【实战】轻轻松松使用StyleGAN(三):基于ResNet50构造StyleGAN的逆向网络,从目标图像提取特征码
在前面的文章里,我们可以利用StyleGAN创建令人惊讶的黄种人脸和专属于自己的老婆动漫头像,内容请参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41943311/article/details/100539707
并且,我们知道,可以对特征码进行混合与编辑,改变这些人脸和动漫头像的风格,内容请参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41943311/article/details/100694599
那么,能不能给出一个目标图像,使用神经网络自动提取出它的特征码呢?
如果可以,那么我们就可以方便地对这些图像进行编辑,创造出各种各样“酷炫”的风格人像。
这个工作可以分为两步:
(1)先利用StyleGAN生成的特征码和生成的人脸图像训练一个网络,把人脸图像作为输入,把特征码作为输出,理论上可以得到一个StyleGAN的逆向网络模型,如果训练成功的话,这个模型可以自动将人脸图像转换为特征码;
(2)利用真实人脸图像对上面得到的模型进行进一步训练和“微调”,使之能够用于真实人脸的特征码提取。
这篇文章先说明第一步的工作。
我们构造了一个如下图所示的神经网络,并计划对它进行训练。这个网络的输入为256x256的图片,输出为18x512的dlatents(StyleGAN的中间数据层,即:w)
构建这个模型的代码如下,我们这里把这个模型叫做lotus_body():
# 定义StyleGAN的逆向网络模型lotus
# 下面的功能函数均使用keras原生函数构造
def lotus_body(x):
# input: (none, 256, 256, 3), output: (none, 8, 8,2048)
# 必须设定include_top=False, weights=None, 才能将输入设为256x256x3
# resnet输出C5,C5的shape是(none, 8, 8, 2048)
resnet = keras.applications.resnet50.ResNet50(include_top=False, weights=None, input_tensor=x, input_shape=(256,256,3))
y = resnet.output
print('ResNet50 C5 shape : ', y.shape)
# output: (none, 8, 8, 144)
# 输出feature maps = filters = 144, 2D卷积输出的高和宽8 - 1 + 1 = 8
y = keras.layers.convolutional.Conv2D(144, (1, 1), padding='same', activation='relu')(y)
# output: (none, 96, 96)
y = keras.layers.Reshape((96, 96))(y)
for i in range(3):
# output: (none, 96, 96)
# 输出feature maps = filters = 96, 1D卷积输出的长度96 - 1 + 1 = 96
y = keras.layers.local.LocallyConnected1D(96, 1)(y)
# output: (none, 96, 96),(2,1)代表将输入的第二个维度重拍到输出的第一个维度,而将输入的第一个维度重排到第二个维度
y = keras.layers.Permute((2, 1))(y)
# output:(none, 96, 96)
y = keras.layers.local.LocallyConnected1D(96, 1)(y)
# output: (none, 18, 512)
y = keras.layers.Reshape((18, 512))(y)
print('lotus body output shape : ', y.shape)
return y为了训练这个模型,我们用StyleGAN生成了1200个dlatents以及它们所对应的人脸图片,并记录到文件中,训练时我们从文件中加载数据,并训练lotus模型。
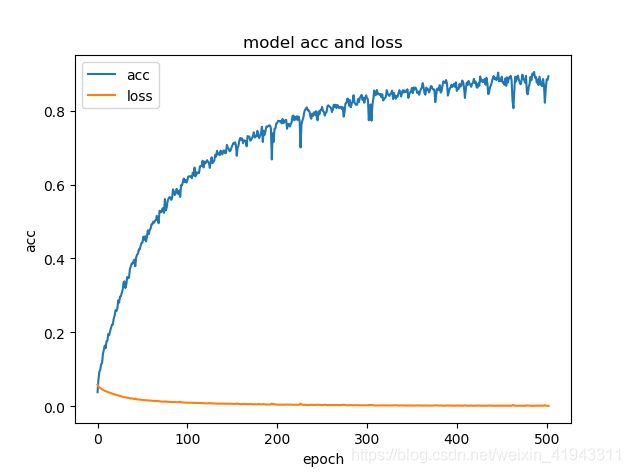
由于lotus模型输出的不是目标的分类,而是18x512的张量,因此我们使用mean_squared_error作为损失函数loss,优化器(optimizer)使用的是adam,epochs = 503,batch_size = 6,最后训练得到的accuracy = 0.8933。
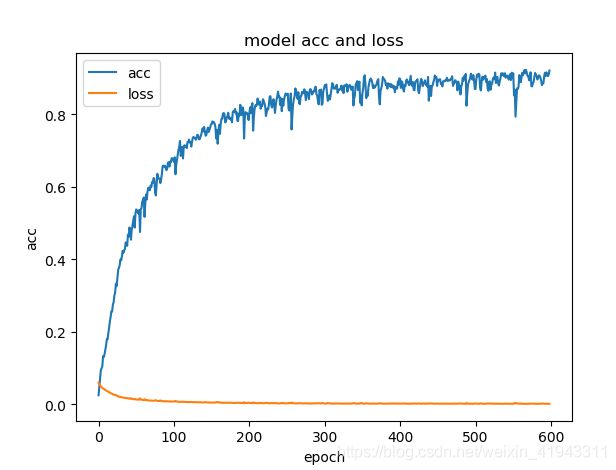
我们用StyleGAN生成了1280个dlatents以及它们所对应的人脸图片,使用mean_squared_error作为损失函数loss,优化器(optimizer)使用的是adam,epochs = 599,batch_size = 8,最后训练得到的accuracy = 0.9201。
完整的lotus网络模型训练及生成测试样片的源代码如下(带中文注释):
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
import os,sys
import numpy as np
import scipy
from scipy import ndimage
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing import image
import keras
import pickle
import PIL.Image
import random
import dnnlib
import dnnlib.tflib as tflib
import config
import glob
# 设置已训练好的模型,用于StyleGAN正向生成人脸图片
Model = './cache/generator_yellow.pkl'
#Model = './cache/karras2019stylegan-ffhq-1024x1024.pkl'
#Model = './cache/2019-03-08-stylegan-animefaces-network-02051-021980.pkl'
synthesis_kwargs = dict(output_transform=dict(func=tflib.convert_images_to_uint8, nchw_to_nhwc=True), minibatch_size=8)
_Gs_cache = dict()
# 设置图片文件的前缀
PREFIX = 'Person'
#PREFIX = 'Animation'
# 训练集和测试集中的图片数量
NUM_FIGURES = 1200
# 定义训练集和测试集的路径,这里创建了 train , 和 test 文件夹
train_path_face = './dataset/train/face/'
train_path_face_dlatents = './dataset/train/face/dlatents/'
test_path_face = './dataset/test/face/'
test_path_face_dlatents = './dataset/test/face/dlatents/'
# 加载StyleGAN已训练好的网络模型
def load_Gs(model):
if model not in _Gs_cache:
model_file = glob.glob(Model)
if len(model_file) == 1:
model_file = open(model_file[0], "rb")
else:
raise Exception('Failed to find the model')
_G, _D, Gs = pickle.load(model_file)
# _G = Instantaneous snapshot of the generator. Mainly useful for resuming a previous training run.
# _D = Instantaneous snapshot of the discriminator. Mainly useful for resuming a previous training run.
# Gs = Long-term average of the generator. Yields higher-quality results than the instantaneous snapshot.
# Print network details.
Gs.print_layers()
_Gs_cache[model] = Gs
return _Gs_cache[model]
# 用StyleGAN生成图像,保存dlatents和图像到文件
def generate_dlatents_and_figures(Gs, w, h, num):
# 生成的latents,大小是512
for i in range(num):
# 生成latents.
SEED = i
rnd = np.random.RandomState(SEED)
latents = rnd.randn(1, Gs.input_shape[1])
# 按照StyleGAN的网络架构,从z变换到w
dlatents = Gs.components.mapping.run(latents, None)
# 保存dlatents到文件
save_name = PREFIX + '_' + str(SEED) + '.npy'
os.makedirs(train_path_face_dlatents, exist_ok=True)
save_path = os.path.join(train_path_face_dlatents, save_name)
np.save(save_path, dlatents)
os.makedirs(test_path_face_dlatents, exist_ok=True)
save_path = os.path.join(test_path_face_dlatents, save_name)
np.save(save_path, dlatents)
# 从w生成图像
images = Gs.components.synthesis.run(dlatents, randomize_noise=False, **synthesis_kwargs)
# 保存图像到文件
save_name = PREFIX + '_' + str(SEED) + '.png'
os.makedirs(train_path_face, exist_ok=True)
save_path = os.path.join(train_path_face, save_name)
PIL.Image.fromarray(images[0], 'RGB').save(save_path)
os.makedirs(test_path_face, exist_ok=True)
save_path = os.path.join(test_path_face, save_name)
PIL.Image.fromarray(images[0], 'RGB').save(save_path)
# 准备Resnet50的训练集,把StyleGAN生成的图片作为输入,对应的dlatents作为输出的验证,训练Resnet50,生成StyleGAN的一个反向网络
def DataSet():
# os.listdir(path) 是 python 中的函数,它会列出 path 下的所有文件名
os.makedirs(train_path_face, exist_ok=True)
imglist_train_face = os.listdir(train_path_face)
os.makedirs(train_path_face_dlatents, exist_ok=True)
# 读取 /test/face 下的所有图片文件名
os.makedirs(test_path_face, exist_ok=True)
imglist_test_face = os.listdir(test_path_face)
os.makedirs(test_path_face_dlatents, exist_ok=True)
# 定义两个 numpy 对象,X_train 和 Y_train
# X_train 对象用来存放训练集的图片。每张图片都需要转换成 numpy 向量形式
# X_train 的 shape 是 (,256,256,3)
# resnet50 缺省的输入图片尺寸是 (224,224) ,我们这里设置为(256,256)
# 3 是图片的通道数(rgb)
# Y_train 用来存放训练集中每张图片对应的dlatents
# Y_train 的 shape 是 (,18,512),与StyleGAN的dlatents一致
X_train = np.empty((len(imglist_train_face), 256, 256, 3))
Y_train = np.empty((len(imglist_train_face), 18, 512))
# count 对象用来计数,每添加一张图片便加 1
count = 0
# 遍历 /train/face 下所有图片,即训练集下所有的图片
for img_name in imglist_train_face:
# 得到图片的路径
if img_name.endswith('png') or img_name.endswith('jpg'):
img_path = os.path.join(train_path_face, img_name)
# 通过 image.load_img() 函数读取对应的图片,并转换成目标大小
# image 是 tensorflow.keras.preprocessing 中的一个对象
img = image.load_img(img_path, target_size=(256, 256))
# 将图片转换成 numpy 数组,并除以 255 ,归一化
# 转换之后 img 的 shape 是 (256,256,3)
img = image.img_to_array(img) / 255.0
# 将处理好的图片装进定义好的 X_train 对象中
X_train[count] = img
# 将对应的标签装进 Y_train 对象中
# 这里需要载入StyleGAN生成图片s时对应的dlatents
only_name = os.path.splitext(img_name)[0]
img_name = only_name + '.npy'
img_path = os.path.join(train_path_face_dlatents, img_name)
Y_train[count] = np.load(img_path)
count += 1
# 准备测试集的数据
X_test = np.empty((len(imglist_test_face), 256, 256, 3))
Y_test = np.empty((len(imglist_test_face), 18, 512))
count = 0
for img_name in imglist_test_face:
if img_name.endswith('png') or img_name.endswith('jpg'):
img_path = os.path.join(test_path_face, img_name)
img = image.load_img(img_path, target_size=(256, 256))
img = image.img_to_array(img) / 255.0
X_test[count] = img
only_name = os.path.splitext(img_name)[0]
img_name = only_name + '.npy'
img_path = os.path.join(test_path_face_dlatents, img_name)
Y_test[count] = np.load(img_path)
count += 1
# 打乱训练集中的数据
index = [i for i in range(len(X_train))]
random.shuffle(index)
X_train = X_train[index]
Y_train = Y_train[index]
# 打乱测试集中的数据
index = [i for i in range(len(X_test))]
random.shuffle(index)
X_test = X_test[index]
Y_test = Y_test[index]
return X_train, Y_train, X_test, Y_test
# 定义StyleGAN的逆向网络模型lotus
# 下面的功能函数均使用keras原生函数构造
def lotus_body(x):
# input: (none, 256, 256, 3), output: (none, 8, 8,2048)
# 必须设定include_top=False, weights=None, 才能将输入设为256x256x3
# resnet输出C5,C5的shape是(none, 8, 8, 2048)
resnet = keras.applications.resnet50.ResNet50(include_top=False, weights=None, input_tensor=x, input_shape=(256,256,3))
y = resnet.output
print('ResNet50 C5 shape : ', y.shape)
# output: (none, 8, 8, 144)
# 输出feature maps = filters = 144, 2D卷积输出的高和宽8 - 1 + 1 = 8
y = keras.layers.convolutional.Conv2D(144, (1, 1), padding='same', activation='relu')(y)
# output: (none, 96, 96)
y = keras.layers.Reshape((96, 96))(y)
for i in range(3):
# output: (none, 96, 96)
# 输出feature maps = filters = 96, 1D卷积输出的长度96 - 1 + 1 = 96
y = keras.layers.local.LocallyConnected1D(96, 1)(y)
# output: (none, 96, 96),(2,1)代表将输入的第二个维度重拍到输出的第一个维度,而将输入的第一个维度重排到第二个维度
y = keras.layers.Permute((2, 1))(y)
# output:(none, 96, 96)
y = keras.layers.local.LocallyConnected1D(96, 1)(y)
# output: (none, 18, 512)
y = keras.layers.Reshape((18, 512))(y)
print('lotus body output shape : ', y.shape)
return y
# 主程序
def main():
tflib.init_tf()
# 第一次生成训练数据时使用,生成后可以注释掉,使得主程序专注于训练
generate_dlatents_and_figures(load_Gs(Model), w=1024, h=1024, num=NUM_FIGURES)
X_train, Y_train, X_test, Y_test = DataSet()
inputs = keras.Input(shape=(256, 256, 3))
model = keras.Model(inputs, lotus_body(inputs))
# 损失函数使用mean_squared_error
model.compile(optimizer="adam", loss="mean_squared_error", metrics=["mae", "acc"])
training = model.fit(X_train, Y_train, epochs=503, batch_size=6)
# 画图看一下训练的效果
plt.plot(training.history['acc'])
plt.plot(training.history['loss'])
plt.title('model acc and loss')
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.ylabel('acc')
plt.legend(['acc', 'loss'], loc='upper left')
plt.show()
# model.evaluate(X_test, Y_test, batch_size=32)
# 把训练好的模型保存到文件
model.save('resnet50_model_face.h5')
print('Trainning completed!')
# 用逆向网络lotus生成一个StyleGan的对比样片
model = keras.models.load_model('resnet50_model_face.h5')
img_path = "f:/images_family/Person_579.png"
img = image.load_img(img_path, target_size=(256, 256))
plt.imshow(img)
img = image.img_to_array(img) / 255.0
img = np.expand_dims(img, axis=0) # 为batch添加第四维
predict_dlatents = model.predict(img)
print('predict_dlatents.shape: ', predict_dlatents.shape)
# 从w生成图像
Gs = load_Gs(Model)
resnet50_images = Gs.components.synthesis.run(predict_dlatents, randomize_noise=False, **synthesis_kwargs)
# 画空白画布
num = len(resnet50_images)
canvas = PIL.Image.new('RGB', (1024, 1024 * num ), 'white')
# 绘制图像
for row, resnet50_image in enumerate(list(resnet50_images)):
canvas.paste(PIL.Image.fromarray(resnet50_image, 'RGB'), (0, 1024 * row))
canvas.save(os.path.join(config.family_dir, 'resnet50_001.png'))
print('resnet50_001.png generated.')
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()用训练成功的lotus逆向网络,从目标图像自动提取特征码,然后可以重新生成一个新图像。
基于已训练好的模型,重新生成新图像的源代码如下(带中文注释):
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
import os
import pickle
import numpy as np
import PIL.Image
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing import image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import dnnlib
import dnnlib.tflib as tflib
import config
import glob
import keras
# 设置已训练好的模型,用于StyleGAN正向生成人脸图片
Model = './cache/generator_yellow.pkl'
#Model = './cache/karras2019stylegan-ffhq-1024x1024.pkl'
#Model = './cache/2019-03-08-stylegan-animefaces-network-02051-021980.pkl'
synthesis_kwargs = dict(output_transform=dict(func=tflib.convert_images_to_uint8, nchw_to_nhwc=True), minibatch_size=8)
_Gs_cache = dict()
# 加载StyleGAN已训练好的网络模型
def load_Gs(model):
if model not in _Gs_cache:
model_file = glob.glob(Model)
if len(model_file) == 1:
model_file = open(model_file[0], "rb")
else:
raise Exception('Failed to find the model')
_G, _D, Gs = pickle.load(model_file)
# _G = Instantaneous snapshot of the generator. Mainly useful for resuming a previous training run.
# _D = Instantaneous snapshot of the discriminator. Mainly useful for resuming a previous training run.
# Gs = Long-term average of the generator. Yields higher-quality results than the instantaneous snapshot.
# Print network details.
Gs.print_layers()
_Gs_cache[model] = Gs
return _Gs_cache[model]
def draw_resnet50_figure(pic_name, Gs, w, h):
model = keras.models.load_model('resnet50_model_face.h5')
#img_path = "f:/images_family/steve_001_fake.png"
img_path = "f:/images_family/Person_9402.png"
img = image.load_img(img_path, target_size=(256, 256))
plt.imshow(img)
img = image.img_to_array(img) / 255.0
img = np.expand_dims(img, axis=0) # 为batch添加第四维
predict_dlatents = model.predict(img)
print('predict_dlatents.shape: ', predict_dlatents.shape)
# 可以考虑暂存一下predict_dlatents
# np.save('predict_dlatents.npy', predict_dlatents)
# predict_dlatents = np.load('predict_dlatents.npy')
# 从w生成图像
Gs = load_Gs(Model)
resnet50_images = Gs.components.synthesis.run(predict_dlatents, randomize_noise=False, **synthesis_kwargs)
# 画空白画布
num = len(resnet50_images)
canvas = PIL.Image.new('RGB', (w, h * num ), 'white')
# 绘制图像
for row, resnet50_image in enumerate(list(resnet50_images)):
canvas.paste(PIL.Image.fromarray(resnet50_image, 'RGB'), (0, h * row))
canvas.save(pic_name)
# Main program.
def main():
os.makedirs(config.family_dir, exist_ok=True)
tflib.init_tf()
draw_resnet50_figure(os.path.join(config.family_dir, 'resnet50_002.png'), load_Gs(Model), w=1024, h=1024)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()左边为目标图像,右边为重新生成的图像,两个图像相当接近。根据这样的结果,我们可以判定,训练成功的lotus逆向网络可以完成从目标图像成功提取特征码(当然,这个模型还有进一步进行优化的空间)。
vs
参考:
http://www.seeprettyface.com/index.html
下一篇:
轻轻松松使用StyleGAN(四):对StyleGAN的逆向网络的训练过程进行优化