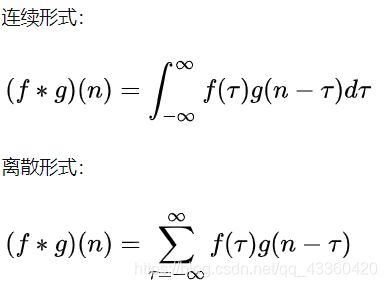Python图像处理笔记——卷积
Python图像处理——卷积
- 一、什么是卷积?
-
- 1. 数学定义
- 2. 引入库
- 3. python实现对图像的卷积
- 二、相关与卷积
-
- 1. 相关的定义
- 2. Python实现
- 扩展阅读
一、什么是卷积?
1. 数学定义
函数 [公式] 的卷积 [公式] 如下:
2. 引入库
代码如下:
import matplotlib.pylab as pylab
from skimage.color import rgb2gray
from skimage.io import imread
import numpy as np
from scipy import signal, misc, ndimage
from skimage.filters import threshold_otsu
3. python实现对图像的卷积
对图像进行卷积可以实现模糊、浮雕、边缘提取等效果,是一种常用的图像处理基础算法。为了在此过程中熟悉不同的图像处理模块,这里使用了多种处理方式,它们实现的功能是相同的。 具体实现代码如下:#(1) 对灰度图像进行卷积,模糊
def grayCon():
img = rgb2gray(imread(r'..\cameraman.jpg').astype(float))
# print(np.max(img)) #255
# print(img.shape) #(255,255)
blur_kernel = np.ones((3, 3)) / 9 # box模糊卷积核
laplace_kernel = np.array([[0, 1, 0], [1, -4, 1], [0, 1, 0]]) # 拉普拉斯边缘检测卷积核
img_blured = signal.convolve2d(img, blur_kernel)
img_edge = np.clip(signal.convolve2d(img, laplace_kernel), 0, 10) # 给数组限定范围 np.clip(array,min,max)
img_edge[img_edge < 0] = 0
im_edges = img / (np.max(img_edge) - np.min(img_edge))
thresh = threshold_otsu(im_edges)
im_edges_binary = img > thresh
print(img_blured.shape, im_edges.shape, im_edges_binary.shape)
fig, axes = pylab.subplots(ncols=4, sharex=True, sharey=True, figsize=(24, 6))
axes[0].imshow(img, cmap=pylab.cm.gray)
axes[0].set_title('original image', size=20)
axes[1].imshow(img_blured, cmap=pylab.cm.gray)
axes[1].set_title('box blured image', size=20)
axes[2].imshow(img_edge, cmap=pylab.cm.gray)
axes[2].set_title('laplace edge detection', size=20)
axes[3].imshow(im_edges_binary, cmap=pylab.cm.gray)
axes[3].set_title('binary edge detection', size=20)
for ax in axes:
ax.axis('off')
pylab.show()
# (2) 对彩色图像的每个通道进行卷积,浮雕
def RGBcon():
im = np.array(imread(r'..\tajmahal.jpg')) / 255
print('max pixel value: ' + str(np.max(im)))
print('shape of image: ' + str(im.shape))
emboss_kernel = np.array([[-2, -1, 0], [-1, 1, 1], [0, 1, 2]])
edge_scharr_kernel = np.array(
[[-3 - 3j, 0 - 10j, +3 - 3j], [-10 + 0j, 0 + 0j, +10 + 0j], [-3 + 3j, 0 + 10j, +3 + 3j]])
im_embossed = np.ones(im.shape)
im_edges = np.ones(im.shape)
for i in range(3):
im_embossed[:, :, i] = np.clip(signal.convolve2d(im[..., i], emboss_kernel,
mode='same', boundary="symm"), 0, 1)
for i in range(3):
im_edges[:, :, i] = np.clip(np.real(signal.convolve2d(im[..., i], edge_scharr_kernel,
mode='same', boundary="symm")), 0, 1)
fig, axes = pylab.subplots(ncols=3, figsize=(20, 30))
axes[0].imshow(im)
axes[0].set_title('original image', size=20)
axes[1].imshow(im_embossed)
axes[1].set_title('embossed image', size=20)
axes[2].imshow(im_edges)
axes[2].set_title('scharr edge detection', size=20)
for ax in axes:
ax.axis('off')
pylab.show()
# (3) 直接对彩色图像进行卷积,锐化
def RGBconv1():
im = imread(r'..\vic.png').astype(np.float)
# print('max pixel value: ' + str(np.max(im))) # 255
# print('shape of image: ' + str(im.shape)) # (540,720,4)
sharpen_kernel = np.array([0, -1, 0, -1, 5, -1, 0, -1, 0]).reshape(3, 3, 1)
emboss_kernel = np.array([[-2, -1, 0], [-1, 1, 1], [0, 1, 2]]).reshape(3, 3, 1)
im_sharp = ndimage.convolve(im, sharpen_kernel, mode='nearest')
im_sharp = np.clip(im_sharp, 0, 255).astype(np.uint8) # unsigned int
im_emboss = ndimage.convolve(im, emboss_kernel, mode='nearest')
# im_emboss = np.clip(im_emboss, 0, 255).astype(np.uint8)
im_emboss = im_emboss.astype(np.uint8)
pylab.figure(figsize=(10, 30))
pylab.subplot(1, 3, 1), pylab.imshow(im.astype(np.uint8)), pylab.axis('off')
pylab.title('original image', size=20)
pylab.subplot(1, 3, 2), showimage(im_sharp, 'sharpened Image')
pylab.subplot(1, 3, 3), showimage(im_emboss, 'embossed image')
pylab.tight_layout()
pylab.show()
上述代码封装为三个独立的函数。
最简单的是实现对灰度图像卷积,直接调用signal.convolve2d(image, kernel)即可。
对彩色图像的卷积可以用两种方式实现:
(1)对多个通道分别进行卷积操作后叠加;
(2)调用ndimage.convolve(image, sharpen_kernel)实现。
二、相关与卷积
1. 相关的定义
2. Python实现
def corre():
face_image = misc.face(gray=True) - misc.face(gray=True).mean()
template_image = np.copy(face_image[300:365, 670:750]) # 选择右眼区域
template_image -= template_image.mean()
face_image = face_image + np.random.randn(*face_image.shape) * 50 # random noise
correlation = signal.correlate2d(face_image, template_image, boundary="symm", mode='same')
y, x = np.unravel_index(np.argmax(correlation), correlation.shape) # find the match
fig, axes = pylab.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(15, 5))
axes[0].imshow(face_image, cmap='gray')
axes[0].set_title('Original Image', size=20)
axes[0].plot(x, y, 'ro')
axes[1].imshow(template_image, cmap='gray')
axes[1].set_title('Template Image', size=20)
axes[2].imshow(correlation, cmap='afmhot')
axes[2].set_title('cross-correlation Image', size=20)
pylab.show()
扩展阅读
关于卷积的概念可以阅读:
https://www.zhihu.com/question/22298352