Java并发编程的艺术 -- 原子操作类和并发工具类(第七、八章)
文章目录
- 1、原子操作类
-
- 1.1、原子更新基本类型
-
- 1.1.1、原子更新基本类型常用类
- 1.1.2、AtomicInteger的常用方法
- 1.1.3、AtomicInteger的使用
- 1.1.4、getAndIncrement是如何实现原子操作的呢?
- 1.1.5、AtomicInteger 类的原理
- 1.2、原子更新数组
-
- 1.2.1、原子更新数组常用类
- 1.2.2、AtomicIntegerArray的使用
- 1.3、原子更新引用类型
-
- 1.3.1、原子更新引用类型常用类
- 1.3.2、AtomicReference的使用
- 1.4、原子更新字段类
-
- 1.4.1、原子更新字段类常用类
- 1.4.2、AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater的使用
- 2、并发工具类
-
- 2.1、CountDownLatch
-
- 2.1.1、简介
- 2.1.2、CountDownLatch的使用
- 2.1.3、应用场景
- 2.2、CyclicBarrier
-
- 2.2.1、简介
- 2.2.2、CyclicBarrier的使用
- 2.2.3、应用场景
- 2.2.4、CyclicBarrier和CountDownLatch的区别
- 2.3、Semaphore
-
- 2.3.1、简介
- 2.3.2、Semaphore的使用
- 2.3.3、应用场景
- 2.3.4、其他方法
- 2.4、Exchanger
-
- 2.4.1、简介
- 2.4.2、Exchanger的使用
- 2.4.3、应用场景
本文参考于《Java并发编程的艺术》
1、原子操作类
1.1、原子更新基本类型
1.1.1、原子更新基本类型常用类
- AtomicBoolean:原子更新布尔类型。
- AtomicInteger:原子更新整型。
- AtomicLong:原子更新长整型。
1.1.2、AtomicInteger的常用方法
int addAndGet(int delta):以原子方式将输入的数值与实例中的值(AtomicInteger里的value)相加,并返回结果。boolean compareAndSet(int expect,int update):如果输入的数值等于预期值,则以原子方式将该值设置为输入的值。int getAndIncrement():以原子方式将当前值加1,注意,这里返回的是自增前的值。void lazySet(int newValue):最终会设置成newValue,使用lazySet设置值后,可能导致其他线程在之后的一小段时间内还是可以读到旧的值。int getAndSet(int newValue):以原子方式设置为newValue的值,并返回旧值。
1.1.3、AtomicInteger的使用
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class AtomicIntegerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AtomicInteger i = new AtomicInteger(0);
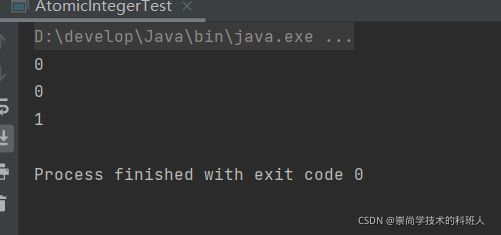
System.out.println(i.get());
System.out.println(i.getAndIncrement());
System.out.println(i.get());
}
}
输出结果
1.1.4、getAndIncrement是如何实现原子操作的呢?
源码
public final int getAndIncrement() {
for (;;) {
int current = get();
int next = current + 1;
if (compareAndSet(current, next))
return current;
}
}
public final boolean compareAndSet(int expect, int update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, valueOffset, expect, update);
}
- 源码中for循环体的第一步先取得AtomicInteger里存储的数值。
- 第二步对AtomicInteger的当前数值进行加1操作。
- 关键的第三步调用compareAndSet方法来进行原子更新操作,
该方法先检查当前数值是否等于current,等于意味着AtomicInteger的值没有被其他线程修改过,则将AtomicInteger的当前数值更新成next的值。 - 如果不等compareAndSet方法会返回false,
程序会进入for循环重新进行compareAndSet操作。
1.1.5、AtomicInteger 类的原理
1.AtomicInteger的部分源码
// setup to use Unsafe.compareAndSwapInt for updates(更新操作时提供“比较并替换”的作用)
private static final Unsafe unsafe = Unsafe.getUnsafe();
private static final long valueOffset;
static {
try {
valueOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset
(AtomicInteger.class.getDeclaredField("value"));
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new Error(ex); }
}
private volatile int value;
- Atomic包里的类
基本都是使用Unsafe实现的
2.Unsafe的源码
/**
* 如果当前数值是expected,则原子的将Java变量更新成x
* @return 如果更新成功则返回true
*/
public final native boolean compareAndSwapObject(Object o,
long offset,
Object expected,
Object x);
public final native boolean compareAndSwapInt(Object o, long offset,
int expected,
int x);
public final native boolean compareAndSwapLong(Object o, long offset,
long expected,
long x);
3.AtomicInteger 类的原理
AtomicInteger 类主要利用 CAS (compare and swap) + volatile 和 native 方法来保证原子操作,从而避免 synchronized 的高开销,执行效率大为提升。
- CAS 的原理是
拿期望的值和原本的一个值作比较,如果相同则更新成新的值。 - UnSafe 类的 objectFieldOffset() 方法是一个本地方法,这个方法是
用来拿到“原来的值”的内存地址,返回值是valueOffset。 - 另外 value 是一个
volatile变量,在内存中可见,因此 JVM 可以保证任何时刻任何线程总能拿到该变量的最新值。
1.2、原子更新数组
1.2.1、原子更新数组常用类
- AtomicIntegerArray:原子更新整型数组里的元素。
- AtomicLongArray:原子更新长整型数组里的元素。
- AtomicReferenceArray:原子更新引用类型数组里的元素。
1.2.2、AtomicIntegerArray的使用
代码
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicIntegerArray;
public class AtomicIntegerArrayTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {
1,3,4,5,2};
AtomicIntegerArray i = new AtomicIntegerArray(a);
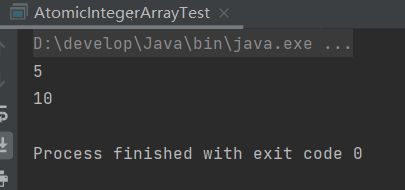
System.out.println(i.get(3));
System.out.println(i.addAndGet(3, 5));
}
}
输出结果
1.3、原子更新引用类型
1.3.1、原子更新引用类型常用类
- AtomicReference:原子更新引用类型。
- AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater:原子更新引用类型里的字段。
- AtomicMarkableReference:原子更新
带有标记位的引用类型。可以原子更新一个布尔类型的标记位和引用类型。
1.3.2、AtomicReference的使用
代码
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference;
class User{
private String name;
private int age;
public User() {
}
public User(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
public class AtomicReferenceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AtomicReference<User> userAtomicReference = new AtomicReference<>();
User user1 = new User("xiaoming", 22);
userAtomicReference.set(user1);
User updateUser = new User("Shinichi", 17);
userAtomicReference.compareAndSet(user1, updateUser);
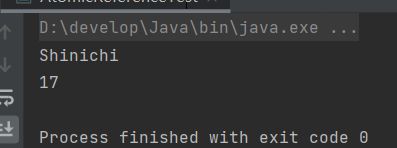
System.out.println(userAtomicReference.get().getName());
System.out.println(userAtomicReference.get().getAge());
}
}
输出结果
1.4、原子更新字段类
1.4.1、原子更新字段类常用类
- AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater:原子更新整型的字段的更新器。
- AtomicLongFieldUpdater:原子更新长整型字段的更新器。
- AtomicStampedReference:原子更新带有版本号的引用类型。该类将整数值与引用关联起来,可用于原子的更新数据和数据的版本号,可以解决使用CAS进行原子更新时可能出现的ABA问题。
1.4.2、AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater的使用
代码
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater;
class Person{
private String name;
public volatile int age;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
public class AtomicIntegerFieldUpdaterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<Person> personAtomicIntegerFieldUpdater = AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(Person.class,"age");
Person person = new Person("xiaoming",22);
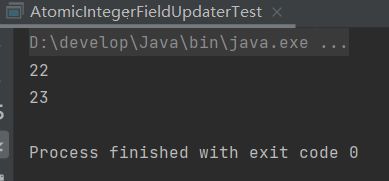
System.out.println(personAtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.getAndIncrement(person));
System.out.println(personAtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.get(person));
}
}
输出结果
2、并发工具类
2.1、CountDownLatch
2.1.1、简介
CountDownLatch允许一个或多个线程等待其他线程完成操作。它的工作原理就是设置了一个计数器,而该计数器的初始值可以由我们初始构造的时候进行传递进去。而每一个线程完成任务之后就会对其进行计数器减一操作。然后当计数器数值等于0的时候,就会触发相应的最终操作。
2.1.2、CountDownLatch的使用
代码
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
public class CountDownLatchDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(6);
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 号同学离开了教室");
countDownLatch.countDown();
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
countDownLatch.await();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 班长锁门走人了");
}
}
说明
CountDownLatch的构造函数接收一个int类型的参数作为计数器,如果你想等待N个点完成,这里就传入N。- 当我们调用
CountDownLatch的countDown方法时,N就会减1,CountDownLatch的await方法会阻塞当前线程,直到N变成零。由于countDown方法可以用在任何地方,所以这里说的N个点,可以是N个线程,也可以是1个线程里的N个执行步骤。 - 如果有某个线程处理得比较慢,我们不可能让主线程一直等待,所以可以使用另外一个带指定时间的
await方法——await(long time,TimeUnit unit),这个方法等待特定时间后,就会不再阻塞当前线程。 计数器必须大于等于0,只是等于0时候,计数器就是零,调用await方法时不会阻塞当前线程。- 一个线程调用
countDown方法happen-before另外一个线程调用await方法。
2.1.3、应用场景
我们需要解析一个Excel里多个sheet的数据,此时可以考虑使用多线程,每个线程解析一个sheet里的数据,等到所有的sheet都解析完之后,程序需要提示解析完成。
2.2、CyclicBarrier
2.2.1、简介
CyclicBarrier的字面意思是可循环使用(Cyclic)的屏障(Barrier)。它要做的事情是,让一组线程到达一个屏障(也可以叫同步点)时被阻塞,直到最后一个线程到达屏障时,屏障才会开门,所有被屏障拦截的线程才会继续运行。
2.2.2、CyclicBarrier的使用
代码
import java.util.concurrent.BrokenBarrierException;
import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier;
public class CyclicBarrierDemo {
private static final int NUMBER = 7;
public static void main(String[] args) {
CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(NUMBER, () -> {
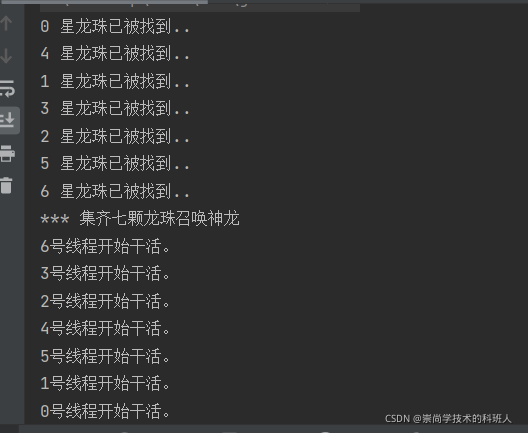
System.out.println("*** 集齐七颗龙珠召唤神龙");
});
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 星龙珠已被找到..");
try {
cyclicBarrier.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "号线程开始干活。");
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
}
}
输出结果
CyclicBarrier还提供一个更高级的构造函数CyclicBarrier(int parties,Runnable barrierAction)用于在线程到达屏障时,优先执行barrierAction。- 在最后一个线程到达屏障之前,其他线程都会被堵塞。直到最后一个线程到达屏障之后,所有被屏障拦截的线程才会继续运行。
2.2.3、应用场景
CyclicBarrier可以用于多线程计算数据,最后合并计算结果的场景。
- 例如,用一个Excel保存了用户所有银行流水,每个Sheet保存一个账户近一年的每笔银行流水,现在需要统计用户的日均银行流水,先用多线程处理每个sheet里的银行流水,都执行完之后,得到每个sheet的日均银行流水,最后,再用barrierAction用这些线程的计算结果,计算出整个Excel的日均银行流水。
2.2.4、CyclicBarrier和CountDownLatch的区别
CountDownLatch的计数器只能使用一次,而CyclicBarrier的计数器可以使用reset()方法重置。 所以CyclicBarrier能处理更为复杂的业务场景。例如,如果计算发生错误,可以重置计数器,并让线程重新执行一次。CyclicBarrier还提供其他有用的方法,比如getNumberWaiting方法可以获得Cyclic-Barrier阻塞的线程数量。isBroken()方法用来了解阻塞的线程是否被中断。
2.3、Semaphore
2.3.1、简介
Semaphore(信号量)是用来控制同时访问特定资源的线程数量,它通过协调各个线程,以保证合理的使用公共资源。
比喻说明
只能把它比作是控制流量的红绿灯。比如××马路要限制流量,只允许同时有一百辆车在这条路上行使,其他的都必须在路口等待,所以前一百辆车会看到绿灯,可以开进这条马路,后面的车会看到红灯,不能驶入××马路,但是如果前一百辆中有5辆车已经离开了××马路,那么后面就允许有5辆车驶入马路,这个例子里说的车就是线程,驶入马路就表示线程在执行,离开马路就表示线程执行完成,看见红灯就表示线程被阻塞,不能执行。
2.3.2、Semaphore的使用
代码
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class SemaphoreDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 三个车位,每个信号量只能够被一个线程占用
Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(3);
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
try {
semaphore.acquire();//进行抢占车位
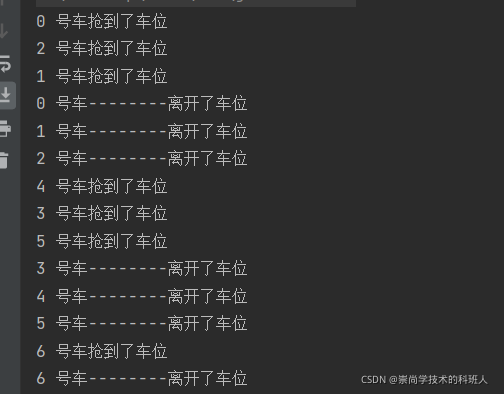
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 号车抢到了车位");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 号车--------离开了车位");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
semaphore.release(); // 该车离开车位
}
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
}
}
输出结果
- 代码中的信号量允许的最大线程数量为3,就好像有三个空车位允许停车。当停满的时候,其他车就不允许再进去停车,必须等有车开走后才能进行停车。
semaphore.acquire()就好比进行抢占车位;semaphore.release()就好比该车离开车位
2.3.3、应用场景
Semaphore可以用于做流量控制,特别是公用资源有限的应用场景,比如数据库连接。
例如
假如有一个需求,要读取几万个文件的数据,因为都是IO密集型任务,我们可以启动几十个线程并发地读取,但是如果读到内存后,还需要存储到数据库中,而数据库的连接数只有10个,这时我们必须控制最多只有10个线程同时获取数据库连接保存数据,否则会报错无法获取数据库连接。
2.3.4、其他方法
int availablePermits():返回此信号量中当前可用的许可证数。int getQueueLength():返回正在等待获取许可证的线程数。boolean hasQueuedThreads():是否有线程正在等待获取许可证。void reducePermits(int reduction):减少reduction个许可证,是个protected方法。Collection getQueuedThreads():返回所有等待获取许可证的线程集合,是个protected方法。
2.4、Exchanger
2.4.1、简介
Exchanger(交换者)是一个用于线程间协作的工具类。Exchanger用于进行线程间的数据交换。它提供一个同步点,在这个同步点,两个线程可以交换彼此的数据。这两个线程通过exchange方法交换数据,如果第一个线程先执行exchange()方法,它会一直等待第二个线程也执行exchange方法,当两个线程都到达同步点时,这两个线程就可以交换数据,将本线程生产出来的数据互相传递给对方。
2.4.2、Exchanger的使用
代码
public class ExchangerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Exchanger<String> exger = new Exchanger<>();
new Thread(()->{
String A = "银行A";
try {
String exchange = exger.exchange(A);
System.out.println(exchange);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"A").start();
new Thread(()->{
String B = "银行B";
try {
Thread.sleep(1000L);
System.out.println(B);
String A = exger.exchange("B");
System.out.println("A和B数据是否一致:" + A.equals(B) + ",A录入的是:"
+ A + ",B录入是:" + B);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"B").start();
}
}
输出结果
- 调用exchange()方法,双方线程会相互将数据传递给对方。
- 如果两个线程有一个没有执行exchange()方法,则会一直等待,如果担心有特殊情况发生,避免一直等待,可以使用
exchange(V x,longtimeout,TimeUnit unit)设置最大等待时长。
2.4.3、应用场景
Exchanger可以用于遗传算法,遗传算法里需要选出两个人作为交配对象,这时候会交换两人的数据,并使用交叉规则得出2个交配结果。Exchanger也可以用于校对工作,比如我们需要将纸制银行流水通过人工的方式录入成电子银行流水,为了避免错误,采用AB岗两人进行录入,录入到Excel之后,系统需要加载这两个Excel,并对两个Excel数据进行校对,看看是否录入一致