ShardingSphere分库分表实战与核心原理
ShardingSphere分库分表实战与核心原理
- ShardingSphere
-
- ShardingJDBC
- ShardingProxy
- 两者区别
- ShardingJDBC实战
-
- 核心概念
- ShardingJDBC的分片算法
- 案例演示
-
- 分表案例
- 分库案例
-
- 精确查询
- 范围查询
- Complex支持多个分片键
- hint强制路由
- 广播表
- 绑定表
- 读写分离
- ShardingSphere的SQL使用限制
- 分库分表带来的问题
ShardingSphere
ShardingSphere是一整套以数据分片为基础的数据生态圈。
ShardingSphere包含三个重要的产品,ShardingJDBC、ShardingProxy和ShardingSidecar。其中sidecar是针对service mesh定位的一个分库分表插件,目前在规划中。
其中,ShardingJDBC是用来做客户端分库分表的产品,而ShardingProxy是用来做服务端分库分表的产品
ShardingJDBC

shardingJDBC定位为轻量级 Java 框架,在 Java 的 JDBC 层提供的额外服务。它使⽤客户端直连数据库,以 jar 包形式提供服务,⽆需额外部署和依赖,可理解为增强版的 JDBC 驱动,完全兼容 JDBC 和各种 ORM 框架。
ShardingProxy

ShardingProxy定位为透明化的数据库代理端,提供封装了数据库⼆进制协议的服务端版本,⽤于完成对异构语⾔的⽀持。⽬前提供 MySQL 和 PostgreSQL 版本,它可以使⽤任何兼容 MySQL/PostgreSQL 协议的访问客户端。
两者区别
很显然,ShardingJDBC只是客户端的一个工具包,可以理解为一个特殊的JDBC驱动包,所有分库分表逻辑均由业务方自己控制,所以他的功能相对灵活,支持的数据库也非常多,但是对业务侵入大,需要业务方自己定制所有的分库分表逻辑。
而ShardingProxy是一个独立部署的服务,对业务方无侵入,业务方可以像用一个普通的MySQL服务一样进行数据交互,基本上感觉不到后端分库分表逻辑的存在,但是这也意味着功能会比较固定,能够支持的数据库也比较少。这两者各有优劣。
ShardingJDBC实战
shardingjdbc的核心功能是数据分片和读写分离,通过ShardingJDBC,应用可以透明的使用JDBC访问已经分库分表、读写分离的多个数据源,而不用关心数据源的数量以及数据如何分布。
核心概念
- 逻辑表:水平拆分的数据库的相同逻辑和数据结构表的总称
- 真实表:在分片的数据库中真实存在的物理表。
- 数据节点:数据分片的最小单元。由数据源名称和数据表组成
- 绑定表:分片规则一致的主表和子表。
- 广播表:也叫公共表,指素有的分片数据源中都存在的表,表结构和表中的数据在每个数据库中都完全一致。例如字典表。
- 分片键:用于分片的数据库字段,是将数据库(表)进行水平拆分的关键字段。SQL中若没有分片字段,将会执行全路由,性能会很差。
- 分片算法:通过分片算法将数据进行分片,支持通过=、BETWEEN和IN分片。分片算法需要由应用开发者自行实现,可实现的灵活度非常高。
- 分片策略:真正用于进行分片操作的是分片键+分片算法,也就是分片策略。在ShardingJDBC中一般采用基于Groovy表达式的inline分片策略,通过一个包含分片键的算法表达式来制定分片策略,如t_user_$->{u_id%8}标识根据u_id模8,分成8张表,表名称为t_user_0到t_user_7。
ShardingJDBC的分片算法
ShardingSphere目前提供了一共五种分片策略:
- NoneShardingStrategy
不分片。这种严格来说不算是一种分片策略了。只是ShardingSphere也提供了这么一个配置。 - InlineShardingStrategy
最常用的分片方式
配置参数: inline.shardingColumn 分片键;inline.algorithmExpression 分片表达式
实现方式: 按照分片表达式来进行分片。 - StandardShardingStrategy
只支持单分片键的标准分片策略。
配置参数:standard.sharding-column 分片键;standard.precise-algorithm-class-name 精确分片算法类名;standard.range-algorithm-class-name 范围分片算法类名
实现方式:
shardingColumn指定分片算法。
preciseAlgorithmClassName 指向一个实现了io.shardingsphere.api.algorithm.sharding.standard.PreciseShardingAlgorithm接口的java类名,提供按照 = 或者 IN 逻辑的精确分片
rangeAlgorithmClassName 指向一个实现了 io.shardingsphere.api.algorithm.sharding.standard.RangeShardingAlgorithm接口的java类名,提供按照Between 条件进行的范围分片。
说明:
其中精确分片算法是必须提供的,而范围分片算法则是可选的。 - ComplexShardingStrategy
支持多分片键的复杂分片策略。
配置参数:complex.sharding-columns 分片键(多个); complex.algorithm-class-name 分片算法实现类。
实现方式:
shardingColumn指定多个分片列。
algorithmClassName指向一个实现了org.apache.shardingsphere.api.sharding.complex.ComplexKeysShardingAlgorithm接口的java类名。提供按照多个分片列进行综合分片的算法。 - HintShardingStrategy
不需要分片键的强制分片策略。这个分片策略,简单来理解就是说,他的分片键不再跟SQL语句相关联,而是用程序另行指定。对于一些复杂的情况,例如select count(*) from (select userid from t_user where userid in (1,3,5,7,9)) 这样的SQL语句,就没法通过SQL语句来指定一个分片键。这个时候就可以通过程序,给他另行执行一个分片键,例如在按userid奇偶分片的策略下,可以指定1作为分片键,然后自行指定他的分片策略。
配置参数:hint.algorithm-class-name 分片算法实现类。
实现方式:
algorithmClassName指向一个实现了org.apache.shardingsphere.api.sharding.hint.HintShardingAlgorithm接口的java类名。
在这个算法类中,同样是需要分片键的。而分片键的指定是通过HintManager.addDatabaseShardingValue方法(分库)和HintManager.addTableShardingValue(分表)来指定。
使用时要注意,这个分片键是线程隔离的,只在当前线程有效,所以通常建议使用之后立即关闭,或者用try资源方式打开。
Hint分片策略并没有完全按照SQL解析树来构建分片策略,是绕开了SQL解析的,所有对某些比较复杂的语句,Hint分片策略性能有可能会比较好(情况太多了,无法一一分析)。
但是要注意,Hint强制路由在使用时有非常多的限制:
– 不支持UNION
SELECT * FROM t_order1 UNION SELECT * FROM t_order2
INSERT INTO tbl_name (col1, col2, …) SELECT col1, col2, … FROM tbl_name WHERE col3 = ?
– 不支持多层子查询
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM (SELECT * FROM t_order o WHERE o.id IN (SELECT id FROM t_order WHERE status = ?))
– 不支持函数计算。ShardingSphere只能通过SQL字面提取用于分片的值
SELECT * FROM t_order WHERE to_date(create_time, ‘yyyy-mm-dd’) = ‘2019-01-01’;
案例演示
分表案例
- 引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shardingspheregroupId>
<artifactId>sharding-jdbc-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>4.1.1version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starterartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>druidartifactId>
<version>1.1.22version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidougroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>3.0.5version>
dependency>
- 定义类
package com.roy.shardingDemo.entity;
public class Course {
private Long cid;
private String cname;
private Long userId;
private String cstatus;
public Long getCid() {
return cid;
}
public void setCid(Long cid) {
this.cid = cid;
}
public String getCname() {
return cname;
}
public void setCname(String cname) {
this.cname = cname;
}
public Long getUserId() {
return userId;
}
public void setUserId(Long userId) {
this.userId = userId;
}
public String getCstatus() {
return cstatus;
}
public void setCstatus(String cstatus) {
this.cstatus = cstatus;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Course{" +
"cid=" + cid +
", cname='" + cname + '\'' +
", userId=" + userId +
", cstatus='" + cstatus + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
package com.roy.shardingDemo.mapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.roy.shardingDemo.entity.Course;
public interface CourseMapper extends BaseMapper<Course> {
}
package com.roy.shardingDemo;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@MapperScan("com.roy.shardingDemo.mapper")
@SpringBootApplication
public class ShardingJDBCApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ShardingJDBCApplication.class,args);
}
}
- 单元测试类
@Test
public void addCourse(){
for(int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i ++){
Course c = new Course();
// c.setCid(Long.valueOf(i));
c.setCname("shardingsphere");
c.setUserId(Long.valueOf(""+(1000+i)));
c.setCstatus("1");
courseMapper.insert(c);
}
}
- 配置文件
application.properties
spring.profiles.active=dev1
application-dev1.properties
#配置数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=m1
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.1.104:3306/coursedb?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.password=123
#配置真实表分布
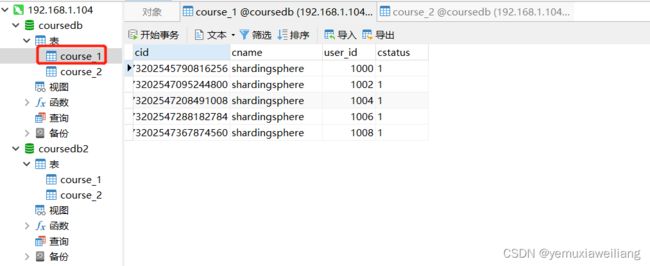
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.actual-data-nodes=m1.course_$->{1..2}
#主键生成策略
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.key-generator.column=cid
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.key-generator.props.worker.id=1
#配置分表策略
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=cid
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=course_$->{cid%2+1}
#其他运行属性
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show = true
spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding=true
分库案例
精确查询
- 配置文件变更
spring.profiles.active=dev2
#配置多个数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=m1,m2
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.1.104:3306/coursedb?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.password=123
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
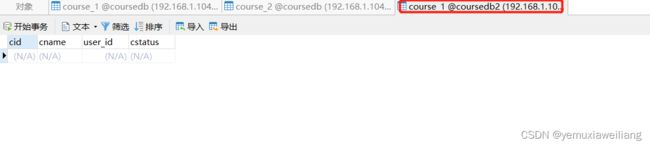
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.1.104:3306/coursedb2?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.password=123
#真实表分布,分库,分表
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.actual-data-nodes=m$->{
1..2}.course_$->{
1..2}
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.key-generator.column=cid
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.key-generator.props.worker.id=1
#inline分片策略
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=cid
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=course_$->{
cid%2+1}
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.database-strategy.inline.sharding-column=cid
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.database-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=m$->{
cid%2+1}
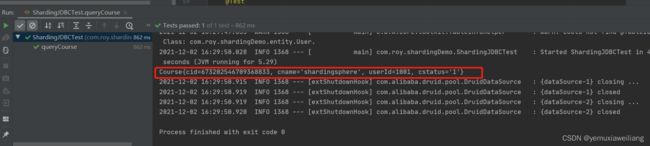
@Test
public void queryCourse(){
//select * from course
QueryWrapper<Course> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.orderByDesc("cid");
wrapper.eq("cid",673202546709368833L);
// wrapper.in()
List<Course> courses = courseMapper.selectList(wrapper);
courses.forEach(course -> System.out.println(course));
}
范围查询
- 增加范围查询用例
@Test
public void queryOrderRange(){
//select * from course
QueryWrapper<Course> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.between("cid",673202546709368833L,673202547405623297L);
// wrapper.in()
List<Course> courses = courseMapper.selectList(wrapper);
courses.forEach(course -> System.out.println(course));
}

发现上述报错,inline这种方式不支持范围查询。需要配置成标准模式,因此需要修改配置文件
# 表的配置
tables.course.table-strategy.standard.sharding-column=cid
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.table-strategy.standard.precise-algorithm-class-name=com.roy.shardingDemo.algorithem.MyPreciseTableShardingAlgorithm
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.table-strategy.standard.range-algorithm-class-name=com.roy.shardingDemo.algorithem.MyRangeTableShardingAlgorithm
# 库的配置
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.database-strategy.standard.sharding-column=cid
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.database-strategy.standard.precise-algorithm-class-name=com.roy.shardingDemo.algorithem.MyPreciseDSShardingAlgorithm
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.database-strategy.standard.range-algorithm-class-name=com.roy.shardingDemo.algorithem.MyRangeDSShardingAlgorithm
库的精确配置类
package com.roy.shardingDemo.algorithem;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.api.sharding.standard.PreciseShardingAlgorithm;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.api.sharding.standard.PreciseShardingValue;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.Collection;
public class MyPreciseDSShardingAlgorithm implements PreciseShardingAlgorithm<Long> {
//select * from course where cid = ? or cid in (?,?)
@Override
public String doSharding(Collection<String> availableTargetNames, PreciseShardingValue<Long> shardingValue) {
String logicTableName = shardingValue.getLogicTableName();
String cid = shardingValue.getColumnName();
Long cidValue = shardingValue.getValue();
//实现 m$->{cid%2+1}
BigInteger shardingValueB = BigInteger.valueOf(cidValue);
BigInteger resB = (shardingValueB.mod(new BigInteger("2"))).add(new BigInteger("1"));
String key = "m"+resB;
if(availableTargetNames.contains(key)){
return key;
}
//couse_1, course_2
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("route "+ key +" is not supported ,please check your config");
}
}
库的范围配置类
package com.roy.shardingDemo.algorithem;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.api.sharding.standard.RangeShardingAlgorithm;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.api.sharding.standard.RangeShardingValue;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
public class MyRangeDSShardingAlgorithm implements RangeShardingAlgorithm<Long> {
@Override
public Collection<String> doSharding(Collection<String> availableTargetNames, RangeShardingValue<Long> shardingValue) {
//select * from course where cid between 1 and 100;
Long upperVal = shardingValue.getValueRange().upperEndpoint();//100
Long lowerVal = shardingValue.getValueRange().lowerEndpoint();//1
String logicTableName = shardingValue.getLogicTableName();
return Arrays.asList("m1","m2");
}
}
表的精确配置类
package com.roy.shardingDemo.algorithem;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.api.sharding.standard.PreciseShardingAlgorithm;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.api.sharding.standard.PreciseShardingValue;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.Collection;
public class MyPreciseTableShardingAlgorithm implements PreciseShardingAlgorithm<Long> {
//select * from course where cid = ? or cid in (?,?)
@Override
public String doSharding(Collection<String> availableTargetNames, PreciseShardingValue<Long> shardingValue) {
String logicTableName = shardingValue.getLogicTableName();
String cid = shardingValue.getColumnName();
Long cidValue = shardingValue.getValue();
//实现 course_$->{cid%2+1)
BigInteger shardingValueB = BigInteger.valueOf(cidValue);
BigInteger resB = (shardingValueB.mod(new BigInteger("2"))).add(new BigInteger("1"));
String key = logicTableName+"_"+resB;
if(availableTargetNames.contains(key)){
return key;
}
//couse_1, course_2
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("route "+ key +" is not supported ,please check your config");
}
}
库的范围配置类
package com.roy.shardingDemo.algorithem;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.api.sharding.standard.RangeShardingAlgorithm;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.api.sharding.standard.RangeShardingValue;
import sun.rmi.runtime.Log;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
/**
* @author :楼兰
* @date :Created in 2021/1/6
* @description:
**/
public class MyRangeTableShardingAlgorithm implements RangeShardingAlgorithm<Long> {
@Override
public Collection<String> doSharding(Collection<String> availableTargetNames, RangeShardingValue<Long> shardingValue) {
//select * from course where cid between 1 and 100;
Long upperVal = shardingValue.getValueRange().upperEndpoint();//100
Long lowerVal = shardingValue.getValueRange().lowerEndpoint();//1
String logicTableName = shardingValue.getLogicTableName();
return Arrays.asList(logicTableName+"_1",logicTableName+"_2");
}
}
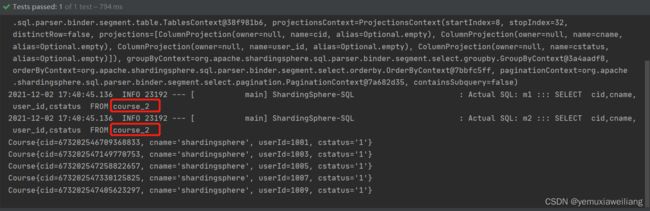
Complex支持多个分片键
@Test
public void queryCourseComplex(){
QueryWrapper<Course> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.between("cid",673202546709368833L,673202547405623297L);
wrapper.eq("user_id",1009L);
// wrapper.in()
List<Course> courses = courseMapper.selectList(wrapper);
courses.forEach(course -> System.out.println(course));
}
#complex复杂分片策略
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.table-strategy.complex.sharding-columns= cid, user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.table-strategy.complex.algorithm-class-name=com.roy.shardingDemo.algorithem.MyComplexTableShardingAlgorithm
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.database-strategy.complex.sharding-columns=cid, user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.database-strategy.complex.algorithm-class-name=com.roy.shardingDemo.algorithem.MyComplexDSShardingAlgorithm
package com.roy.shardingDemo.algorithem;
import com.google.common.collect.Range;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.api.sharding.complex.ComplexKeysShardingAlgorithm;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.api.sharding.complex.ComplexKeysShardingValue;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class MyComplexDSShardingAlgorithm implements ComplexKeysShardingAlgorithm<Long> {
// SELECT cid,cname,user_id,cstatus FROM course
// WHERE cid BETWEEN ? AND ? AND user_id = ?
@Override
public Collection<String> doSharding(Collection<String> availableTargetNames, ComplexKeysShardingValue<Long> shardingValue) {
Range<Long> cidRange = shardingValue.getColumnNameAndRangeValuesMap().get("cid");
Collection<Long> userIdCol = shardingValue.getColumnNameAndShardingValuesMap().get("user_id");
Long upperVal = cidRange.upperEndpoint();
Long lowerVal = cidRange.lowerEndpoint();
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
for(Long userId: userIdCol){
//course_{userID%2+1}
BigInteger userIdB = BigInteger.valueOf(userId);
BigInteger target = (userIdB.mod(new BigInteger("2"))).add(new BigInteger("1"));
res.add("m"+target);
}
return res;
}
}
package com.roy.shardingDemo.algorithem;
import com.google.common.collect.Range;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.api.sharding.complex.ComplexKeysShardingAlgorithm;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.api.sharding.complex.ComplexKeysShardingValue;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
public class MyComplexTableShardingAlgorithm implements ComplexKeysShardingAlgorithm<Long> {
@Override
public Collection<String> doSharding(Collection<String> availableTargetNames, ComplexKeysShardingValue<Long> shardingValue) {
Range<Long> cidRange = shardingValue.getColumnNameAndRangeValuesMap().get("cid");
Collection<Long> userIdCol = shardingValue.getColumnNameAndShardingValuesMap().get("user_id");
Long upperVal = cidRange.upperEndpoint();
Long lowerVal = cidRange.lowerEndpoint();
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
for(Long userId: userIdCol){
//course_{userID%2+1}
BigInteger userIdB = BigInteger.valueOf(userId);
BigInteger target = (userIdB.mod(new BigInteger("2"))).add(new BigInteger("1"));
res.add(shardingValue.getLogicTableName()+"_"+target);
}
return res;
}
}
hint强制路由
@Test
public void queryCourseByHint(){
HintManager hintManager = HintManager.getInstance();
hintManager.addTableShardingValue("course",2);
List<Course> courses = courseMapper.selectList(null);
courses.forEach(course -> System.out.println(course));
hintManager.close();
}
#hint强制路由策略
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.table-strategy.hint.algorithm-class-name=com.roy.shardingDemo.algorithem.MyHintTableShardingAlgorithm
package com.roy.shardingDemo.algorithem;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.api.sharding.hint.HintShardingAlgorithm;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.api.sharding.hint.HintShardingValue;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
public class MyHintTableShardingAlgorithm implements HintShardingAlgorithm<Integer> {
@Override
public Collection<String> doSharding(Collection<String> availableTargetNames, HintShardingValue<Integer> shardingValue) {
String key = shardingValue.getLogicTableName() + "_" + shardingValue.getValues().toArray()[0];
if(availableTargetNames.contains(key)){
return Arrays.asList(key);
}
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("route "+ key +" is not supported ,please check your config");
}
}
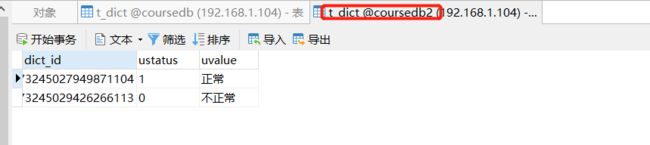
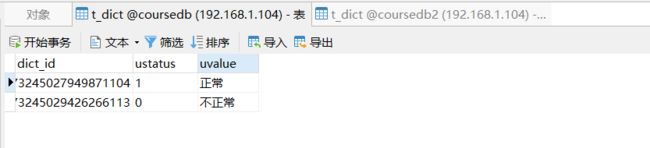
广播表
#广播表配置
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.broadcast-tables=t_dict
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_dict.key-generator.column=dict_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_dict.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
@Test
public void addDict(){
Dict d1 = new Dict();
d1.setUstatus("1");
d1.setUvalue("正常");
dictMapper.insert(d1);
Dict d2 = new Dict();
d2.setUstatus("0");
d2.setUvalue("不正常");
dictMapper.insert(d2);
}
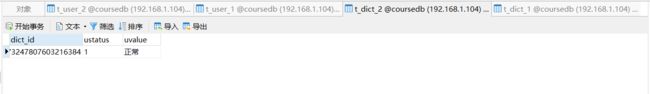
绑定表
spring.profiles.active=dev3
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=m1
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.1.104:3306/coursedb?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.password=123
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_dict.actual-data-nodes=m1.t_dict_$->{
1..2}
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_dict.key-generator.column=dict_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_dict.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_dict.key-generator.props.worker.id=1
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_dict.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=ustatus
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_dict.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=t_dict_$->{
ustatus.toInteger()%2+1}
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.actual-data-nodes=m1.t_user_$->{
1..2}
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.key-generator.column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.key-generator.props.worker.id=1
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=ustatus
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=t_user_$->{
ustatus.toInteger()%2+1}
#绑定表示例
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.binding-tables[0]=user,t_dict
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show = true
spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding=true
@Test
public void addDict(){
Dict d1 = new Dict();
d1.setUstatus("1");
d1.setUvalue("正常");
dictMapper.insert(d1);
Dict d2 = new Dict();
d2.setUstatus("0");
d2.setUvalue("不正常");
dictMapper.insert(d2);
for(int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i ++){
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("user No "+i);
user.setUstatus(""+(i%2));
user.setUage(i*10);
userMapper.insert(user);
}
}
@Test
public void queryUserStatus(){
List<User> users = userMapper.queryUserStatus();
users.forEach(user -> System.out.println(user));
}
package com.roy.shardingDemo.mapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.roy.shardingDemo.entity.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import java.util.List;
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
@Select("select u.user_id,u.username,d.uvalue ustatus from user u left join t_dict d on u.ustatus = d.ustatus")
public List<User> queryUserStatus();
}
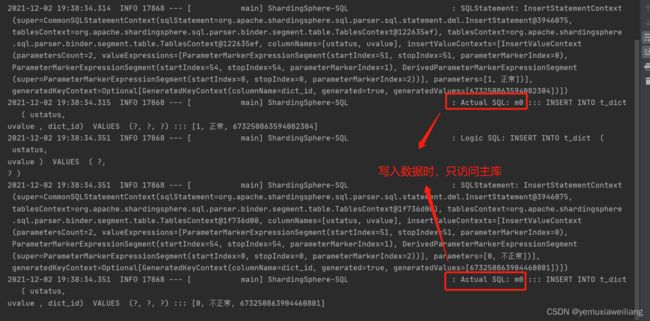
读写分离
spring.profiles.active=dev4
#配置主从数据源,要基于MySQL主从架构。
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=m0,s0
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m0.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m0.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m0.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.1.104:3306/masterdemo?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m0.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m0.password=123
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.s0.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.s0.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.s0.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.1.105:3306/masterdemo?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.s0.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.s0.password=123
#读写分离规则, m0 主库,s0 从库
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.master-slave-rules.ds0.master-data-source-name=m0
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.master-slave-rules.ds0.slave-data-source-names[0]=s0
#基于读写分离的表分片
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_dict.actual-data-nodes=ds0.t_dict
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_dict.key-generator.column=dict_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_dict.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_dict.key-generator.props.worker.id=1
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show = true
spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding=true
@Test
public void addDictByMS(){
Dict d1 = new Dict();
d1.setUstatus("1");
d1.setUvalue("正常");
dictMapper.insert(d1);
Dict d2 = new Dict();
d2.setUstatus("0");
d2.setUvalue("不正常");
dictMapper.insert(d2);
}
@Test
public void queryDictByMS(){
List<Dict> dicts = dictMapper.selectList(null);
dicts.forEach(dict -> System.out.println(dict));
}
ShardingSphere的SQL使用限制
参见官网文档: https://shardingsphere.apache.org/document/current/cn/features/sharding/use-norms/sql/ 文档中详细列出了非常多ShardingSphere目前版本支持和不支持的SQL类型。这些东西要经常关注。
分库分表带来的问题
1、分库分表,其实围绕的都是一个核心问题,就是单机数据库容量的问题。我们要了解,在面对这个问题时,解决方案是很多的,并不止分库分表这一种。但是ShardingSphere的这种分库分表,是希望在软件层面对硬件资源进行管理,从而便于对数据库的横向扩展,这无疑是成本很小的一种方式。
大家想想还有哪些比较好的解决方案?
2、一般情况下,如果单机数据库容量撑不住了,应先从缓存技术着手降低对数据库的访问压力。如果缓存使用过后,数据库访问量还是非常大,可以考虑数据库读写分离策略。如果数据库压力依然非常大,且业务数据持续增长无法估量,最后才考虑分库分表,单表拆分数据应控制在1000万以内。
当然,随着互联网技术的不断发展,处理海量数据的选择也越来越多。在实际进行系统设计时,最好是用MySQL数据库只用来存储关系性较强的热点数据,而对海量数据采取另外的一些分布式存储产品。例如PostGreSQL、VoltDB甚至HBase、Hive、ES等这些大数据组件来存储。
3、从上一部分ShardingJDBC的分片算法中我们可以看到,由于SQL语句的功能实在太多太全面了,所以分库分表后,对SQL语句的支持,其实是步步为艰的,稍不小心,就会造成SQL语句不支持、业务数据混乱等很多很多问题。所以,实际使用时,我们会建议这个分库分表,能不用就尽量不要用。
如果要使用优先在OLTP场景下使用,优先解决大量数据下的查询速度问题。而在OLAP场景中,通常涉及到非常多复杂的SQL,分库分表的限制就会更加明显。当然,这也是ShardingSphere以后改进的一个方向。
4、如果确定要使用分库分表,就应该在系统设计之初开始对业务数据的耦合程度和使用情况进行考量,尽量控制业务SQL语句的使用范围,将数据库往简单的增删改查的数据存储层方向进行弱化。并首先详细规划垂直拆分的策略,使数据层架构清晰明了。而至于水平拆分,会给后期带来非常非常多的数据问题,所以应该谨慎、谨慎再谨慎。一般也就在日志表、操作记录表等很少的一些边缘场景才偶尔用用。