patch_norm
self.num_features = int(embed_dim * 2 ** (self.num_layers - 1))
self.mlp_ratio = mlp_ratio
# split image into non-overlapping patches
self.patch_embed = PatchEmbed(
img_size=img_size, patch_size=patch_size, in_chans=in_chans, embed_dim=embed_dim,
norm_layer=norm_layer if self.patch_norm else None)
num_patches = self.patch_embed.num_patches
patches_resolution = self.patch_embed.patches_resolution
self.patches_resolution = patches_resolution
# absolute position embedding
if self.ape:
self.absolute_pos_embed = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, num_patches, embed_dim))
trunc_normal_(self.absolute_pos_embed, std=.02)
self.pos_drop = nn.Dropout(p=drop_rate)
# stochastic depth
dpr = [x.item() for x in torch.linspace(0, drop_path_rate, sum(depths))] # stochastic depth decay rule
# build layers
self.layers = nn.ModuleList()
for i_layer in range(self.num_layers):
layer = BasicLayer(dim=int(embed_dim * 2 ** i_layer),
input_resolution=(patches_resolution[0] // (2 ** i_layer),
patches_resolution[1] // (2 ** i_layer)),
depth=depths[i_layer],
num_heads=num_heads[i_layer],
window_size=window_size,
mlp_ratio=self.mlp_ratio,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale,
drop=drop_rate, attn_drop=attn_drop_rate,
drop_path=dpr[sum(depths[:i_layer]):sum(depths[:i_layer + 1])],
norm_layer=norm_layer,
downsample=PatchMerging if (i_layer < self.num_layers - 1) else None,
use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint)
self.layers.append(layer)
self.norm = norm_layer(self.num_features)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool1d(1)
self.head = nn.Linear(self.num_features, num_classes) if num_classes > 0 else nn.Identity()
self.apply(self._init_weights)
def forward_features(self, x):
x = self.patch_embed(x)
if self.ape:
x = x + self.absolute_pos_embed
x = self.pos_drop(x)
for layer in self.layers:
x = layer(x)
x = self.norm(x) # B L C
x = self.avgpool(x.transpose(1, 2)) # B C 1
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
return x
def forward(self, x):
x = self.forward_features(x)
x = self.head(x)
return x
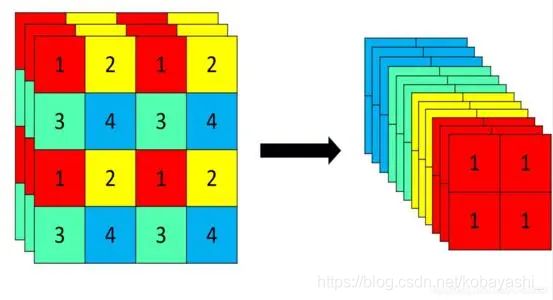
A1:Patch Merging
Patch Merging在每个stage开始的时候降低分辨率
microsoft/Swin-Transformer
class PatchMerging(nn.Module):
r""" Patch Merging Layer.
Args:
input_resolution (tuple[int]): Resolution of input feature.
dim (int): Number of input channels.
norm_layer (nn.Module, optional): Normalization layer. Default: nn.LayerNorm
"""
def __init__(self, input_resolution, dim, norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm):
super().__init__()
self.input_resolution = input_resolution
self.dim = dim
self.reduction = nn.Linear(4 * dim, 2 * dim, bias=False)
self.norm = norm_layer(4 * dim)
def forward(self, x):
"""
x: B, H*W, C
"""
H, W = self.input_resolution
B, L, C = x.shape
assert L == H * W, "input feature has wrong size"
assert H % 2 == 0 and W % 2 == 0, f"x size ({
H}*{
W}) are not even."
x = x.view(B, H, W, C)
x0 = x[:, 0::2, 0::2, :] # B H/2 W/2 C
x1 = x[:, 1::2, 0::2, :] # B H/2 W/2 C
x2 = x[:, 0::2, 1::2, :] # B H/2 W/2 C
x3 = x[:, 1::2, 1::2, :] # B H/2 W/2 C
x = torch.cat([x0, x1, x2, x3], -1) # B H/2 W/2 4*C
x = x.view(B, -1, 4 * C) # B H/2*W/2 4*C
x = self.norm(x)
x = self.reduction(x)
return x
def extra_repr(self) -> str:
return f"input_resolution={
self.input_resolution}, dim={
self.dim}"
def flops(self):
H, W = self.input_resolution
flops = H * W * self.dim
flops += (H // 2) * (W // 2) * 4 * self.dim * 2 * self.dim
return flops
原文:
To produce a hierarchical representation, the number of tokens is reduced by patch merging layers as the network gets deeper. The first patch merging layer concatenates the features of each group of 2 × 2 neighboring patches, and applies a linear layer on the 4C-dimensional concatenated features. This reduces the number of tokens by a multiple of 2×2 = 4 (2× downsampling of resolution), and the output dimension is set to 2C.
通过代码理解:
先下采样,通道变为 4 C 4C 4C。
然后,使用一个线性层将它们融合为 2 C 2C 2C
nn.LayerNorm
LayerNorm - PyTorch 1.9.0 documentation
reduction之前,将数据reshape为 ( B , H 2 ∗ W 2 , 4 ∗ C ) (B,\frac{H}{2}*\frac{W}{2},4*C) (B,2H∗2W,4∗C),因为reduction layer是linear layer.
A2.Patch Partition
源代码中没找到以这个名字命名的类或函数。相对的,在SwinTransformer 类中,实例化了一个PatchEmbed类,该类上面的注释为“# split image into non-overlapping patches”。
microsoft/Swin-Transformer
定位到该类
microsoft/Swin-Transformer
class PatchEmbed(nn.Module):
r""" Image to Patch Embedding
Args:
img_size (int): Image size. Default: 224.
patch_size (int): Patch token size. Default: 4.
in_chans (int): Number of input image channels. Default: 3.
embed_dim (int): Number of linear projection output channels. Default: 96.
norm_layer (nn.Module, optional): Normalization layer. Default: None
"""
def __init__(self, img_size=224, patch_size=4, in_chans=3, embed_dim=96, norm_layer=None):
super().__init__()
img_size = to_2tuple(img_size)
patch_size = to_2tuple(patch_size)
patches_resolution = [img_size[0] // patch_size[0], img_size[1] // patch_size[1]]
self.img_size = img_size
self.patch_size = patch_size
self.patches_resolution = patches_resolution
self.num_patches = patches_resolution[0] * patches_resolution[1]
self.in_chans = in_chans
self.embed_dim = embed_dim
self.proj = nn.Conv2d(in_chans, embed_dim, kernel_size=patch_size, stride=patch_size)
if norm_layer is not None:
self.norm = norm_layer(embed_dim)
else:
self.norm = None
def forward(self, x):
B, C, H, W = x.shape
# FIXME look at relaxing size constraints
assert H == self.img_size[0] and W == self.img_size[1], \
f"Input image size ({
H}*{
W}) doesn't match model ({
self.img_size[0]}*{
self.img_size[1]})."
x = self.proj(x).flatten(2).transpose(1, 2) # B Ph*Pw C
if self.norm is not None:
x = self.norm(x)
return x
def flops(self):
Ho, Wo = self.patches_resolution
flops = Ho * Wo * self.embed_dim * self.in_chans * (self.patch_size[0] * self.patch_size[1])
if self.norm is not None:
flops += Ho * Wo * self.embed_dim
return flops
看forward 方法,直接用一个不重合(non-overlapping)的卷积操作(kernel size = patch size, stride = patch size),将一个patch 内的图像投影(project)到96维度的空间内——Embedding。最后将卷积得到的feature map展开为一个向量。
Q2 每个stage是怎么实现的?
从SwinTransformer 类中,有一个for循环,对应构建每个stage的代码
# build layers
self.layers = nn.ModuleList()
for i_layer in range(self.num_layers):
layer = BasicLayer(dim=int(embed_dim * 2 ** i_layer),
input_resolution=(patches_resolution[0] // (2 ** i_layer),
patches_resolution[1] // (2 ** i_layer)),
depth=depths[i_layer],
num_heads=num_heads[i_layer],
window_size=window_size,
mlp_ratio=self.mlp_ratio,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale,
drop=drop_rate, attn_drop=attn_drop_rate,
drop_path=dpr[sum(depths[:i_layer]):sum(depths[:i_layer + 1])],
norm_layer=norm_layer,
downsample=PatchMerging if (i_layer < self.num_layers - 1) else None,
use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint)
self.layers.append(layer)
由此出发,索引到BasicLayer类。
microsoft/Swin-Transformer
直接看forward。很明显,downsample对应patch merging,那么剩下的就是block了。
def forward(self, x):
for blk in self.blocks:
if self.use_checkpoint:
x = checkpoint.checkpoint(blk, x)
else:
x = blk(x)
if self.downsample is not None:
x = self.downsample(x)
return x
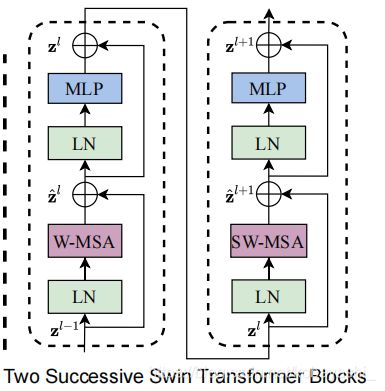
定位到SwinTransformerBlock ⚠️。
Q3 SwinTransformerBlock怎么实现的?
SwinTransformerBlock
microsoft/Swin-Transformer
直接看forward
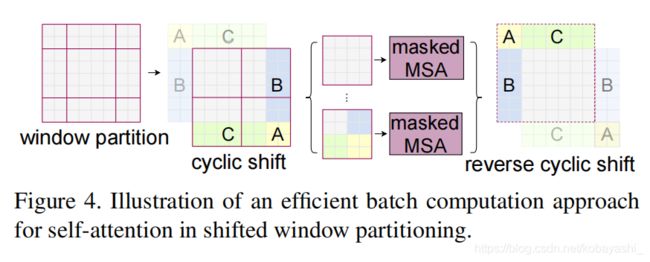
step1:先对输入的数据进行reshape,从 B L C → B H W C BLC \rightarrow BHWC BLC→BHWC, L = H ∗ W L=H*W L=H∗W。
step2:然后用torch.roll 对数据进行cyclic shift(周期转换)。
torch.roll - PyTorch 1.9.0 documentation
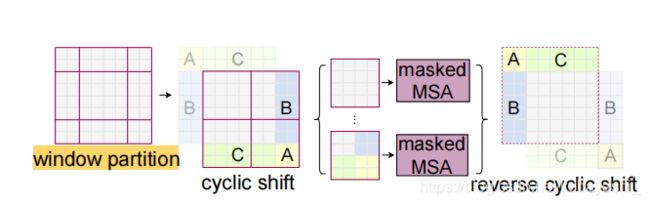
对于右图,对应代码为:
# cyclic shift
if self.shift_size > 0:
shifted_x = torch.roll(x, shifts=(-self.shift_size, -self.shift_size), dims=(1, 2))
else:
shifted_x = x
# partition windows
x_windows = window_partition(shifted_x, self.window_size) # nW*B, window_size, window_size, C
x_windows = x_windows.view(-1, self.window_size * self.window_size, C) # nW*B, window_size*window_size, C
# W-MSA/SW-MSA
attn_windows = self.attn(x_windows, mask=self.attn_mask) # nW*B, window_size*window_size, C
# merge windows
attn_windows = attn_windows.view(-1, self.window_size, self.window_size, C)
shifted_x = window_reverse(attn_windows, self.window_size, H, W) # B H' W' C
# reverse cyclic shift
if self.shift_size > 0:
x = torch.roll(shifted_x, shifts=(self.shift_size, self.shift_size), dims=(1, 2))
else:
x = shifted_x
至于里面的流程,下节再说。⚠️
step3 最后对结果进行DropPath(Stochastic Depth)操作
DropPath将layer随机去掉,具体实现就是在mini-batch层面随机将数据失效,这样失效的sample就无法作用该层。
DropPath具体实现
rwightman/pytorch-image-models
一个issue
question about dropconnect · Issue #494 · tensorflow/tpu
key point:
for each mini-batch, randomly drop a subset of layers and bypass them with the identity function.
原文中,两个相继的block一个是W-MSA,一个是SW-MSA
而在实现中,通过在实例化SwinTransformerBlock 时,对参数shift_size做一判断赋值,后将属性.shift_size 作为条件,如果大于0则是SW-MSA,否则则是WSA.
# build blocks
self.blocks = nn.ModuleList([
SwinTransformerBlock(dim=dim, input_resolution=input_resolution,
num_heads=num_heads, window_size=window_size,
**shift_size**=0 if (i % 2 == 0) else window_size // 2,
mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale,
drop=drop, attn_drop=attn_drop,
drop_path=drop_path[i] if isinstance(drop_path, list) else drop_path,
norm_layer=norm_layer)
for i in range(depth)])
Q4 W-MSA?SW-MSA?
W-MSA:Windows based multi-head self attention
SW-MSA:Shift W-MSA
相对位置比绝对位置对语义的影响大
比如:
- I like this movie because it doesn’t have an overhead history.
Positive - I don’t like this movie because it has an overhead history.
Negative
A1 W-MSA
这两类实现的都是同一个类:WindowAttention
microsoft/Swin-Transformer
通过代码及注释理解
class WindowAttention(nn.Module):
r""" Window based multi-head self attention (W-MSA) module with relative position bias.
It supports both of shifted and non-shifted window.
Args:
dim (int): Number of input channels.
window_size (tuple[int]): The height and width of the window.
num_heads (int): Number of attention heads.
qkv_bias (bool, optional): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key, value. Default: True
qk_scale (float | None, optional): Override default qk scale of head_dim ** -0.5 if set
attn_drop (float, optional): Dropout ratio of attention weight. Default: 0.0
proj_drop (float, optional): Dropout ratio of output. Default: 0.0
"""
def __init__(self, dim, window_size, num_heads, qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None, attn_drop=0., proj_drop=0.):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.window_size = window_size # Wh, Ww
self.num_heads = num_heads
head_dim = dim // num_heads
self.scale = qk_scale or head_dim ** -0.5
# define a parameter table of relative position bias
self.relative_position_bias_table = nn.Parameter(
torch.zeros((2 * window_size[0] - 1) * (2 * window_size[1] - 1), num_heads)) # 2*Wh-1 * 2*Ww-1, nH
# get pair-wise relative position index for each token inside the window
# 1.在window内获取每个token的成对相对位置索引
# #生成一对网格
coords_h = torch.arange(self.window_size[0])
coords_w = torch.arange(self.window_size[1])
coords = torch.stack(torch.meshgrid([coords_h, coords_w])) # 2, Wh, Ww,成对
--> outputs: window size=2
(tensor([[0, 0],
[1, 1]]),
tensor([[0, 1],
[0, 1]]))
coords_flatten = torch.flatten(coords, 1) # 2, Wh*Ww
-->outputs:
tensor([[0, 0, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 0, 1]])
#上面竖着从左往右看(0,0),(0,1),(1,0),(1,1)
# 插入一个维度,并作差,得到相对坐标,解析见1
relative_coords = coords_flatten[:, :, None] - coords_flatten[:, None, :] # 2, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
-->outputs:
tensor([[[ 0, 0, -1, -1],
[ 0, 0, -1, -1],
[ 1, 1, 0, 0],
[ 1, 1, 0, 0]],
[[ 0, -1, 0, -1],
[ 1, 0, 1, 0],
[ 0, -1, 0, -1],
[ 1, 0, 1, 0]]])
relative_coords = relative_coords.permute(1, 2, 0).contiguous() # Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww, 2
--outputs:
tensor([[[ 0, 0, -1, -1],
[ 0, 0, -1, -1],
[ 1, 1, 0, 0],
[ 1, 1, 0, 0]],
[[ 0, -1, 0, -1],
[ 1, 0, 1, 0],
[ 0, -1, 0, -1],
[ 1, 0, 1, 0]]])
#见解析2
relative_coords[:, :, 0] += self.window_size[0] - 1 # shift to start from 0
relative_coords[:, :, 1] += self.window_size[1] - 1
relative_coords[:, :, 0] *= 2 * self.window_size[1] - 1
relative_position_index = relative_coords.sum(-1) # Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
self.register_buffer("relative_position_index", relative_position_index)
#见官网:https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.Module.html?highlight=self%20register_buffer
self.qkv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 3, bias=qkv_bias)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop)
#截断正态分布初始化:https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/d5ed58d623be27aada78035d2a19e2854f8b6437/timm/models/layers/weight_init.py#L44
trunc_normal_(self.relative_position_bias_table, std=.02)
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)
def forward(self, x, mask=None):
"""
Args:
x: input features with shape of (num_windows*B, N, C)
mask: (0/-inf) mask with shape of (num_windows, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww) or None
"""
B_, N, C = x.shape
qkv = self.qkv(x).reshape(B_, N, 3, self.num_heads, C // self.num_heads).permute(2, 0, 3, 1, 4)
q, k, v = qkv[0], qkv[1], qkv[2] # make torchscript happy (cannot use tensor as tuple)
q = q * self.scale
attn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1))
relative_position_bias = self.relative_position_bias_table[self.relative_position_index.view(-1)].view(
self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], -1) # Wh*Ww,Wh*Ww,nH
relative_position_bias = relative_position_bias.permute(2, 0, 1).contiguous() # nH, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
attn = attn + relative_position_bias.unsqueeze(0)
if mask is not None:
nW = mask.shape[0]
attn = attn.view(B_ // nW, nW, self.num_heads, N, N) + mask.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(0)
attn = attn.view(-1, self.num_heads, N, N)
attn = self.softmax(attn)
else:
attn = self.softmax(attn)
attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
x = (attn @ v).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B_, N, C)
x = self.proj(x)
x = self.proj_drop(x)
return x
def extra_repr(self) -> str:
return f'dim={
self.dim}, window_size={
self.window_size}, num_heads={
self.num_heads}'
def flops(self, N):
# calculate flops for 1 window with token length of N
flops = 0
# qkv = self.qkv(x)
flops += N * self.dim * 3 * self.dim
# attn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1))
flops += self.num_heads * N * (self.dim // self.num_heads) * N
# x = (attn @ v)
flops += self.num_heads * N * N * (self.dim // self.num_heads)
# x = self.proj(x)
flops += N * self.dim * self.dim
return flops
A2 Window Attention的__init__方法解析
解析1:相对位置编码指所有坐标与剩余坐标的偏移量,右方向、下方向为正,左方向、上方向为负。
形如一个[2,2](形状为[2,2*2])的坐标系,那么相对坐标表示的形状为22,2,22。相对坐标表示如下
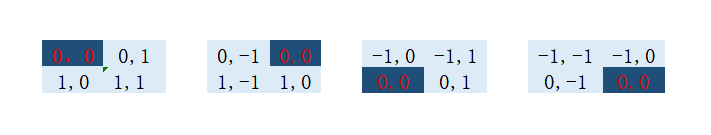
对于一个(M,M)的坐标,应最终有 ( M ∗ M , 2 , M ∗ M ) (M*M,2,M*M) (M∗M,2,M∗M)的维度
对对应代码解析:
coords_flatten[:, :, None]
这个操作将原本的coords_flatten .shape=[2,4]变为了[2,4,1]
而下面的操作
coords_flatten[:, None, :]
将coords_flatten .shape=[2,4]变为了[2,1,4]
由于广播机制,最终变为了[2,4,4],形状形状表示为 [ H , W , N ] [H,W,N] [H,W,N]。
解析2:因为使用的是减法,我们需要将偏移量变为为正
比如[3,3]的坐标系,原来是
tensor([[[ 0, 0, -1, -1],
[ 0, 0, -1, -1],
[ 1, 1, 0, 0],
[ 1, 1, 0, 0]],
[[ 0, -1, 0, -1],
[ 1, 0, 1, 0],
[ 0, -1, 0, -1],
[ 1, 0, 1, 0]]])
经过如下变换后
relative_coords = relative_coords.permute(1, 2, 0).contiguous() # Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww, 2
relative_coords[:, :, 0] += self.window_size[0] - 1 # shift to start from 0
relative_coords[:, :, 1] += self.window_size[1] - 1
元素全变为正数
tensor([[[1, 1],
[1, 0],
[0, 1],
[0, 0]],
[[1, 2],
[1, 1],
[0, 2],
[0, 1]],
[[2, 1],
[2, 0],
[1, 1],
[1, 0]],
[[2, 2],
[2, 1],
[1, 2],
[1, 1]]])
后面又进行了如下的操作
relative_coords[:, :, 0] *= 2 * window_size[1] - 1
可以理解为将x坐标与y坐标区分开来。
加上求和之后的流程如下
图解Swin Transformer
A3 Window Attention的forward方法解析
根据原论文中,带有相对位置偏置的自注意力公式(self-attention including a realtive posotion bias)为
A t t e n t i o n ( Q , K , V ) = S o f t m a x ( Q K T / d + B ) V \mathcal{Attention}(Q,K,V)=Softmax(QK^T/\sqrt d +B)V Attention(Q,K,V)=Softmax(QKT/d+B)V
括号里面
qkv = self.qkv(x).reshape(B_, N, 3, self.num_heads, C // self.num_heads).permute(2, 0, 3, 1, 4)
q, k, v = qkv[0], qkv[1], qkv[2] # make torchscript happy (cannot use tensor as tuple)
q = q * self.scale
attn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1))
relative_position_bias = self.relative_position_bias_table[self.relative_position_index.view(-1)].view(
self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], -1) # Wh*Ww,Wh*Ww,nH
relative_position_bias = relative_position_bias.permute(2, 0, 1).contiguous() # nH, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
attn = attn + relative_position_bias.unsqueeze(0)
值得注意的是,这里的bias是根据相对位置编码索引的
self.relative_position_bias_table[self.relative_position_index.view(-1)]
在forward中,还有个参数:mask 它和SW-MSA有关。
A4 Shift Window MSA
对于SW-MSA,对应于这些代码:
1.生成attention mask
if self.shift_size > 0
# calculate attention mask for SW-MSA
#step1
H, W = self.input_resolution
img_mask = torch.zeros((1, H, W, 1)) # 1 H W 1
h_slices = (slice(0, -self.window_size),
slice(-self.window_size, -self.shift_size),
slice(-self.shift_size, None))
w_slices = (slice(0, -self.window_size),
slice(-self.window_size, -self.shift_size),
slice(-self.shift_size, None))
cnt = 0
for h in h_slices:
for w in w_slices:
img_mask[:, h, w, :] = cnt
cnt += 1
#step2
mask_windows = window_partition(img_mask, self.window_size) # nW, window_size, window_size, 1
mask_windows = mask_windows.view(-1, self.window_size * self.window_size)
attn_mask = mask_windows.unsqueeze(1) - mask_windows.unsqueeze(2)
#stpe3
attn_mask = attn_mask.masked_fill(attn_mask != 0, float(-100.0)).masked_fill(attn_mask == 0, float(0.0))
根据代码的作用解析。
解析1:
step1:
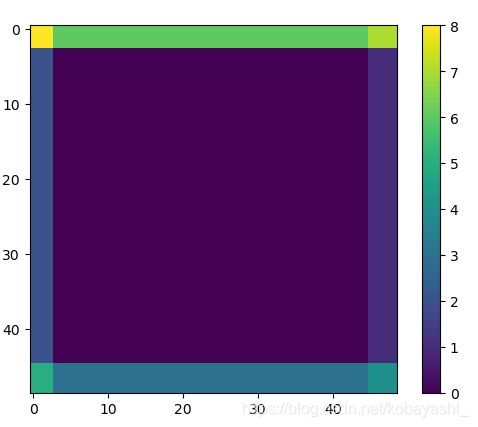
当如下参数时,生成了右边的img mask
window_size=2
shift_size=window_size//2
H, W = 4,4
-->output
[[0 0 1 2]
[0 0 1 2]
[3 3 4 5]
[6 6 7 8]]
如果使用
python x = torch.roll(img_mask, shifts=(shift_size, shift_size), dims=(1, 2))
最终的结果如右图所示,和原论文符合。因为在代码中特征图已经进行了torch.roll操作
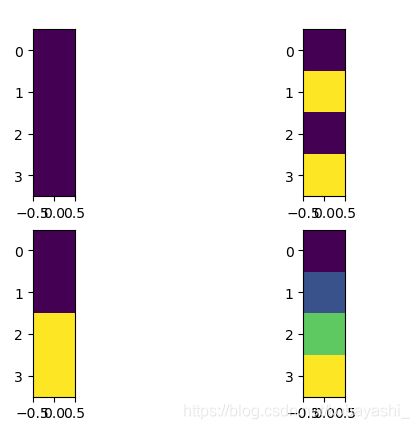
step2:
两个方向做差
print(mask_windows.unsqueeze(1).shape)# [4,1,4]
-->[[[0. 0. 0. 0.]]
[[1. 2. 1. 2.]]
[[3. 3. 6. 6.]]
[[4. 5. 7. 8.]]]
print(mask_windows.unsqueeze(2).shape)#[4,4,1]
-->output
[[[0.]
[0.]
[0.]
[0.]]
[[1.]
[2.]
[1.]
[2.]]
[[3.]
[3.]
[6.]
[6.]]
[[4.]
[5.]
[7.]
[8.]]]
attn_mask = mask_windows.unsqueeze(1) - mask_windows.unsqueeze(2) #x轴与y轴做差
-->outputs
[[[ 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[ 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[ 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[ 0. 0. 0. 0.]]
[[ 0. 1. 0. 1.]
[-1. 0. -1. 0.]
[ 0. 1. 0. 1.]
[-1. 0. -1. 0.]]
[[ 0. 0. 3. 3.]
[ 0. 0. 3. 3.]
[-3. -3. 0. 0.]
[-3. -3. 0. 0.]]
[[ 0. 1. 3. 4.]
[-1. 0. 2. 3.]
[-3. -2. 0. 1.]
[-4. -3. -1. 0.]]]
具体理解可以看下面资料的Attention Mask 段
图解Swin Transformer
[4,1,4]
[4,4,1]
attn_mask
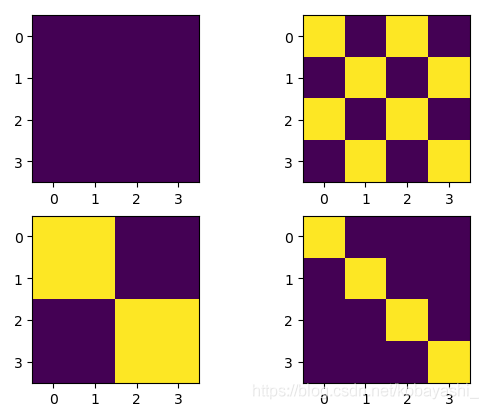
step3
赋值,不为0的赋值为-100,等于零的赋值为0
黄色值为0
当window size =3时
winodw size=5
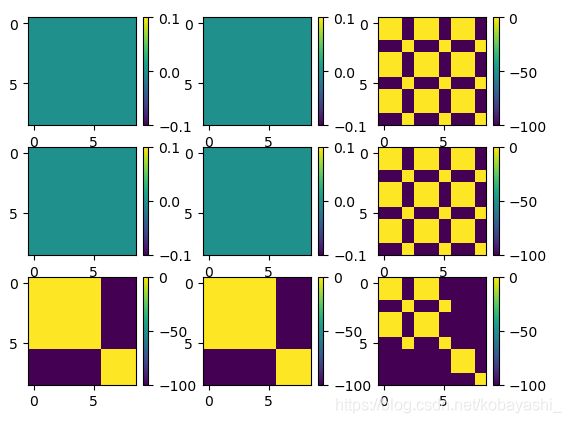
最后将结果加在
attn = attn.view(B_ // nW, nW, self.num_heads, N, N) + mask.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(0)
#https://github.com/microsoft/Swin-Transformer/blob/3dc2a55301a02d71e956b382b50943a35c4abee9/models/swin_transformer.py#L133
attn = attn.view(-1, self.num_heads, N, N)
attn = self.softmax(attn)#加了-100的值将会被忽略
至此,SW-MSA的流程已经完整出来了