golang字符串拼接方式及其性能分析
golang字符串拼接方式及其性能分析
目录
golang字符串拼接方式及其性能分析
1、什么是字符串string?
2、字符串拼接的方式
1)运算符+=
2)fmt.Sprintf
3)strings.Join
4)bytes.Buffer
5)strings.Builder
3、性能分析
1)底层分析:
2)benchmark压力测试:
1、什么是字符串string?
go源码src/builtin/builtin.go中释义:
// string is the set of all strings of 8-bit bytes, conventionally but not
// necessarily representing UTF-8-encoded text. A string may be empty, but
// not nil. Values of string type are immutable.
type string string字符串是一系列8位字节的集合,通常但不一定代表UTF-8编码的文本。字符串可以为空,但不能为nil。而且字符串的值是不能改变的。
go源码src/runtime/string.go中string的定义:
type stringStruct struct {
str unsafe.Pointer
len int
}string是个结构体,其中str是个指针,指向某个数组的首地址
2、字符串拼接的方式
1)运算符+=
hello := "hello"
world := "world"
hello += world
2)fmt.Sprintf
hello := "hello"
world := "world"
hello = fmt.Sprintf("%s,%s", hello, world)
3)strings.Join
hello := "hello"
world := "world"
hello = strings.Join([]string{hello}, world)
4)bytes.Buffer
hello := "hello"
world := "world"
var buffer bytes.Buffer
buffer.WriteString(hello)
buffer.WriteString(world)
hello = buffer.String()
5)strings.Builder
hello := "hello"
world := "world"
var builder strings.Builder
builder.WriteString(hello)
builder.WriteString(world)
hello = builder.String()
3、性能分析
1)底层分析:
运算符+=:string指针指向的内容是不可更改的,+=生成一个新的字符串,需要重新分配内存,之前的字符串分配的内存由gc回收
fmt.Sprintf:实现用到了[]byte,不会像string那样产生临时的字符串,但是实现逻辑比较复杂,而且还用到了interface,所以效率也不高
strings.Join:根据字符串数组的内容计算出一个拼接字符串的长度,并申请相应大小的内存,然后一个一个字符写入,这种方式在已存在字符串数组的情况下,效率很不错,反之,会产生很大的开销,反而影响性能
bytes.Buffer:使用缓存[]byte存放拼接的字符串,但最终转化string的时候会有一次类型转换,会进行内存分配和内容拷贝
strings.Builder:实现原理与bytes.Buffer类似,对转换string做了优化
2)benchmark压力测试:
package string_test
import (
"bytes"
"fmt"
"strings"
"testing"
)
func BenchmarkConnectStringWithOperator(b *testing.B) {
hello := "hello"
world := "world"
for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ {
hello = hello + world
}
}
func BenchmarkConnectStringWithSprintf(b *testing.B) {
hello := "hello"
world := "world"
for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ {
hello = fmt.Sprintf("%s,%s", hello, world)
}
}
func BenchmarkConnectStringWithJoin(b *testing.B) {
hello := "hello"
world := "world"
for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ {
hello = strings.Join([]string{hello}, world)
}
}
func BenchmarkConnectStringWithBuffer(b *testing.B) {
hello := "hello"
world := "world"
var buffer bytes.Buffer
buffer.WriteString(hello)
for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ {
buffer.WriteString(world)
}
_ = buffer.String()
}
func BenchmarkConnectStringWithBuilder(b *testing.B) {
hello := "hello"
world := "world"
var builder strings.Builder
builder.WriteString(hello)
for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ {
builder.WriteString(world)
}
_ = builder.String()
}
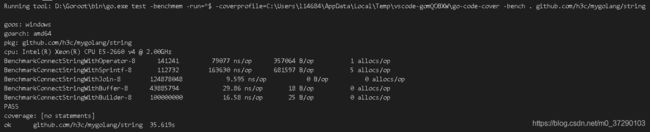
运行后的结果过如下:
从结果我们可以得出结论各字符串拼接方式的性能优劣为:strings.Join > strings.Builder > bytes.Buffer > 运算符+= > fmt.Sprintf,strings.Join方法性能最优,fmt.Sprintf方法性能最差