1、前言
当提及如何终止一个线程时,部分读者通常立马想到的方法肯定是stop(),但是stop()方法并不被推荐使用(很多规范中是禁止使用的),其原因是强制终止一个线程,会导致程序不正常的结束,会出现资源未正确释放、程序结果不正确等等问题。而是否终止一个线程应该把这个控制权转交给当前被终止的线程本身,此时采用的办法就是 ****interrupt()方法来终止,该方法相当于修改一个共享变量的值,当运行中的线程判断当前值为false则继续运行,如果有地方调用当前thread的interrupt()方法,那么这个值将变为true,此时当前线程可以根据这个值的修改来正确的终止线程的运行。
2、API
在java.lang.Thread中主要提供了如下与线程中断相关的方法,其具体方法名与主要作用如下表所示。
| 方法名 | 方法作用 |
|---|---|
| public void interrupt() | 中断此线程 |
| public static boolean interrupted() | 测试当前线程是否被中断,该方法会恢复(清除)中断标志 |
| public boolean isInterrupted() | 测试当前线程是否被中断,该方法只会获取中断标志,不会恢复(清除)中断标志 |
| private native boolean isInterrupted(boolean ClearInterrupted); | interrupted()和isInterrupted()最终调用,该方法是native本地方法,在jvm中具体实现,也是获取线程中断标志真正调用的方法,参数ClearInterrupted意思是是否恢复(清除)中断标志 |
源码:
/**
* 中断此线程
*/
public void interrupt() {
if (this != Thread.currentThread())
checkAccess();
synchronized (blockerLock) {
Interruptible b = blocker;
if (b != null) {
interrupt0(); // Just to set the interrupt flag
b.interrupt(this);
return;
}
}
interrupt0();
}
/**
* 测试当前线程是否被中断,返回中断标志
*/
public static boolean interrupted() {
return currentThread().isInterrupted(true);
}
/**
* 测试当前线程是否被中断,返回中断标志
*/
public boolean isInterrupted() {
return isInterrupted(false);
}
/**
* 线程是否被中断native方法,ClearInterrupted为是否清除中断标志参数
*/
private native boolean isInterrupted(boolean ClearInterrupted);
/**
* 中断当前线程的native方法
*/
private native void interrupt0();
3、interrupted()和isInterrupted()区别
看了上述API讲述和Thread中的源码,已经清楚interrupted()和isInterrupted()的主要区别了
interrupted()为静态方法,isInterrupted()为普通方法
interrupted() 返回中断标志且清除(恢复)中断标志,isInterrupted()仅返回中断标志
3.1 使用方法
我们先验证中断异常响应,通过如下两种方法的使用示例来介绍,注意Runner中的run方法的部分区别
方法一
package com.liziba.p7; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; /** ** *
* * @Author: Liziba * @Date: 2021/6/24 21:05 */ public class ThreadInterruptedDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runner(), "Thread-01"); t1.start(); // 主线程睡眠1秒,保证t1的充分执行 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); // 发起中断 t1.interrupt(); } static class Runner implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " is running ."); } } } }
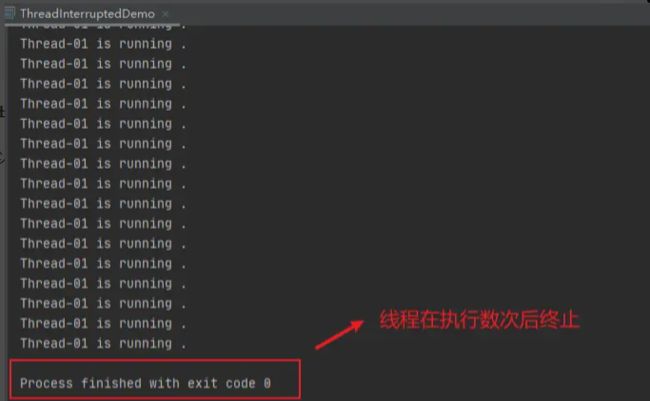
输出结果:
可以看到线程在执行数次后终止运行
方法二
package com.liziba.p7; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; /** ** *
* * @Author: Liziba * @Date: 2021/6/24 21:18 */ public class ThreadInterruptedDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runner(), "Thread-01"); t1.start(); // 主线程睡眠2秒,保证t1的充分执行 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); // 发起中断 t1.interrupt(); } static class Runner implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " is running ."); try { // 睡眠2秒,保证主线程发起的中断能被捕获 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // 不对中断做任何处理,try住异常,打印 e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
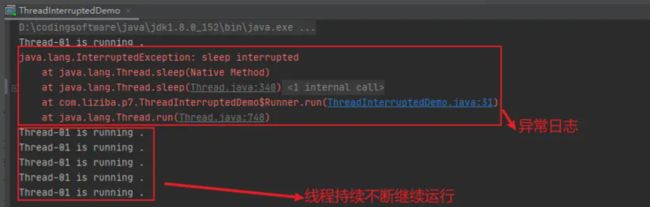
输出结果:
可以看到main线程中发起的t1线程中断,被捕获住异常后,未做任何处理,线程继续持续不断的运行
总结上述两种方式:
方法一和方法二,均通过判断Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()的值来运行run方法中的逻辑,Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()在线程未中断时返回false,当main线程中执行 t1.interrupt()时,线程t1被中断,Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()的值变为false;在方法一中,获取到这个变化后直接结束运行;在方法二中,由于sleep()使得线程阻塞会响应中断,但是此时我仅仅catch住异常,并没有对中断做任何处理,这里有个知识点是,线程响应中断抛出异常时,会恢复(清除)中断标志,所以t1.interrupt()对中断标志的修改又被恢复了,程序仍然不断的运行。
接下来我们来验证interrupted()对于中断的标志的清除
package com.liziba.p7; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; /** ** isInterrupted() *
* * @Author: Liziba * @Date: 2021/6/24 21:20 */ public class ThreadInterruptDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread thread = new Thread(new Runner(), "Thread-1"); thread.start(); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); thread.interrupt(); } static class Runner implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +" interrupted flag is " + Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()); while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) { try { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " is running ."); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // 响应中断,抛出异常后中断位置会被复位,自己中断自己 Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); // 这里调用isInterrupted()获取当前的中断标志 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +" interrupted flag is " + Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()); } } } } }
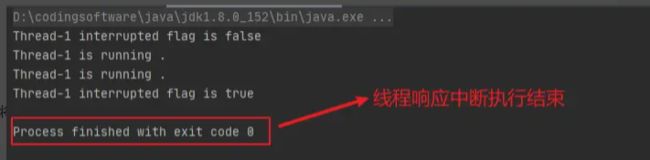
输出结果:
这里证明interrupted()不清楚中断标志,线程在获取到 thread.interrupt()发起中断后,执行结束。
将上述catch中的Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()修改为Thread.interrupted()再次运行
package com.liziba.p7; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; /** ** *
* * @Author: Liziba * @Date: 2021/6/24 21:23 */ public class ThreadInterruptDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread thread = new Thread(new Runner(), "Thread-1"); thread.start(); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); thread.interrupt(); } // 区别在catch中 static class Runner implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +" interrupted flag is " + Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()); while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) { try { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " is running ."); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // 响应中断,抛出异常后中断位置会被复位,自己中断自己 Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); // 注意区别在这里 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +" interrupted flag is " + Thread.interrupted()); } } } } }
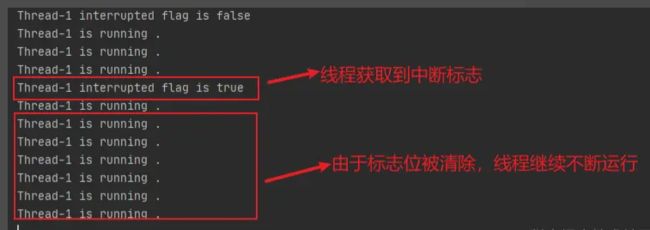
输出结果:
线程也响应到了 thread.interrupt()的中断,但是由于catch中调用了Thread.interrupted(),对中断标志进行了清除,所以!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()判断仍然等于true,线程继续不断的运行
看到这里,应该已经理解了这两个方法的主要区别和其使用,最后我们来看下一个源码中的使用案例。我们通过观看AbstractQueuedSynchronizer(AQS)中的await()方法,来看其在源码中的使用。
public final void await() throws InterruptedException {
// 判断当前线程是否被中断,如果被中断则恢复中断标志
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
Node node = addConditionWaiter();
int savedState = fullyRelease(node);
int interruptMode = 0;
while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) {
LockSupport.park(this);
if ((interruptMode = checkInterruptWhileWaiting(node)) != 0)
break;
}
if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) && interruptMode != THROW_IE)
interruptMode = REINTERRUPT;
if (node.nextWaiter != null) // clean up if cancelled
unlinkCancelledWaiters();
if (interruptMode != 0)
reportInterruptAfterWait(interruptMode);
}
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer(AQS)源码中使用静态Thread.interrupted(),判断当前线程是否被中断,并恢复中断标志,如果线程已被中断则抛出InterruptedException中断异常。清除标志位的作用就是为了当前线程响应过中断后,再次进入的时候可以进行后续操作。
到此这篇关于Java中的interrupted()和isInterrupted()的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关interrupted()和isInterrupted()内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!