安卓学习专栏——实战项目酷欧天气(3)显示天气信息
步骤
- 系列文章
- 前言
-
- 实现效果
- 项目结构
- 1.定义GSON实体类
-
- 1.1gson包下建立一个Basic 类
- 1.2gson包下建立一个AQI类
- 1.3gson包下建立一个Now类
- 1.4gson包下建立一个Suggestion类
- 1.5gson包下建立一个Forecast类
- 1.6gson包下建立一个Weather类
- 2.编写天气界面
-
- 2.1新建一个title.xml
- 2.2新建一个now.xml
- 2.3新建一个forecast.xml
- 2.4新建一个forecast_item.xml
- 2.5新建一个aqi.xml
- 2.6新建一个suggestion.xml
- 2.7新建一个forecast_item.xml
- 3.将天气显示到界面上
-
- 3.1添加一个用于解析天气JSON数据的方法
- 3.2修改WeatherActivity中的代码
- 3.3修改ChooseAreaFragment
- 3.4修改MainActivity
- 附录.参考资料
- 下载资源
- 总结
系列文章
提示:转到安卓学习专栏,观看更多内容!
点我直达–>安卓学习专栏
本项目注意包名前缀的修改,改成你自己的,我的包名是:
com.example.coolweather,不然会报错。
前言
本次主题:显示天气信息
项目实战继承前面的文章
上一篇文章
安卓学习专栏——实战项目酷欧天气(2)遍历全国省市县数据
传送门:
https://blog.csdn.net/u011027547/article/details/121508186
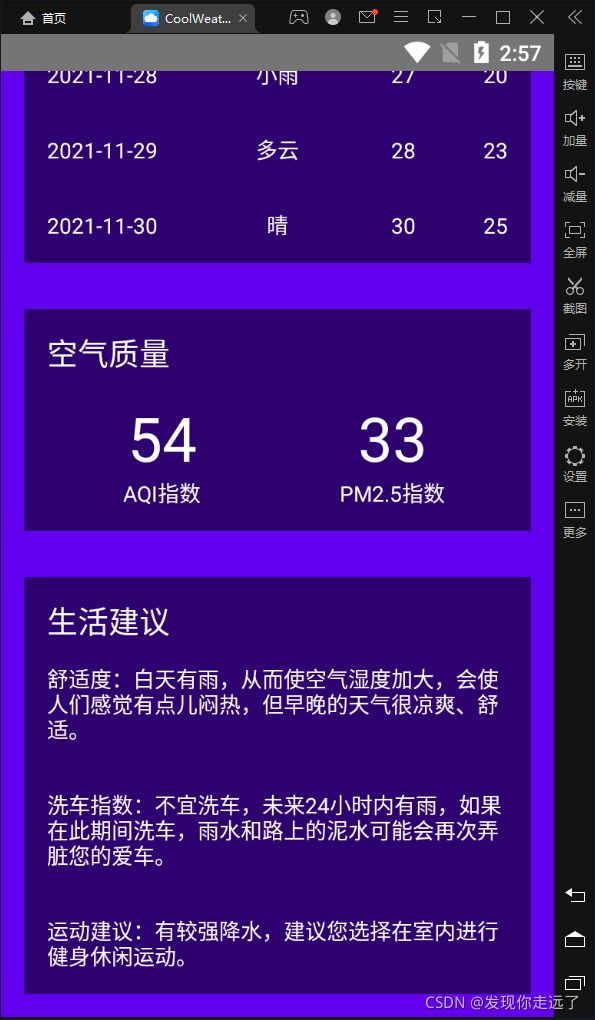
实现效果
选择浙江→绍兴→绍兴 (这里的第二个绍兴市绍兴市区)
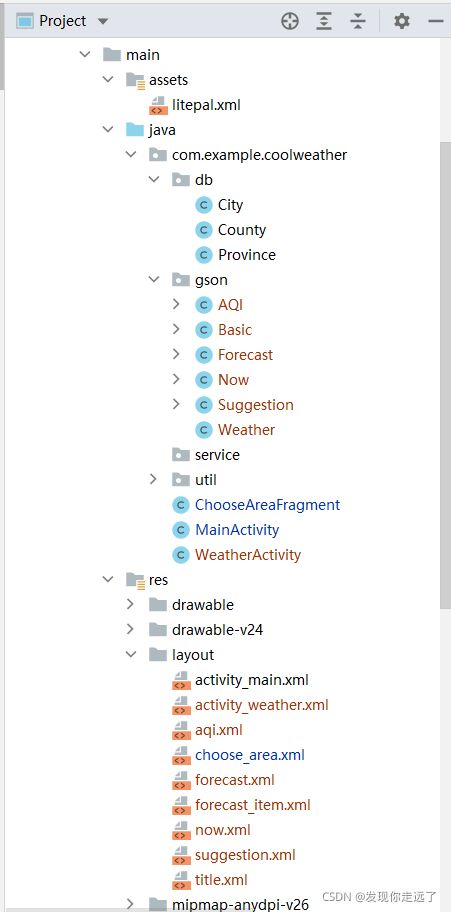
项目结构
在com.coolweather.android包下几个包
- db包用于存放数据库模型相关的代码
- gson包用于存放GSON模型相关的代码
- service包用于存放服务相关的代码
- util包用于存放工具相 关的代码。
1.定义GSON实体类
返回数据的大致格式
{
"HeWeather": [{
"status": "ok",
"basic": {},
"aqi": {},
"now": {},
"suggestion": {},
"daily_forecast": []
}]
}
basic 、aqi 、now 、suggestion 和daily_forecast 的内部又都会有具体的内容,那么我们就可以将这5个部分定义成5个实体类。
1.1gson包下建立一个Basic 类
basic 中原来的具体内容
"basic":{
"city":"苏州",
"id":"CN101190401",
"update":{
"loc":"2016-08-08 21:58"
}
}
JSON中的一些字段可能不太适合直接作为Java字段来命名,因此这里使用了@SerializedName注解的方式来让JSON字段和Java字段之间建立映射关系。
gson包下建立一个Basic 类
package com.example.coolweather.gson;
import com.google.gson.annotations.SerializedName;
public class Basic {
@SerializedName("city")
public String cityName;
@SerializedName("id")
public String weatherId;
public Update update;
public class Update {
@SerializedName("loc")
public String updateTime;
}
}
1.2gson包下建立一个AQI类
AQI中原来的具体内容
"aqi":{
"city":{
"aqi":"44",
"pm25":"13"
}
}
在gson包下新建一个AQI 类
package com.example.coolweather.gson;
public class AQI {
public AQICity city;
public class AQICity {
public String aqi;
public String pm25;
}
}
1.3gson包下建立一个Now类
Now中原来的具体内容
"now":{
"tmp":"29",
"cond":{
"txt":"阵雨"
}
}
在gson包下新建一个Now类
package com.example.coolweather.gson;
import com.google.gson.annotations.SerializedName;
public class Now {
@SerializedName("tmp")
public String temperature;
@SerializedName("cond")
public More more;
public class More {
@SerializedName("txt")
public String info;
}
}
1.4gson包下建立一个Suggestion类
Suggestion中原来的具体内容
"suggestion":{
"comf":{
"txt":"白天天气较热,虽然有雨,但仍然无法削弱较高气温给人们带来的暑意,这种天气会让您感到不很舒适。"
},
"cw":{
"txt":"不宜洗车,未来24小时内有雨,如果在此期间洗车,雨水和路上的泥水可能会再次弄脏您的爱车。"
},
"sport":{
"txt":"有降水,且风力较强,推荐您在室内进行低强度运动;若坚持户外运动,请选择避雨防风的地点。"
}
}
在gson包下新建一个Suggestion类
package com.example.coolweather.gson;
import com.google.gson.annotations.SerializedName;
public class Suggestion {
@SerializedName("comf")
public Comfort comfort;
@SerializedName("cw")
public CarWash carWash;
public Sport sport;
public class Comfort {
@SerializedName("txt")
public String info;
}
public class CarWash {
@SerializedName("txt")
public String info;
}
public class Sport {
@SerializedName("txt")
public String info;
}
}
1.5gson包下建立一个Forecast类
接下来的一项数据daily_forecast比较特殊。
Forecast中原来的具体内容
"daily_forecast": [{
"date": "2016-08-08",
"cond": {
"txt_d": "阵雨"
},
"tmp": {
"max": "34",
"min": "27"
}
},
{
"date": "2016-08-09",
"cond": {
"txt_d": "多云"
},
"tmp": {
"max": "35",
"min": "29"
}
},
...
}]
在gson包下新建一个Forecast类
daily_forecast 中包含的是一个数组,数组中的每一项都代表着未来一天的天气信息。针对于这种情况,我们只需要定义出单日天气的实体类就可以了,然后在声明实体类引用的时候使用集合类型来进行声明。
package com.example.coolweather.gson;
import com.google.gson.annotations.SerializedName;
public class Forecast {
public String date;
@SerializedName("tmp")
public Temperature temperature;
@SerializedName("cond")
public More more;
public class Temperature {
public String max;
public String min;
}
public class More {
@SerializedName("txt_d")
public String info;
}
}
1.6gson包下建立一个Weather类
把basic 、aqi 、now 、suggestion 和daily_forecast对应的实体类全部都创建好了,接下来还需要再创建一个总的实例类来引用刚刚创建的各个实体类。
在Weather 类中,我们对Basic 、AQI 、Now 、Suggestion 和
Forecast 类进行了引用。其中,由于daily_forecast 中包含的是一
个数组,因此这里使用了List集合来引用Forecast 类。另外,返回的天
气数据中还会包含一项status数据,成功返回ok,失败则会返回具体的
原因,那么这里也需要添加一个对应的status 字段。
在gson包下新建一个Weather 类
package com.example.coolweather.gson;
import com.google.gson.annotations.SerializedName;
import java.util.List;
public class Weather {
public String status;
public Basic basic;
public AQI aqi;
public Now now;
public Suggestion suggestion;
@SerializedName("daily_forecast")
public List<Forecast> forecastList;
}
2.编写天气界面
创建一个用于显示天气信息的活动
首先创建一个用于显示天气信息的活动。右击com.coolweather.android包→New→Activity→Empty Activity,创建一个WeatherActivity,并将布局 名指定成activity_weather.xml。
由于所有的天气信息都将在同一个界面上显示,因此 activity_weather.xml会是一个很长的布局文件。那么为了让里面的代码不至于混乱不堪,使用的引入布局技术,即将 界面的不同部分写在不同的布局文件里面,再通过引入布局的方式集成到activity_weather.xml中,这样整个布局文件就会显得非常工整。
2.1新建一个title.xml
右击res/layout→New→Layout resource file,新建一个title.xml作为头布
局

头布局中放置了两个TextView,一个居中显示城市名,一个居右显示更新时间。
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="?attr/actionBarSize">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/title_city"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:textColor="#fff"
android:textSize="20sp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/title_update_time"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:layout_marginRight="10dp"
android:textColor="#fff"
android:textSize="16sp" />
RelativeLayout>
2.2新建一个now.xml
新建一个now.xml作为当前天气信息的布局。
当前天气信息的布局中也是放置了两个TextView,一个用于显示当前气
温,一个用于显示天气概况。
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="15dp">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/degree_text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="end"
android:textColor="#fff"
android:textSize="60sp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/weather_info_text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="end"
android:textColor="#fff"
android:textSize="20sp" />
LinearLayout>
2.3新建一个forecast.xml
新建forecast.xml作为未来几天天气信息的布局
里最外层使用LinearLayout定义了一个半透明的背景,然后使用TextView定义了一个标题,接着又使用一个LinearLayout定义了一个用于显示未来几天天气信息的布局。不过这个布局中并没有放入任何内容,因为这是要根据服务器返回的数据在代码中动态添加的。
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="15dp"
android:background="#8000"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="15dp"
android:layout_marginTop="15dp"
android:text="预报"
android:textColor="#fff"
android:textSize="20sp" />
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/forecast_layout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical">LinearLayout>
LinearLayout>
2.4新建一个forecast_item.xml
定义一个未来天气信息的子项布局forecast_item.xml
子项布局中放置了4个TextView,一个用于显示天气预报日期,一个用于显示天气概况,另外两个分别用于显示当天的最高温度和最低温度。
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="15dp">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/date_text"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
android:layout_weight="2"
android:textColor="#fff" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/info_text"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:textColor="#fff" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/max_text"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="right"
android:textColor="#fff" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/min_text"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="right"
android:textColor="#fff" />
LinearLayout>
2.5新建一个aqi.xml
新建aqi.xml作为空气质量信息的布局。
前面都是一样的,使用LinearLayout定义了一个半透明的背景,然后使用TextView定义了一个标题。接下来,这里使用LinearLayout和RelativeLayout嵌套的方式实现了一个左右平分并且居中对齐的布局,分别用于显示AQI指数和PM 2.5指数。相信你只要仔细看一看,这个布局还是很好理解的。
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="15dp"
android:background="#8000"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="15dp"
android:layout_marginTop="15dp"
android:text="空气质量"
android:textColor="#fff"
android:textSize="20sp" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="15dp">
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/aqi_text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:textColor="#fff"
android:textSize="40sp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:text="AQI指数"
android:textColor="#fff" />
LinearLayout>
RelativeLayout>
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/pm25_text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:textColor="#fff"
android:textSize="40sp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:text="PM2.5指数"
android:textColor="#fff" />
LinearLayout>
RelativeLayout>
LinearLayout>
LinearLayout>
2.6新建一个suggestion.xml
新建suggestion.xml作为生活建议信息的布局
先定义了一个半透明的背景和一个标题,然后下面使用了3个TextView分别用于显示舒适度、洗车指数和运动建议的相关数据。
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="15dp"
android:background="#8000"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="15dp"
android:layout_marginTop="15dp"
android:text="生活建议"
android:textColor="#fff"
android:textSize="20sp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/comfort_text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="15dp"
android:textColor="#fff" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/car_wash_text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="15dp"
android:textColor="#fff" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/sport_text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="15dp"
android:textColor="#fff" />
LinearLayout>
2.7新建一个forecast_item.xml
天气界面上每个部分的布局文件都编写好了,然后将它们引入到activity_weather.xml。
首先最外层布局使用了一个FrameLayout,并将它的背景色设置成colorPrimary。然后在FrameLayout中嵌套了一个ScrollView,这是因为天气界面中的内容比较多,使用ScrollView可以允许我们通过滚动的方式查看屏幕以外的内容。由于ScrollView的内部只允许存在一个直接子布局,因此这里又嵌套了一个垂直方向的LinearLayout,然后在LinearLayout中将刚才定义的所有布局逐个引入。
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@color/colorPrimary">
<ScrollView
android:id="@+id/weather_layout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:overScrollMode="never"
android:scrollbars="none">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical">
<include layout="@layout/title" />
<include layout="@layout/now" />
<include layout="@layout/forecast" />
<include layout="@layout/aqi" />
<include layout="@layout/suggestion" />
LinearLayout>
ScrollView>
FrameLayout>
3.将天气显示到界面上
3.1添加一个用于解析天气JSON数据的方法
在Utility 类中添加一个用于解析天气JSON数据的方法。
handleWeatherResponse() 方法中先是通过JSONObject和JSONArray 将天气数据中的主体内容解析出来。
添加的代码
/**
* 将返回的JSON数据解析成Weather实体类
*/
public static Weather handleWeatherResponse(String response) {
try {
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject(response);
JSONArray jsonArray = jsonObject.getJSONArray("HeWeather");
String weatherContent = jsonArray.getJSONObject(0).toString();
return new Gson().fromJson(weatherContent, Weather.class);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
全部代码
package com.example.coolweather.util;
import android.text.TextUtils;
import com.example.coolweather.db.City;
import com.example.coolweather.db.County;
import com.example.coolweather.db.Province;
import com.example.coolweather.gson.Weather;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import org.json.JSONArray;
import org.json.JSONException;
import org.json.JSONObject;
public class Utility {
/**
* 解析和处理服务器返回的省级数据
*/
public static boolean handleProvinceResponse(String response) {
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(response)) {
try {
JSONArray allProvinces = new JSONArray(response);
for (int i = 0; i < allProvinces.length(); i++) {
JSONObject provinceObject = allProvinces.getJSONObject(i);
Province province = new Province();
province.setProvinceName(provinceObject.getString("name"));
province.setProvinceCode(provinceObject.getInt("id"));
province.save();
}
return true;
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 解析和处理服务器返回的市级数据
*/
public static boolean handleCityResponse(String response, int provinceId) {
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(response)) {
try {
JSONArray allCities = new JSONArray(response);
for (int i = 0; i < allCities.length(); i++) {
JSONObject cityObject = allCities.getJSONObject(i);
City city = new City();
city.setCityName(cityObject.getString("name"));
city.setCityCode(cityObject.getInt("id"));
city.setProvinceId(provinceId);
city.save();
}
return true;
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 解析和处理服务器返回的县级数据
*/
public static boolean handleCountyResponse(String response, int cityId) {
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(response)) {
try {
JSONArray allCounties = new JSONArray(response);
for (int i = 0; i < allCounties.length(); i++) {
JSONObject countyObject = allCounties.getJSONObject(i);
County county = new County();
county.setCountyName(countyObject.getString("name"));
county.setWeatherId(countyObject.getString("weather_id"));
county.setCityId(cityId);
county.save();
}
return true;
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 将返回的JSON数据解析成Weather实体类
*/
public static Weather handleWeatherResponse(String response) {
try {
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject(response);
JSONArray jsonArray = jsonObject.getJSONArray("HeWeather");
String weatherContent = jsonArray.getJSONObject(0).toString();
return new Gson().fromJson(weatherContent, Weather.class);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
3.2修改WeatherActivity中的代码
我们之前已经按照上面的数据格式定义过相应的GSON实体类,因此只需要通过调用fromJson() 方法就能直接将JSON数据转换成Weather 对象了。接下来的工作是我们如何在活动中去请求天气数据,以及将数据展示到界面上。
在onCreate()方法中仍然先是去获取一些控件的实例,然后会尝试从本地缓存中读取 天气数据。那么第一次肯定是没有缓存的,因此就会从Intent中取出天 气id,并调用requestWeather() 方法来从服务器请求天气数据。注 意,请求数据的时候先将ScrollView进行隐藏,不然空数据的界面看上 去会很奇怪。requestWeather() 方法中先是使用了参数中传入的天气id和我们之前 申请好的API Key拼装出一个接口地址,接着调 用HttpUtil.sendOkHttpRequest() 方法来向该地址发出请求,服务 器会将相应城市的天气信息以JSON格式返回。然后我们 在onResponse() 回调中先调用Utility.handleWeatherResponse()方法将返回的JSON数据转换成Weather 对象,再将当前线程切换到主 线程。然后进行判断,如果服务器返回的status状态是ok,就说明请求天气成功了,此时将返回的数据缓存到SharedPreferences当中,并调用showWeatherInfo() 方法来进行内容显示。showWeatherInfo() 方法中的逻辑就比较简单了,其实就是从 Weather 对象中获取数据,然后显示到相应的控件上。注意在未来几天 天气预报的部分我们使用了一个for循环来处理每天的天气信息,在循环 中动态加载forecast_item.xml布局并设置相应的数据,然后添加到父布 局当中。设置完了所有数据之后,记得要将ScrollView重新变成可见。这样我们就将首次进入WeatherActivity时的逻辑全部梳理完了,那么当 下一次再进入WeatherActivity时,由于缓存已经存在了,因此会直接解 析并显示天气数据,而不会再次发起网络请求了。
package com.example.coolweather;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.content.SharedPreferences;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.preference.PreferenceManager;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
import android.widget.ScrollView;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
import com.example.coolweather.gson.Forecast;
import com.example.coolweather.gson.Weather;
import com.example.coolweather.util.HttpUtil;
import com.example.coolweather.util.Utility;
import java.io.IOException;
import okhttp3.Call;
import okhttp3.Callback;
import okhttp3.Response;
public class WeatherActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private ScrollView weatherLayout;
private TextView titleCity;
private TextView titleUpdateTime;
private TextView degreeText;
private TextView weatherInfoText;
private LinearLayout forecastLayout;
private TextView aqiText;
private TextView pm25Text;
private TextView comfortText;
private TextView carWashText;
private TextView sportText;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_weather);
// 初始化各控件
weatherLayout = (ScrollView) findViewById(R.id.weather_layout);
titleCity = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.title_city);
titleUpdateTime = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.title_update_time);
degreeText = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.degree_text);
weatherInfoText = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.weather_info_text);
forecastLayout = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.forecast_layout);
aqiText = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.aqi_text);
pm25Text = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.pm25_text);
comfortText = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.comfort_text);
carWashText = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.car_wash_text);
sportText = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.sport_text);
SharedPreferences prefs = PreferenceManager.getDefaultSharedPreferences
(this);
String weatherString = prefs.getString("weather", null);
if (weatherString != null) {
// 有缓存时直接解析天气数据
Weather weather = Utility.handleWeatherResponse(weatherString);
showWeatherInfo(weather);
} else {
// 无缓存时去服务器查询天气
String weatherId = getIntent().getStringExtra("weather_id");
weatherLayout.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
requestWeather(weatherId);
}
}
/**
* 根据天气id请求城市天气信息
*/
public void requestWeather(final String weatherId) {
String weatherUrl = "http://guolin.tech/api/weather?cityid=" +
weatherId + "&key=bc0418b57b2d4918819d3974ac1285d9";
HttpUtil.sendOkHttpRequest(weatherUrl, new Callback() {
@Override
public void onResponse(Call call, Response response) throws IOException {
final String responseText = response.body().string();
final Weather weather = Utility.handleWeatherResponse(responseText);
runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (weather != null && "ok".equals(weather.status)) {
SharedPreferences.Editor editor = PreferenceManager
.getDefaultSharedPreferences(WeatherActivity.this)
.edit();
editor.putString("weather", responseText);
editor.apply();
showWeatherInfo(weather);
} else {
Toast.makeText(WeatherActivity.this, "获取天气信息失败",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
});
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Call call, IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Toast.makeText(WeatherActivity.this, "获取天气信息失败",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
}
});
}
/**
* 处理并展示Weather实体类中的数据
*/
private void showWeatherInfo(Weather weather) {
String cityName = weather.basic.cityName;
String updateTime = weather.basic.update.updateTime.split(" ")[1];
String degree = weather.now.temperature + "℃";
String weatherInfo = weather.now.more.info;
titleCity.setText(cityName);
titleUpdateTime.setText(updateTime);
degreeText.setText(degree);
weatherInfoText.setText(weatherInfo);
forecastLayout.removeAllViews();
for (Forecast forecast : weather.forecastList) {
View view = LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.forecast_item, forecastLayout, false);
TextView dateText = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.date_text);
TextView infoText = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.info_text);
TextView maxText = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.max_text);
TextView minText = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.min_text);
dateText.setText(forecast.date);
infoText.setText(forecast.more.info);
maxText.setText(forecast.temperature.max);
minText.setText(forecast.temperature.min);
forecastLayout.addView(view);
}
if (weather.aqi != null) {
aqiText.setText(weather.aqi.city.aqi);
pm25Text.setText(weather.aqi.city.pm25);
}
String comfort = "舒适度:" + weather.suggestion.comfort.info;
String carWash = "洗车指数:" + weather.suggestion.carWash.info;
String sport = "运动建议:" + weather.suggestion.sport.info;
comfortText.setText(comfort);
carWashText.setText(carWash);
sportText.setText(sport);
weatherLayout.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}
}
3.3修改ChooseAreaFragment
从省市县列表界面跳转到天气界面,修改ChooseAreaFragment
在onItemClick() 方法中加入了一个if 判断,如果当前级别是LEVEL_COUNTY ,就启动WeatherActivity,并把当前选中县的天气id传递过去。
修改后的listView.setOnItemClickListener方法
listView.setOnItemClickListener(new AdapterView.OnItemClickListener() {
@Override
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position,
long id) {
if (currentLevel == LEVEL_PROVINCE) {
selectedProvince = provinceList.get(position);
queryCities();
} else if (currentLevel == LEVEL_CITY) {
selectedCity = cityList.get(position);
queryCounties();
} else if (currentLevel == LEVEL_COUNTY) {
String weatherId = countyList.get(position).getWeatherId();
Intent intent = new Intent(getActivity(), WeatherActivity.
class);
intent.putExtra("weather_id", weatherId);
startActivity(intent);
getActivity().finish();
}
}
});
完整代码
package com.example.coolweather;
import android.app.ProgressDialog;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.AdapterView;
import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
import com.example.coolweather.R;
import com.example.coolweather.db.City;
import com.example.coolweather.db.County;
import com.example.coolweather.db.Province;
import com.example.coolweather.util.HttpUtil;
import com.example.coolweather.util.Utility;
import org.litepal.crud.DataSupport;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import androidx.fragment.app.Fragment;
import okhttp3.Call;
import okhttp3.Callback;
import okhttp3.Response;
public class ChooseAreaFragment extends Fragment {
public static final int LEVEL_PROVINCE = 0;
public static final int LEVEL_CITY = 1;
public static final int LEVEL_COUNTY = 2;
private ProgressDialog progressDialog;
private TextView titleText;
private Button backButton;
private ListView listView;
private ArrayAdapter<String> adapter;
private List<String> dataList = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* 省列表
*/
private List<Province> provinceList;
/**
* 市列表
*/
private List<City> cityList;
/**
* 县列表
*/
private List<County> countyList;
/**
* 选中的省份
*/
private Province selectedProvince;
/**
* 选中的城市
*/
private City selectedCity;
/**
* 当前选中的级别
*/
private int currentLevel;
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.choose_area, container, false);
titleText = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.title_text);
backButton = (Button) view.findViewById(R.id.back_button);
listView = (ListView) view.findViewById(R.id.list_view);
adapter = new ArrayAdapter<>(getContext(), android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, dataList);
listView.setAdapter(adapter);
return view;
}
@Override
public void onActivityCreated(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState);
listView.setOnItemClickListener(new AdapterView.OnItemClickListener() {
@Override
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position,
long id) {
if (currentLevel == LEVEL_PROVINCE) {
selectedProvince = provinceList.get(position);
queryCities();
} else if (currentLevel == LEVEL_CITY) {
selectedCity = cityList.get(position);
queryCounties();
} else if (currentLevel == LEVEL_COUNTY) {
String weatherId = countyList.get(position).getWeatherId();
Intent intent = new Intent(getActivity(), WeatherActivity.
class);
intent.putExtra("weather_id", weatherId);
startActivity(intent);
getActivity().finish();
}
}
});
backButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if (currentLevel == LEVEL_COUNTY) {
queryCities();
} else if (currentLevel == LEVEL_CITY) {
queryProvinces();
}
}
});
queryProvinces();
}
/**
* 查询全国所有的省,优先从数据库查询,如果没有查询到再去服务器上查询
*/
private void queryProvinces() {
titleText.setText("中国");
backButton.setVisibility(View.GONE);
provinceList = DataSupport.findAll(Province.class);
if (provinceList.size() > 0) {
dataList.clear();
for (Province province : provinceList) {
dataList.add(province.getProvinceName());
}
adapter.notifyDataSetChanged();
listView.setSelection(0);
currentLevel = LEVEL_PROVINCE;
} else {
String address = "http://guolin.tech/api/china";
queryFromServer(address, "province");
}
}
/**
* 查询选中省内所有的市,优先从数据库查询,如果没有查询到再去服务器上查询
*/
private void queryCities() {
titleText.setText(selectedProvince.getProvinceName());
backButton.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
cityList = DataSupport.where("provinceid = ?", String.valueOf(selectedProvince.getId())).find(City.class);
if (cityList.size() > 0) {
dataList.clear();
for (City city : cityList) {
dataList.add(city.getCityName());
}
adapter.notifyDataSetChanged();
listView.setSelection(0);
currentLevel = LEVEL_CITY;
} else {
int provinceCode = selectedProvince.getProvinceCode();
String address = "http://guolin.tech/api/china/" + provinceCode;
queryFromServer(address, "city");
}
}
/**
* 查询选中市内所有的县,优先从数据库查询,如果没有查询到再去服务器上查询
*/
private void queryCounties() {
titleText.setText(selectedCity.getCityName());
backButton.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
countyList = DataSupport.where("cityid = ?", String.valueOf(selectedCity.
getId())).find(County.class);
if (countyList.size() > 0) {
dataList.clear();
for (County county : countyList) {
dataList.add(county.getCountyName());
}
adapter.notifyDataSetChanged();
listView.setSelection(0);
currentLevel = LEVEL_COUNTY;
} else {
int provinceCode = selectedProvince.getProvinceCode();
int cityCode = selectedCity.getCityCode();
String address = "http://guolin.tech/api/china/" + provinceCode + "/" +
cityCode;
queryFromServer(address, "county");
}
}
/**
* 根据传入的地址和类型从服务器上查询省市县数据
*/
private void queryFromServer(String address, final String type) {
showProgressDialog();
HttpUtil.sendOkHttpRequest(address, new Callback() {
@Override
public void onResponse(Call call, Response response) throws IOException {
String responseText = response.body().string();
boolean result = false;
if ("province".equals(type)) {
result = Utility.handleProvinceResponse(responseText);
} else if ("city".equals(type)) {
result = Utility.handleCityResponse(responseText,
selectedProvince.getId());
} else if ("county".equals(type)) {
result = Utility.handleCountyResponse(responseText,
selectedCity.getId());
}
if (result) {
getActivity().runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
closeProgressDialog();
if ("province".equals(type)) {
queryProvinces();
} else if ("city".equals(type)) {
queryCities();
} else if ("county".equals(type)) {
queryCounties();
}
}
});
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Call call, IOException e) {
// 通过runOnUiThread()方法回到主线程处理逻辑
getActivity().runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
closeProgressDialog();
Toast.makeText(getContext(), "加载失败", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).
show();
}
});
}
});
}
/**
* 显示进度对话框
*/
private void showProgressDialog() {
if (progressDialog == null) {
progressDialog = new ProgressDialog(getActivity());
progressDialog.setMessage("正在加载...");
progressDialog.setCanceledOnTouchOutside(false);}
progressDialog.show();
}
/**
* 关闭进度对话框
*/
private void closeProgressDialog() {
if (progressDialog != null) {
progressDialog.dismiss();
}
}
}
3.4修改MainActivity
在MainActivity中加入一个缓存数据的判断。
在onCreate() 方法的一开始先从SharedPreferences文件中读取缓存数据,如果不为null 就说明之前已经请求过天气数据了,那么就没必要让用户再次选择城市,而是直接跳转到WeatherActivity即可。
package com.example.coolweather;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
SharedPreferences prefs = PreferenceManager.getDefaultSharedPreferences
(this);
if (prefs.getString("weather", null) != null) {
Intent intent = new Intent(this, WeatherActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
finish();
}
}
}
附录.参考资料
《第一行代码》14.5 显示天气信息
下载资源
gitee地址
https://gitee.com/miao-zehao/cool-weather
安卓学习者实战项目酷欧天气(3)显示天气信息示例
总结
大家喜欢的话,给个,点个关注!继续跟大家分享敲代码过程中遇到的问题!