定义
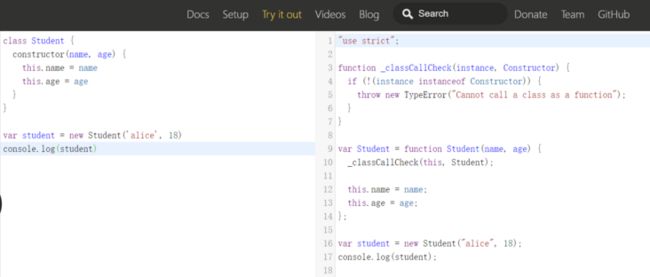
类是构造函数、原型链的语法糖。
定义类有两种方式
class Student {
}
var Student = class {
}某些浏览器可能无法解析es6及以上的语法,这时候需要通过babel将代码解析成浏览器可识别的语法,定义类的语法通过babel编译之后就是通过function定义的构造函数。
类和构造函数是一样的,通过new关键字创建,具有prototype属性
class Student{}
var student = new Student()
console.log(Student.prototype)
console.log(Student.prototype.constructor)
console.log(student.__proto__ === Student.prototype)
console.log(student instanceof Student)
console.log(typeof Student)执行结果如下
类的方法
构造方法
通过constructor来定义类的构造方法,通过new关键字来创建类的实例时会执行构造方法中的代码
class Student {
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
}
var student = new Student('alice', 18)
console.log(student)执行结果如下,创建了一个Student的实例对象
babel解析结果如下
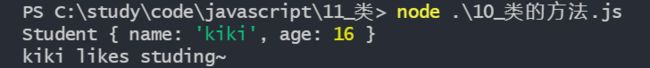
实例方法
实例方法就是挂载在类(构造函数)原型上的方法,可以供所有的实例对象使用,不会在每个实例对象上保存一份
class Student {
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
studying() {
console.log(`${this.name} likes studing~`)
}
}
var student = new Student('kiki', 16)
console.log(student)
student.studying()执行结果如下
访问器方法
访问器方法可以用于获取/修改类中的属性
class Student {
constructor(){
this.mainSubject = 'Chinese'
}
get subject(){
console.log('获取主修课')
return this.mainSubject
}
set subject(value){
console.log('修改主修课')
this.mainSubject = value
}
}
var student = new Student()
console.log(student)
student.mainSubject = 'Math'
console.log(student)执行结果如下
静态方法
定义在类(构造函数)上,且仅供类(构造函数)自身可使用
class Student {
static showInfo(){
console.log('我是一个Student类')
}
}
Student.showInfo()执行结果如下
继承
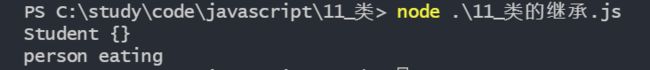
类中实现继承要比构造函数中更为简单,通过extends关键字就可以实现两个类的继承关系。
class Person{
eating(){
console.log('person eating')
}
}
class Student extends Person{
}
var student = new Student()
console.log(student)
student.eating()执行结果如下
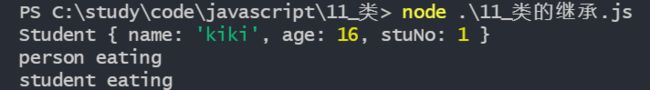
如果要共享构造方法中的数据,则需要通过super来实现
class Person{
constructor(name, age){
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
eating(){
console.log('person eating')
}
}
class Student extends Person{
constructor(name, age, stuNo){
super(name, age)
this.stuNo = stuNo
}
eating(){
super.eating()
console.log('student eating')
}
}
var student = new Student('kiki', 16, 1)
console.log(student)
student.eating()执行结果如下
继承内置类
当我们需要对javascript内置的函数做一些扩充的时候,可以继承自内置的函数。比如对数组进行补充,新增一个返回数组中第一个元素的方法。
class iArray extends Array {
firstItem(){
return this[0]
}
}
let arr = new iArray(1, 2, 3)
console.log(arr)
console.log(arr.firstItem())执行结果如下
混入
javascript中只能单继承,不支持多个父类,当子类希望获取多个父类的属性和方法时,可以自定义mixin的方式来实现继承关系
function mixinRunner(BaseClass) {
return class extends BaseClass {
running() {
console.log('running')
}
}
}
function mixinEater(BaseClass){
return class extends BaseClass {
eating() {
console.log('eating')
}
}
}
class Person {
}
const Student = mixinEater(mixinRunner(Person))
const student = new Student()
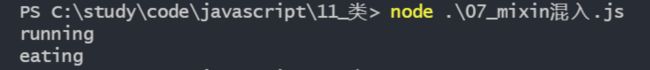
student.running()
student.eating()执行结果如下
多态
不同的数据类型操作执行同一个操作时,表现出来的行为不一致,就称为多态。
function calcArea(foo) {
console.log(foo.getArea())
}
var circle = {
radius: 6,
getArea() {
return this.radius * 3.14
}
}
function Person() {
this.getArea = function(){
return 20
}
}
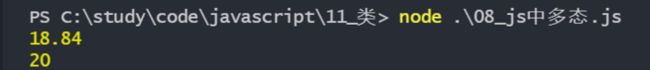
calcArea(circle)
calcArea(new Person())执行结果如下
以上执行两次calcArea函数,传入的参数分别为普通对象和实例对象,执行他们各自的getArea方法,最后获取的结果也不一样
以上就是ES6之类(class)使用的具体介绍,关于js高级,还有很多需要开发者掌握的地方,可以看看我写的其他博文,持续更新中~