二:SpringBoot启动原理
目录
SpringBoot 是如何通过jar包启动的
java -jar做了什么
Jar包的打包插件及核心方法
jar包目录结构
META-INF内容
Archive的概念
JarLauncher
URLStreamHandler
Spring Boot的Jar应用启动流程总结
在IDE/开放目录启动Spring boot应用
总结
SpringBoot是如何启动Spring容器源码:
使用外部Servlet容器
外部Servlet容器启动SpringBoot应用原理
什么是SPI
SpringBoot启动原理脑图
SpringBoot 是如何通过jar包启动的
得益于SpringBoot的封装,我们可以只通过jar -jar一行命令便启动一个web项目。再也不用操心搭建tomcat等相关web容器。那么,你是否探究过SpringBoot是如何达到这一操作的呢?只有了解了底层实现原理,才能更好的掌握该项技术带来的好处以及性能调优。本篇文章带大家聊一探究竟。
java -jar做了什么
先要弄清楚java -jar命令做了什么,在oracle官网找到了该命令的描述:
If the -jar option is specified, its argument is the name of the JAR file containing class and resource files for the application. The startup class must be indicated by the Main-Class manifest header in its source code.
再次秀出我蹩脚的英文翻译:
使用-jar参数时,后面的参数是的jar文件名(本例中是springbootstarterdemo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar);
该jar文件中包含的是class和资源文件;
在manifest文件中有Main-Class的定义;
Main-Class的源码中指定了整个应用的启动类;(in its source code)
小结一下:
java -jar会去找jar中的manifest文件,在那里面找到真正的启动类;
疑惑出现
在MANIFEST.MF文件中有这么一行内容:
Start-Class: com.tulingxueyuan.Application前面的java官方文档中,只提到过Main-Class ,并没有提到Start-Class;
Start-Class的值是com.tulingxueyuan.Application,这是我们的java代码中的唯一类,也只真正的应用启动类;
所以问题就来了:理论上看,执行java -jar命令时JarLauncher类会被执行,但实际上是com.tulingxueyuan.Application被执行了,这其中发生了什么呢?为什么要这么做呢?
- Java没有提供任何标准的方式来加载嵌套的jar文件(即,它们本身包含在jar中的jar文件)。
Jar包的打包插件及核心方法
Spring Boot项目的pom.xml文件中默认使用如下插件进行打包:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
执行maven clean package之后,会生成两个文件:
spring-learn-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
spring-learn-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar.originalspring-boot-maven-plugin项目存在于spring-boot-tools目录中。spring-boot-maven-plugin默认有5个goals:repackage、run、start、stop、build-info。在打包的时候默认使用的是repackage。
spring-boot-maven-plugin的repackage能够将mvn package生成的软件包,再次打包为可执行的软件包,并将mvn package生成的软件包重命名为*.original。
spring-boot-maven-plugin的repackage在代码层面调用了RepackageMojo的execute方法,而在该方法中又调用了repackage方法。repackage方法代码及操作解析如下:
private void repackage() throws MojoExecutionException {
// maven生成的jar,最终的命名将加上.original后缀
Artifact source = getSourceArtifact();
// 最终为可执行jar,即fat jar
File target = getTargetFile();
// 获取重新打包器,将maven生成的jar重新打包成可执行jar
Repackager repackager = getRepackager(source.getFile());
// 查找并过滤项目运行时依赖的jar
Set artifacts = filterDependencies(this.project.getArtifacts(),
getFilters(getAdditionalFilters()));
// 将artifacts转换成libraries
Libraries libraries = new ArtifactsLibraries(artifacts, this.requiresUnpack,
getLog());
try {
// 获得Spring Boot启动脚本
LaunchScript launchScript = getLaunchScript();
// 执行重新打包,生成fat jar
repackager.repackage(target, libraries, launchScript);
}catch (IOException ex) {
throw new MojoExecutionException(ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
// 将maven生成的jar更新成.original文件
updateArtifact(source, target, repackager.getBackupFile());
} 执行以上命令之后,便生成了打包结果对应的两个文件。下面针对文件的内容和结构进行一探究竟。
jar包目录结构
首先来看看jar的目录结构,都包含哪些目录和文件,解压jar包可以看到如下结构:
spring-boot-learn-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
├── META-INF
│ └── MANIFEST.MF
├── BOOT-INF
│ ├── classes
│ │ └── 应用程序类
│ └── lib
│ └── 第三方依赖jar
└── org
└── springframework
└── boot
└── loader
└── springboot启动程序META-INF内容
在上述目录结构中,META-INF记录了相关jar包的基础信息,包括入口程序等。
Manifest-Version: 1.0
Implementation-Title: spring-learn
Implementation-Version: 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
Start-Class: com.tulingxueyuan.Application
Spring-Boot-Classes: BOOT-INF/classes/
Spring-Boot-Lib: BOOT-INF/lib/
Build-Jdk-Spec: 1.8
Spring-Boot-Version: 2.1.5.RELEASE
Created-By: Maven Archiver 3.4.0
Main-Class: org.springframework.boot.loader.JarLauncher可以看到有Main-Class是org.springframework.boot.loader.JarLauncher ,这个是jar启动的Main函数。
还有一个Start-Class是com.tulingxueyuan.Application,这个是我们应用自己的Main函数。
Archive的概念
在继续了解底层概念和原理之前,我们先来了解一下Archive的概念:
- archive即归档文件,这个概念在linux下比较常见。
- 通常就是一个tar/zip格式的压缩包。
- jar是zip格式。
SpringBoot抽象了Archive的概念,一个Archive可以是jar(JarFileArchive),可以是一个文件目录(ExplodedArchive),可以抽象为统一访问资源的逻辑层。关于Spring Boot中Archive的源码如下:
public interface Archive extends Iterable {
// 获取该归档的url
URL getUrl() throws MalformedURLException;
// 获取jar!/META-INF/MANIFEST.MF或[ArchiveDir]/META-INF/MANIFEST.MF
Manifest getManifest() throws IOException;
// 获取jar!/BOOT-INF/lib/*.jar或[ArchiveDir]/BOOT-INF/lib/*.jar
List getNestedArchives(EntryFilter filter) throws IOException;
} SpringBoot定义了一个接口用于描述资源,也就是org.springframework.boot.loader.archive.Archive。该接口有两个实现,分别是org.springframework.boot.loader.archive.ExplodedArchive和org.springframework.boot.loader.archive.JarFileArchive。前者用于在文件夹目录下寻找资源,后者用于在jar包环境下寻找资源。而在SpringBoot打包的fatJar中,则是使用后者。
JarFile:对jar包的封装,每个JarFileArchive都会对应一个JarFile。JarFile被构造的时候会解析内部结构,去获取jar包里的各个文件或文件夹,这些文件或文件夹会被封装到Entry中,也存储在JarFileArchive中。如果Entry是个jar,会解析成JarFileArchive。
比如一个JarFileArchive对应的URL为:
jar:file:/Users/format/Develop/gitrepository/springboot-analysis/springboot-executable-jar/target/executable-jar-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar!/它对应的JarFile为:
/Users/format/Develop/gitrepository/springboot-analysis/springboot-executable-jar/target/executable-jar-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar这个JarFile有很多Entry,比如:
META-INF/
META-INF/MANIFEST.MF
spring/
spring/study/
....
spring/study/executablejar/ExecutableJarApplication.class
lib/spring-boot-starter-1.3.5.RELEASE.jar
lib/spring-boot-1.3.5.RELEASE.jar
...JarFileArchive内部的一些依赖jar对应的URL(SpringBoot使用org.springframework.boot.loader.jar.Handler处理器来处理这些URL):
jar:file:/Users/Format/Develop/gitrepository/springboot-analysis/springboot-executable-jar/target/executable-jar-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar!/lib/spring-boot-starter-web-1.3.5.RELEASE.jar!/jar:file:/Users/Format/Develop/gitrepository/springboot-analysis/springboot-executable-jar/target/executable-jar-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar!/lib/spring-boot-loader-1.3.5.RELEASE.jar!/org/springframework/boot/loader/JarLauncher.class我们看到如果有jar包中包含jar,或者jar包中包含jar包里面的class文件,那么会使用 !/ 分隔开,这种方式只有org.springframework.boot.loader.jar.Handler能处理,它是SpringBoot内部扩展出来的一种URL协议。
JarLauncher
从MANIFEST.MF可以看到Main函数是JarLauncher,下面来分析它的工作流程。JarLauncher类的继承结构是:
class JarLauncher extends ExecutableArchiveLauncher
class ExecutableArchiveLauncher extends LauncherLauncher for JAR based archives. This launcher assumes that dependency jars are included inside a /BOOT-INF/lib directory and that application classes are included inside a /BOOT-INF/classes directory.
按照定义,JarLauncher可以加载内部/BOOT-INF/lib下的jar及/BOOT-INF/classes下的应用class,其实JarLauncher实现很简单:
public class JarLauncher extends ExecutableArchiveLauncher {
public JarLauncher() {}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new JarLauncher().launch(args);
}
}其主入口新建了JarLauncher并调用父类Launcher中的launch方法启动程序。在创建JarLauncher时,父类ExecutableArchiveLauncher找到自己所在的jar,并创建archive。
JarLauncher继承于org.springframework.boot.loader.ExecutableArchiveLauncher。该类的无参构造方法最主要的功能就是构建了当前main方法所在的FatJar的JarFileArchive对象。下面来看launch方法。该方法主要是做了2个事情:
- 以FatJar为file作为入参,构造JarFileArchive对象。获取其中所有的资源目标,取得其Url,将这些URL作为参数,构建了一个URLClassLoader。
- 以第一步构建的ClassLoader加载MANIFEST.MF文件中Start-Class指向的业务类,并且执行静态方法main。进而启动整个程序。
public abstract class ExecutableArchiveLauncher extends Launcher {
private final Archive archive;
public ExecutableArchiveLauncher() {
try {
// 找到自己所在的jar,并创建Archive
this.archive = createArchive();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
}
}
public abstract class Launcher {
protected final Archive createArchive() throws Exception {
ProtectionDomain protectionDomain = getClass().getProtectionDomain();
CodeSource codeSource = protectionDomain.getCodeSource();
URI location = (codeSource == null ? null : codeSource.getLocation().toURI());
String path = (location == null ? null : location.getSchemeSpecificPart());
if (path == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to determine code source archive");
}
File root = new File(path);
if (!root.exists()) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unable to determine code source archive from " + root);
}
return (root.isDirectory() ? new ExplodedArchive(root)
: new JarFileArchive(root));
}
}在Launcher的launch方法中,通过以上archive的getNestedArchives方法找到/BOOT-INF/lib下所有jar及/BOOT-INF/classes目录所对应的archive,通过这些archives的url生成LaunchedURLClassLoader,并将其设置为线程上下文类加载器,启动应用。
至此,才执行我们应用程序主入口类的main方法,所有应用程序类文件均可通过/BOOT-INF/classes加载,所有依赖的第三方jar均可通过/BOOT-INF/lib加载。
URLStreamHandler
java中描述资源常使用URL。而URL有一个方法用于打开链接java.net.URL#openConnection()。由于URL用于表达各种各样的资源,打开资源的具体动作由java.net.URLStreamHandler这个类的子类来完成。根据不同的协议,会有不同的handler实现。而JDK内置了相当多的handler实现用于应对不同的协议。比如jar、file、http等等。URL内部有一个静态HashTable属性,用于保存已经被发现的协议和handler实例的映射。
获得URLStreamHandler有三种方法:
- 实现URLStreamHandlerFactory接口,通过方法URL.setURLStreamHandlerFactory设置。该属性是一个静态属性,且只能被设置一次。
- 直接提供URLStreamHandler的子类,作为URL的构造方法的入参之一。但是在JVM中有固定的规范要求:
子类的类名必须是Handler,同时最后一级的包名必须是协议的名称。比如自定义了Http的协议实现,则类名必然为xx.http.Handler;
JVM启动的时候,需要设置java.protocol.handler.pkgs系统属性,如果有多个实现类,那么中间用|隔开。因为JVM在尝试寻找Handler时,会从这个属性中获取包名前缀,最终使用包名前缀.协议名.Handler,使用Class.forName方法尝试初始化类,如果初始化成功,则会使用该类的实现作为协议实现。
为了实现这个目标,SpringBoot首先从支持jar in jar中内容读取做了定制,也就是支持多个!/分隔符的url路径。SpringBoot定制了以下两个方面:
- 实现了一个java.net.URLStreamHandler的子类org.springframework.boot.loader.jar.Handler。该Handler支持识别多个!/分隔符,并且正确的打开URLConnection。打开的Connection是SpringBoot定制的org.springframework.boot.loader.jar.JarURLConnection实现。
- 实现了一个java.net.JarURLConnection的子类org.springframework.boot.loader.jar.JarURLConnection。该链接支持多个!/分隔符,并且自己实现了在这种情况下获取InputStream的方法。而为了能够在org.springframework.boot.loader.jar.JarURLConnection正确获取输入流,SpringBoot自定义了一套读取ZipFile的工具类和方法。这部分和ZIP压缩算法规范紧密相连,就不拓展了。
Spring Boot的Jar应用启动流程总结
总结一下Spring Boot应用的启动流程:
(1)Spring Boot应用打包之后,生成一个Fat jar,包含了应用依赖的jar包和Spring Boot loader相关的类。
(2)Fat jar的启动Main函数是JarLauncher,它负责创建一个LaunchedURLClassLoader来加载/lib下面的jar,并以一个新线程启动应用的Main函数。
那么,ClassLoader是如何读取到Resource,它又需要哪些能力?查找资源和读取资源的能力。对应的API:
public URL findResource(String name)
public InputStream getResourceAsStream(String name)SpringBoot构造LaunchedURLClassLoader时,传递了一个URL[]数组。数组里是lib目录下面的jar的URL。
对于一个URL,JDK或者ClassLoader如何知道怎么读取到里面的内容的?流程如下:
- LaunchedURLClassLoader.loadClass
- URL.getContent()
- URL.openConnection()
- Handler.openConnection(URL)
最终调用的是JarURLConnection的getInputStream()函数。
//org.springframework.boot.loader.jar.JarURLConnection
@Override
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
connect();
if (this.jarEntryName.isEmpty()) {
throw new IOException("no entry name specified");
}
return this.jarEntryData.getInputStream();
}从一个URL,到最终读取到URL里的内容,整个过程是比较复杂的,总结下:
- Spring boot注册了一个Handler来处理”jar:”这种协议的URL。
- Spring boot扩展了JarFile和JarURLConnection,内部处理jar in jar的情况。
- 在处理多重jar in jar的URL时,Spring Boot会循环处理,并缓存已经加载到的JarFile。
- 对于多重jar in jar,实际上是解压到了临时目录来处理,可以参考JarFileArchive里的代码。
- 在获取URL的InputStream时,最终获取到的是JarFile里的JarEntryData。
细节很多,上面只列出比较重要的步骤。最后,URLClassLoader是如何getResource的呢?URLClassLoader在构造时,有URL[]数组参数,它内部会用这个数组来构造一个URLClassPath:
URLClassPath ucp = new URLClassPath(urls);
在URLClassPath内部会为这些URLS都构造一个Loader,然后在getResource时,会从这些Loader里一个个去尝试获取。如果获取成功的话,就像下面那样包装为一个Resource。
Resource getResource(final String name, boolean check) {
final URL url;
try {
url = new URL(base, ParseUtil.encodePath(name, false));
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("name");
}
final URLConnection uc;
try {
if (check) {
URLClassPath.check(url);
}
uc = url.openConnection();
InputStream in = uc.getInputStream();
if (uc instanceof JarURLConnection) {
/* Need to remember the jar file so it can be closed
* in a hurry.
*/
JarURLConnection juc = (JarURLConnection)uc;
jarfile = JarLoader.checkJar(juc.getJarFile());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
return null;
}
return new Resource() {
public String getName() { return name; }
public URL getURL() { return url; }
public URL getCodeSourceURL() { return base; }
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
return uc.getInputStream();
}
public int getContentLength() throws IOException {
return uc.getContentLength();
}
};
}
JarURLConnection juc = (JarURLConnection)uc;从代码里可以看到,实际上是调用了url.openConnection()。这样完整的链条就可以连接起来了。
在IDE/开放目录启动Spring boot应用
在上面只提到在一个fat jar里启动SpringBoot应用的过程,那么IDE里Spring boot是如何启动的呢?
在IDE里,直接运行的Main函数是应用的Main函数:
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootDemoApplication.class, args);
}
}其实在IDE里启动SpringBoot应用是最简单的一种情况,因为依赖的Jar都让IDE放到classpath里了,所以Spring boot直接启动就完事了。
还有一种情况是在一个开放目录下启动SpringBoot启动。所谓的开放目录就是把fat jar解压,然后直接启动应用。
这时,Spring boot会判断当前是否在一个目录里,如果是的,则构造一个ExplodedArchive(前面在jar里时是JarFileArchive),后面的启动流程类似fat jar的。
总结
通过spring-boot-plugin 生成了MANIFEST.MF main-class 指定运行java -jar的主程序
把依赖的jar文件 打包在fat jar.
JarLauncher通过加载BOOT-INF/classes目录及BOOT-INF/lib目录下jar文件,实现了fat jar的启动。
SpringBoot通过扩展JarFile、JarURLConnection及URLStreamHandler,实现了jar in jar中资源的加载。
SpringBoot通过扩展URLClassLoader–LauncherURLClassLoader,实现了jar in jar中class文件的加载。
WarLauncher通过加载WEB-INF/classes目录及WEB-INF/lib和WEB-INF/lib-provided目录下的jar文件,实现了war文件的直接启动及web容器中的启动。
SpringBoot是如何启动Spring容器源码:
内嵌tomcat实例代码.rar
SpringBoot 事假监听器发布顺序:
1.ApplicationStartingEvent在运行开始时发送,但在进行任何处理之前(侦听器和初始化程序的注册除外)发送。
2.在创建上下文之前,将发送ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent。
3.准备ApplicationContext并调用ApplicationContextInitializers之后,将发送ApplicationContextInitializedEvent。
4.读取完配置类后发送ApplicationPreparedEvent。
5.在刷新上下文之后但在调用任何应用程序和命令行运行程序之前,将发送ApplicationStartedEvent。
6.紧随其后发送带有LivenessState.CORRECT的AvailabilityChangeEvent,以指示该应用程序被视为处于活动状态。
7.在调用任何应用程序和命令行运行程序之后,将发送ApplicationReadyEvent。
8.紧随其后发送ReadabilityState.ACCEPTING_TRAFFIC的AvailabilityChangeEvent,以指示应用程序已准备就绪,可以处理请求。
如果启动时发生异常,则发送ApplicationFailedEvent。1.ApplicationStartingEvent
2.ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent
1 调用SpringApplication.run启动springboot应用
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);2. 使用自定义SpringApplication进行启动
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class[] primarySources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}1. 创建SpringApplication
- new SpringApplication(primarySources)
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
// 将启动类放入primarySources
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
// 根据classpath 下的类,推算当前web应用类型(webFlux, servlet)
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
// 就是去spring.factories 中去获取所有key:org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
//就是去spring.factories 中去获取所有key: org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
// 根据main方法推算出mainApplicationClass
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}- org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer
- org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener
总结:
- 获取启动类:根据启动类加载ioc容器
- 获取web应用类型
- spring.factories读取了对外扩展的ApplicationContextInitializer ,ApplicationListener 对外扩展, 对类解耦(比如全局配置文件、热部署插件)
- 根据main推算出所在的类
就是去初始化了一些信息
2. 启动
- run
- 启动springboot最核心的逻辑
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// 用来记录当前springboot启动耗时
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
// 就是记录了启动开始时间
stopWatch.start();
// 它是任何spring上下文的接口, 所以可以接收任何ApplicationContext实现
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
// 开启了Headless模式:
configureHeadlessProperty();
// 去spring.factroies中读取了SpringApplicationRunListener 的组件, 就是用来发布事件或者运行监听器
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
// 发布1.ApplicationStartingEvent事件,在运行开始时发送
listeners.starting();
try {
// 根据命令行参数 实例化一个ApplicationArguments
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// 预初始化环境: 读取环境变量,读取配置文件信息(基于监听器)
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
// 忽略beaninfo的bean
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
// 打印Banner 横幅
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
// 根据webApplicationType创建Spring上下文
context = createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
//预初始化spring上下文
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
// 加载spring ioc 容器 **相当重要 由于是使用AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext 启动的spring容器所以springboot对它做了扩展:
// 加载自动配置类:invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors , 创建servlet容器onRefresh
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
} - prepareEnvironment
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// 根据webApplicationType 创建Environment 创建就会读取: java环境变量和系统环境变量
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
// 将命令行参数读取环境变量中
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
// 将@PropertieSource的配置信息 放在第一位, 因为读取配置文件@PropertieSource优先级是最低的
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
// 发布了ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent 的监听器 读取了全局配置文件
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
// 将所有spring.main 开头的配置信息绑定SpringApplication
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment,
deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
//更新PropertySources
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}- prepareContext
- 预初始化上下文
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
context.setEnvironment(environment);
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
// 拿到之前读取到所有ApplicationContextInitializer的组件, 循环调用initialize方法
applyInitializers(context);
// 发布了ApplicationContextInitializedEvent
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
// 获取当前spring上下文beanFactory (负责创建bean)
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
// 在Spring下 如果出现2个重名的bean, 则后读取到的会覆盖前面
// 在SpringBoot 在这里设置了不允许覆盖, 当出现2个重名的bean 会抛出异常
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory)
.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
// 设置当前spring容器是不是要将所有的bean设置为懒加载
if (this.lazyInitialization) {
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor());
}
// Load the sources
Set总结:
- 初始化SpringApplication 从spring.factories 读取 listener ApplicationContextInitializer 。
- 运行run方法
- 读取 环境变量 配置信息.....
- 创建springApplication上下文:ServletWebServerApplicationContext
- 预初始化上下文 : 读取启动类
- 调用refresh 加载ioc容器加载所有的,加载所有的自动配置类,创建servlet容器
ps.在这个过程中springboot会调用很多监听器对外进行扩展
使用外部Servlet容器
- 外部servlet容器
- 服务器、本机 安装tomcat 环境变量...
- 部署: war---运维--->tomcat webapp startup.sh 启动
- 开发: 将开发绑定本地tomcat
- 开发 、 运维 服务器配置 war
- 内嵌servlet容器:
- 部署: jar---> 运维---java -jar 启动
使用:
- 下载tomcat服务
- 设置当前maven项目的打包方式
war -
让tomcat相关的依赖不参与打包部署 ,因为外置tomcat服务器已经有这些jar包
spring-boot-starter-tomcat org.springframework.boot provided -
为了让它支持springboot需要加上: 才能启动springboot应用
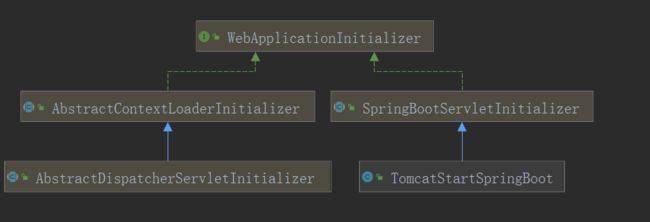
public class TomcatStartSpringBoot extends SpringBootServletInitializer { @Override protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder builder) { return builder.sources(Application.class); } } -
在idea中运行
外部Servlet容器启动SpringBoot应用原理
tomcat---> web.xml--filter servlet listener 3.0+
tomcat不会主动去启动springboot应用 ,所以tomcat启动的时候肯定调用了SpringBootServletInitializer的SpringApplicationBuilder , 就会启动springboot
public class TomcatStartSpringBoot extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder (SpringApplicationBuilder builder) {
return builder.sources(Application.class);
}
}servlet3.0 规范官方文档: 8.2.4
什么是SPI
SPI ,全称为 Service Provider Interface(服务提供者接口),是一种服务发现机制。它通过在ClassPath路径下的META-INF/services文件夹查找文件,自动加载文件里所定义的类。
代码示例:java spi-demo示例
大概: 当servlet容器启动时候 就会去META-INF/services 文件夹中找到javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer, 这个文件里面肯定绑定一个ServletContainerInitializer. 当servlet容器启动时候就会去该文件中找到ServletContainerInitializer的实现类,从而创建它的实例调用onstartUp
- @HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class).
- @HandlesTypes传入的类为ServletContainerInitializer感兴趣的
- 容器会自动在classpath中找到 WebApplicationInitializer 会传入到onStartup方法的webAppInitializerClasses中
- Set> webAppInitializerClasses 这里面也包括之前定义的TomcatStartSpringBoot
@HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class)
public class SpringServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(@Nullable Set> webAppInitializerClasses, ServletContext servletContext)
throws ServletException {
List initializers = new LinkedList<>();
if (webAppInitializerClasses != null) {
for (Class waiClass : webAppInitializerClasses) {
// 如果不是接口 不是抽象 跟WebApplicationInitializer有关系 就会实例化
if (!waiClass.isInterface() && !Modifier.isAbstract(waiClass.getModifiers()) &&
WebApplicationInitializer.class.isAssignableFrom(waiClass)) {
try {
initializers.add((WebApplicationInitializer)
ReflectionUtils.accessibleConstructor(waiClass).newInstance());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ServletException("Failed to instantiate WebApplicationInitializer class", ex);
}
}
}
}
if (initializers.isEmpty()) {
servletContext.log("No Spring WebApplicationInitializer types detected on classpath");
return;
}
servletContext.log(initializers.size() + " Spring WebApplicationInitializers detected on classpath");
// 排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(initializers);
for (WebApplicationInitializer initializer : initializers) {
initializer.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
// Logger initialization is deferred in case an ordered
// LogServletContextInitializer is being used
this.logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
WebApplicationContext rootApplicationContext = createRootApplicationContext(servletContext);
if (rootApplicationContext != null) {
servletContext.addListener(new SpringBootContextLoaderListener(rootApplicationContext, servletContext));
}
else {
this.logger.debug("No ContextLoaderListener registered, as createRootApplicationContext() did not "
+ "return an application context");
}
}- SpringBootServletInitializer
- 之前定义的TomcatStartSpringBoot 就是继承它
protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
SpringApplicationBuilder builder = createSpringApplicationBuilder();
builder.main(getClass());
ApplicationContext parent = getExistingRootWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
if (parent != null) {
this.logger.info("Root context already created (using as parent).");
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, null);
builder.initializers(new ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer(parent));
}
builder.initializers(new ServletContextApplicationContextInitializer(servletContext));
builder.contextClass(AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext.class);
// 调用configure
builder = configure(builder);
builder.listeners(new WebEnvironmentPropertySourceInitializer(servletContext));
SpringApplication application = builder.build();
if (application.getAllSources().isEmpty()
&& MergedAnnotations.from(getClass(), SearchStrategy.TYPE_HIERARCHY).isPresent(Configuration.class)) {
application.addPrimarySources(Collections.singleton(getClass()));
}
Assert.state(!application.getAllSources().isEmpty(),
"No SpringApplication sources have been defined. Either override the "
+ "configure method or add an @Configuration annotation");
// Ensure error pages are registered
if (this.registerErrorPageFilter) {
application.addPrimarySources(Collections.singleton(ErrorPageFilterConfiguration.class));
}
application.setRegisterShutdownHook(false);
return run(application);
}- 当调用configure就会来到TomcatStartSpringBoot .configure
- 将Springboot启动类传入到builder.source
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder builder) {
return builder.sources(Application.class);
}// 调用SpringApplication application = builder.build(); 就会根据传入的Springboot启动类来构建一个SpringApplication
public SpringApplication build(String... args) {
configureAsChildIfNecessary(args);
this.application.addPrimarySources(this.sources);
return this.application;
}// 调用 return run(application); 就会帮我启动springboot应用
protected WebApplicationContext run(SpringApplication application) {
return (WebApplicationContext) application.run();
}
它就相当于我们的
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}其实这2个实现类就是帮我创建ContextLoaderListener 和DispatcherServlet
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
contextConfigLocation
classpath:spring-core.xml
dispatcherServlet
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
contextConfigLocation
classpath:spring-mvc.xml
1
dispatcherServlet
/