python计算机视觉-图像检索和识别
目录
一、原理解析
1.1计算机视觉领域的图像分类是什么意思?
1.2图像分类要如何实现?
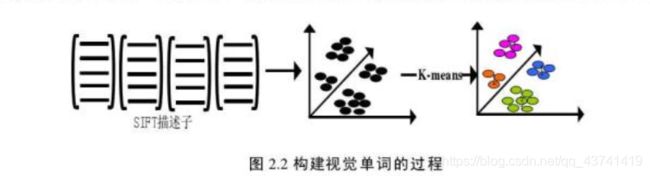
1.3Bag-of-features算法和过程?
1)提取图像特征
2)训练字典( visual vocabulary )
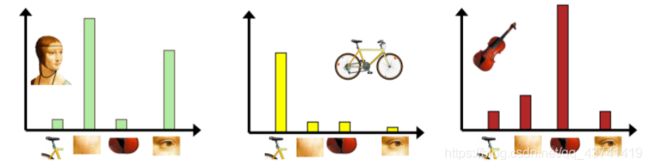
3)图片直方图表示
4)训练分类器
1.4TF-IDF?
1.5当前图像分类中会遇到一些值得挑战的问题?
二、代码解析
2.1创建词汇
2.2 建立数据库
2.3在数据库中搜索图像
三、实验结果详细分析
3.1基于聚类维度k=10
3.11一些比较好的实验结果示例:
3.12值得一提的出现的一些结果:
3.2基于不同聚类维度的讨论:
四、实验过程中遇到的问题和解决方法以及自己的一些实验总结和思考
4.1遇到的问题以及解决方法:
4.2一些思考和值得改进和提升的地方:
一、原理解析
1.1计算机视觉领域的图像分类是什么意思?
1.2图像分类要如何实现?
1.3Bag-of-features算法和过程?
1)提取图像特征
2)训练字典( visual vocabulary )
提取完特征后,我们会采用一些 聚类算法对这些特征向量进行聚类。 最常用的聚类算法是k-means。
3)图片直方图表示
4)训练分类器
1.4TF-IDF?
TF-IDF用以评估一字词对于一个文件集或一个语料库中的其中一份文件的重要程度。字词的重要性随着它在文件中出现的次数成正比增加,但同时会随着它在语料库中出现的频率成反比下降。就目前来说,如果一个 关键词只在很少的网页中出现,我们通过它就 容易锁定搜索目标,它的 权重也就应该 大。反之如果一个词在大量网页中出现,我们看到它仍然 不是很清楚要找什么内容,因此它应该 小。
1.5当前图像分类中会遇到一些值得挑战的问题?
二、代码解析
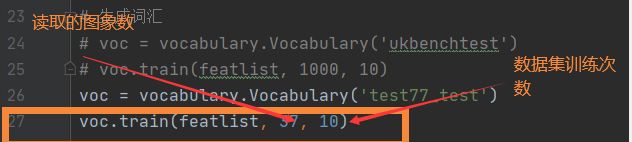
2.1创建词汇
对每张图片生成相应的sif文件,及视觉词汇,以便建立BOW模型。我所用的是图像集为37张。如果需要增加图像或减少只需要改代码里读取训练图像的数量。要得到不同维度的量级,需要修改数据集训练次数。
def train(self,featurefiles,k=100,subsampling=10):
""" 用含有k个单词的 K-means 列出在 featurefiles 中的特征文件训练出一个词汇。对训练数据下采样可以加快训练速度 """
nbr_images = len(featurefiles)
# 从文件中读取特征
descr = []
descr.append(sift.read_features_from_file(featurefiles[0])[1])
# 将所有的特征并在一起,以便后面进行 K-means 聚类
descriptors = descr[0]
for i in arange(1,nbr_images):
descr.append(sift.read_features_from_file(featurefiles[i])[1])
descriptors = vstack((descriptors,descr[i]))
#K-means: 最后一个参数决定运行次数
self.voc,distortion = kmeans(descriptors[::subsampling,:],k,1)
self.nbr_words = self.voc.shape[0]
# 遍历所有的训练图像,并投影到词汇上
imwords = zeros((nbr_images,self.nbr_words))
for i in range( nbr_images ):
imwords[i] = self.project(descr[i])
nbr_occurences = sum( (imwords > 0)*1 ,axis=0)
self.idf = log( (1.0*nbr_images) / (1.0*nbr_occurences+1) )
self.trainingdata = featurefiles
def project(self,descriptors):
""" 将描述子投影到词汇上,以创建单词直方图 """
# 图像单词直方图
imhist = zeros((self.nbr_words))
words,distance = vq(descriptors,self.voc)
for w in words:
imhist[w] += 1
return imhist示例代码:
# -*- codeing =utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2021/6/1 14:25
# @Author : ArLin
# @File : demo1.py
# @Software: PyCharm
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import pickle
from PCV.imagesearch import vocabulary
from PCV.tools.imtools import get_imlist
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
# 获取图像列表
imlist = get_imlist('datasets/')
nbr_images = len(imlist)
# 获取特征列表
featlist = [imlist[i][:-3] + 'sift' for i in range(nbr_images)]
# 提取文件夹下图像的sift特征
for i in range(nbr_images):
sift.process_image(imlist[i], featlist[i])
# 生成词汇
voc = vocabulary.Vocabulary('test77_test')
voc.train(featlist, 37, 10)
# 保存词汇
# saving vocabulary
with open('BOW\\vocabulary.pkl', 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(voc, f)
print('vocabulary is:', voc.name, voc.nbr_words)运行结果:
同时生成了数据模型vocabulary.pkl,如果数据模型为空,在后面存入数据库会出现报错,读入数据为空。判断.pkl是否为空可根据查看它的大小,如图所示,这里pkl为41KB,故不为空
2.2 建立数据库
将上面得到的数据模型存放数据库testImaAdd.db中,即运行下面代码会生成一个testImaAdd.db数据库文件。
# -*- codeing =utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2021/6/1 14:52
# @Author : ArLin
# @File : demo2.py
# @Software: PyCharm
import pickle
from PCV.imagesearch import imagesearch
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
import sqlite3
from PCV.tools.imtools import get_imlist
# 获取图像列表
# imlist = get_imlist('E:/Python37_course/test7/first1000/')
imlist = get_imlist('datasets/')
nbr_images = len(imlist)
# 获取特征列表
featlist = [imlist[i][:-3] + 'sift' for i in range(nbr_images)]
# load vocabulary
# 载入词汇
'''with open('E:/Python37_course/test7/first1000/vocabulary.pkl', 'rb') as f:
voc = pickle.load(f)'''
with open('BOW\\vocabulary.pkl', 'rb') as f:
voc = pickle.load(f)
# 创建索引
indx = imagesearch.Indexer('testImaAdd.db', voc)
indx.create_tables()
# go through all images, project features on vocabulary and insert
# 遍历所有的图像,并将它们的特征投影到词汇上
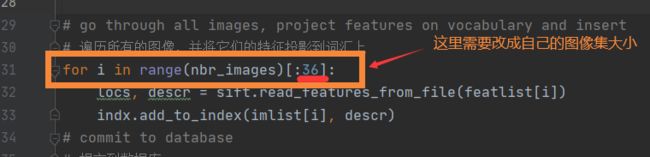
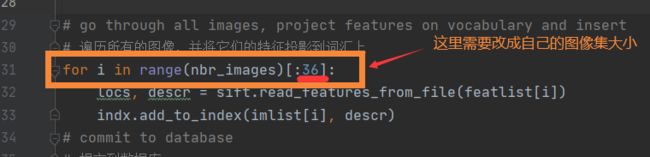
for i in range(nbr_images)[:36]:
locs, descr = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[i])
indx.add_to_index(imlist[i], descr)
# commit to database
# 提交到数据库
indx.db_commit()
con = sqlite3.connect('testImaAdd.db')
print(con.execute('select count (filename) from imlist').fetchone())
print(con.execute('select * from imlist').fetchone())运行结果:
2.3在数据库中搜索图像
Searcher 类:
class Searcher(object):
def __init__(self,db,voc):
""" Initialize with the name of the database. """
self.con = sqlite3.connect(db)
self.voc = voc
def __del__(self):
self.con.close()
def get_imhistogram(self,imname):
""" Return the word histogram for an image. """
im_id = self.con.execute(
"select rowid from imlist where filename='%s'" % imname).fetchone()
s = self.con.execute(
"select histogram from imhistograms where rowid='%d'" % im_id).fetchone()
# use pickle to decode NumPy arrays from string
return pickle.loads(s[0])
def candidates_from_word(self,imword):
""" Get list of images containing imword. """
im_ids = self.con.execute(
"select distinct imid from imwords where wordid=%d" % imword).fetchall()
return [i[0] for i in im_ids]
def candidates_from_histogram(self,imwords):
""" Get list of images with similar words. """
# get the word ids
words = imwords.nonzero()[0]
# find candidates
candidates = []
for word in words:
c = self.candidates_from_word(word)
candidates+=c
# take all unique words and reverse sort on occurrence
tmp = [(w,candidates.count(w)) for w in set(candidates)]
tmp.sort(key=cmp_to_key(lambda x,y:operator.gt(x[1],y[1])))
tmp.reverse()
# return sorted list, best matches first
return [w[0] for w in tmp]
def query(self,imname):
""" Find a list of matching images for imname. """
h = self.get_imhistogram(imname)
candidates = self.candidates_from_histogram(h)
matchscores = []
for imid in candidates:
# get the name
cand_name = self.con.execute(
"select filename from imlist where rowid=%d" % imid).fetchone()
cand_h = self.get_imhistogram(cand_name)
cand_dist = sqrt( sum( self.voc.idf*(h-cand_h)**2 ) )
matchscores.append( (cand_dist,imid) )
# return a sorted list of distances and database ids
matchscores.sort()
return matchscores
def get_filename(self,imid):
""" Return the filename for an image id. """
s = self.con.execute(
"select filename from imlist where rowid='%d'" % imid).fetchone()
return s[0]
def tf_idf_dist(voc,v1,v2):
v1 /= sum(v1)
v2 /= sum(v2)
return sqrt( sum( voc.idf*(v1-v2)**2 ) )
def compute_ukbench_score(src,imlist):
""" Returns the average number of correct
images on the top four results of queries. """
nbr_images = len(imlist)
pos = zeros((nbr_images,4))
# get first four results for each image
for i in range(nbr_images):
pos[i] = [w[1]-1 for w in src.query(imlist[i])[:4]]
# compute score and return average
score = array([ (pos[i]//4)==(i//4) for i in range(nbr_images)])*1.0
return sum(score) / (nbr_images)Searcher 类中
-
init() 方法用于初始化数据库的名称。
-
__ del__() 方法可以确保关闭数据库连接。
-
candidates_from_word() 用于获得包含特定单词的所有图像id号。
-
candidates_from_histogram() 方法从图像单词直方图的非零项创建单词id列表,检索每个单词获得候选集并将其合并到candidates列表中,然后创建一个元组列表每个元组由单词id和次数count构成,其中次数count是候选列表中每个单词出现的次数。同时,还以元组中的第二个元素为准,用sort()方法和一个自定义的比较函数对列表进行排序。该自定义比较函数进行用lambda函数内联声明,对于单行函数声明,使用lambda函数非常方便。最后结果返回一个包含图像id的列表,排在列表最前面的是最好的匹配图像。
-
get_imhistogram() 用于返回一幅图像的单词直方图。query() 方法用于获取图像的文件名,检索其单词直方图及候选图像列表。对于每个候选图像,用标准的欧氏距离比较它和查询图像间的直方图,并返回一个经排序的包含距离及图像id的元组列表。
# -*- codeing =utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2021/6/1 15:29
# @Author : ArLin
# @File : demo3.py
# @Software: PyCharm
import pickle
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
from PCV.imagesearch import imagesearch
from PCV.geometry import homography
from PCV.tools.imtools import get_imlist
# load image list and vocabulary
# 载入图像列表
imlist = get_imlist('datasets/') # 存放数据集的路径
nbr_images = len(imlist)
# 载入特征列表
featlist = [imlist[i][:-3] + 'sift' for i in range(nbr_images)]
# 载入词汇
with open('BOW\\vocabulary.pkl', 'rb') as f: # 存放模型的路径
voc = pickle.load(f)
src = imagesearch.Searcher('testImaAdd.db', voc)
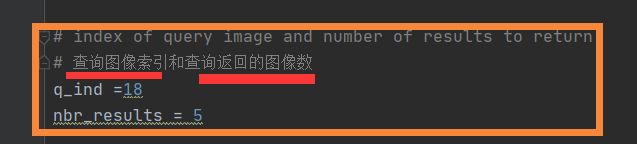
# index of query image and number of results to return
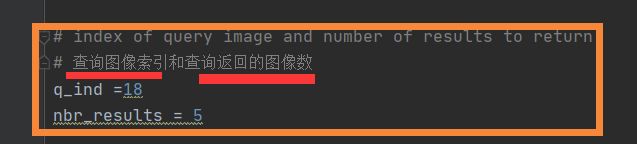
# 查询图像索引和查询返回的图像数
q_ind =18
nbr_results = 5
# regular query
# 常规查询(按欧式距离对结果排序)
res_reg = [w[1] for w in src.query(imlist[q_ind])[:nbr_results]]
print('top matches (regular):', res_reg)
# load image features for query image
# 载入查询图像特征
q_locs, q_descr = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[q_ind])
fp = homography.make_homog(q_locs[:, :2].T)
# RANSAC model for homography fitting
# 用单应性进行拟合建立RANSAC模型
model = homography.RansacModel()
rank = {}
# load image features for result
# 载入候选图像的特征
for ndx in res_reg[1:]:
locs, descr = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[ndx]) # because 'ndx' is a rowid of the DB that starts at 1
# get matches
# 获取匹配数 # get matches执行完后会出现两张图片
matches = sift.match(q_descr, descr)
ind = matches.nonzero()[0]
ind2 = matches[ind]
tp = homography.make_homog(locs[:, :2].T)
# compute homography, count inliers. if not enough matches return empty list
# 计算单应性,对内点技术。如果没有足够的匹配书则返回空列表
try:
H, inliers = homography.H_from_ransac(fp[:, ind], tp[:, ind2], model, match_theshold=4)
except:
inliers = []
# store inlier count
rank[ndx] = len(inliers)
# sort dictionary to get the most inliers first
# 将字典排序,以首先获取最内层的内点数
sorted_rank = sorted(rank.items(), key=lambda t: t[1], reverse=True)
res_geom = [res_reg[0]] + [s[0] for s in sorted_rank]
print('top matches (homography):', res_geom)
# 显示查询结果
imagesearch.plot_results(src, res_reg[:8]) # 常规查询
imagesearch.plot_results(src, res_geom[:8]) # 重排后的结果
三、实验结果详细分析
3.1基于聚类维度k=10:
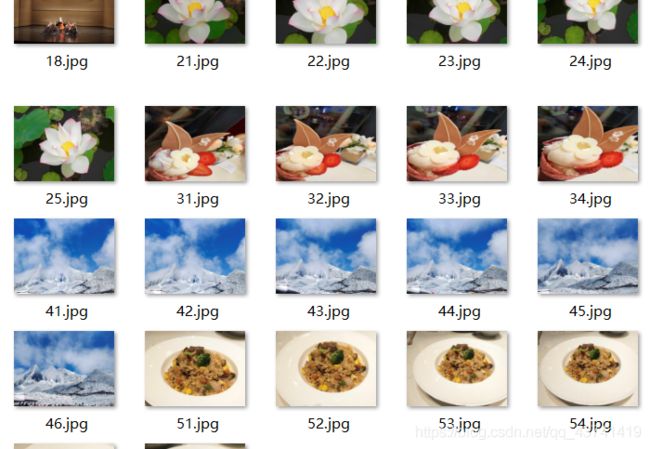
3.11一些比较好的实验结果示例:
3.12值得一提的出现的一些结果:
最右是我们的查询图像,而后面是按图像列表检索的前几幅图像,
我们可以看到常规查询的结果和重排后的查询结果相比较后,
重排后的查询结果会比常规查询结果更为准确些,
重排用单应性进行拟合建立RANSAC模型,再导入候选图像特征进行排序查询;
常规查询只是进行了简单的索引和查询,找到相似即可。
第二组:
原图片集合中我们可以看到冰淇淋这类的照片中只有四张,但是程序中要求返回的是5张最相似的,于是就会从照片集中再挑选出最为相似的作为第五张,因为冰淇淋是花的形状,所以这里自然就传回了这朵花的照片传回来了。
这是显著的类间差异的例子,冰淇淋和荷花是不同类别的图像,但在这里被归为同一类别,这是因为它们又比较相似的底层特征-花朵,外形和纹理较为相似,所以由底层特征推导出的中层语义特征和高层语义特征也具有一定的相似性,这就导致了不同类别的图像被归类为同一类别,出现了识别错误的情况
以及在我观察后发现在这些图片中荷花这组的匹配准确率是比较低的,相对于匹配准确性较高的音乐会而言,对此我有个大胆的推测,我认为是因为荷花这组图基本色调少,基本就是绿和白,而且也是近拍荷花,而常用的图像特征有图像颜色、纹理、灰度等信息,即图像特征不多,这就导致了特征得不到有效提取,则图像分类的精度大大降低。
3.2基于不同聚类维度的讨论:
四、实验过程中遇到的问题和解决方法以及自己的一些实验总结和思考
4.1遇到的问题以及解决方法:
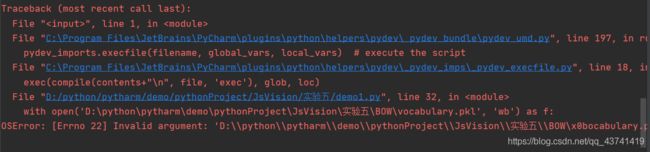
问题1:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "", line 1, in
File "C:\Program Files\JetBrains\PyCharm\plugins\python\helpers\pydev\_pydev_bundle\pydev_umd.py", line 197, in runfile
pydev_imports.execfile(filename, global_vars, local_vars) # execute the script
File "C:\Program Files\JetBrains\PyCharm\plugins\python\helpers\pydev\_pydev_imps\_pydev_execfile.py", line 18, in execfile
exec(compile(contents+"\n", file, 'exec'), glob, loc)
File "D:/python/pytharm/demo/pythonProject/JsVision/实验五/demo1.py", line 32, in
with open('D:\python\pytharm\demo\pythonProject\JsVision\实验五\BOW\vocabulary.pkl', 'wb') as f:
OSError: [Errno 22] Invalid argument: 'D:\\python\\pytharm\\demo\\pythonProject\\JsVision\\实验五\\BOW\x0bocabulary.pkl'
回溯(最近一次呼叫):
文件“”,第1行,在
文件“C:\Program Files\JetBrains\PyCharm\plugins\python\helpers\pydev\\u pydev\u bundle\pydev\u umd.py”,第197行,在runfile中
pydev#imports.execfile(文件名,全局变量,本地变量)#执行脚本
文件“C:\Program Files\JetBrains\PyCharm\plugins\python\helpers\pydev\\u pydev\u imps\\u pydev\u execfile.py”,第18行,在execfile中
exec(compile(contents+“\n”,file,'exec'),glob,loc)
文件“D:/python/pytharm/demo/pythonProject/JsVision/实验五/demo1.py“,第32行,在
打开('D:\python\pytharm\demo\pythonProject\JsVision\实验五\BOW\词汇表.pkl,','wb')作为f:
OSError:[Errno 22]无效参数:“D:\\python\\pytharm\\demo\\pythonProject\\JsVision”\\实验五\\弓\x0bocabulary.pkl' 原来是文件名路径的问题,根据之前的经验可能是\vocabulary.pkl这个地方出了问题,把斜杠换成双斜杠即可或者在读取路径前面加个r
问题2:
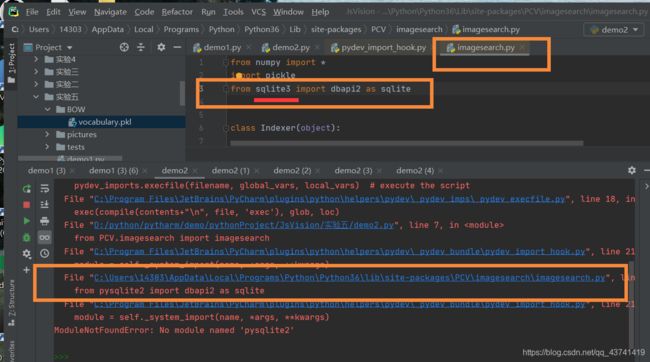
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'pysqlite2'
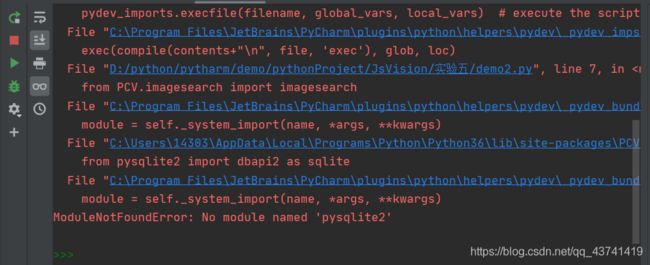 经过网上查阅,python3已经不支持pysqlite2这个库了
经过网上查阅,python3已经不支持pysqlite2这个库了
解决方法:
按照上面那个图找自己文件的所在的路径,把红线区域的修改为如图示,并且保证自己的settings已经成功安装了 pysqlite3
问题3
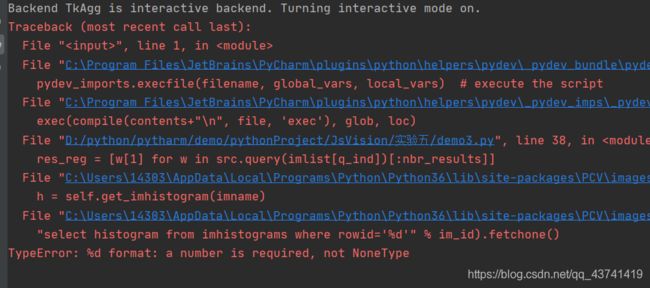
TypeError: %d format: a number is required, not NoneType
这里出现这种错误有三种可能性,
1.检查sift的路径是否存放正确
2.检查一下PCV中的imagesearch.py文件
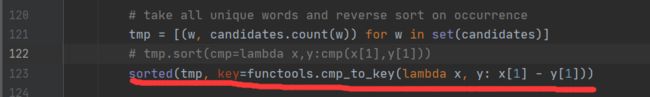 检查一下这两个地方的代码,改成这个方式,主要是因为Python3和Python2的字符串兼容问题,因为数据文件是在Python2下序列化的,所以使用Python3读取时,需要将‘str’转化为'bytes'。
检查一下这两个地方的代码,改成这个方式,主要是因为Python3和Python2的字符串兼容问题,因为数据文件是在Python2下序列化的,所以使用Python3读取时,需要将‘str’转化为'bytes'。
3查询图像的索引(下图2)是否超出了你在生成一个testImaAdd.db数据库文件的遍历图象数(下图1),即
4.2一些思考和值得改进和提升的地方:
1.本次的图像查询我是建立在原本的图像库里面取出的查询图像和图像匹配,而我觉得我应该深一步做到的是,输入自己的照片(非图像库内图像),然后再与图像库图像进行查询和匹配。
2.本次我的图像集其实并不多,就是30多张,都是取自于自己的手机相册,BOF的一个主要缺点是在用视觉单词表示图像时不包含图像特征的位置信息,而图像特征的位置信息在人眼识别图像时起到了很好的作用,而我本次的实验结果并没有体现出这个缺点。
3.由于图像集数目不足和通用数据库的影响其实我的聚类影响并没有体现出现,在我自己的通用数据库基础上,我应该增加每个类别的图像数量,感觉最好一个类别20-30张最佳,然后再设置一个专用的数据库(即对于同一个对象)也是有充足的图像数量,以此来进行聚类影响的体现。
4.通过在知网参考文献,我发现有许多的算法其实对于前面说的BOF的缺点有了改进的作用,进一步学习的时候可以考虑用改进算法查看一下准确率的差异
参考文献:
基于词袋模型的图像分类方法研究-王娜娜-兰州理工大学