Python Django框架连接金仓数据库
Python Django框架连接金仓数据库
- 一、安装软件
-
- 1.安装python
- 2.安装Django
- 3.安装psycopg2
- 4.安装kingbase ES 7.0数据库
- 二、Django项目开发
-
- 1. 使用django管理工具 django-admin.py在想要的文件目录下(如D:\djangoProject)创建一个项目HelloWord
- 2.在项目HelloWorld中创建叫TestModel 的app
- 3.5. 在项目配置文件setting.py中配置kingbase数据库(本文重点)
- 4.同步model到数据库
- 三、定制后台数据库
Kingbase(金仓数据库)是北京人大金仓信息技术股份有限公司经过多年努力,自主研制开发的具有自主知识产权的通用关系型数据库管理系统,属于国产数据库,在与其他软件的连接上参考资料较少。作者由于实验要求使用此数据库开发,期间遇到很多问题,最后经过老师的一篇文档完成实验。写下此文章以便参考。
一、安装软件
Python 3.6
Django 1.8
KingbaseES 7.0
1.安装python
下载地址: https://www.python.org/downloads/
在此网站下载python 并安装。一定要勾选pip。注意勾选第一个安装界面的下部分加入path的选项。
图片:
2.安装Django
• 在命令提示符下用安装django:
A. 打开命令提示符窗口(win+R,输入cmd)
B. 执行django 安装命令: pip install Django
3.安装psycopg2
使用pip install psycopg2 安装
4.安装kingbase ES 7.0数据库
(1) 安装数据库
(2) 初始化数据库
使用下图所示的“数据库初始化工具”。 完成后,任务管理器的“服务”会发现对应的kingbase_instance。
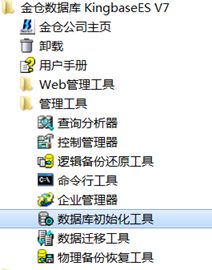
具体安装教程参照kingbase相关文件。
二、Django项目开发
1. 使用django管理工具 django-admin.py在想要的文件目录下(如D:\djangoProject)创建一个项目HelloWord
django-admin.py startproject HelloWorld
 生成结果如下:
生成结果如下:

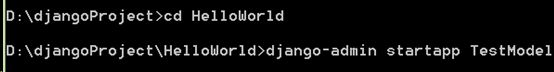
2.在项目HelloWorld中创建叫TestModel 的app
使用命令 django-admin startapp TestModel
 配置TestModel参照:http://www.runoob.com/django/django-tutorial.html
配置TestModel参照:http://www.runoob.com/django/django-tutorial.html
3.5. 在项目配置文件setting.py中配置kingbase数据库(本文重点)
Django中内置了多种数据库,如postgresql、oracle、mysql,如果使用kingbase数据库,需要自己定制数据库后台,详见第三部分:定制数据库后台。
HelloWorld/HelloWorld/settings.py: 文件代码
DATABASES = {
'default': {
‘ENGINE’: ‘TestModel.backends.kingbase’, # kingbase
‘NAME’: ‘HELLO’, # 数据库名,已创建
‘USER’: ‘SYSTEM’, #用户名
‘PASSWORD’: ‘123456’, #密码
‘HOST’: ‘127.0.0.1’, #服务器所在ip
‘PORT’: ‘54321’, #端口号
}
}
4.同步model到数据库
A .使用python manage.py makemigrations , 通知Django修改Model, TestModel\migrations下生成0001_initial.py
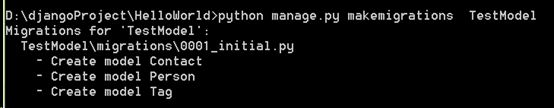
B. python manage.py sqlmigrate , 查看model对应的SQL语句

C . python manage.py migrate , 执行SQL语句到数据库
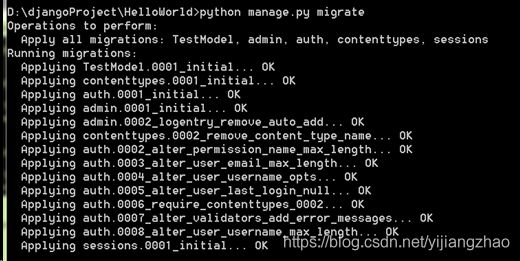
注意:如果使用命令行语句不能自动执行,则需要在python平台手动执行,对于第三步则需要将生成的0001_initial中SQL语句复制到数据库中执行。

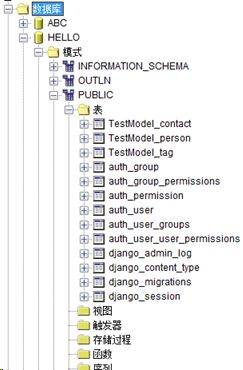
查看kingbase中HELLO数据库,发现自动生成数据库表。
 7 在view中使用model,渲染相应的模板(html)
7 在view中使用model,渲染相应的模板(html)
8 在url中创建请求和响应(view)的映射
9 将在模板(html)中使用Form表单简化html控件
7.8.9同网上参考教程.
三、定制后台数据库
由于kingbase的底层是postgresql,使用psycog2能够连接kingbase,因此我们继承已有的postgresql数据库后台,修改kingbase特有的部分。
A. 在TestModel目录下创建backends\kingbase文件夹,在kingbase文件夹下创建3个文件: init.py,base.py,introspection.py
B. init.py 内容为空,告诉python这是python文件而已。
C. base.py 中代码如下:
from django.db.backends.postgresql import base # 从postgresql中导入base
from .introspection import DatabaseIntrospection #从introspection.py导入DatabaseIntrospection类
class DatabaseWrapper(base.DatabaseWrapper): #继承postgresql的DatabaseWrapper
data_types = {
'AutoField': 'int identity(1,1)', #设置 Model Field和kingbase数据类型的转换
'BigAutoField': 'bigserial',
'BinaryField': 'bytea',
'BooleanField': 'boolean',
'CharField': 'varchar(%(max_length)s)',
'CommaSeparatedIntegerField': 'varchar(%(max_length)s)',
'DateField': 'date',
'DateTimeField': 'timestamp with time zone',
'DecimalField': 'numeric(%(max_digits)s, %(decimal_places)s)',
'DurationField': 'interval',
'FileField': 'varchar(%(max_length)s)',
'FilePathField': 'varchar(%(max_length)s)',
'FloatField': 'double precision',
'IntegerField': 'integer',
'BigIntegerField': 'bigint',
'IPAddressField': 'inet',
'GenericIPAddressField': 'inet',
'NullBooleanField': 'boolean',
'OneToOneField': 'integer',
'PositiveIntegerField': 'integer',
'PositiveSmallIntegerField': 'smallint',
'SlugField': 'varchar(%(max_length)s)',
'SmallIntegerField': 'smallint',
'TextField': 'text',
'TimeField': 'time',
'UUIDField': 'uuid',
}
introspection_class = DatabaseIntrospection # introspection_class类使用introspection.py中DatabaseIntrospection类
def get_new_connection(self, conn_params):
conn = super(DatabaseWrapper,
self).get_new_connection(conn_params)
return conn
D. introspection.py 中代码如下:
主要修改kingbase与postgresql不同的系统命名表(postgresql中用pg_作前缀,kingbase中用sys_做前缀)和其他不一致的地方。
from django.db.backends.base.introspection import TableInfo
from django.db.backends.postgresql import introspection
class DatabaseIntrospection(introspection.DatabaseIntrospection):
_get_indexes_query = """
SELECT attr.attname, idx.indkey, idx.indisunique, idx.indisprimary
FROM sys_catalog.sys_class c, sys_catalog.sys_class c2,
sys_catalog.sys_index idx, sys_catalog.sys_attribute attr
WHERE c.oid = idx.indrelid
AND idx.indexrelid = c2.oid
AND attr.attrelid = c.oid
AND attr.attnum = idx.indkey[0]
AND c.relname = %s"""
def get_table_list(self, cursor):
"""
Returns a list of table and view names in the current database.
"""
cursor.execute("""
SELECT c.relname, c.relkind
FROM sys_catalog.sys_class c
LEFT JOIN sys_catalog.sys_namespace n ON n.oid = c.relnamespace
WHERE c.relkind IN ('r', 'v')
AND n.nspname NOT IN ('sys_catalog', 'sys_toast')
AND sys_catalog.sys_table_is_visible(c.oid)""")
return [TableInfo(row[0], {
'r': 't', 'v': 'v'}.get(row[1]))
for row in cursor.fetchall()
if row[0] not in self.ignored_tables]
def get_relations(self, cursor, table_name):
"""
Returns a dictionary of {
field_name: (field_name_other_table, other_table)}
representing all relationships to the given table.
"""
cursor.execute("""
SELECT c2.relname, a1.attname, a2.attname
FROM sys_constraint con
LEFT JOIN sys_class c1 ON con.conrelid = c1.oid
LEFT JOIN sys_class c2 ON con.confrelid = c2.oid
LEFT JOIN sys_attribute a1 ON c1.oid = a1.attrelid AND a1.attnum = con.conkey[1]
LEFT JOIN sys_attribute a2 ON c2.oid = a2.attrelid AND a2.attnum = con.confkey[1]
WHERE c1.relname = %s
AND con.contype = 'f'""", [table_name])
relations = {
}
for row in cursor.fetchall():
relations[row[1]] = (row[2], row[0])
return relations
def get_constraints(self, cursor, table_name):
"""
Retrieve any constraints or keys (unique, pk, fk, check, index) across
one or more columns. Also retrieve the definition of expression-based
indexes.
"""
constraints = {
}
# Loop over the key table, collecting things as constraints. The column
# array must return column names in the same order in which they were
# created.
# The subquery containing generate_series can be replaced with
# "WITH ORDINALITY" when support for PostgreSQL 9.3 is dropped.
cursor.execute("""
SELECT
c.conname,
array(
SELECT attname
FROM (
SELECT unnest(c.conkey) AS colid,
generate_series(1, array_length(c.conkey, 1)) AS arridx
) AS cols
JOIN sys_attribute AS ca ON cols.colid = ca.attnum
WHERE ca.attrelid = c.conrelid
ORDER BY cols.arridx
),
c.contype,
(SELECT fkc.relname || '.' || fka.attname
FROM sys_attribute AS fka
JOIN sys_class AS fkc ON fka.attrelid = fkc.oid
WHERE fka.attrelid = c.confrelid AND fka.attnum = c.confkey[1]),
cl.reloptions
FROM sys_constraint AS c
JOIN sys_class AS cl ON c.conrelid = cl.oid
JOIN sys_namespace AS ns ON cl.relnamespace = ns.oid
WHERE ns.nspname = %s AND cl.relname = %s
""", ["public", table_name])
for constraint, columns, kind, used_cols, options in cursor.fetchall():
constraints[constraint] = {
"columns": columns,
"primary_key": kind == "p",
"unique": kind in ["p", "u"],
"foreign_key": tuple(used_cols.split(".", 1)) if kind == "f" else None,
"check": kind == "c",
"index": False,
"definition": None,
"options": options,
}
# Now get indexes
# The row_number() function for ordering the index fields can be
# replaced by WITH ORDINALITY in the unnest() functions when support
# for PostgreSQL 9.3 is dropped.
cursor.execute("""
SELECT
indexname, array_agg(attname), indisunique, indisprimary,
array_agg(ordering), amname, exprdef, s2.attoptions
FROM (
SELECT
row_number() OVER () as rnum, c2.relname as indexname,
idx.*, attr.attname, am.amname,
CASE
WHEN idx.indexprs IS NOT NULL THEN
sys_get_indexdef(idx.indexrelid)
END AS exprdef,
CASE am.amname
WHEN 'btree' THEN
CASE (option & 1)
WHEN 1 THEN 'DESC' ELSE 'ASC'
END
END as ordering,
c2.reloptions as attoptions
FROM (
SELECT
*, unnest(i.indkey) as key, unnest(i.indoption) as option
FROM sys_index i
) idx
LEFT JOIN sys_class c ON idx.indrelid = c.oid
LEFT JOIN sys_class c2 ON idx.indexrelid = c2.oid
LEFT JOIN sys_am am ON c2.relam = am.oid
LEFT JOIN sys_attribute attr ON attr.attrelid = c.oid AND attr.attnum = idx.key
WHERE c.relname = %s
) s2
GROUP BY indexname, indisunique, indisprimary, amname, exprdef, attoptions;
""", [table_name])
for index, columns, unique, primary, orders, type_, definition, options in cursor.fetchall():
if index not in constraints:
constraints[index] = {
"columns": columns if columns != [None] else [],
"orders": orders if orders != [None] else [],
"primary_key": primary,
"unique": unique,
"foreign_key": None,
"check": False,
"index": True,
"type": Index.suffix if type_ == 'btree' else type_,
"definition": definition,
"options": options,
}
return constraints
至此,Django搭建完成,读者可以根据自己的需求开发相应的系统。