Redisson 管道批量发送命令流程分析
一、示例代码
管道功能就是REDIS的批量发送,实际上是客户端的功能,与服务端无关。相当于把多个请求的命令放在一个数据包通过TCP发送到服务端,然后客户端再一次性读取所有的命令回应,节省多次命令的网络请求。
RBatch rBatch = redissonClient.createBatch();
RBatch rBatch = redissonClient.createBatch();
rBatch.getBucket("goodsName", StringCodec.INSTANCE).getAsync();
rBatch.getSet("goodsSet",StringCodec.INSTANCE).readAllAsync();
BatchResult res = rBatch.execute();
log.debug(" tt execute end. res:{}",JSONUtil.toJsonStr(res.getResponses()));二、创建批处理和添加命令流程
1.创建批处理对象,包括批量命令执行器,并且创建的RBucket等各种REDIS容器对象都会传入批量命令执行器。
public class RedissonBatch implements RBatch {
private final EvictionScheduler evictionScheduler;
private final CommandBatchService executorService;
private final BatchOptions options;
public RedissonBatch(EvictionScheduler evictionScheduler, ConnectionManager connectionManager, BatchOptions options) {
this.executorService = new CommandBatchService(connectionManager, options);
this.evictionScheduler = evictionScheduler;
this.options = options;
}
@Override
public RBucketAsync getBucket(String name) {
return new RedissonBucket(executorService, name);
} 批量命令执行器继承于通用命令执行器(CommandAsyncService) ,只是重写了发送命令函数(SendCommand,async(异步发送命令)).
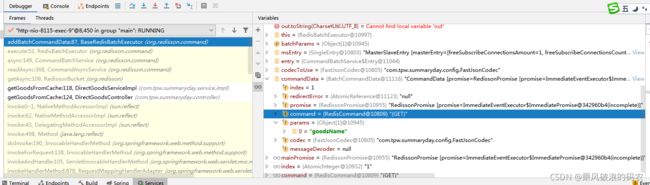
2.rBatch.getBucket("goodsName").getAsync()调用批量命令执行器的异步发送命令。
CommandBatchService
@Override
public void async(boolean readOnlyMode, NodeSource nodeSource,
Codec codec, RedisCommand command, Object[] params, RPromise mainPromise, boolean ignoreRedirect) {
if (isRedisBasedQueue()) {
boolean isReadOnly = options.getExecutionMode() == ExecutionMode.REDIS_READ_ATOMIC;
RedisExecutor executor = new RedisQueuedBatchExecutor<>(isReadOnly, nodeSource, codec, command, params, mainPromise,
false, connectionManager, objectBuilder, commands, connections, options, index, executed, latch);
executor.execute();
} else {
RedisExecutor executor = new RedisBatchExecutor<>(readOnlyMode, nodeSource, codec, command, params, mainPromise,
false, connectionManager, objectBuilder, commands, options, index, executed);
executor.execute();
}
} 3.接着调用了RedisBatchExecutor.execute方法,
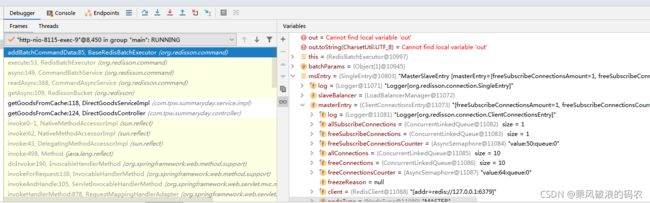
和BaseRedisBatchExecutor.addBatchCommandData
public class RedisBatchExecutor extends BaseRedisBatchExecutor {
@Override
public void execute() {
addBatchCommandData(params);
}
}
public class BaseRedisBatchExecutor extends RedisExecutor {
final ConcurrentMap commands;
final BatchOptions options;
final AtomicInteger index;
final AtomicBoolean executed;
protected final void addBatchCommandData(Object[] batchParams) {
MasterSlaveEntry msEntry = getEntry(source);
Entry entry = commands.get(msEntry);
if (entry == null) {
entry = new Entry();
Entry oldEntry = commands.putIfAbsent(msEntry, entry);
if (oldEntry != null) {
entry = oldEntry;
}
}
if (!readOnlyMode) {
entry.setReadOnlyMode(false);
}
Codec codecToUse = getCodec(codec);
BatchCommandData commandData = new BatchCommandData(mainPromise, codecToUse, command, batchParams, index.incrementAndGet());
entry.getCommands().add(commandData);
}
这里的commands为以主节点为KEY,以待发送命令队列列表为VALUE(Entry),保存一个MAP.然后会把命令都添加到entry的commands命令队列中。
public static class Entry {
Deque> commands = new LinkedBlockingDeque<>();
volatile boolean readOnlyMode = true;
三、批量执行命令
1.调用rBatch.executeAsync(),接着会调用到CommandBatchService.executeAsync
CommandBatchService
public RFuture> executeAsync() {
AtomicInteger slots = new AtomicInteger(commands.size());
for (Map.Entry, List> entry : nestedServices.entrySet()) {
slots.incrementAndGet();
for (CommandBatchService service : entry.getValue()) {
service.executeAsync();
}
entry.getKey().onComplete((res, e) -> {
handle(voidPromise, slots, entry.getKey());
});
}
for (Map.Entry e : commands.entrySet()) {
RedisCommonBatchExecutor executor = new RedisCommonBatchExecutor(new NodeSource(e.getKey()), voidPromise,
connectionManager, this.options, e.getValue(), slots);
executor.execute();
}
return promise;
} 2.接着跳到RedisCommonBatchExecutor.execute方法,这个调用了基类RedisExecutor的execute方法,
RedisExecutor
public void execute() {
codec = getCodec(codec);
RFuture connectionFuture = getConnection();
RPromise attemptPromise = new RedissonPromise();
mainPromiseListener = (r, e) -> {
if (mainPromise.isCancelled() && connectionFuture.cancel(false)) {
log.debug("Connection obtaining canceled for {}", command);
timeout.cancel();
if (attemptPromise.cancel(false)) {
free();
}
}
};
if (attempt == 0) {
mainPromise.onComplete((r, e) -> {
if (this.mainPromiseListener != null) {
this.mainPromiseListener.accept(r, e);
}
});
}
scheduleRetryTimeout(connectionFuture, attemptPromise);
connectionFuture.onComplete((connection, e) -> {
if (connectionFuture.isCancelled()) {
connectionManager.getShutdownLatch().release();
return;
}
if (!connectionFuture.isSuccess()) {
connectionManager.getShutdownLatch().release();
exception = convertException(connectionFuture);
return;
}
sendCommand(attemptPromise, connection);
writeFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
checkWriteFuture(writeFuture, attemptPromise, connection);
}
});
releaseConnection(attemptPromise, connectionFuture);
});
attemptPromise.onComplete((r, e) -> {
checkAttemptPromise(attemptPromise, connectionFuture);
});
} 3.接着调用到RedisCommonBatchExecutor.sendCommand方法,进行命令发送。
@Override
protected void sendCommand(RPromise attemptPromise, RedisConnection connection) {
boolean isAtomic = options.getExecutionMode() != ExecutionMode.IN_MEMORY;
List> list = new ArrayList<>(entry.getCommands().size());
for (CommandData c : entry.getCommands()) {
if ((c.getPromise().isCancelled() || c.getPromise().isSuccess())
&& !isWaitCommand(c)
&& !isAtomic) {
// skip command
continue;
}
list.add(c);
}
writeFuture = connection.send(new CommandsData(attemptPromise, list, options.isSkipResult(), isAtomic, isQueued, options.getSyncSlaves() > 0));
} 注意这里的CommandsData里面的命令是一个列表,可以支持多个。
public class CommandsData implements QueueCommand {
private final List> commands;
private final List> attachedCommands;
public CommandsData(RPromise promise, List> commands, boolean queued, boolean syncSlaves) {
this(promise, commands, null, false, false, queued, syncSlaves);
}
public CommandsData(RPromise promise, List> commands, boolean skipResult, boolean atomic, boolean queued, boolean syncSlaves) {
this(promise, commands, null, skipResult, atomic, queued, syncSlaves);
} 4.接着会调用RedisConnection.send方法来发送数据,其实是调用netty中生成的NioSocketChannel来写入命令数据。
RedisConnection
public ChannelFuture send(CommandsData data) {
return channel.writeAndFlush(data);
}5.netty的channel的writeAndFlush会调用管道中所有的outHandler进行处理。那在这里就是
CommandEncoder,CommandBatchEncoder,这里首先会调用到CommandBatchEncoder的encode方法
CommandBatchEncoder
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, CommandsData msg, ByteBuf out) throws Exception {
CommandEncoder encoder = ctx.pipeline().get(CommandEncoder.class);
for (CommandData commandData : msg.getCommands()) {
encoder.encode(ctx, commandData, out);
}
}这里面就是循环取出命令,逐个调用CommandEncoder单个命令编码器进行编码,最后再加到out列表中,一个网络包发送出去。
这里就是对两个命令编码的过程,接着就是调用socket.write将命令数据发送到服务端。
四、接收命令回应。
1.这个是接收的结果为一次性接收到的网络数据,格式为REDIS的协议。
2021-11-19 10:14:08.418 tt TRACE 28472 --- [sson-netty-2-23] o.r.c.h.CommandDecoder.decode(CommandDecoder.java:114) : reply: $5
xdwww
*2
$4
word
$5
hello
2.接收回调处理,CommandDecoder.decode,在handleResult中会通知结果。
protected void decode(ByteBuf in, CommandData data, List 3.handleResult
private void handleResult(CommandData data, List parts, Object result, boolean skipConvertor) {
if (data != null && !skipConvertor) {
result = data.getCommand().getConvertor().convert(result);
}
if (parts != null) {
parts.add(result);
} else {
completeResponse(data, result);
}
} 4.解码列表。
private void decodeList(ByteBuf in, CommandData data, List parts,
Channel channel, long size, List respParts, boolean skipConvertor, List> commandsData)
throws IOException {
if (parts == null && commandsData != null) {
for (int i = respParts.size(); i < size; i++) {
int suffix = 0;
if (RedisCommands.MULTI.getName().equals(commandsData.get(0).getCommand().getName())) {
suffix = 1;
}
CommandData commandData = (CommandData) commandsData.get(i+suffix);
decode(in, commandData, respParts, channel, skipConvertor, commandsData);
if (commandData.getPromise().isDone() && !commandData.getPromise().isSuccess()) {
data.tryFailure(commandData.cause());
}
}
} else {
for (int i = respParts.size(); i < size; i++) {
decode(in, data, respParts, channel, skipConvertor, null);
}
}
MultiDecoder decoder = messageDecoder(data, respParts);
if (decoder == null) {
return;
}
Object result = decoder.decode(respParts, state());
decodeResult(data, parts, channel, result);
}
5.设置commandData的等待PROMISE的结果值。
protected void completeResponse(CommandData data, Object result) {
if (data != null) {
data.getPromise().trySuccess(result);
}
}
private void handleResult(CommandData data, List parts, Object result, boolean skipConvertor) {
if (data != null && !skipConvertor) {
result = data.getCommand().getConvertor().convert(result);
}
if (parts != null) {
parts.add(result);
} else {
completeResponse(data, result);
}
}