目标检测(IOU) + 语义分割(mIOU) +NMS
一、IOU--目标检测
我们先来看下IOU的公式:
现在我们知道矩形T的左下角坐标(X0,Y0),右上角坐标(X1,Y1);
矩形G的左下角坐标(A0,B0),右上角坐标(A1,B1)
这里我们可以看到![]() 和
和![]() 在确定坐标而不确定两个矩形是否相交的情况下,为已知的常量.
在确定坐标而不确定两个矩形是否相交的情况下,为已知的常量.
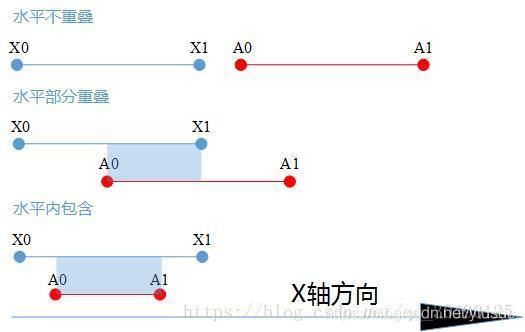
这里我们先来看一下水平方向上的情况:
从上述的三种情况中我们可以看出:
当有重叠或者是内含的情况时,我们可以通过
![]()
计算得到重叠部分的长度.当满足第一种情况时,我们发现W<=0
竖直方向上的处理方式类似.得到H
所以处理成代码的时候可得:
下面的代码使用的坐标是,左下角和右上角。这是为了计算方便。
#RT:RightTop 右上角坐标
#LB:LeftBottom 左下角坐标
def IOU(rectangle A, rectangleB):
W = min(A.RT.x, B.RT.x) - max(A.LB.x, B.LB.x)
H = min(A.RT.y, B.RT.y) - max(A.LB.y, B.LB.y)
if W <= 0 or H <= 0:
return 0;
SA = (A.RT.x - A.LB.x) * (A.RT.y - A.LB.y)
SB = (B.RT.x - B.LB.x) * (B.RT.y - B.LB.y)
cross = W * H
return cross/(SA + SB - cross)def bb_intersection_over_union(boxA, boxB):
# determine the (x, y)-coordinates of the intersection rectangle
xA = max(boxA[0], boxB[0])
yA = max(boxA[1], boxB[1])
xB = min(boxA[2], boxB[2])
yB = min(boxA[3], boxB[3])
# compute the area of intersection rectangle
interArea = (xB - xA + 1) * (yB - yA + 1)
# compute the area of both the prediction and ground-truth
# rectangles
boxAArea = (boxA[2] - boxA[0] + 1) * (boxA[3] - boxA[1] + 1)
boxBArea = (boxB[2] - boxB[0] + 1) * (boxB[3] - boxB[1] + 1)
# compute the intersection over union by taking the intersection
# area and dividing it by the sum of prediction + ground-truth
# areas - the interesection area
iou = interArea / float(boxAArea + boxBArea - interArea)
# return the intersection over union value
return iou参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_30490125/article/details/52887389
目标窗口检测算法-NMS非极大值抑制
这篇文章总结的很好:https://oldpan.me/archives/iu-iou-intersection-over-union-python
二、NMS(非极大值抑制--Non-Maximum Suppression)
NMS具体原理描述参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/makefile/p/nms.html
https://oldpan.me/archives/write-hard-nms-c
一文打尽目标检测NMS——精度提升篇
目标检测算法中检测框合并策略技术综述
优化后的:
# dets(N, 5) 的二维数组: box的集合,N为框的数量,5即4(位置信息)+1(可能为物体的概率得分)
def nms2(dets, thresh):
# x1、y1、x2、y2、以及score赋值
x1 = dets[:, 0]
y1 = dets[:, 1]
x2 = dets[:, 2]
y2 = dets[:, 3]
scores = dets[:, 4]
areas = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1) # 每一个检测框box面积
order = scores.argsort()[::-1] # 按照score置信度从大到小排列,得到排序后的坐标索引
keep = [] # 保留的结果框集合(索引)
while order.size > 0:
i = order[0] # 最大得分box的坐标索引
keep.append(i)
# 第一个索引(0)已经保留, 取剩下的素有索引
# 要与 order[0] 计算IOU
order = order[1:]
# 得到相交区域,左上及右下
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[order])
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[order])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[order])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[order])
# 计算相交的面积,不重叠时面积为0
w = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 1) # 求高和宽,并使数值合法化
inter = w * h # 其他所有box的面积
# 计算IoU:交并比 =重叠面积 /(面积1+面积2-重叠面积)
ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order] - inter)
# 保留IoU小于阈值的box, ovr小表示两个box交集少,可能是另一个物体的框,故需要保留
inds = np.where(ovr <= thresh)[0]
# 保留所有iou小于阈值的框的索引
order = order[inds]
return keep# dets(N, 5) 的二维数组: box的集合,N为框的数量,5即4(位置信息)+1(可能为物体的概率得分)
def py_cpu_nms(dets, thresh):
# x1、y1、x2、y2、以及score赋值
x1 = dets[:, 0]
y1 = dets[:, 1]
x2 = dets[:, 2]
y2 = dets[:, 3]
scores = dets[:, 4]
areas = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1) #每一个检测框box面积
order = scores.argsort()[::-1] # 按照score置信度从大到小排列,得到排序后的坐标索引
keep = [] #保留的结果框集合(索引)
while order.size > 0:
i = order[0] # 最大得分box的坐标索引
keep.append(i)
# 得到相交区域,左上及右下
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[order[1:]])
# 计算相交的面积,不重叠时面积为0
w = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 1) # 求高和宽,并使数值合法化
inter = w * h # 其他所有box的面积
# 计算IoU:交并比 =重叠面积 /(面积1+面积2-重叠面积)
ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter)
# 保留IoU小于阈值的box, ovr小表示两个box交集少,可能是另一个物体的框,故需要保留
inds = np.where(ovr <= thresh)[0]
# iou小于阈值的框,因为ovr数组的长度比order数组少一个,所以这里要将所有下标后移一位
# 算iou的时候没把第一个参考框索引考虑进来,所以这里都要+1
order = order[inds + 1]
return keep代码确实很精炼,其中一些可能需要解释,能够理解更充分:
1、argsort() 的作用是:返回数组从小到大排序后的索引值
2、np.where(condition): 输出满足条件condition元素的坐标。这里的坐标以tuple的形式给出,通常原数组有多少维,输出的tuple中就包含几个数组,分别对应符合条件元素的各维坐标。 需要注意的是如果原数组是一维数组,返回元组是(index,),因此用[0]取出tuple中的第一个元素。
3、order = order[inds + 1] :order存储的是原数组score排序后的索引值,inds 存储的是 ovr 数组中面积小于阈值的ovr 数组元素的索引值,但是因为ovr数组的长度比order数组少一个(第一个元素,也就是得分最高的元素,已经去除放到keep中),所以这里要将 order 中所有下标后移一位。
给出一个测试程序:具体可以打印出来
#coding=utf-8
import cv2
import numpy as np
import random
def mainfun():
img = np.zeros((300, 400), np.uint8)
dets = np.array([[83, 54, 165, 163, 0.8], [67, 48, 118, 132, 0.5], [91, 38, 192, 171, 0.6],[77, 40, 100, 100, 0.7]], np.float)
img_cp = img.copy()
for box in dets.tolist(): # 显示待测试框及置信度
x1, y1, x2, y2, score = int(box[0]), int(box[1]), int(box[2]), int(box[3]), box[-1]
y_text = int(random.uniform(y1, y2))
cv2.rectangle(img_cp, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (255, 255, 255), 2)
cv2.putText(img_cp, str(score), (x2 - 30, y_text), 2, 1, (255, 255, 0))
cv2.imshow("ori_img", img_cp)
rtn_box = nms(dets, 0.3) # 改成自己的nms实现函数
cls_dets = dets[rtn_box, :]
print "nms box:", cls_dets
img_cp = img.copy()
for box in cls_dets.tolist():
x1, y1, x2, y2, score = int(box[0]), int(box[1]), int(box[2]), int(box[3]), box[-1]
y_text = int(random.uniform(y1, y2))
cv2.rectangle(img_cp, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (255, 255, 255), 2)
cv2.putText(img_cp, str(score), (x2 - 30, y_text), 2, 1, (255, 255, 0))
cv2.imshow("nms box:", img_cp)
cv2.waitKey(0)
if __name__ == "__main__":
mainfun()NMS C++ 实现:
typedef struct {
int x;
int y;
int w;
int h;
float score;
}Bbox;
//从大到小排序
bool compScore(Bbox box1,Bbox box2){
return box1.score > box2.score ? true : false;
}
float iou(Bbox box1,Bbox box2){
int x1 = max(box1.x,box2.x);
int y1 = max(box1.y,box2.y);
int x2 = min(box1.x+box1.w,box2.x+box2.w);
int y2 = min(box1.y+box1.h,box2.y+box2.h);
int w = max(0,x2 - x1 + 1);
int h = max(0,y2 - y1 + 1);
if( w == 0 || h == 0 ){
retrun 0;
}
float over_area = w*h;
return over_area/(box1.w * box1.h + box2.w * box2.h - over_area);
}
//第一种写法
vector nms(vector &vec_boxs,float threshold){
vector results;
sort(vec_boxs.begin(),vec_boxs.end(),compScore);
while(vec_boxs.size() > 0)
{
results.push_back(vec_boxs[0]);
index = 1 ;
while(index < vec_boxs.size()){
float iou_value = iou(vec_boxs[0],vec_boxs[index]);
if(iou_value > threshold)
vec_boxs.erase(vec_boxs.begin() + index);
else
index++;
}
//删除第一个,已经保存
vec_boxs.erase(vec_boxs.begin());
}
return results;
}
//第二种写法
vector nms(vector &vec_boxs,float threshold){
vector results;
sort(vec_boxs.begin(),vec_boxs.end(),compScore);
while(vec_boxs.size() > 0)
{
// 保存第一个最大的IOU,并从原vec中删除
Bbox temp_box = vec_boxs[0]
results.push_back(temp_box);
vec_boxs.erase(vec_boxs.begin());
// vec_boxs.begin()
vector::iterator it ;
for (it = vec_boxs.begin(); it != vec_boxs.end();)
{
float iou_value = iou(vec_boxs[0], *it);
if(iou_value > threshold)
vec_boxs.erase(it); //erase返回删除元素的下一个元素
else
it++;
}
}
return results;
} 三、soft-NMS
参考:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/42018282
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/41046620
python代码:
# soft_nms操作,这里假设boxes是无序(未按score做降序)的,所以每轮soft_nms迭代都需要类似冒泡排序操作,选择当前top-1 bbox做NMS
# Nt:计算IoU的阈值,IoU > Nt,对应bbox的score权重就要降低 score*weight
# threshold:上面的降权后,如果 score*weight < threshold 则要剔除掉这个box
def soft_nms(boxes, sigma=0.5, Nt=0.1, threshold=0.001, method=1):
N = boxes.shape[0]
for i in range(N):
# 找到最大得分的box 的位置maxpos
maxpos = np.argmax(boxes[:, 4])
# 交换位置 i 和 maxpos 的box值
# tx1,ty1,tx2,ty2,ts 现在当前 i 位置的坐标和score 不一定是最大
tx1 = boxes[i, 0]
ty1 = boxes[i, 1]
tx2 = boxes[i, 2]
ty2 = boxes[i, 3]
ts = boxes[i, 4]
# add max box as a detection
boxes[i, 0] = boxes[maxpos, 0]
boxes[i, 1] = boxes[maxpos, 1]
boxes[i, 2] = boxes[maxpos, 2]
boxes[i, 3] = boxes[maxpos, 3]
boxes[i, 4] = boxes[maxpos, 4]
# swap ith box with position of max box
boxes[maxpos, 0] = tx1
boxes[maxpos, 1] = ty1
boxes[maxpos, 2] = tx2
boxes[maxpos, 3] = ty2
boxes[maxpos, 4] = ts
# 此时 位置 i 保存的是最大score的bbox信息了
# 上面交换后,位置 i 处的 tx1,ty1,tx2,ty2,ts 就是现在保存的是最大的分box的坐标和score
tx1 = boxes[i, 0]
ty1 = boxes[i, 1]
tx2 = boxes[i, 2]
ty2 = boxes[i, 3]
ts = boxes[i, 4]
# 现在pos位置是得分最大的box,从pos+1位置开始与最大得分的bbox比较
pos = i + 1
# NMS iterations, note that N changes if detection boxes fall below threshold
while pos < N: # 向后做NMS比较
x1 = boxes[pos, 0] # 当前位置的bbox
y1 = boxes[pos, 1]
x2 = boxes[pos, 2]
y2 = boxes[pos, 3]
s = boxes[pos, 4]
area = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
iw = (min(tx2, x2) - max(tx1, x1) + 1)
if iw > 0: # 计算Insection的宽iw,如果iw < 0,说明没相交,可以直接忽略了
ih = (min(ty2, y2) - max(ty1, y1) + 1)
if ih > 0: # 计算Insection的宽ih,如果ih < 0,说明没相交,可以直接忽略了
ua = float((tx2 - tx1 + 1) * (ty2 - ty1 + 1) + area - iw * ih)
ov = iw * ih / ua # iou between max box and detection box
if method == 1: # linear降权操作
if ov > Nt:
weight = 1 - ov
else:
weight = 1
elif method == 2: # gaussian 降权
weight = np.exp(-(ov * ov) / sigma)
else: # original NMS weight = 0就直接把score置0
if ov > Nt:
weight = 0
else:
weight = 1
boxes[pos, 4] = weight * boxes[pos, 4]
print(boxes[:, 4])
# update N
# 如果bbox调整后的权重,已经小于阈值threshold,那么这个bbox就可以忽略了
# 操作方式是直接用最后一个N-1位置的有效的bbox替换当前pos上的bbox
if boxes[pos, 4] < threshold:
boxes[pos, 0] = boxes[N - 1, 0]
boxes[pos, 1] = boxes[N - 1, 1]
boxes[pos, 2] = boxes[N - 1, 2]
boxes[pos, 3] = boxes[N - 1, 3]
boxes[pos, 4] = boxes[N - 1, 4]
N = N - 1 # 更新N, 最后一个box(小于阈值)忽略掉
# 当 第 N-1 位置的 box 被 替换到 pos 位置时,这个box是还没有计算过IOU的,
# 因此再次进行计算一遍IOU,因此 pos = pos
pos = pos
else:
# 当box 没有置换时, 则计算 pos + 1 位置IOU
# 因此再次进行计算一遍IOU,因此 pos = pos
pos = pos + 1
# bbox也做了对应的调整、筛选,bbox list中top-N就对应着最高score,且soft-nms筛选通过的bbox
keep = [i for i in range(N)]
return keep
# 测试代码
boxes = np.array([[100, 100, 150, 168, 0.63], [166, 70, 312, 190, 0.55],
[221, 250, 389, 500, 0.79], [12, 190, 300, 399, 0.9], [28, 130, 134, 302, 0.3]])
keep = soft_nms(boxes)
print(keep)四、mIOU - 语义分割
参考文章(必须读):语义分割之MIoU原理与实现
mIoU相关
在计算机视觉深度学习图像分割领域中,mIoU值是一个衡量图像分割精度的重要指标。mIoU可解释为平均交并比,即在每个类别上计算IoU值,然后求平均值。Pixel Accuracy(PA,像素精度),mIoU的介绍参考链接:论文笔记 | 基于深度学习的图像语义分割技术概述之5.1度量标准
混淆矩阵介绍
fast_hist()函数用于产生n*n的分类统计表,还不理解的可以看如下分析:
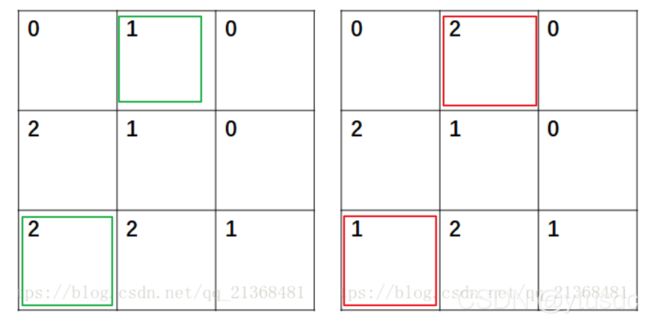
假如输入的标签图a是3*3的,如下左图,图中的数字表示该像素点的归属,即每个像素点所属的类别(其中n=3,即共有三种类别);预测标签图b的大小和a相同,如右图所示(图中的数字也代表每个像素点的类别归属)。
直观上看,b中预测的标签有两个像素点预测出错,即上图所示 b01, b20
源码中的这句语句是精华:
np.bincount( num_cls * label_true[mask].astype(int) +
label_pred[mask], minlength=num_cls ** 2).reshape(num_cls, num_cls)其作用是产生一行n*n个元素的向量,向量中的每个元素存储统计结果,假如该向量为d,则其中的d(i*n+j)表示预测结果为类别 j,实际标签为类别 i 的所有像素点的数目。
将上述的a、b和n输入fast_hist(a, b, n),所产生的d为:d=(3,0,0,0,2,1,0,1,2),其中的d(1*3+1)=d(4)表示预测类别为1,实际标签也为1的所有像素点数目为2。
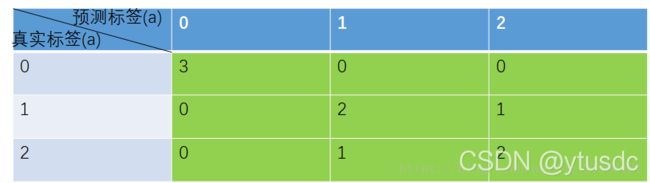
通过reshape(n, n)将向量d转换为3*3的矩阵,其结果如下表(该矩阵即为下表中的绿色部分):
其中绿色的3*3表格统计的含义,拿数字3所在的这一格为例,即预测标签中被预测为类别0的且其真实标签也为0的所有像素点数目之和。
上述表格有几点需要注意的是(这三条是用于计算一开始所讲的四个指标的基础):
①绿色表格中对角线元素上的数字即为该类别预测正确的像素点(样本)数,非对角线元素都是预测错误的,拿最后一行的数字1为例,其含义即为有一个原本应属于类别2的像素点被错误地预测为类别1;
②绿色表格的每一行求和得到的数字的含义是真实标签中属于某一类别的所有像素点(样本)数,拿第一行为例,3+0+0=3,即真实属于类别0的像素点一共3个;
③绿色表格的每一列求和得到的数字的含义是被预测为某一类别的所有像素点数,拿第二列为例,0+2+1=3,即预测为类别1的所有像素点共有3个。
'''
产生n×n的分类统计表
参数a:标签图(转换为一维数组),即真实的标签
参数b:score层输出的预测图(转换为一维数组),即预测的标签
参数n: 类别数
'''
def fast_hist(label_pred, label_true, num_cls):
# 找出标签中需要计算的类别,去掉了背景
mask = (label_true >= 0) & (label_true < num_cls)
# np.bincount计算了从0到n**2-1这n**2个数中每个数出现的次数,返回值形状(n, n)
hist = np.bincount(
num_cls * label_true[mask].astype(int) +
label_pred[mask], minlength=num_cls ** 2).reshape(num_cls, num_cls)
return hist
# 输入:预测值和真实值
# 语义分割的任务是为每个像素点分配一个label
def evaluate(predictions, gts):
hist = np.zeros((num_cls, num_cls))
for lp, lt in zip(predictions, gts):
assert len(lp.flatten()) == len(lt.flatten())
# 对每一(预测,真实)标签,生成num_cls×num_cls矩阵,并累加
hist += fast_hist(lp.flatten(), lt.flatten())
# 分别为每个类别计算mIoU,hist的形状(n, n)
iou = np.diag(hist) / (hist.sum(axis=1) + hist.sum(axis=0) - np.diag(hist))
miou = np.nanmean(iou) # 求所有类别平均的mIoU值,计算时忽略NaN值
return miou代码释意:
1、np.bincount计算了从0到n**2-1这n**2个数中每个数出现的次数,返回值形状(n, n)
bincount()函数用于统计数组内每个非负整数的个数
详见 https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.bincount.html
2、iou = np.diag(hist) / (hist.sum(axis=1) + hist.sum(axis=0) - np.diag(hist))
np.diag(hist) -- 矩阵的对角线上的值组成的一维数组
(hist.sum(axis=1) + hist.sum(axis=0) - np.diag(hist)) -- 矩阵的所有某一类别行列元素之和组成的一维数组,返回值形状(n,)
参考文章:
深度学习计算机视觉图像分割领域指标mIoU(平均交并比)计算代码与逐行解析
FCN源码解读之score.py
语义分割代码阅读---评价指标mIoU的计算