【Java数据结构-线性表】两万字硬核详细总结,附详细图解源代码,你值得收藏
目录
写在在前面
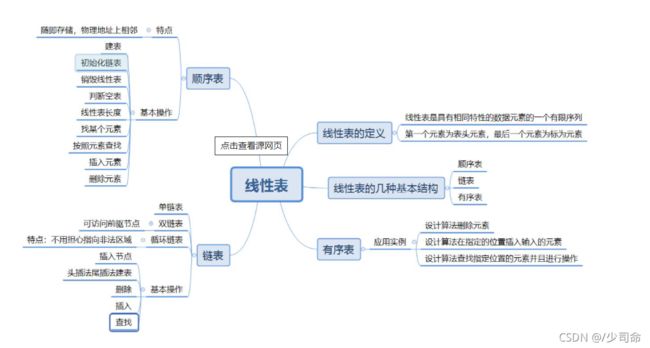
线性表
顺序表
概念及结构
接口实现
创建顺序表
打印顺序表
获取顺序表有效长度
在pos位置增加元素
判断是否由某个元素
查找某个元素对应的位置,找不到返回-1
获取 pos 位置的元素
给 pos 位置的元素设为/更新 value
删除第一次出现的关键字key
✨完整代码✨
❤️Textdemo.java
❤️MyArrayLinst.java
链表
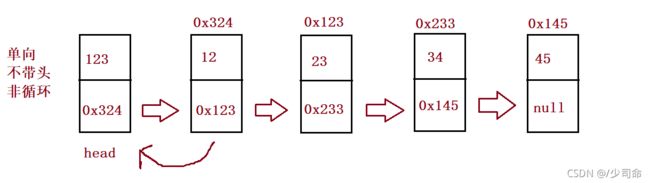
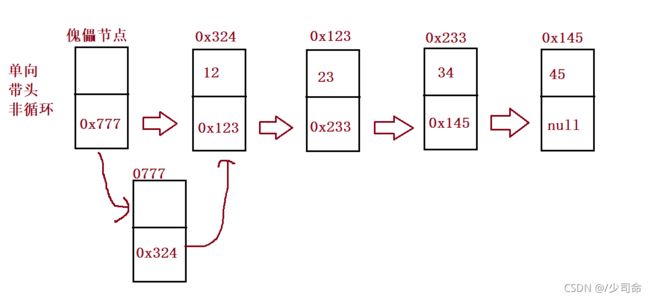
链表的概念及结构
链表分类
链表的实现
创建节点
创建链表
打印链表
查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
得到单链表的长度
头插法
尾插法
找到index-1位置的节点的地址
插入元素
找到要删除的关键字的前驱
删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
删除所有值为key的节点
清空链表
✨全部代码✨
❤️TextDemo.java
❤️MyLinlLinst.java
写在在前面
线性表和链表是学习的重中之重,它能放在数据结构的最前面,就说明了它的重要性。学好数据结构最重要的是画图,多写代码,有些固定的结构都是固定的语法,了解多了就能孰能手巧。如果你认为本篇文章写的不错的话,求点赞,求收藏,求评论,你的三连是我学习最大的进步,废话不多说,让我们学起来吧!
线性表
线性表(linear list)是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。 线性表是一种在实际中广泛使用的数据结构,常见 的线性表:顺序表、链表、栈、队列、字符串.
线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,也就说是连续的一条直线。但是在物理结构上并不一定是连续的,线性表在物理上存储 时,通常以数组和链式结构的形式存储。
顺序表
概念及结构
顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储。在数组上完成数 据的增删查改。
顺序表一般可以分为:
静态顺序表:使用定长数组存储。
动态顺序表:使用动态开辟的数组存储。
静态顺序表适用于确定知道需要存多少数据的场景
静态顺序表的定长数组导致N定大了,空间开多了浪费,开少了不够用
相比之下动态顺序表更灵活, 根据需要动态的分配空间大小。
接口实现
class SeqList {
// 打印顺序表
public void display() {
}
// 在 pos 位置新增元素
public void add(int pos, int data) {
}
// 判定是否包含某个元素
public boolean contains(int toFind) {
return true;
}
// 查找某个元素对应的位置
public int search(int toFind) {
return -1;
}
// 获取 pos 位置的元素
public int getPos(int pos) {
return -1;
}
// 给 pos 位置的元素设为 value
public void setPos(int pos, int value) {
}
//删除第一次出现的关键字key
public void remove(int toRemove) {
}
// 获取顺序表长度
public int size() {
return 0;
}
// 清空顺序表
public void clear() {
}
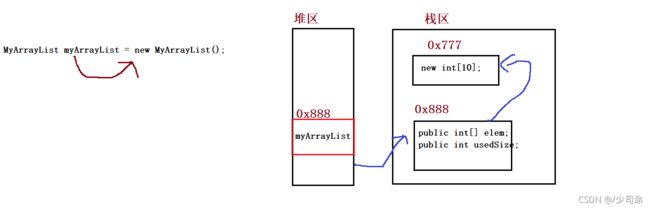
}创建顺序表
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;//有效的数据个数
public MyArrayList() {
this.elem = new int[10];
}打印顺序表
// 打印顺序表
public void display() {
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
System.out.print(this.elem[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}获取顺序表有效长度
// 获取顺序表的有效数据长度
public int size() {
return this.usedSize;
}
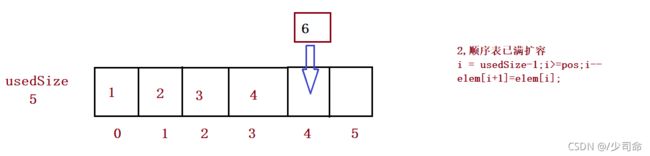
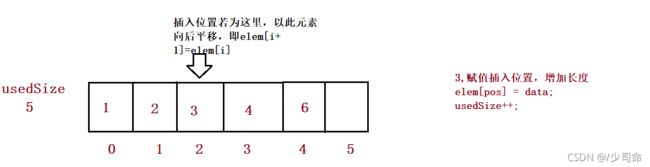
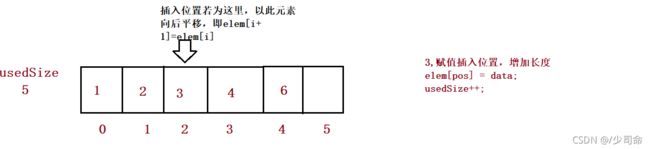
在pos位置增加元素
public boolean isFull() {
return this.usedSize == this.elem.length;
} // 在 pos 位置新增元素
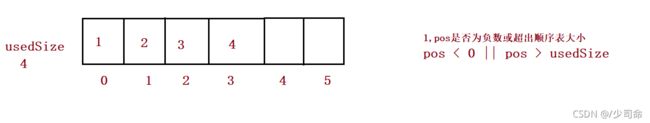
public void add(int pos, int data) {
if(pos < 0 || pos > usedSize) {
System.out.println("pos 位置不合法!");
return;
}
if(isFull()) {
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,2*this.elem.length);
}
//3、
for (int i = this.usedSize-1; i >= pos ; i--) {
this.elem[i+1] = this.elem[i];
}
this.elem[pos] = data;
this.usedSize++;
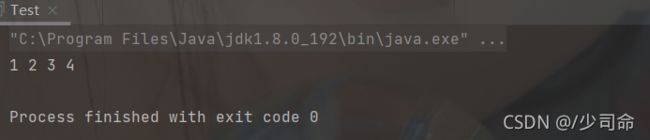
}public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArrayList myArrayList = new MyArrayList();
myArrayList.add(0,1);
myArrayList.add(1,2);
myArrayList.add(2,3);
myArrayList.add(3,4);
myArrayList.display();
} 判断是否由某个元素
判断是否由某个元素
// 判定是否包含某个元素
public boolean contains(int toFind) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
if(this.elem[i] == toFind) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}查找某个元素对应的位置,找不到返回-1
public int search(int toFind) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
if(this.elem[i] == toFind) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}获取 pos 位置的元素
public int getPos(int pos) {
if(pos < 0 || pos >= this.usedSize) {
System.out.println("pos 位置不合法");
return -1;//所以 这里说明一下,业务上的处理,这里不考虑 后期可以抛异常
}
if(isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("顺序表为空!");
return -1;
}
return this.elem[pos];
}public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.usedSize==0;
}给 pos 位置的元素设为/更新 value
public void setPos(int pos, int value) {
if(pos < 0 || pos >= this.usedSize) {
System.out.println("pos位置不合法");
return;
}
if(isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("顺序表为空!");
return;
}
this.elem[pos] = value;
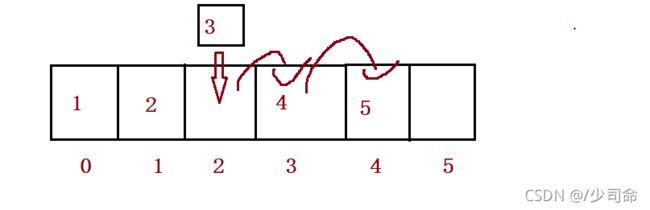
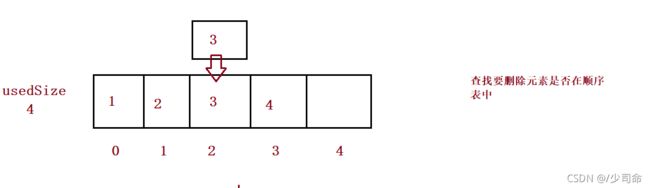
}删除第一次出现的关键字key
public void remove(int toRemove) {
if(isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("顺序表为空!");
return;
}
int index = search(toRemove);
if(index == -1) {
System.out.println("没有你要删除的数字!");
return;
}
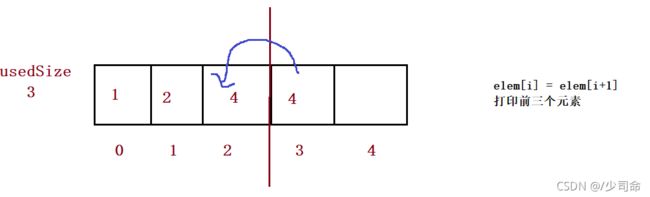
for (int i = index; i < this.usedSize-1; i++) {
this.elem[i] = this.elem[i+1];
}
this.usedSize--;
//this.elem[usedSize] = null; 如果数组当中是引用数据类型。
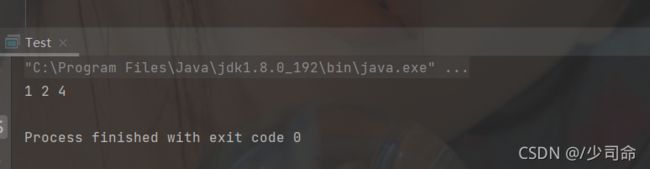
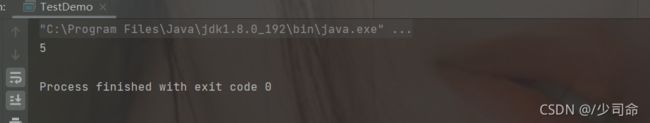
}public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArrayList myArrayList = new MyArrayList();
myArrayList.add(0,1);
myArrayList.add(1,2);
myArrayList.add(2,3);
myArrayList.add(3,4);
myArrayList.remove(3);
myArrayList.display();
}✨完整代码✨
❤️Textdemo.java
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArrayList myArrayList = new MyArrayList();
myArrayList.add(0, 1);
myArrayList.add(1, 2);
myArrayList.add(2, 3);
myArrayList.add(3, 4);
myArrayList.display();
myArrayList.remove(29);
System.out.println("==============");
myArrayList.clear();
myArrayList.display();
System.out.println(myArrayList.contains(3));
System.out.println(myArrayList.getPos(21));
}❤️MyArrayLinst.java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
* User: 12629
* Date: 2021/10/31
* Time: 10:28
* Description:顺序表
*/
public class MyArrayList {
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;//有效的数据个数
public MyArrayList() {
this.elem = new int[10];
}
// 打印顺序表
public void display() {
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
System.out.print(this.elem[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
// 获取顺序表的有效数据长度
public int size() {
return this.usedSize;
}
// 在 pos 位置新增元素
public void add(int pos, int data) {
if(pos < 0 || pos > usedSize) {
System.out.println("pos 位置不合法!");
return;
}
if(isFull()) {
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,2*this.elem.length);
}
//3、
for (int i = this.usedSize-1; i >= pos ; i--) {
this.elem[i+1] = this.elem[i];
}
this.elem[pos] = data;
this.usedSize++;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return this.usedSize == this.elem.length;
}
// 判定是否包含某个元素
public boolean contains(int toFind) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
if(this.elem[i] == toFind) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// 查找某个元素对应的位置,找不到返回-1
public int search(int toFind) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
if(this.elem[i] == toFind) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
// 获取 pos 位置的元素
public int getPos(int pos) {
if(pos < 0 || pos >= this.usedSize) {
System.out.println("pos 位置不合法");
return -1;//所以 这里说明一下,业务上的处理,这里不考虑 后期可以抛异常
}
if(isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("顺序表为空!");
return -1;
}
return this.elem[pos];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.usedSize==0;
}
// 给 pos 位置的元素设为/更新 value
public void setPos(int pos, int value) {
if(pos < 0 || pos >= this.usedSize) {
System.out.println("pos位置不合法");
return;
}
if(isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("顺序表为空!");
return;
}
this.elem[pos] = value;
}
//删除第一次出现的关键字key
public void remove(int toRemove) {
if(isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("顺序表为空!");
return;
}
int index = search(toRemove);
if(index == -1) {
System.out.println("没有你要删除的数字!");
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < this.usedSize-1; i++) {
this.elem[i] = this.elem[i+1];
}
this.usedSize--;
//this.elem[usedSize] = null; 如果数组当中是引用数据类型。
}
// 清空顺序表
public void clear() {
this.usedSize = 0;
/*for (int i = 0; i < usedSize; i++) {
this.elem[i] = null;
}
this.usedSize = 0;
*/
}
}
链表
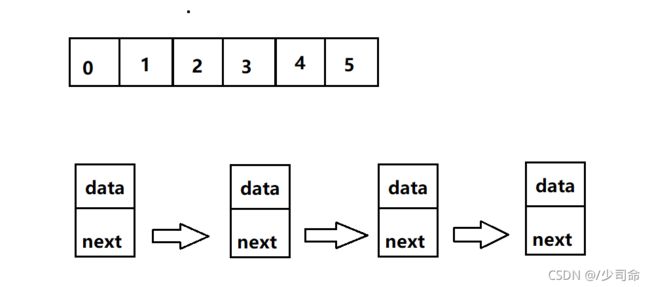
链表的概念及结构
链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的引用链接次序实现的 。
链表分类
链表的实现
// 1、无头单向非循环链表实现
public class SingleLinkedList {
//头插法
}
public void addFirst(int data){
//尾插法
}
public void addLast(int data){
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
}
public boolean addIndex(int index,int data){
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
}
public boolean contains(int key){
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
}
public void remove(int key){
//删除所有值为key的节点
}
public void removeAllKey(int key){
//得到单链表的长度
}
public int size(){
}
public void display(){
}
public void clear(){
}
}
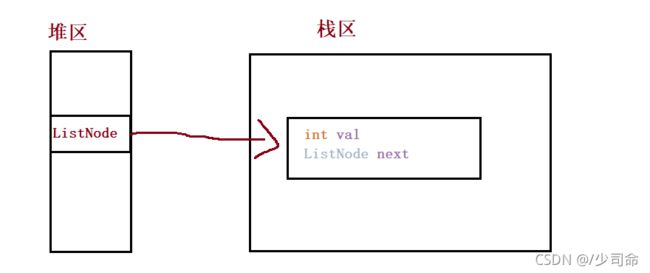
创建节点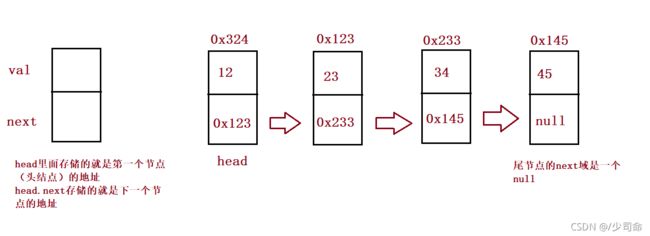
public ListNode head;//链表的头引用lass ListNode {
public int val;
public ListNode next;//null
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}创建链表
public void createList() {
ListNode listNode1 = new ListNode(12);
ListNode listNode2 = new ListNode(23);
ListNode listNode3 = new ListNode(34);
ListNode listNode4 = new ListNode(45);
ListNode listNode5 = new ListNode(56);
listNode1.next = listNode2;
listNode2.next = listNode3;
listNode3.next = listNode4;
listNode4.next = listNode5;
//listNode5.next = null;
this.head = listNode1;
}打印链表
public void display() {
//this.head.next != null
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val+" ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
} public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
//myLinkedList.createList();
myLinkedList.addLast(12);
myLinkedList.addLast(23);
myLinkedList.addLast(34);
myLinkedList.addLast(45);
myLinkedList.addLast(56);
myLinkedList.display();
}查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public boolean contains(int key){
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
if(cur.val == key) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
//myLinkedList.createList();
myLinkedList.addLast(12);
myLinkedList.addLast(23);
myLinkedList.addLast(34);
myLinkedList.addLast(45);
myLinkedList.addLast(56);
myLinkedList.display();
boolean flg = myLinkedList.contains(56);
}得到单链表的长度
public int size(){
int count = 0;
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
//myLinkedList.createList();
myLinkedList.addLast(12);
myLinkedList.addLast(23);
myLinkedList.addLast(34);
myLinkedList.addLast(45);
myLinkedList.addLast(56);
System.out.println(myLinkedList.size());
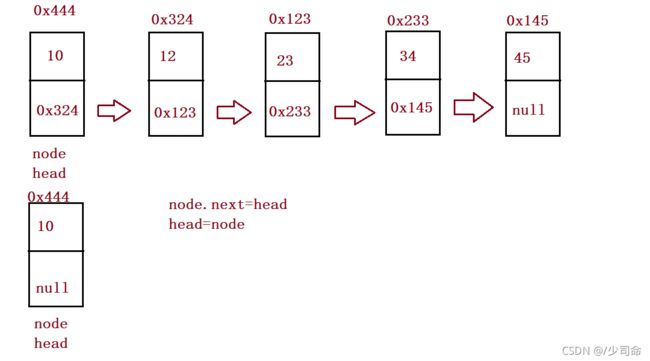
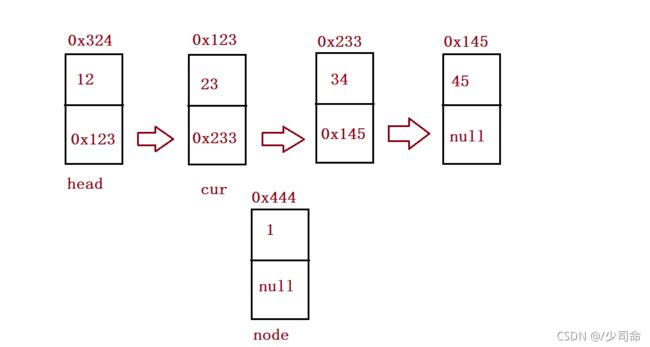
}头插法
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data){
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
node.next = this.head;
this.head = node;
/*if(this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
}else {
node.next = this.head;
this.head = node;
}*/
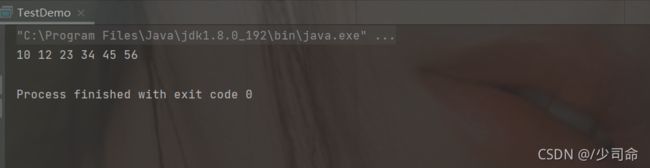
} public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
//myLinkedList.createList();
myLinkedList.addLast(12);
myLinkedList.addLast(23);
myLinkedList.addLast(34);
myLinkedList.addLast(45);
myLinkedList.addLast(56);
myLinkedList.addFirst(10);
myLinkedList.display();
}尾插法
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data){
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
}else {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
//cur.next == null;
cur.next = node;
}
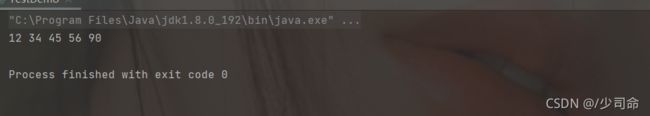
} public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
//myLinkedList.createList();
myLinkedList.addLast(12);
myLinkedList.addLast(23);
myLinkedList.addLast(34);
myLinkedList.addLast(45);
myLinkedList.addLast(56);
myLinkedList.addLast(90);
myLinkedList.display();
}找到index-1位置的节点的地址
public ListNode findIndex(int index) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (index-1 != 0) {
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
return cur;
}插入元素
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index,int data){
if(index < 0 || index > size()) {
System.out.println("index位置不合法!");
return;
}
if(index == 0) {
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if(index == size()) {
addLast(data);
return;
}
ListNode cur = findIndex(index);
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
//myLinkedList.createList();
myLinkedList.addLast(12);
myLinkedList.addLast(23);
myLinkedList.addLast(34);
myLinkedList.addLast(45);
myLinkedList.addLast(56);
myLinkedList.addLast(90);
myLinkedList.addIndex(2,20);
myLinkedList.display();
}找到要删除的关键字的前驱
public ListNode searchPerv(int key) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
if(cur.next.val == key) {
return cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
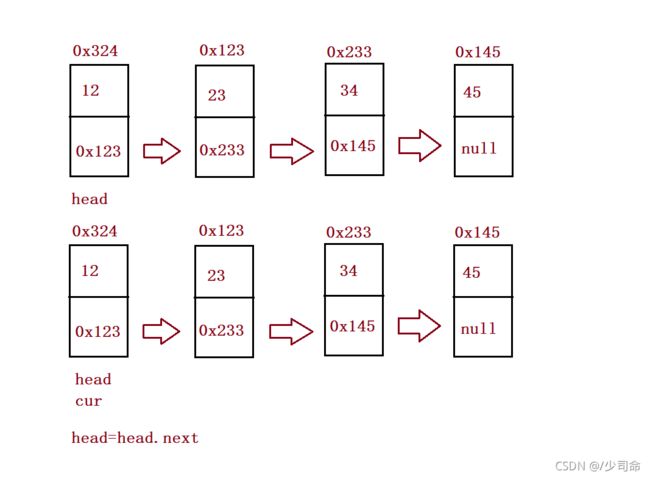
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key){
if(this.head == null) {
System.out.println("单链表为空,不能删除!");
return;
}
if(this.head.val == key) {
this.head = this.head.next;
return;
}
ListNode cur = searchPerv(key);
if(cur == null) {
System.out.println("没有你要删除的节点!");
return;
}
ListNode del = cur.next;
cur.next = del.next;
} public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
//myLinkedList.createList();
myLinkedList.addLast(12);
myLinkedList.addLast(23);
myLinkedList.addLast(34);
myLinkedList.addLast(45);
myLinkedList.addLast(56);
myLinkedList.addLast(90);
myLinkedList.remove(23);
myLinkedList.display();
}删除所有值为key的节点
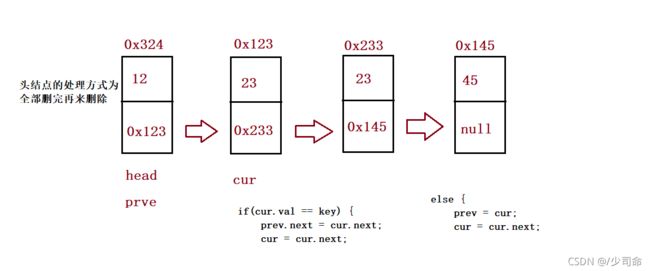
//删除所有值为key的节点
public ListNode removeAllKey(int key){
if(this.head == null) return null;
ListNode prev = this.head;
ListNode cur = this.head.next;
while (cur != null) {
if(cur.val == key) {
prev.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
}else {
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
//最后处理头
if(this.head.val == key) {
this.head = this.head.next;
}
return this.head;
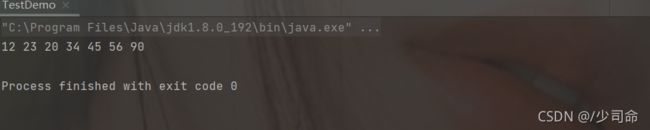
}public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
//myLinkedList.createList();
myLinkedList.addLast(12);
myLinkedList.addLast(23);
myLinkedList.addLast(23);
myLinkedList.addLast(23);
myLinkedList.addLast(56);
myLinkedList.addLast(90);
myLinkedList.removeAllKey(23);
myLinkedList.display();
}清空链表
public void clear(){
//this.head == null
while (this.head != null) {
ListNode curNext = head.next;
this.head.next = null;
this.head = curNext;
}
}✨全部代码✨
❤️TextDemo.java
class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
//myLinkedList.createList();
myLinkedList.addLast(12);
myLinkedList.addLast(23);
myLinkedList.addLast(23);
myLinkedList.addLast(23);
myLinkedList.addLast(56);
myLinkedList.addLast(90);
myLinkedList.display();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
//myLinkedList.createList();
myLinkedList.addLast(12);
myLinkedList.addLast(23);
myLinkedList.addLast(34);
myLinkedList.addLast(45);
myLinkedList.addLast(45);
myLinkedList.addFirst(156);
myLinkedList.addIndex(31,99);
myLinkedList.display();
boolean flg = myLinkedList.contains(56);
}
}❤️MyLinlLinst.java
**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
* User: 12629
* Date: 2021/11/2
* Time: 19:00
* Description:
*/
//ListNode代表一个节点
class ListNode {
public int val;
public ListNode next;//null
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public class MyLinkedList {
public ListNode head;//链表的头引用
public void createList() {
ListNode listNode1 = new ListNode(12);
ListNode listNode2 = new ListNode(23);
ListNode listNode3 = new ListNode(34);
ListNode listNode4 = new ListNode(45);
ListNode listNode5 = new ListNode(56);
listNode1.next = listNode2;
listNode2.next = listNode3;
listNode3.next = listNode4;
listNode4.next = listNode5;
//listNode5.next = null;
this.head = listNode1;
}
public void display() {
//this.head.next != null
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val+" ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public boolean contains(int key){
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
if(cur.val == key) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
//得到单链表的长度
public int size(){
int count = 0;
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data){
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
node.next = this.head;
this.head = node;
/*if(this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
}else {
node.next = this.head;
this.head = node;
}*/
}
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data){
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
}else {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
//cur.next == null;
cur.next = node;
}
}
/**
* 找到index-1位置的节点的地址
* @param index
* @return
*/
public ListNode findIndex(int index) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (index-1 != 0) {
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
return cur;
}
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index,int data){
if(index < 0 || index > size()) {
System.out.println("index位置不合法!");
return;
}
if(index == 0) {
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if(index == size()) {
addLast(data);
return;
}
ListNode cur = findIndex(index);
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
}
/**
* 找到 要删除的关键字的前驱
* @param key
* @return
*/
public ListNode searchPerv(int key) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
if(cur.next.val == key) {
return cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key){
if(this.head == null) {
System.out.println("单链表为空,不能删除!");
return;
}
if(this.head.val == key) {
this.head = this.head.next;
return;
}
ListNode cur = searchPerv(key);
if(cur == null) {
System.out.println("没有你要删除的节点!");
return;
}
ListNode del = cur.next;
cur.next = del.next;
}
//删除所有值为key的节点
public ListNode removeAllKey(int key){
if(this.head == null) return null;
ListNode prev = this.head;
ListNode cur = this.head.next;
while (cur != null) {
if(cur.val == key) {
prev.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
}else {
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
//最后处理头
if(this.head.val == key) {
this.head = this.head.next;
}
return this.head;
}
public void clear(){
//this.head == null
while (this.head != null) {
ListNode curNext = head.next;
this.head.next = null;
this.head = curNext;
}
}
}