ELASTIC SEARCH
本文根据尚硅谷谷粒商城相关内容编写详情请前往尚硅谷电商教程《谷粒商城》对标阿里P6/P7,40-60万年薪_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
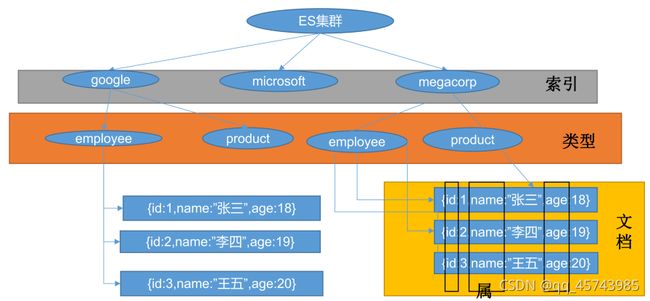
0、简介
mysql用作持久化存储,ES用作检索
基本概念:index库>type表>document文档
-
index索引 动词:相当于mysql的insert
名词:相当于mysql的db
-
Type类型 在index中,可以定义一个或多个类型
类似于mysql的table,每一种类型的数据放在一起
-
Document文档 保存在某个index下,某种type的一个数据document,文档是json格式的,document就像是mysql中的某个table里面的内容。每一行对应的列叫属性
为什么ES搜索快?倒排索引
保存的记录
-
红海行动
-
探索红海行动
-
红海特别行动
-
红海记录片
-
特工红海特别探索
将内容分词就记录到索引中
| 词 | 记录 |
|---|---|
| 红海 | 1,2,3,4,5 |
| 行动 | 1,2,3 |
| 探索 | 2,5 |
| 特别 | 3,5 |
| 纪录片 | 4, |
| 特工 | 5 |
检索:
1)、红海特工行动?查出后计算相关性得分:3号记录命中了2次,且3号本身才有3个单词,2/3,所以3号最匹配 2)、红海行动?
关系型数据库中两个数据表示是独立的,即使他们里面有相同名称的列也不影响使用,但ES中不是这样的。elasticsearch是基于Lucene开发的搜索引擎,而ES中不同type下名称相同的filed最终在Lucene中的处理方式是一样的。
两个不同type下的两个user_name,在ES同一个索引下其实被认为是同一个filed,你必须在两个不同的type中定义相同的filed映射。否则,不同type中的相同字段名称就会在处理中出现冲突的情况,导致Lucene处理效率下降。 去掉type就是为了提高ES处理数据的效率。 Elasticsearch 7.xURL中的type参数为可选。比如,索引一个文档不再要求提供文档类型。 Elasticsearch 8.x不再支持URL中的type参数。 解决:将索引从多类型迁移到单类型,每种类型文档一个独立索引
1、安装elastic search
dokcer中安装elastic search
(1)下载ealastic search(存储和检索)和kibana(可视化检索)
docker pull elasticsearch:7.4.2 docker pull kibana:7.4.2 # 版本要统一 # free -m 查看剩余内存 free -m
(2)配置
# 将docker里的目录挂载到linux的/mydata目录中 # 修改/mydata就可以改掉docker里的 mkdir -p /mydata/elasticsearch/config mkdir -p /mydata/elasticsearch/data # es可以被远程任何机器访问 echo "http.host: 0.0.0.0" >>/mydata/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml # 递归更改权限,es需要访问权限 保证权限问题 chmod -R 777 /mydata/elasticsearch/
(3)启动Elastic search
# 9200是用户交互端口 9300是集群心跳端口(节点之间的通信端口) # -e指定是单节点运行 # -e指定占用的内存大小,生产时可以设置32G 不指定的话会占满内存,导致虚拟机卡死 # -v 挂载 将docker容器内的elasticsearch.yml配置跟外部虚拟机的elasticsearch.yml进行一一关联 # -d 后台启动elasticsearch 使用的镜像为 elasticsearch:7.4.2 docker run --name elasticsearch -p 9200:9200 -p 9300:9300 \ -e "discovery.type=single-node" \ -e ES_JAVA_OPTS="-Xms64m -Xmx512m" \ -v /mydata/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml:/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml \ -v /mydata/elasticsearch/data:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data \ -v /mydata/elasticsearch/plugins:/usr/share/elasticsearch/plugins \ -d elasticsearch:7.4.2 # 查看elasticsearch docker logs elasticsearch # 设置开机启动elasticsearch docker update elasticsearch --restart=always
因为容器里的文件映射到了外面,所以删除容器和新建容器数据还在
第一次查docker ps启动了,第二次查的时候发现关闭了,docker logs elasticsearch
http://192.168.43.65:9200
数据挂载到外面,但是访问权限不足
把/mydata/elasticsearch下文件夹的权限设置好,上面已经设置过了
(4)启动kibana:
# kibana指定了了ES交互端口9200 # 5600位kibana主页端口 docker run --name kibana -e ELASTICSEARCH_HOSTS=http://192.168.43.65:9200 -p 5601:5601 -d kibana:7.4.2 # 设置开机启动kibana docker update kibana --restart=always
(5)测试
查看elasticsearch版本信息: http://192.168.43.65:9200
{
"name": "c8b36d408187",
"cluster_name": "elasticsearch",
"cluster_uuid": "vbacPMqOR4S9F_clVRVc9w",
"version": {
"number": "7.4.2",
"build_flavor": "default",
"build_type": "docker",
"build_hash": "2f90bbf7b93631e52bafb59b3b049cb44ec25e96",
"build_date": "2019-10-28T20:40:44.881551Z",
"build_snapshot": false,
"lucene_version": "8.2.0",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version": "6.8.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version": "6.0.0-beta1"
},
"tagline": "You Know, for Search"
}
显示elasticsearch 节点信息http://192.168.43.65:9200/_cat/nodes
127.0.0.1 60 93 3 0.08 0.11 0.28 dilm * c8b36d408187 curl -XDELETE http://192.168.43.65:9200/.kibana_1 c8b36d408187代表上面的结点 *代表是主节点
kibana
访问Kibana: http://192.168.43.65:5601/app/kibana
2、初步检索
1)检索es信息
(1)GET /_cat/nodes:查看所有节点
如:http://192.168.43.65:9200/_cat/nodes
以直接浏览器输入上面的url,也可以在kibana中输入GET /_cat/nodes
(2)GET /_cat/health:查看es健康状况
如: http://192.168.43.65:9200/_cat/health
1625223887 11:04:47 elasticsearch green 1 1 3 3 0 0 0 0 - 100.0%
注:green表示健康值正常
(3)GET /_cat/master:查看主节点
如: http://192.168.43.65:9200/_cat/master
XQtZ2VbTTUGUd5WJl7Ycaw 127.0.0.1 127.0.0.1 c8b36d408187
(4)GET/_cat/indices:查看所有索引 ,等价于mysql数据库的show databases;
如:http://192.168.43.65:9200/_cat/indices
green open .kibana_task_manager_1 iUc_ztT4T96e5DDhXIwVoA 1 0 2 0 46.2kb 46.2kb green open .apm-agent-configuration s4W-UP1ZTQKVwerVxad1lw 1 0 0 0 283b 283b green open .kibana_1 v1X5zAtYQ5uinjOdc1c3Rg 1 0 3 0 14.8kb 14.8kb
2)新增文档
保存一个数据,保存在哪个索引的哪个类型下(哪张数据库哪张表下),保存时用唯一标识指定
# # 在customer索引下的external类型下保存1号数据
PUT customer/external/1
# POSTMAN输入
http://192.168.43.65:9200/customer/external/1
{
"name":"John Doe"
}
PUT和POST区别
-
POST新增。如果不指定id,会自动生成id。指定id就会修改这个数据,并新增版本号;
-
可以不指定id,不指定id时永远为创建
-
指定不存在的id为创建
-
指定存在的id为更新,而版本号会根据内容变没变而觉得版本号递增与否
-
-
PUT可以新增也可以修改。PUT必须指定id;由于PUT需要指定id,我们一般用来做修改操作,不指定id会报错。
-
必须指定id
-
版本号总会增加
-
-
怎么记:put和java里map.put一样必须指定key-value。而post相当于mysql insertseq_no和version的区别:
seq_no和version的区别: 每个文档的版本号"_version" 起始值都为1 每次对当前文档成功操作后都加1 而序列号"_seq_no"则可以看做是索引的信息 在第一次为索引插入数据时为0,每对索引内数据操作成功一次sqlNO加1, 并且文档会记录是第几次操作使它成为现在的情况的 可以参考https://www.cnblogs.com/Taeso/p/13363136.html
在postman中创建数据成功后,显示201 created表示插入记录成功。
返回数据:
带有下划线开头的,称为元数据,反映了当前的基本信息。
{
"_index": "customer", 表明该数据在哪个数据库下;
"_type": "external", 表明该数据在哪个类型下;
"_id": "1", 表明被保存数据的id;
"_version": 1, 被保存数据的版本
"result": "created", 这里是创建了一条数据,如果重新put一条数据,则该状态会变为updated,并且版本号也会发生变化。
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 0,
"_primary_term": 1
}
下面选用POST方式:
添加数据的时候,不指定ID,会自动的生成id,并且类型是新增:
{
"_index": "customer",
"_type": "external",
"_id": "5MIjvncBKdY1wAQm-wNZ",
"_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 11,
"_primary_term": 6
}
再次使用POST插入数据,不指定ID,仍然是新增的:
{
"_index": "customer",
"_type": "external",
"_id": "5cIkvncBKdY1wAQmcQNk",
"_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 12,
"_primary_term": 6
}
3)查看文档
GET /customer/external/1
http://192.168.43.65:9200/customer/external/1
{
"_index": "customer", // 在那个索引
"_type": "external", // 在哪个类型
"_id": "1", // 记录id
"_version": 10, // 版本号
"_seq_no": 18, //并发控制字段,每次更新都会+1,用来做乐观锁
"_primary_term": 6, //同上,主分片重新分配,如重启,就会变化
"found": true,
"_source": { // 真正的内容
"name": "John Doe"
}
}
乐观锁用法:通过“`if_seq_no=1&if_primary_term=1`”,当序列号匹配的时候,才进行修改,否则不修改。
实例:将id=1的数据更新为name=1,然后再次更新为name=2,起始1_seq_no=18,_primary_term=6
(1)将name更新为1
PUT http://192.168.43.65:9200/customer/external/1?if_seq_no=18&if_primary_term=6
(2)将name更新为2,更新过程中使用seq_no=18
PUT http://192.168.56.10:9200/customer/external/1?if_seq_no=18&if_primary_term=6
结果为:
{
"error": {
"root_cause": [
{
"type": "version_conflict_engine_exception",
"reason": "[1]: version conflict, required seqNo [18], primary term [6]. current document has seqNo [19] and primary term [6]",
"index_uuid": "mG9XiCQISPmfBAmL1BPqIw",
"shard": "0",
"index": "customer"
}
],
"type": "version_conflict_engine_exception",
"reason": "[1]: version conflict, required seqNo [18], primary term [6]. current document has seqNo [19] and primary term [6]",
"index_uuid": "mG9XiCQISPmfBAmL1BPqIw",
"shard": "0",
"index": "customer"
},
"status": 409
}
出现更新错误。
(3)查询新的数据
GET http://192.168.43.65:9200/customer/external/1
{
"_index": "customer",
"_type": "external",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 11,
"_seq_no": 19,
"_primary_term": 6,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"name": "1"
}
}
能够看到_seq_no变为19
(4)再次更新,更新成功
PUT http://192.168.56.10:9200/customer/external/1?if_seq_no=19&if_primary_term=1
4)更新文档_update
POST customer/externel/1/_update
{
"doc":{
"name":"111"
}
}
或者
POST customer/externel/1
{
"doc":{
"name":"222"
}
}
或者
PUT customer/externel/1
{
"doc":{
"name":"222"
}
}
不同:带有update情况下
-
POST操作会对比源文档数据,如果相同不会有什么操作,文档version不增加。
-
PUT操作总会重新保存并增加version版本 POST时带_update对比元数据如果一样就不进行任何操作。
看场景:
-
对于大并发更新,不带update
-
对于大并发查询偶尔更新,带update;对比更新,重新计算分配规则 (1)POST更新文档,带有_update
http://192.168.43.65:9200/customer/external/1/_update
如果再次执行更新,则不执行任何操作,序列号也不发生变化
返回
{
"_index": "customer",
"_type": "external",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 12,
"result": "noop", // 无操作
"_shards": {
"total": 0,
"successful": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 20,
"_primary_term": 6
}
POST更新方式,会对比原来的数据,和原来的相同,则不执行任何操作(version和_seq_no)都不变。
(2)POST更新文档,不带_update
在更新过程中,重复执行更新操作,数据也能够更新成功,不会和原来的数据进行对比。
{
"_index": "customer",
"_type": "external",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 13,
"result": "updated",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 21,
"_primary_term": 6
}
5)删除文档或索引
DELETE customer/external/1 DELETE customer
注:elasticsearch并没有提供删除类型的操作,只提供了删除索引和文档的操作。
实例:删除id=1的数据,删除后继续查询
DELETE http://192.168.43.65:9200/customer/external/1
{
"_index": "customer",
"_type": "external",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 14,
"result": "deleted",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 22,
"_primary_term": 6
}
再次执行DELETE http://192.168.43.65:9200/customer/external/1
{
"_index": "customer",
"_type": "external",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 15,
"result": "not_found",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 23,
"_primary_term": 6
}
GET http://192.168.43.65:9200/customer/external/1
{
"_index": "customer",
"_type": "external",
"_id": "1",
"found": false
}
删除索引
实例:删除整个costomer索引数据
删除前,所有的索引http://192.168.43.65:9200/_cat/indices
green open .kibana_task_manager_1 DhtDmKrsRDOUHPJm1EFVqQ 1 0 2 0 31.3kb 31.3kb green open .apm-agent-configuration vxzRbo9sQ1SvMtGkx6aAHQ 1 0 0 0 283b 283b green open .kibana_1 rdJ5pejQSKWjKxRtx-EIkQ 1 0 8 3 28.8kb 28.8kb yellow open customer mG9XiCQISPmfBAmL1BPqIw 1 1 9 1 8.6kb 8.6kb
删除“ customer ”索引
DELTE http://192.168.43.65:9200/customer
# 响应
{
"acknowledged": true
}
删除后,所有的索引http://192.168.43.65:9200/_cat/indices
green open .kibana_task_manager_1 DhtDmKrsRDOUHPJm1EFVqQ 1 0 2 0 31.3kb 31.3kb green open .apm-agent-configuration vxzRbo9sQ1SvMtGkx6aAHQ 1 0 0 0 283b 283b green open .kibana_1 rdJ5pejQSKWjKxRtx-EIkQ 1 0 8 3 28.8kb 28.8kb
6)ES的批量操作——bulk
匹配导入数据
POST http://192.168.43.65:9200/customer/external/_bulk
# 两行为一个整体
{"index":{"_id":"1"}}
{"name":"a"}
{"index":{"_id":"2"}}
{"name":"b"}
# 注意格式json和text均不可,要去kibana里Dev Tools
语法格式:
{action:{metadata}}\n
{request body }\n
{action:{metadata}}\n
{request body }\n
这里的批量操作,当发生某一条执行发生失败时,其他的数据仍然能够接着执行,也就是说彼此之间是独立的。
bulk api以此按顺序执行所有的action(动作)。如果一个单个的动作因任何原因失败,它将继续处理它后面剩余的动作。当bulk api返回时,它将提供每个动作的状态(与发送的顺序相同),所以您可以检查是否一个指定的动作是否失败了。 实例1: 执行多条数据
POST /customer/external/_bulk
{"index":{"_id":"1"}}
{"name":"John Doe"}
{"index":{"_id":"2"}}
{"name":"John Doe"}
执行结果
#! Deprecation: [types removal] Specifying types in bulk requests is deprecated.
{
"took" : 318, 花费了多少ms
"errors" : false, 没有发生任何错误
"items" : [ 每个数据的结果
{
"index" : { 保存
"_index" : "customer", 索引
"_type" : "external", 类型
"_id" : "1", 文档
"_version" : 1, 版本
"result" : "created", 创建
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 1,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 0,
"_primary_term" : 1,
"status" : 201 新建完成
}
},
{
"index" : { 第二条记录
"_index" : "customer",
"_type" : "external",
"_id" : "2",
"_version" : 1,
"result" : "created",
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 1,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 1,
"_primary_term" : 1,
"status" : 201
}
}
]
}
实例2:对于整个索引执行批量操作
POST /_bulk
{"delete":{"_index":"website","_type":"blog","_id":"123"}}
{"create":{"_index":"website","_type":"blog","_id":"123"}}
{"title":"my first blog post"}
{"index":{"_index":"website","_type":"blog"}}
{"title":"my second blog post"}
{"update":{"_index":"website","_type":"blog","_id":"123"}}
{"doc":{"title":"my updated blog post"}}
运行结果:
#! Deprecation: [types removal] Specifying types in bulk requests is deprecated.
{
"took" : 304,
"errors" : false,
"items" : [
{
"delete" : { 删除
"_index" : "website",
"_type" : "blog",
"_id" : "123",
"_version" : 1,
"result" : "not_found", 没有该记录
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 1,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 0,
"_primary_term" : 1,
"status" : 404 没有该
}
},
{
"create" : { 创建
"_index" : "website",
"_type" : "blog",
"_id" : "123",
"_version" : 2,
"result" : "created",
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 1,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 1,
"_primary_term" : 1,
"status" : 201
}
},
{
"index" : { 保存
"_index" : "website",
"_type" : "blog",
"_id" : "5sKNvncBKdY1wAQmeQNo",
"_version" : 1,
"result" : "created",
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 1,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 2,
"_primary_term" : 1,
"status" : 201
}
},
{
"update" : { 更新
"_index" : "website",
"_type" : "blog",
"_id" : "123",
"_version" : 3,
"result" : "updated",
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 1,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 3,
"_primary_term" : 1,
"status" : 200
}
}
]
}
7)样本测试数据
准备了一份顾客银行账户信息的虚构的JSON文档样本。每个文档都有下列的schema(模式)。
{
"account_number": 1,
"balance": 39225,
"firstname": "Amber",
"lastname": "Duke",
"age": 32,
"gender": "M",
"address": "880 Holmes Lane",
"employer": "Pyrami",
"email": "[email protected]",
"city": "Brogan",
"state": "IL"
}
es测试数据.json · 坐看云起时/common_content - Gitee.com,导入测试数据,
POST bank/account/_bulk
上面的数据
二、进阶检索
3.1)search检索文档
ES支持两种基本方式检索;
-
通过REST request uri 发送搜索参数 (uri +检索参数);
-
通过REST request body 来发送它们(uri+请求体);
信息检索
API:[Start searching | Elasticsearch Guide 7.5] | Elastic
请求参数方式检索 GET bank/_search?q=*&sort=account_number:asc 说明: q=* # 查询所有 sort # 排序字段 asc #升序 检索bank下所有信息,包括type和docs GET bank/_search
返回内容:
-
took – 花费多少ms搜索
-
timed_out – 是否超时
-
shards – 多少分片被搜索了,以及多少成功/失败的搜索分片
-
max_score –文档相关性最高得分
-
hits.total.value - 多少匹配文档被找到
-
hits.sort - 结果的排序key(列),没有的话按照score排序
-
hits._score - 相关得分 (not applicable when using match_all)
GET bank/_search?q=*&sort=account_number:asc 检索了1000条数据,但是根据相关性算法,只返回10条
uri+请求体进行检索
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": { "match_all": {} },
"sort": [
{ "account_number": "asc" },
{ "balance":"desc"}
]
POSTMAN中get不能携带请求体,我们变为post也是一样的,我们post一个jsob风格的查询请求体到_search
需要了解,一旦搜索的结果被返回,es就完成了这次请求,不能切不会维护任何服务端的资源或者结果的cursor游标
3.2)DSL领域特定语言
这节教我们如何写复杂查询
Elasticsearch提供了一个可以执行查询的Json风格的DSL(domain-specific language领域特定语言)。这个被称为Query DSL,该查询语言非常全面。
(1)基本语法格式
一个查询语句的典型结构
# 如果针对于某个字段,那么它的结构如下:
{
QUERY_NAME:{ # 使用的功能
FIELD_NAME:{ # 功能参数
ARGUMENT:VALUE,
ARGUMENT:VALUE,...
}
}
}
# 示例 使用时不要加#注释内容
GET bank/_search
{
"query": { # 查询的字段
"match_all": {}
},
"from": 0, # 从第几条文档开始查
"size": 5,
"_source":["balance"],
"sort": [
{
"account_number": { # 返回结果按哪个列排序
"order": "desc" # 降序
}
}
]
}
_source为要返回的字段
query定义如何查询;
match_all查询类型【代表查询所有的索引】,es中可以在query中组合非常多的查询类型完成复杂查询; 除了query参数之外,我们可也传递其他的参数以改变查询结果,如sort,size; from+size限定,完成分页功能; sort排序,多字段排序,会在前序字段相等时后续字段内部排序,否则以前序为准;
(2)from返回部分字段
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"from": 0,
"size": 5,
"sort": [
{
"account_number": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
],
"_source": ["balance","firstname"]
}
查询结果:
{
"took" : 18, # 花了18ms
"timed_out" : false, # 没有超时
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1000, # 命令1000条
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "bank",
"_type" : "account",
"_id" : "999", # 第一条数据id是999
"_score" : null, # 得分信息
"_source" : {
"firstname" : "Dorothy",
"balance" : 6087
},
"sort" : [ # 排序字段的值
999
]
},
省略。。。
(3)query/match匹配查询
如果是非字符串,会进行精确匹配。如果是字符串,会进行全文检索
-
基本类型(非字符串),精确控制
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"account_number": "20"
}
}
}
match返回account_number=20的数据。
查询结果:
{
"took" : 1,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1, // 得到一条
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.0, # 最大得分
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "bank",
"_type" : "account",
"_id" : "20",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : { # 该条文档信息
"account_number" : 20,
"balance" : 16418,
"firstname" : "Elinor",
"lastname" : "Ratliff",
"age" : 36,
"gender" : "M",
"address" : "282 Kings Place",
"employer" : "Scentric",
"email" : "[email protected]",
"city" : "Ribera",
"state" : "WA"
}
}
]
}
}
-
字符串,全文检索
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"address": "kings"
}
}
}
全文检索,最终会按照评分进行排序,会对检索条件进行分词匹配。
查询结果:
{
"took" : 30,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 2,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 5.990829,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "bank",
"_type" : "account",
"_id" : "20",
"_score" : 5.990829,
"_source" : {
"account_number" : 20,
"balance" : 16418,
"firstname" : "Elinor",
"lastname" : "Ratliff",
"age" : 36,
"gender" : "M",
"address" : "282 Kings Place",
"employer" : "Scentric",
"email" : "[email protected]",
"city" : "Ribera",
"state" : "WA"
}
},
{
"_index" : "bank",
"_type" : "account",
"_id" : "722",
"_score" : 5.990829,
"_source" : {
"account_number" : 722,
"balance" : 27256,
"firstname" : "Roberts",
"lastname" : "Beasley",
"age" : 34,
"gender" : "F",
"address" : "305 Kings Hwy",
"employer" : "Quintity",
"email" : "[email protected]",
"city" : "Hayden",
"state" : "PA"
}
}
]
}
}
(4) query/match_phrase [不拆分匹配]
将需要匹配的值当成一整个单词(不分词)进行检索
-
match_phrase:不拆分字符串进行检索 -
字段.keyword:必须全匹配上才检索成功
前面的是包含mill或road就查出来,我们现在要都包含才查出
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"address": "mill road" # 就是说不要匹配只有mill或只有road的,要匹配mill road一整个子串
}
}
}
查处address中包含mill road的所有记录,并给出相关性得分
查看结果:
{
"took" : 32,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 8.926605,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "bank",
"_type" : "account",
"_id" : "970",
"_score" : 8.926605,
"_source" : {
"account_number" : 970,
"balance" : 19648,
"firstname" : "Forbes",
"lastname" : "Wallace",
"age" : 28,
"gender" : "M",
"address" : "990 Mill Road", # "mill road"
"employer" : "Pheast",
"email" : "[email protected]",
"city" : "Lopezo",
"state" : "AK"
}
}
]
}
}
match_phrase和match的区别,观察如下实例:
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"address": "990 Mill"
}
}
}
查询结果:
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1, # 1
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 10.806405,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "bank",
"_type" : "account",
"_id" : "970",
"_score" : 10.806405,
"_source" : {
"account_number" : 970,
"balance" : 19648,
"firstname" : "Forbes",
"lastname" : "Wallace",
"age" : 28,
"gender" : "M",
"address" : "990 Mill Road", # "990 Mill"
"employer" : "Pheast",
"email" : "[email protected]",
"city" : "Lopezo",
"state" : "AK"
}
}
]
}
}
使用match的keyword
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"address.keyword": "990 Mill" # 字段后面加上 .keyword
}
}
}
查询结果,一条也未匹配到
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 0, # 因为要求完全equal,所以匹配不到
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
}
}
修改匹配条件为“990 Mill Road”
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"address.keyword": "990 Mill Road" # 正好有这条文档,所以能匹配到
}
}
}
查询出一条数据
{
"took" : 1,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1, # 1
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 6.5032897,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "bank",
"_type" : "account",
"_id" : "970",
"_score" : 6.5032897,
"_source" : {
"account_number" : 970,
"balance" : 19648,
"firstname" : "Forbes",
"lastname" : "Wallace",
"age" : 28,
"gender" : "M",
"address" : "990 Mill Road", # equal
"employer" : "Pheast",
"email" : "[email protected]",
"city" : "Lopezo",
"state" : "AK"
}
}
]
}
}
文本字段的匹配,使用keyword,匹配的条件就是要显示字段的全部值,要进行精确匹配的。
match_phrase是做短语匹配,只要文本中包含匹配条件,就能匹配到。
(5)query/multi_math【多字段匹配】
state或者address中包含mill,并且在查询过程中,会对于查询条件进行分词。
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": { # 前面的match仅指定了一个字段。
"query": "mill",
"fields": [ # state和address有mill子串 不要求都有
"state",
"address"
]
}
}
}
查询结果:
{
"took" : 28,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 4,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 5.4032025,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "bank",
"_type" : "account",
"_id" : "970",
"_score" : 5.4032025,
"_source" : {
"account_number" : 970,
"balance" : 19648,
"firstname" : "Forbes",
"lastname" : "Wallace",
"age" : 28,
"gender" : "M",
"address" : "990 Mill Road", # 有mill
"employer" : "Pheast",
"email" : "[email protected]",
"city" : "Lopezo",
"state" : "AK" # 没有mill
}
},
{
"_index" : "bank",
"_type" : "account",
"_id" : "136",
"_score" : 5.4032025,
"_source" : {
"account_number" : 136,
"balance" : 45801,
"firstname" : "Winnie",
"lastname" : "Holland",
"age" : 38,
"gender" : "M",
"address" : "198 Mill Lane", # mill
"employer" : "Neteria",
"email" : "[email protected]",
"city" : "Urie",
"state" : "IL" # 没有mill
}
},
{
"_index" : "bank",
"_type" : "account",
"_id" : "345",
"_score" : 5.4032025,
"_source" : {
"account_number" : 345,
"balance" : 9812,
"firstname" : "Parker",
"lastname" : "Hines",
"age" : 38,
"gender" : "M",
"address" : "715 Mill Avenue", #
"employer" : "Baluba",
"email" : "[email protected]",
"city" : "Blackgum",
"state" : "KY" # 没有mill
}
},
{
"_index" : "bank",
"_type" : "account",
"_id" : "472",
"_score" : 5.4032025,
"_source" : {
"account_number" : 472,
"balance" : 25571,
"firstname" : "Lee",
"lastname" : "Long",
"age" : 32,
"gender" : "F",
"address" : "288 Mill Street", #
"employer" : "Comverges",
"email" : "[email protected]",
"city" : "Movico",
"state" : "MT" # 没有mill
}
}
]
}
}
(6)query/bool/must复合查询 复合语句可以合并,任何其他查询语句,包括符合语句。这也就意味着,复合语句之间可以互相嵌套,可以表达非常复杂的逻辑。
-
must:必须达到must所列举的所有条件
-
must_not:必须不匹配must_not所列举的所有条件。
-
should:应该满足should所列举的条件。满足条件最好,不满足也可以,满足得分更高 实例:查询gender=m,并且address=mill的数据
GET bank/_search
{
"query":{
"bool":{ #
"must":[ # 必须有这些字段
{"match":{"address":"mill"}},
{"match":{"gender":"M"}}
]
}
}
}
查询结果:
{
"took" : 1,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 3,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 6.0824604,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "bank",
"_type" : "account",
"_id" : "970",
"_score" : 6.0824604,
"_source" : {
"account_number" : 970,
"balance" : 19648,
"firstname" : "Forbes",
"lastname" : "Wallace",
"age" : 28,
"gender" : "M", # M
"address" : "990 Mill Road", # mill
"employer" : "Pheast",
"email" : "[email protected]",
"city" : "Lopezo",
"state" : "AK"
}
},
{
"_index" : "bank",
"_type" : "account",
"_id" : "136",
"_score" : 6.0824604,
"_source" : {
"account_number" : 136,
"balance" : 45801,
"firstname" : "Winnie",
"lastname" : "Holland",
"age" : 38,
"gender" : "M", #
"address" : "198 Mill Lane", #
"employer" : "Neteria",
"email" : "[email protected]",
"city" : "Urie",
"state" : "IL"
}
},
{
"_index" : "bank",
"_type" : "account",
"_id" : "345",
"_score" : 6.0824604,
"_source" : {
"account_number" : 345,
"balance" : 9812,
"firstname" : "Parker",
"lastname" : "Hines",
"age" : 38,
"gender" : "M", #
"address" : "715 Mill Avenue", #
"employer" : "Baluba",
"email" : "[email protected]",
"city" : "Blackgum",
"state" : "KY"
}
}
]
}
}
must_not:必须不是指定的情况
实例:查询gender=m,并且address=mill的数据,但是age不等于38的
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{ "match": { "gender": "M" }},
{ "match": {"address": "mill"}}
],
"must_not": [ # 不可以是指定值
{ "match": { "age": "38" }}
]
}
}
查询结果:
{
"took" : 4,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 6.0824604,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "bank",
"_type" : "account",
"_id" : "970",
"_score" : 6.0824604,
"_source" : {
"account_number" : 970,
"balance" : 19648,
"firstname" : "Forbes",
"lastname" : "Wallace",
"age" : 28, # 不是38
"gender" : "M", #
"address" : "990 Mill Road", #
"employer" : "Pheast",
"email" : "[email protected]",
"city" : "Lopezo",
"state" : "AK"
}
}
]
}
}
should:应该达到should列举的条件,如果到达会增加相关文档的评分,并不会改变查询的结果。如果query中只有should且只有一种匹配规则,那么should的条件就会被作为默认匹配条件二区改变查询结果。
实例:匹配lastName应该等于Wallace的数据
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"gender": "M"
}
},
{
"match": {
"address": "mill"
}
}
],
"must_not": [
{
"match": {
"age": "18"
}
}
],
"should": [
{
"match": {
"lastname": "Wallace"
}
}
]
}
}
}
查询结果:
{
"took" : 5,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 3,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 12.585751,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "bank",
"_type" : "account",
"_id" : "970",
"_score" : 12.585751,
"_source" : {
"account_number" : 970,
"balance" : 19648,
"firstname" : "Forbes",
"lastname" : "Wallace", # 因为匹配了should,所以得分第一
"age" : 28, # 不是18
"gender" : "M", #
"address" : "990 Mill Road", #
"employer" : "Pheast",
"email" : "[email protected]",
"city" : "Lopezo",
"state" : "AK"
}
},
{
"_index" : "bank",
"_type" : "account",
"_id" : "136",
"_score" : 6.0824604,
"_source" : {
"account_number" : 136,
"balance" : 45801,
"firstname" : "Winnie",
"lastname" : "Holland",
"age" : 38,
"gender" : "M",
"address" : "198 Mill Lane",
"employer" : "Neteria",
"email" : "[email protected]",
"city" : "Urie",
"state" : "IL"
}
},
{
"_index" : "bank",
"_type" : "account",
"_id" : "345",
"_score" : 6.0824604,
"_source" : {
"account_number" : 345,
"balance" : 9812,
"firstname" : "Parker",
"lastname" : "Hines",
"age" : 38,
"gender" : "M",
"address" : "715 Mill Avenue",
"employer" : "Baluba",
"email" : "[email protected]",
"city" : "Blackgum",
"state" : "KY"
}
}
]
}
}
能够看到相关度越高,得分也越高。
(7)query/filter【结果过滤】
-
must 贡献得分
-
should 贡献得分
-
must_not 不贡献得分
-
filter 不贡献得分
上面的must和should影响相关性得分,而must_not仅仅是一个filter ,不贡献得分 must改为filter就使must不贡献得分 如果只有filter条件的话,我们会发现得分都是0 一个key多个值可以用terms
并不是所有的查询都需要产生分数,特别是哪些仅用于filtering过滤的文档。为了不计算分数,elasticsearch会自动检查场景并且优化查询的执行。
不参与评分更快
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{ "match": {"address": "mill" } }
],
"filter": { # query.bool.filter
"range": {
"balance": { # 哪个字段
"gte": "10000",
"lte": "20000"
}
}
}
}
}
}
这里先是查询所有匹配address=mill的文档,然后再根据10000<=balance<=20000进行过滤查询结果
查询结果:
{
"took" : 2,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 5.4032025,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "bank",
"_type" : "account",
"_id" : "970",
"_score" : 5.4032025,
"_source" : {
"account_number" : 970,
"balance" : 19648, # 1W到2W之间
"firstname" : "Forbes",
"lastname" : "Wallace",
"age" : 28,
"gender" : "M",
"address" : "990 Mill Road", #
"employer" : "Pheast",
"email" : "[email protected]",
"city" : "Lopezo",
"state" : "AK"
}
}
]
}
}
Each must,should, and must_not element in a Boolean query is referred to as a query clause. How well a document meets the criteria in each must or should clause contributes to the document’s relevance score. The higher the score, the better the document matches your search criteria. By default, Elasticsearch returns documents ranked by these relevance scores.
在boolean查询中,must, should 和must_not 元素都被称为查询子句 。 文档是否符合每个“must”或“should”子句中的标准,决定了文档的“相关性得分”。 得分越高,文档越符合您的搜索条件。 默认情况下,Elasticsearch返回根据这些相关性得分排序的文档。
The criteria in a must_not clause is treated as a filter. It affects whether or not the document is included in the results, but does not contribute to how documents are scored. You can also explicitly specify arbitrary filters to include or exclude documents based on structured data.
“must_not”子句中的条件被视为“过滤器”。 它影响文档是否包含在结果中, 但不影响文档的评分方式。 还可以显式地指定任意过滤器来包含或排除基于结构化数据的文档。
filter在使用过程中,并不会计算相关性得分:
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"address": "mill"
}
}
],
"filter": {
"range": {
"balance": {
"gte": "10000",
"lte": "20000"
}
}
}
}
}
}
查询结果:
{
"took" : 1,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 213,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 0.0,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "bank",
"_type" : "account",
"_id" : "20",
"_score" : 0.0,
"_source" : {
"account_number" : 20,
"balance" : 16418,
"firstname" : "Elinor",
"lastname" : "Ratliff",
"age" : 36,
"gender" : "M",
"address" : "282 Kings Place",
"employer" : "Scentric",
"email" : "[email protected]",
"city" : "Ribera",
"state" : "WA"
}
},
{
"_index" : "bank",
"_type" : "account",
"_id" : "37",
"_score" : 0.0,
"_source" : {
"account_number" : 37,
"balance" : 18612,
"firstname" : "Mcgee",
"lastname" : "Mooney",
"age" : 39,
"gender" : "M",
"address" : "826 Fillmore Place",
"employer" : "Reversus",
"email" : "[email protected]",
"city" : "Tooleville",
"state" : "OK"
}
},
省略。。。
能看到所有文档的 “_score” : 0.0。
(8)query/term
和match一样。匹配某个属性的值。
-
全文检索字段用match,
-
其他非text字段匹配用term。
不要使用term来进行文本字段查询
es默认存储text值时用分词分析,所以要搜索text值,使用match
Term query | Elasticsearch Guide [7.6] | Elastic
-
字段.keyword:要一一匹配到
-
match_phrase:子串包含即可
使用term匹配查询
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"address": "mill Road"
}
}
}
查询结果:
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 0, # 没有
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
}
}
一条也没有匹配到
而更换为match匹配时,能够匹配到32个文档
{
"took" : 5,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 32,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 8.926605,
"hits" : [
也就是说,全文检索字段用match,其他非text字段匹配用term。
(9)aggs/agg1(聚合)
前面介绍了存储、检索,但还没介绍分析
聚合提供了从数据中分组和提取数据的能力。最简单的聚合方法大致等于SQL Group by和SQL聚合函数。
在elasticsearch中,执行搜索返回this(命中结果),并且同时返回聚合结果,把以响应中的所有hits(命中结果)分隔开的能力。这是非常强大且有效的,你可以执行查询和多个聚合,并且在一次使用中得到各自的(任何一个的)返回结果,使用一次简洁和简化的API啦避免网络往返。
aggs:执行聚合。聚合语法如下:
"aggs":{ # 聚合
"aggs_name":{ # 这次聚合的名字,方便展示在结果集中
"AGG_TYPE":{} # 聚合的类型(avg,term,terms)
}
}
-
terms:看值的可能性分布,会合并锁查字段,给出计数即可
-
avg:看值的分布平均
例:搜索address中包含mill的所有人的年龄分布以及平均年龄,但不显示这些人的详情
# 分别为包含mill、,平均年龄、
GET bank/_search
{
"query": { # 查询出包含mill的
"match": {
"address": "Mill"
}
},
"aggs": { #基于查询聚合
"ageAgg": { # 聚合的名字,随便起
"terms": { # 看值的可能性分布
"field": "age",
"size": 10
},
"ageAvg": {
"avg": { # 看age值的平均
"field": "age"
}
},
"balanceAvg": {
"avg": { # 看balance的平均
"field": "balance"
}
}
},
"size": 0 # 不看详情
}
查询结果:
{
"took" : 2,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 4, // 命中4条
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"ageAgg" : { // 第一个聚合的结果
"doc_count_error_upper_bound" : 0,
"sum_other_doc_count" : 0,
"buckets" : [
{
"key" : 38, # age为38的有2条
"doc_count" : 2
},
{
"key" : 28,
"doc_count" : 1
},
{
"key" : 32,
"doc_count" : 1
}
]
},
"ageAvg" : { // 第二个聚合的结果
"value" : 34.0 # balance字段的平均值是34
},
"balanceAvg" : {
"value" : 25208.0
}
}
}
aggs/aggName/aggs/aggName子聚合
复杂: 按照年龄聚合,并且求这些年龄段的这些人的平均薪资
写到一个聚合里是基于上个聚合进行子聚合。 下面求每个age分布的平均balance
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"aggs": {
"ageAgg": {
"terms": { # 看分布
"field": "age",
"size": 100
},
"aggs": { # 与terms并列
"ageAvg": { #平均
"avg": {
"field": "balance"
}
}
}
}
},
"size": 0 # 显示0条hits数组记录
}
输出结果:
{
"took" : 49,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1000,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"ageAgg" : {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound" : 0,
"sum_other_doc_count" : 0,
"buckets" : [
{
"key" : 31,
"doc_count" : 61,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 28312.918032786885
}
},
{
"key" : 39,
"doc_count" : 60,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 25269.583333333332
}
},
{
"key" : 26,
"doc_count" : 59,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 23194.813559322032
}
},
{
"key" : 32,
"doc_count" : 52,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 23951.346153846152
}
},
{
"key" : 35,
"doc_count" : 52,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 22136.69230769231
}
},
{
"key" : 36,
"doc_count" : 52,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 22174.71153846154
}
},
{
"key" : 22,
"doc_count" : 51,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 24731.07843137255
}
},
{
"key" : 28,
"doc_count" : 51,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 28273.882352941175
}
},
{
"key" : 33,
"doc_count" : 50,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 25093.94
}
},
{
"key" : 34,
"doc_count" : 49,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 26809.95918367347
}
},
{
"key" : 30,
"doc_count" : 47,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 22841.106382978724
}
},
{
"key" : 21,
"doc_count" : 46,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 26981.434782608696
}
},
{
"key" : 40,
"doc_count" : 45,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 27183.17777777778
}
},
{
"key" : 20,
"doc_count" : 44,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 27741.227272727272
}
},
{
"key" : 23,
"doc_count" : 42,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 27314.214285714286
}
},
{
"key" : 24,
"doc_count" : 42,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 28519.04761904762
}
},
{
"key" : 25,
"doc_count" : 42,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 27445.214285714286
}
},
{
"key" : 37,
"doc_count" : 42,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 27022.261904761905
}
},
{
"key" : 27,
"doc_count" : 39,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 21471.871794871793
}
},
{
"key" : 38,
"doc_count" : 39,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 26187.17948717949
}
},
{
"key" : 29,
"doc_count" : 35,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 29483.14285714286
}
}
]
}
}
}
复杂子聚合:查出所有年龄分布,并且这些年龄段中M的平均薪资和F的平均薪资以及这个年龄段的总体平均薪资
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"aggs": {
"ageAgg": {
"terms": { # 看age分布
"field": "age",
"size": 100
},
"aggs": { # 子聚合
"genderAgg": {
"terms": { # 看gender分布
"field": "gender.keyword" # 注意这里,文本字段应该用.keyword
},
"aggs": { # 子聚合
"balanceAvg": {
"avg": { # 男性的平均
"field": "balance"
}
}
}
},
"ageBalanceAvg": {
"avg": { #age分布的平均(男女)
"field": "balance"
}
}
}
}
},
"size": 0
}
输出结果:
{
"took" : 119,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1000,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"ageAgg" : {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound" : 0,
"sum_other_doc_count" : 0,
"buckets" : [
{
"key" : 31,
"doc_count" : 61,
"genderAgg" : {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound" : 0,
"sum_other_doc_count" : 0,
"buckets" : [
{
"key" : "M",
"doc_count" : 35,
"balanceAvg" : {
"value" : 29565.628571428573
}
},
{
"key" : "F",
"doc_count" : 26,
"balanceAvg" : {
"value" : 26626.576923076922
}
}
]
},
"ageBalanceAvg" : {
"value" : 28312.918032786885
}
}
]
.......//省略其他
}
}
}
nested对象聚合
属性是"type": “nested”,因为是内部的属性进行检索
数组类型的对象会被扁平化处理(对象的每个属性会分别存储到一起)
user.name=["aaa","bbb"]
user.addr=["ccc","ddd"]
# 这种存储方式,可能会发生如下错误:
# 错误检索到{aaa,ddd},这个组合是不存在的
数组的扁平化处理会使检索能检索到本身不存在的,为了解决这个问题,就采用了嵌入式属性,数组里是对象时用嵌入式属性(不是对象无需用嵌入式属性)
nested阅读:ElasticSearch - 嵌套对象 nested_kucw的博客-CSDN博客_es nested
使用聚合:Elastic search中使用nested类型的内嵌对象_大神带我来搬砖的博客-CSDN博客
GET articles/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"nested": { #
"nested": { #
"path": "payment"
},
"aggs": {
"amount_avg": {
"avg": {
"field": "payment.amount"
}
}
}
}
}
}
三、Mapping字段映射
映射定义文档如何被存储和检索的
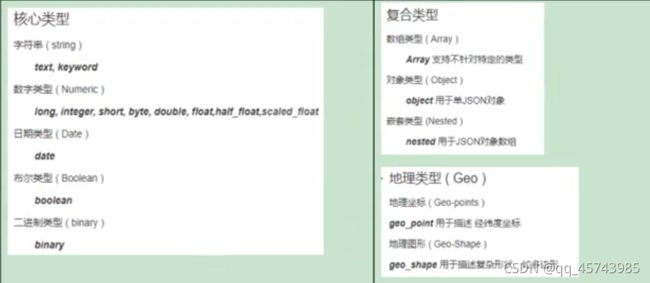
(1)字段类型
Field data types | Elasticsearch Guide [7.x] | Elastic
-
核心类型
-
复合类型
-
地理类型
-
特定类型
核心数据类型
(1)字符串
-
text⽤于全⽂索引,搜索时会自动使用分词器进⾏分词再匹配 -
keyword不分词,搜索时需要匹配完整的值 (2)数值型 -
整型: byte,short,integer,long
-
浮点型: float, half_float, scaled_float,double (3)日期类型:date
(4)范围型
integer_range, long_range, float_range,double_range,date_range
gt是大于,lt是小于,e是equals等于。
age_limit的区间包含了此值的文档都算是匹配。
(5)布尔
-
boolean
(6)二进制
-
binary 会把值当做经过 base64 编码的字符串,默认不存储,且不可搜索
复杂数据类型
(1)对象
-
object一个对象中可以嵌套对象。
(2)数组
-
Array
嵌套类型
-
nested 用于json对象数组
(2)映射
Mapping(映射)是用来定义一个文档(document),以及它所包含的属性(field)是如何存储和索引的。比如:使用maping来定义:
-
哪些字符串属性应该被看做全文本属性(full text fields);
-
哪些属性包含数字,日期或地理位置;
-
文档中的所有属性是否都嫩被索引(all 配置);
-
日期的格式;
-
自定义映射规则来执行动态添加属性;
-
查看mapping信息:GET bank/_mapping
{
"bank" : {
"mappings" : {
"properties" : {
"account_number" : {
"type" : "long" # long类型
},
"address" : {
"type" : "text", # 文本类型,会进行全文检索,进行分词
"fields" : {
"keyword" : { # addrss.keyword
"type" : "keyword", # 该字段必须全部匹配到
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"age" : {
"type" : "long"
},
"balance" : {
"type" : "long"
},
"city" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"email" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"employer" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"firstname" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"gender" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"lastname" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"state" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
-
修改mapping信息
(3)新版本改变
ElasticSearch7-去掉type概念
-
关系型数据库中两个数据表示是独立的,即使他们里面有相同名称的列也不影响使用,但ES中不是这样的。elasticsearch是基于Lucene开发的搜索引擎,而ES中不同type下名称相同的filed最终在Lucene中的处理方式是一样的。
-
两个不同type下的两个user_name,在ES同一个索引下其实被认为是同一个filed,你必须在两个不同的type中定义相同的filed映射。否则,不同type中的相同字段名称就会在处理中出现冲突的情况,导致Lucene处理效率下降。
-
去掉type就是为了提高ES处理数据的效率。
-
-
Elasticsearch 7.x URL中的type参数为可选。比如,索引一个文档不再要求提供文档类型。
-
Elasticsearch 8.x 不再支持URL中的type参数。
-
解决: 将索引从多类型迁移到单类型,每种类型文档一个独立索引
将已存在的索引下的类型数据,全部迁移到指定位置即可。详见数据迁移
Elasticsearch 7.x
Specifying types in requests is deprecated. For instance, indexing a document no longer requires a document type. The new index APIs are PUT {index}/_doc/{id} in case of explicit ids and POST {index}/_doc for auto-generated ids. Note that in 7.0, _doc is a permanent part of the path, and represents the endpoint name rather than the document type.
The include_type_name parameter in the index creation, index template, and mapping APIs will default to false. Setting the parameter at all will result in a deprecation warning.
The _default_ mapping type is removed.
Elasticsearch 8.x
Specifying types in requests is no longer supported.
The include_type_name parameter is removed.
创建映射PUT /my_index
第一次存储数据的时候es就猜出了映射 第一次存储数据前可以指定映射
创建索引并指定映射
PUT /my_index
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"age": {
"type": "integer"
},
"email": {
"type": "keyword" # 指定为keyword
},
"name": {
"type": "text" # 全文检索。保存时候分词,检索时候进行分词匹配
}
}
}
}
输出:
{
"acknowledged" : true,
"shards_acknowledged" : true,
"index" : "my_index"
}
查看映射GET /my_index
GET /my_index
输出结果:
{
"my_index" : {
"aliases" : { },
"mappings" : {
"properties" : {
"age" : {
"type" : "integer"
},
"email" : {
"type" : "keyword"
},
"employee-id" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"index" : false
},
"name" : {
"type" : "text"
}
}
},
"settings" : {
"index" : {
"creation_date" : "1588410780774",
"number_of_shards" : "1",
"number_of_replicas" : "1",
"uuid" : "ua0lXhtkQCOmn7Kh3iUu0w",
"version" : {
"created" : "7060299"
},
"provided_name" : "my_index"
}
}
}
}
添加新的字段映射PUT /my_index/_mapping
PUT /my_index/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"employee-id": {
"type": "keyword",
"index": false # 字段不能被检索。检索
}
}
}
这里的 “index”: false,表明新增的字段不能被检索,只是一个冗余字段。
不能更新映射
对于已经存在的字段映射,我们不能更新。更新必须创建新的索引,进行数据迁移。
数据迁移
先创建new_twitter的正确映射。
然后使用如下方式进行数据迁移。
6.0以后写法
POST reindex
{
"source":{
"index":"twitter"
},
"dest":{
"index":"new_twitters"
}
}
老版本写法
POST reindex
{
"source":{
"index":"twitter",
"twitter":"twitter"
},
"dest":{
"index":"new_twitters"
}
}
更多详情见: Reindex API | Elasticsearch Guide [7.6] | Elastic
案例:原来类型为account,新版本没有类型了,所以我们把他去掉
GET /bank/_search
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1000,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.0,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "bank",
"_type" : "account",//原来类型为account,新版本没有类型了,所以我们把他去掉
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"account_number" : 1,
"balance" : 39225,
"firstname" : "Amber",
"lastname" : "Duke",
"age" : 32,
"gender" : "M",
"address" : "880 Holmes Lane",
"employer" : "Pyrami",
"email" : "[email protected]",
"city" : "Brogan",
"state" : "IL"
}
},
...
GET /bank/_search
查出
"age":{"type":"long"}
想要将年龄修改为integer
先创建新的索引
PUT /newbank
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"account_number": {
"type": "long"
},
"address": {
"type": "text"
},
"age": {
"type": "integer"
},
"balance": {
"type": "long"
},
"city": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"email": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"employer": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"firstname": {
"type": "text"
},
"gender": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"lastname": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
},
"state": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
查看“newbank”的映射:
GET /newbank/_mapping
# 能够看到age的映射类型被修改为了integer.
"age":{"type":"integer"}
将bank中的数据迁移到newbank中
POST _reindex
{
"source": {
"index": "bank",
"type": "account"
},
"dest": {
"index": "newbank"
}
}
运行输出:
#! Deprecation: [types removal] Specifying types in reindex requests is deprecated.
{
"took" : 768,
"timed_out" : false,
"total" : 1000,
"updated" : 0,
"created" : 1000,
"deleted" : 0,
"batches" : 1,
"version_conflicts" : 0,
"noops" : 0,
"retries" : {
"bulk" : 0,
"search" : 0
},
"throttled_millis" : 0,
"requests_per_second" : -1.0,
"throttled_until_millis" : 0,
"failures" : [ ]
}
查看newbank中的数据
GET /newbank/_search
输出
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1000,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.0,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "newbank",
"_type" : "_doc", # 没有了类型
四、分词
一个tokenizer(分词器)接收一个字符流,将之分割为独立的tokens(词元,通常是独立的单词),然后输出tokens流。
例如:whitespace tokenizer遇到空白字符时分割文本。它会将文本"Quick brown fox!"分割为[Quick,brown,fox!]
该tokenizer(分词器)还负责记录各个terms(词条)的顺序或position位置(用于phrase短语和word proximity词近邻查询),以及term(词条)所代表的原始word(单词)的start(起始)和end(结束)的character offsets(字符串偏移量)(用于高亮显示搜索的内容)。
elasticsearch提供了很多内置的分词器(标准分词器),可以用来构建custom analyzers(自定义分词器)。
关于分词器: Text analysis | Elasticsearch Guide [7.6] | Elastic
POST _analyze
{
"analyzer": "standard",
"text": "The 2 Brown-Foxes bone."
}
执行结果:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "the",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 3,
"type" : "",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "2",
"start_offset" : 4,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "brown",
"start_offset" : 6,
"end_offset" : 11,
"type" : "",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "foxes",
"start_offset" : 12,
"end_offset" : 17,
"type" : "",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "bone",
"start_offset" : 18,
"end_offset" : 22,
"type" : "",
"position" : 4
}
]
}
对于中文,我们需要安装额外的分词器
1 安装ik分词器
所有的语言分词,默认使用的都是“Standard Analyzer”,但是这些分词器针对于中文的分词,并不友好。为此需要安装中文的分词器。
注意:不能用默认elasticsearch-plugin install xxx.zip 进行自动安装 https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik/releases
在前面安装的elasticsearch时,我们已经将elasticsearch容器的“/usr/share/elasticsearch/plugins”目录,映射到宿主机的“ /mydata/elasticsearch/plugins”目录下,所以比较方便的做法就是下载“/elasticsearch-analysis-ik-7.4.2.zip”文件,然后解压到该文件夹下即可。安装完毕后,需要重启elasticsearch容器。
如果不嫌麻烦,还可以采用如下的方式。
1)查看elasticsearch版本号:
[vagrant@localhost ~]$ curl http://localhost:9200
{
"name" : "66718a266132",
"cluster_name" : "elasticsearch",
"cluster_uuid" : "xhDnsLynQ3WyRdYmQk5xhQ",
"version" : {
"number" : "7.4.2",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "docker",
"build_hash" : "2f90bbf7b93631e52bafb59b3b049cb44ec25e96",
"build_date" : "2019-10-28T20:40:44.881551Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "8.2.0",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "6.8.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "6.0.0-beta1"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
2)进入es容器内部plugin目录
-
docker exec -it 容器id /bin/bash (docker exec :在运行的容器中执行命令) (-it:交互模式)
-
docker exec [OPTIONS] CONTAINER COMMAND [ARG...]
OPTIONS说明:
-
-d :分离模式: 在后台运行
-
-i :即使没有附加也保持STDIN 打开
-
-t :分配一个伪终端
-
[vagrant@localhost ~]$ sudo docker exec -it elasticsearch /bin/bash [root@66718a266132 elasticsearch]# pwd /usr/share/elasticsearch [root@66718a266132 elasticsearch]# pwd /usr/share/elasticsearch [root@66718a266132 elasticsearch]# yum install wget #下载ik7.4.2 [root@66718a266132 elasticsearch]# wget https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik/releases/download/v7.4.2/elasticsearch-analysis-ik-7.4.2.zip
-
unzip 下载的文件
[root@66718a266132 elasticsearch]# unzip elasticsearch-analysis-ik-7.4.2.zip -d ik #移动到plugins目录下 [root@66718a266132 elasticsearch]# mv ik plugins/ chmod -R 777 plugins/ik docker restart elasticsearch
-
rm -rf *.zip
[root@66718a266132 elasticsearch]# rm -rf elasticsearch-analysis-ik-7.6.2.zip
确认是否安装好了分词器
2 测试分词器
使用默认分词器
GET _analyze
{
"text":"我是中国人"
}
观察执行结果:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "我",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 1,
"type" : "",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "是",
"start_offset" : 1,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "中",
"start_offset" : 2,
"end_offset" : 3,
"type" : "",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "国",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 4,
"type" : "",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "人",
"start_offset" : 4,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "",
"position" : 4
}
]
}
GET _analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_smart",
"text":"我是中国人"
}
输出结果:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "我",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 1,
"type" : "CN_CHAR",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "是",
"start_offset" : 1,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "CN_CHAR",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "中国人",
"start_offset" : 2,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 2
}
]
}
GET _analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"text":"我是中国人"
}
输出结果:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "我",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 1,
"type" : "CN_CHAR",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "是",
"start_offset" : 1,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "CN_CHAR",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "中国人",
"start_offset" : 2,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "中国",
"start_offset" : 2,
"end_offset" : 4,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "国人",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 4
}
]
}
3 自定义词库
-
修改/usr/share/elasticsearch/plugins/ik/config中的IKAnalyzer.cfg.xml
IK Analyzer 扩展配置 http://192.168.43.65/es/fenci.txt
修改完成后,需要重启elasticsearch容器,否则修改不生效。docker restart elasticsearch
更新完成后,es只会对于新增的数据用更新分词。历史数据是不会重新分词的。如果想要历史数据重新分词,需要执行:
POST my_index/_update_by_query?conflicts=proceed
安装笔记1里的安装nginx安装好nginx
mkdir /mydata/nginx/html/es cd /mydata/nginx/html/es vim fenci.txt 输入尚硅谷 1234
测试http://192.168.43.65/es/fenci.txt
,然后创建“fenci.txt”文件,内容如下:
echo "樱桃萨其马,带你甜蜜入夏" > /mydata/nginx/html/fenci.txt
测试效果:
GET _analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"text":"樱桃萨其马,带你甜蜜入夏"
}
输出结果:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "樱桃",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "萨其马",
"start_offset" : 2,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "带你",
"start_offset" : 6,
"end_offset" : 8,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "甜蜜",
"start_offset" : 8,
"end_offset" : 10,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "入夏",
"start_offset" : 10,
"end_offset" : 12,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 4
}
]
}
五、elasticsearch-Rest-Client
java操作es有两种方式
1)9300: TCP
-
spring-data-elasticsearch:transport-api.jar;
-
springboot版本不同,ransport-api.jar不同,不能适配es版本
-
7.x已经不建议使用,8以后就要废弃
-
2)9200: HTTP
有诸多包
-
jestClient: 非官方,更新慢;
-
RestTemplate:模拟HTTP请求,ES很多操作需要自己封装,麻烦;
-
HttpClient:同上;
-
Elasticsearch-Rest-Client:官方RestClient,封装了ES操作,API层次分明,上手简单;
最终选择Elasticsearch-Rest-Client(elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client)
Java High Level REST Client | Java REST Client [7.15] | Elastic
5、附录:安装Nginx
-
随便启动一个nginx实例,只是为了复制出配置
docker run -p80:80 --name nginx -d nginx:1.10
将容器内的配置文件拷贝到/mydata/nginx/conf/ 下
mkdir -p /mydata/nginx/html mkdir -p /mydata/nginx/logs mkdir -p /mydata/nginx/conf docker container cp nginx:/etc/nginx/* /mydata/nginx/conf/ #由于拷贝完成后会在config中存在一个nginx文件夹,所以需要将它的内容移动到conf中 mv /mydata/nginx/conf/nginx/* /mydata/nginx/conf/ rm -rf /mydata/nginx/conf/nginx
-
终止原容器:
docker stop nginx
-
执行命令删除原容器:
docker rm nginx
创建新的Nginx,执行以下命令
docker run -p 80:80 --name nginx \ -v /mydata/nginx/html:/usr/share/nginx/html \ -v /mydata/nginx/logs:/var/log/nginx \ -v /mydata/nginx/conf/:/etc/nginx \ -d nginx:1.10
-
设置开机启动nginx
docker update nginx --restart=always
-
创建“/mydata/nginx/html/index.html”文件,测试是否能够正常访问
echo 'hello nginx!
' >index.html
访问:http://nginx所在主机的IP:80/index.html
六、SpringBoot整合ElasticSearch
创建项目gulimall-search
选择依赖web,但不要在里面选择es
1、导入依赖
这里的版本要和所按照的ELK版本匹配。
org.elasticsearch.client elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client 7.4.2
在spring-boot-dependencies中所依赖的ES版本位6.8.5,要改掉
1.8 7.4.2
请求测试项,比如es添加了安全访问规则,访问es需要添加一个安全头,就可以通过requestOptions设置
官方建议把requestOptions创建成单实例
@Configuration
public class GuliESConfig {
public static final RequestOptions COMMON_OPTIONS;
static {
RequestOptions.Builder builder = RequestOptions.DEFAULT.toBuilder();
COMMON_OPTIONS = builder.build();
}
@Bean
public RestHighLevelClient esRestClient() {
RestClientBuilder builder = null;
// 可以指定多个es
builder = RestClient.builder(new HttpHost(host, 9200, "http"));
RestHighLevelClient client = new RestHighLevelClient(builder);
return client;
}
}
此外还有多种方法
2、测试
1)保存数据
Index API | Java REST Client [7.15] | Elastic
保存方式分为同步和异步,异步方式多了个listener回调
@Test
public void indexData() throws IOException {
// 设置索引
IndexRequest indexRequest = new IndexRequest ("users");
indexRequest.id("1");
User user = new User();
user.setUserName("张三");
user.setAge(20);
user.setGender("男");
String jsonString = JSON.toJSONString(user);
//设置要保存的内容,指定数据和类型
indexRequest.source(jsonString, XContentType.JSON);
//执行创建索引和保存数据
IndexResponse index = client.index(indexRequest, GulimallElasticSearchConfig.COMMON_OPTIONS);
System.out.println(index);
}
2)获取数据
Search API | Java REST Client [7.15] | Elastic
@Test
public void find() throws IOException {
// 1 创建检索请求
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest();
searchRequest.indices("bank");
SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
// 构造检索条件
// sourceBuilder.query();
// sourceBuilder.from();
// sourceBuilder.size();
// sourceBuilder.aggregation();
sourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("address","mill"));
System.out.println(sourceBuilder.toString());
searchRequest.source(sourceBuilder);
// 2 执行检索
SearchResponse response = client.search(searchRequest, GuliESConfig.COMMON_OPTIONS);
// 3 分析响应结果
System.out.println(response.toString());
}
{
"took":198,
"timed_out":false,
"_shards": {"total":1,"successful":1,"skipped":0,"failed":0},
"hits":{
"total":{"value":4,"relation":"eq"},
"max_score":5.4032025,
"hits":[
{"_index":"bank",
"_type":"account",
"_id":"970",
"_score":5.4032025,
"_source":{"account_number":970,"balance":19648,
"firstname":"Forbes","lastname":"Wallace","age":28,
"gender":"M","address":"990 Mill Road","employer":"Pheast",
"email":"[email protected]","city":"Lopezo","state":"AK"}
},
{"_index":"bank","_type":"account","_id":"136",
"_score":5.4032025,
"_source":{"account_number":136,"balance":45801,"firstname":"Winnie",
"lastname":"Holland","age":38,"gender":"M","address":"198 Mill Lane",
"employer":"Neteria","email":"[email protected]","city":"Urie","state":"IL"
}
},
{"_index":"bank","_type":"account","_id":"345",
"_score":5.4032025,
"_source":{"account_number":345,"balance":9812,"firstname":"Parker",
"lastname":"Hines","age":38,"gender":"M",
"address":"715 Mill Avenue","employer":"Baluba","email":"[email protected]",
"city":"Blackgum","state":"KY"
}
},
{"_index":"bank",
"_type":"account","_id":"472",
"_score":5.4032025,
"_source":{"account_number":472,"balance":25571,"firstname":"Lee","lastname":"Long",
"age":32,"gender":"F","address":"288 Mill Street","employer":"Comverges",
"email":"[email protected]","city":"Movico","state":"MT"
}
}
]
}
}
@Test
public void find() throws IOException {
// 1 创建检索请求
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest();
searchRequest.indices("bank");
SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
// 构造检索条件
// sourceBuilder.query();
// sourceBuilder.from();
// sourceBuilder.size();
// sourceBuilder.aggregation();
sourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("address","mill"));
//AggregationBuilders工具类构建AggregationBuilder
// 构建第一个聚合条件:按照年龄的值分布
TermsAggregationBuilder agg1 = AggregationBuilders.terms("agg1").field("age").size(10);// 聚合名称
// 参数为AggregationBuilder
sourceBuilder.aggregation(agg1);
// 构建第二个聚合条件:平均薪资
AvgAggregationBuilder agg2 = AggregationBuilders.avg("agg2").field("balance");
sourceBuilder.aggregation(agg2);
System.out.println("检索条件"+sourceBuilder.toString());
searchRequest.source(sourceBuilder);
// 2 执行检索
SearchResponse response = client.search(searchRequest, GuliESConfig.COMMON_OPTIONS);
// 3 分析响应结果
System.out.println(response.toString());
}
转换bean
// 3.1 获取java bean
SearchHits hits = response.getHits();
SearchHit[] hits1 = hits.getHits();
for (SearchHit hit : hits1) {
hit.getId();
hit.getIndex();
String sourceAsString = hit.getSourceAsString();
Account account = JSON.parseObject(sourceAsString, Account.class);
System.out.println(account);
}
Account(accountNumber=970, balance=19648, firstname=Forbes, lastname=Wallace, age=28, gender=M, address=990 Mill Road, employer=Pheast, [email protected], city=Lopezo, state=AK) Account(accountNumber=136, balance=45801, firstname=Winnie, lastname=Holland, age=38, gender=M, address=198 Mill Lane, employer=Neteria, [email protected], city=Urie, state=IL) Account(accountNumber=345, balance=9812, firstname=Parker, lastname=Hines, age=38, gender=M, address=715 Mill Avenue, employer=Baluba, [email protected], city=Blackgum, state=KY) Account(accountNumber=472, balance=25571, firstname=Lee, lastname=Long, age=32, gender=F, address=288 Mill Street, employer=Comverges, [email protected], city=Movico, state=MT)
Buckets分析信息
// 3.2 获取检索到的分析信息
Aggregations aggregations = response.getAggregations();
Terms agg21 = aggregations.get("agg2");
for (Terms.Bucket bucket : agg21.getBuckets()) {
String keyAsString = bucket.getKeyAsString();
System.out.println(keyAsString);
}
搜索address中包含mill的所有人的年龄分布以及平均年龄,平均薪资
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"address": "Mill"
}
},
"aggs": {
"ageAgg": {
"terms": {
"field": "age",
"size": 10
}
},
"ageAvg": {
"avg": {
"field": "age"
}
},
"balanceAvg": {
"avg": {
"field": "balance"
}
}
}
}
七、product-es准备
P128
ES在内存中,所以在检索中优于mysql。ES也支持集群,数据分片存储。
需求:
-
上架的商品才可以在网站展示。
-
上架的商品需要可以被检索。
分析sku在es中如何存储
商品mapping
分析:商品上架在es中是存sku还是spu?
-
1)、检索的时候输入名字,是需要按照sku的title进行全文检索的
-
2)、检素使用商品规格,规格是spu的公共属性,每个spu是一样的
-
3)、按照分类id进去的都是直接列出spu的,还可以切换。
-
4〕、我们如果将sku的全量信息保存到es中(包括spu属性〕就太多字段了
方案1:
{
skuId:1
spuId:11
skyTitile:华为xx
price:999
saleCount:99
attr:[
{"尺寸":5},
{"CPU":"高通845"},
{"分辨率":"全高清"}
]
## 缺点:如果每个sku都存储规格参数(如尺寸),会有冗余存储,因为每个spu对应的sku的规格参数都一样
方案2:
sku索引
{
spuId:1
skuId:11
}
attr索引
{
skuId:11
attr:[
{"尺寸":5},
{"CPU":"高通945"},
{"分辨率":"全高清"}
]
}
# 先找到4000个符合要求的spu,再根据4000个spu查询对应的属性,封装了4000个id,long 8B*4000=32000B=32KB
# 1K个人检索,就是32MB
因此选用方案1,以空间换时间
建立product索引
最终选用的数据模型:
-
{ “type”: “keyword” }, # 保持数据精度问题,可以检索,但不分词
-
“analyzer”: “ik_smart” # 中文分词器
-
“index”: false, # 不可被检索,不生成index
-
“doc_values”: false # 默认为true,不可被聚合,es就不会维护一些聚合的信息
PUT product
{
"mappings":{
"properties": {
"skuId":{ "type": "long" },
"spuId":{ "type": "keyword" }, # 不可分词
"skuTitle": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_smart" # 中文分词器
},
"skuPrice": { "type": "keyword" }, # 保证精度问题
"skuImg" : {
"type": "keyword",
"index":false,
"doc_values":false
}, # 视频中有false
"saleCount":{ "type":"long" },
"hasStock": { "type": "boolean" },
"hotScore": { "type": "long" },
"brandId": { "type": "long" },
"catalogId": { "type": "long" },
"brandName": {
"type": "keyword",
"index":false,
"doc_values":false
}, # 视频中有false
"brandImg":{
"type": "keyword",
"index": false, # 不可被检索,不生成index,只用做页面使用
"doc_values": false # 不可被聚合,默认为true
},
"catalogName": {
"type": "keyword",
"index":false,
"doc_values":false
}, # 视频里有false
"attrs": {
"type": "nested",
"properties": {
"attrId": {"type": "long" },
"attrName": {
"type": "keyword",
"index": false,
"doc_values": false
},
"attrValue": {"type": "keyword" }
}
}
}
}
}
如果检索不到商品,自己用postman测试一下,可能有的字段需要更改,你也可以把没必要的"keyword"去掉
冗余存储的字段:不用来检索,也不用来分析,节省空间
库存是bool。
检索品牌id,但是不检索品牌名字、图片
用skuTitle检索
nested嵌入式对象
属性是"type": “nested”,因为是内部的属性进行检索
数组类型的对象会被扁平化处理(对象的每个属性会分别存储到一起)
user.name=["aaa","bbb"]
user.addr=["ccc","ddd"]
# 这种存储方式,可能会发生如下错误:
# 错误检索到{aaa,ddd},这个组合是不存在的
数组的扁平化处理会使检索能检索到本身不存在的,为了解决这个问题,就采用了嵌入式属性,数组里是对象时用嵌入式属性(不是对象无需用嵌入式属性)
nested阅读:ElasticSearch - 嵌套对象 nested_kucw的博客-CSDN博客_es nested
使用聚合:Elastic search中使用nested类型的内嵌对象_大神带我来搬砖的博客-CSDN博客
八、商品上架
按skuId上架
POST /product/spuinfo/{spuId}/up
@GetMapping("/skuId/{id}")
public R getSkuInfoBySkuId(@PathVariable("id") Long skuId){
SpuInfoEntity entity = spuInfoService.getSpuInfoBySkuId(skuId);
return R.ok().setData(entity);
}