每天半小时:入门Python,Pandas库十套练习题带你学会数据分析(二)
目录
- 练习6-统计
-
- 探索风速数据
- 练习7-可视化
-
- 探索泰坦尼克灾难数据
- 练习8-创建数据框
-
- 探索Pokemon数据
- 练习9-时间序列
-
- 探索Apple公司股价数据
- 练习10-删除数据
-
- 探索Iris纸鸢花数据
Pandas是入门Python做数据分析必须要掌握的一个库,是一个开放源码、BSD 许可的库,提供高性能、易于使用的数据结构和数据分析的工具。主要数据结构是 Series (一维数据)与 DataFrame(二维数据),这两种数据结构足以处理金融、统计、社会科学、工程等领域里的大多数典型用例。今天就来一起学习。

练习6-统计
探索风速数据
- 第一步:导入必要的库
# 运行以下代码
import pandas as pd
import datetime
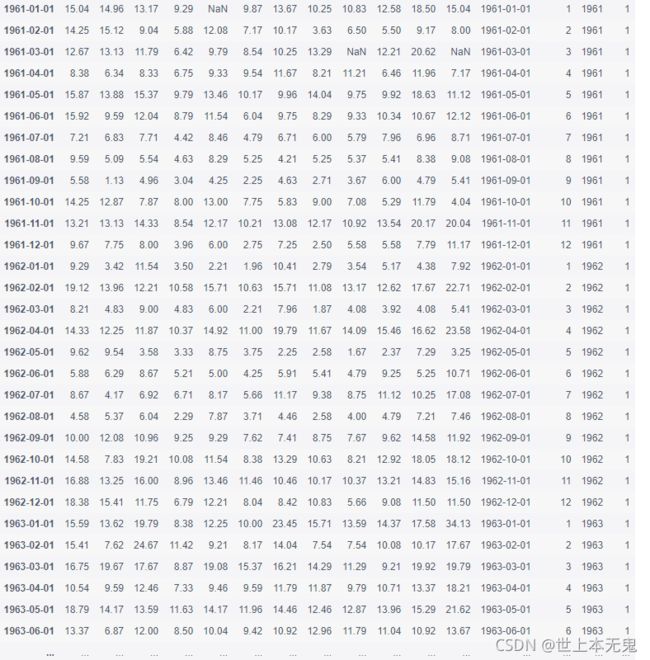
- 第二步:从以下地址导入数据
import pandas as pd
# 运行以下代码
path6 = "../input/pandas_exercise/pandas_exercise/exercise_data/wind.data" # wind.data
- 第三步:将数据作存储并且设置前三列为合适的索引
import datetime
# 运行以下代码
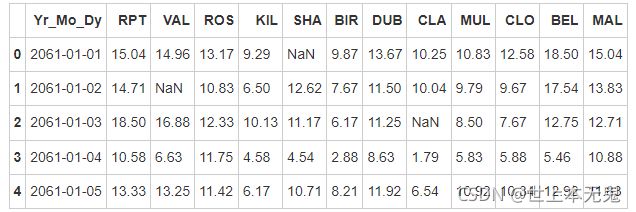
data = pd.read_table(path6, sep = "\s+", parse_dates = [[0,1,2]])
data.head()
- 第四步:2061年?我们真的有这一年的数据?创建一个函数并用它去修复这个bug
# 运行以下代码
def fix_century(x):
year = x.year - 100 if x.year > 1989 else x.year
return datetime.date(year, x.month, x.day)
# apply the function fix_century on the column and replace the values to the right ones
data['Yr_Mo_Dy'] = data['Yr_Mo_Dy'].apply(fix_century)
# data.info()
data.head()
- 第五步:将日期设为索引,注意数据类型,应该是datetime64[ns]
# 运行以下代码
# transform Yr_Mo_Dy it to date type datetime64
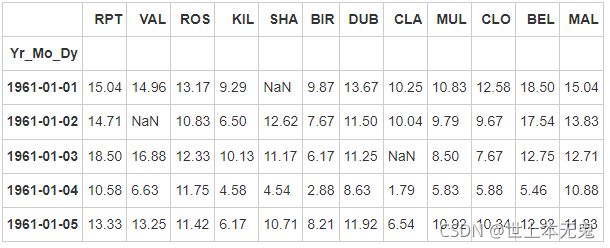
data["Yr_Mo_Dy"] = pd.to_datetime(data["Yr_Mo_Dy"])
# set 'Yr_Mo_Dy' as the index
data = data.set_index('Yr_Mo_Dy')
data.head()
# data.info()
- 第六步:对应每一个location,一共有多少数据值缺失
# 运行以下代码
data.isnull().sum()
- 第七步:对应每一个location,一共有多少完整的数据值
# 运行以下代码
data.shape[0] - data.isnull().sum()
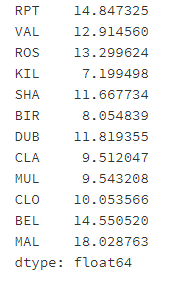
- 第八步:对于全体数据,计算风速的平均值
# 运行以下代码
data.mean().mean()
10.227982360836924
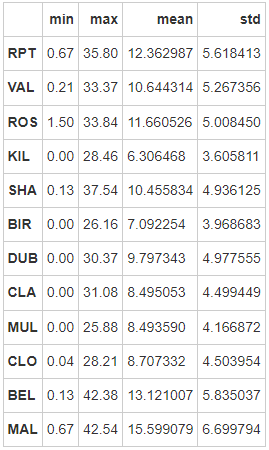
- 第九步:创建一个名为loc_stats的数据框去计算并存储每个location的风速最小值,最大值,平均值和标准差
# 运行以下代码
loc_stats = pd.DataFrame()
loc_stats['min'] = data.min() # min
loc_stats['max'] = data.max() # max
loc_stats['mean'] = data.mean() # mean
loc_stats['std'] = data.std() # standard deviations
loc_stats
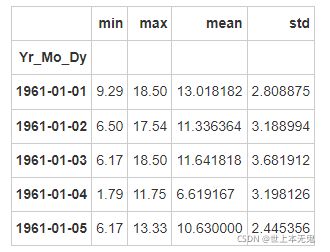
- 第十步:创建一个名为day_stats的数据框去计算并存储所有location的风速最小值,最大值,平均值和标准差
# 运行以下代码
# create the dataframe
day_stats = pd.DataFrame()
# this time we determine axis equals to one so it gets each row.
day_stats['min'] = data.min(axis = 1) # min
day_stats['max'] = data.max(axis = 1) # max
day_stats['mean'] = data.mean(axis = 1) # mean
day_stats['std'] = data.std(axis = 1) # standard deviations
day_stats.head()
- 第十一步:对于每一个location,计算一月份的平均风速
注意:1961年的1月和1962年的1月应该区别对待
# 运行以下代码
# creates a new column 'date' and gets the values from the index
data['date'] = data.index
# creates a column for each value from date
data['month'] = data['date'].apply(lambda date: date.month)
data['year'] = data['date'].apply(lambda date: date.year)
data['day'] = data['date'].apply(lambda date: date.day)
# gets all value from the month 1 and assign to janyary_winds
january_winds = data.query('month == 1')
# gets the mean from january_winds, using .loc to not print the mean of month, year and day
january_winds.loc[:,'RPT':"MAL"].mean()
- 第十二步:对于数据记录按照年为频率取样
# 运行以下代码
data.query('month == 1 and day == 1')
- 第十三步:对于数据记录按照月为频率取样
# 运行以下代码
data.query('day == 1')
练习7-可视化
探索泰坦尼克灾难数据
- 第一步:导入必要的库
# 运行以下代码
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import numpy as np
%matplotlib inline
- 第二步:从以下地址导入数据
# 运行以下代码
path7 = '../input/pandas_exercise/pandas_exercise/exercise_data/train.csv' # train.csv
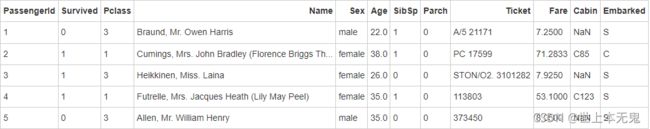
- 第三步:将数据框命名为titanic
# 运行以下代码
titanic = pd.read_csv(path7)
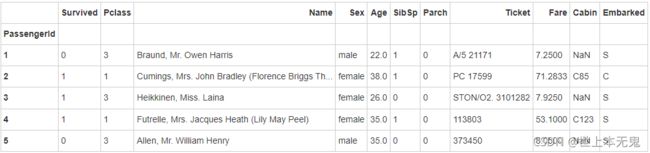
titanic.head()
- 第四步:将PassengerId设置为索引
# 运行以下代码
titanic.set_index('PassengerId').head()
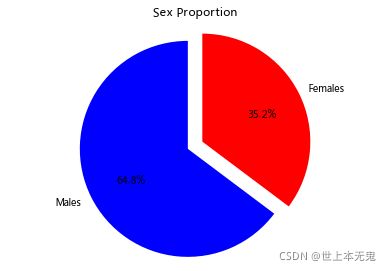
- 第五步:绘制一个展示男女乘客比例的扇形图
# 运行以下代码
# sum the instances of males and females
males = (titanic['Sex'] == 'male').sum()
females = (titanic['Sex'] == 'female').sum()
# put them into a list called proportions
proportions = [males, females]
# Create a pie chart
plt.pie(
# using proportions
proportions,
# with the labels being officer names
labels = ['Males', 'Females'],
# with no shadows
shadow = False,
# with colors
colors = ['blue','red'],
# with one slide exploded out
explode = (0.15 , 0),
# with the start angle at 90%
startangle = 90,
# with the percent listed as a fraction
autopct = '%1.1f%%'
)
# View the plot drop above
plt.axis('equal')
# Set labels
plt.title("Sex Proportion")
# View the plot
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
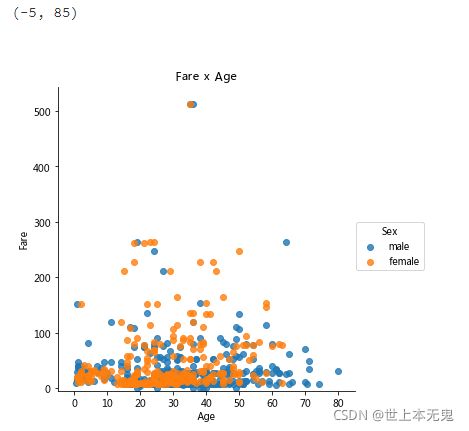
- 第六步:绘制一个展示船票Fare, 与乘客年龄和性别的散点图
# 运行以下代码
# creates the plot using
lm = sns.lmplot(x = 'Age', y = 'Fare', data = titanic, hue = 'Sex', fit_reg=False)
# set title
lm.set(title = 'Fare x Age')
# get the axes object and tweak it
axes = lm.axes
axes[0,0].set_ylim(-5,)
axes[0,0].set_xlim(-5,85)
(-5, 85)
- 第七步:有多少人生还?
# 运行以下代码
titanic.Survived.sum()
342
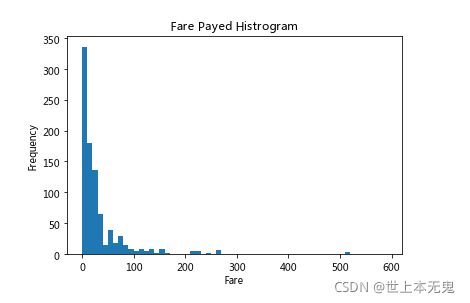
- 第八步:绘制一个展示船票价格的直方图
# 运行以下代码
# sort the values from the top to the least value and slice the first 5 items
df = titanic.Fare.sort_values(ascending = False)
df
# create bins interval using numpy
binsVal = np.arange(0,600,10)
binsVal
# create the plot
plt.hist(df, bins = binsVal)
# Set the title and labels
plt.xlabel('Fare')
plt.ylabel('Frequency')
plt.title('Fare Payed Histrogram')
# show the plot
plt.show()
练习8-创建数据框
探索Pokemon数据
- 第一步:导入必要的库
# 运行以下代码
import pandas as pd
- 第二步:创建一个数据字典
# 运行以下代码
raw_data = {
"name": ['Bulbasaur', 'Charmander','Squirtle','Caterpie'],
"evolution": ['Ivysaur','Charmeleon','Wartortle','Metapod'],
"type": ['grass', 'fire', 'water', 'bug'],
"hp": [45, 39, 44, 45],
"pokedex": ['yes', 'no','yes','no']
}
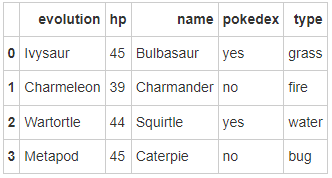
- 第三步:将数据字典存为一个名叫pokemon的数据框中
# 运行以下代码
pokemon = pd.DataFrame(raw_data)
pokemon.head()
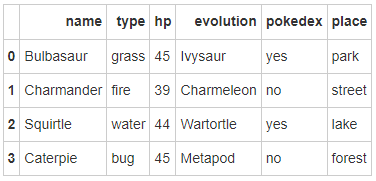
- 第四步:数据框的列排序是字母顺序,请重新修改为name, type, hp, evolution, pokedex这个顺序
# 运行以下代码
pokemon = pokemon[['name', 'type', 'hp', 'evolution','pokedex']]
pokemon
- 第五步:添加一个列place
# 运行以下代码
pokemon['place'] = ['park','street','lake','forest']
pokemon
- 第六步:查看每个列的数据类型
# 运行以下代码
pokemon.dtypes
练习9-时间序列
探索Apple公司股价数据
- 第一步:导入必要的库
# 运行以下代码
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# visualization
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
- 第二步:数据集地址
# 运行以下代码
path9 = '../input/pandas_exercise/pandas_exercise/exercise_data/Apple_stock.csv' # Apple_stock.csv
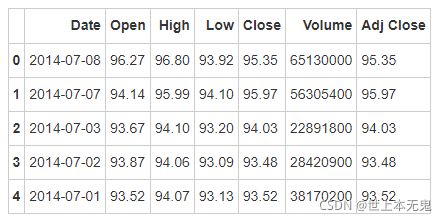
- 第三步:读取数据并存为一个名叫apple的数据框
# 运行以下代码
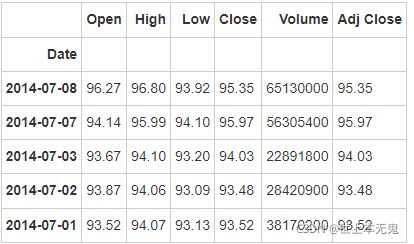
apple = pd.read_csv(path9)
apple.head()
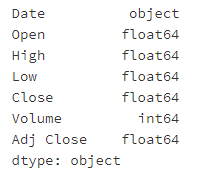
- 第四步:查看每一列的数据类型
# 运行以下代码
apple.dtypes
- 第五步:将Date这个列转换为datetime类型
# 运行以下代码
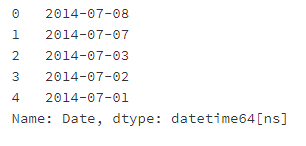
apple.Date = pd.to_datetime(apple.Date)
apple['Date'].head()
- 第六步:将Date设置为索引
# 运行以下代码
apple = apple.set_index('Date')
apple.head()
- 第七步:有重复的日期吗?
# 运行以下代码
apple.index.is_unique
True
- 第八步:将index设置为升序
# 运行以下代码
apple.sort_index(ascending = True).head()
- 第九步:找到每个月的最后一个交易日(business day)
# 运行以下代码
apple_month = apple.resample('BM')
apple_month.head()
- 第十步数据集中最早的日期和最晚的日期相差多少天?
# 运行以下代码
(apple.index.max() - apple.index.min()).days
12261
- 第十一步:步骤11 在数据中一共有多少个月?
# 运行以下代码
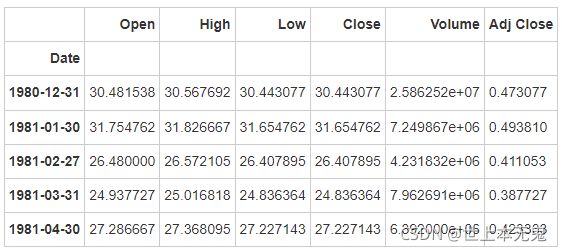
apple_months = apple.resample('BM').mean()
len(apple_months.index)
404
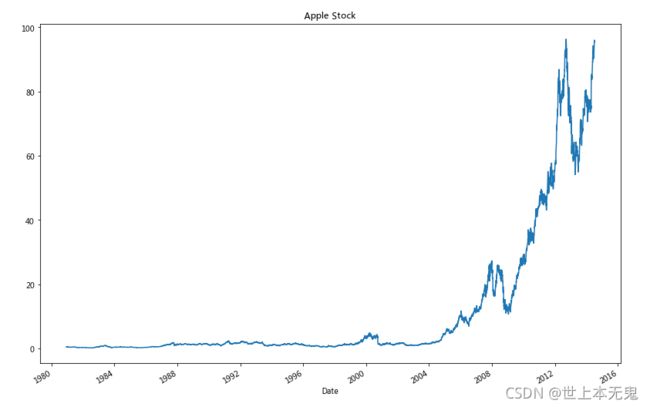
- 第十二步:按照时间顺序可视化Adj Close值
# 运行以下代码
# makes the plot and assign it to a variable
appl_open = apple['Adj Close'].plot(title = "Apple Stock")
# changes the size of the graph
fig = appl_open.get_figure()
fig.set_size_inches(13.5, 9)
练习10-删除数据
探索Iris纸鸢花数据
- 第一步:导入必要的库
# 运行以下代码
import pandas as pd
- 第二步:数据集地址
# 运行以下代码
path10 ='../input/pandas_exercise/pandas_exercise/exercise_data/iris.csv' # iris.csv
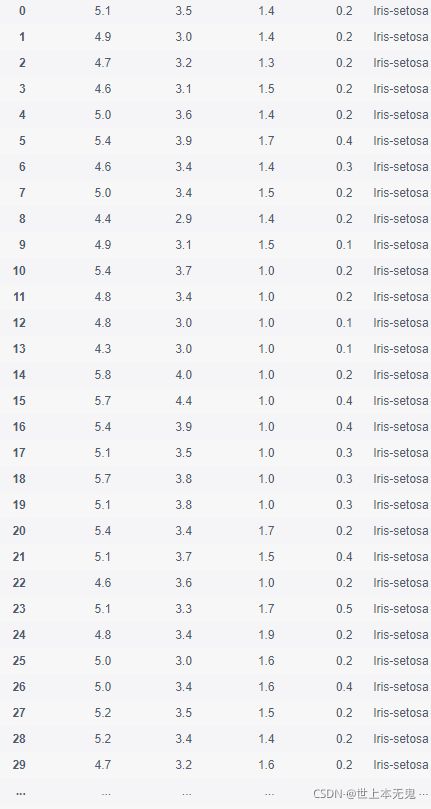
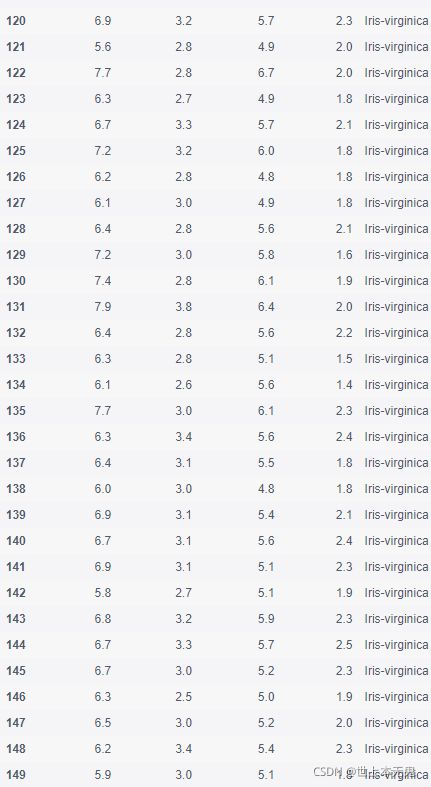
- 第三步:将数据集存成变量iris
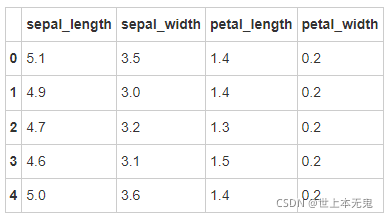
# 运行以下代码
iris = pd.read_csv(path10)
iris.head()
- 第四步:创建数据框的列名称
iris = pd.read_csv(path10,names = ['sepal_length','sepal_width', 'petal_length', 'petal_width', 'class'])
iris.head()
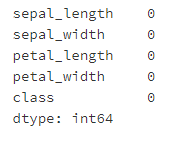
- 第五步: 数据框中有缺失值吗?
# 运行以下代码
pd.isnull(iris).sum()
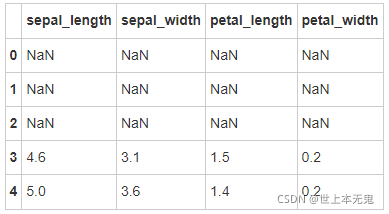
- 第六步:将列petal_length的第10到19行设置为缺失值
# 运行以下代码
iris.iloc[10:20,2:3] = np.nan
iris.head(20)
- 第七步:将缺失值全部替换为1.0
# 运行以下代码
iris.petal_length.fillna(1, inplace = True)
iris
- 第八步:删除列class
# 运行以下代码
del iris['class']
iris.head()
- 第九步:将数据框前三行设置为缺失值
# 运行以下代码
iris.iloc[0:3 ,:] = np.nan
iris.head()
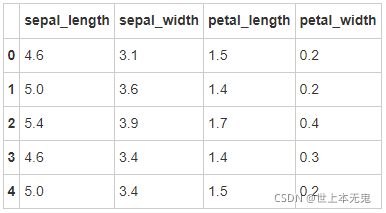
- 第十步: 删除有缺失值的行
# 运行以下代码
iris = iris.dropna(how='any')
iris.head()
- 第十一步:重新设置索引
# 运行以下代码
iris = iris.reset_index(drop = True)
iris.head()
 你们的支持是我持续更新下去的动力,(点赞,关注,评论) 这篇文还未结束,想了解后续的可以关注我,持续更新。
你们的支持是我持续更新下去的动力,(点赞,关注,评论) 这篇文还未结束,想了解后续的可以关注我,持续更新。

点击领取 Q群号: 943192807(纯技术交流和资源共享)以自助拿走。
①行业咨询、专业解答 ②Python开发环境安装教程 ③400集自学视频 ④软件开发常用词汇 ⑤最新学习路线图 ⑥3000多本Python电子书