Yolov5训练自己的数据集(超详细)
文章目录
- 一. 环境
- 二. 准备工作
- 三. 使用labelImg标注图片
-
-
- 1. 安装labellmg
- 2. 使用labellmg
-
- 四. 划分数据集以及配置文件修改
-
-
- 1. 划分训练集、验证集、测试集
- 2. XML格式转yolo_txt格式
- 3. 配置文件
- 3. 聚类获得先验框
-
- 3.1 生成anchors文件
- 3.2 修改模型配置文件
-
- 五. 模型训练
-
-
- 开始训练
- 训练过程
- 训练可视化
- 训练时间
- 相关问题
-
- 六. 测试效果
- 七. 参考链接
一. 环境
本教程使用环境:
-
pytorch: 1.10.0
-
python: 3.9
ps: 如果要使用GPU,cuda版本要 >=10.1
下载安装yolov5:
yolov5官方要求 Python>=3.6 and PyTorch>=1.7
yolov5源码下载:https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5
下载后,进入pytorch环境进入yolov5文件夹
使用换源的方法安装依赖
如果你前面安装时没有换源,我强烈建议你使用换源的方法在安装一次
安装过的模块不会在安装,以防缺少模块,影响后续程序运行以及模型训练。
pip install -r requirements.txt -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
因为本教程主详细讲解训练自己的数据集,避免篇幅过多,因此这里不详细说明了。
二. 准备工作
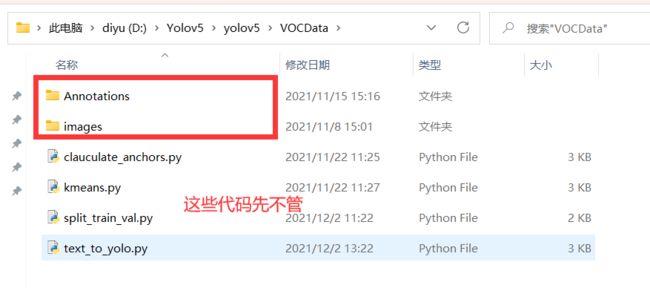
- 在 yolov5目录下 新建文件夹 VOCData
- 新建两个文件夹 Annotations 以及 images
images:用于存放要标注的图片(jpg格式)
Annotations :用于存放标注图片后产生的内容(这里采用XML格式)
后续使用代码保存位置如图
本教程需要用到图中的四个代码文件,这里先不用管,后面会给出代码。
这里提供本人编写的python代码,用于将视频转图片。
只需更改两个参数,视频路径以及间隔多少帧取图片。
python实现视频转图片_diyu-CSDN博客
代码运行,需要装有opencv模块,装opencv模块前需要装numpy模块。
所以,你可以选择进入pytorch环境进入代码所在文件夹,用命令行形式运行程序。
三. 使用labelImg标注图片
1. 安装labellmg
labelImg下载:https://github.com/tzutalin/labelImg
各种安装方法都在此链接中,这里只给出 windows +aconda 进行安装。
aconda安装可以查看我的另一篇博客
ps: 如果你进入不了github,这里给出百度网盘链接
labellImg百度网盘链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1oQroHL94vMhX7bDTX79RGw
提取码:1jbq
此labelImg是采用命令行形式运行,需要使用命令行安装一些依赖。
如果你认为这个太麻烦,网上有人打包好了此软件,可以自行去下载。
本人labellmg存放位置
打开 aconda prompt (类似于cmd)
进入 labellmg文件夹
我建议就在base环境下进行安装labellmg,方便一点,你也可以进入pytorch环境下安装。
在哪个环境安装的就在哪个环境下启动软件。
依次执行下面命令 (不要连接外网)
conda install pyqt=5
conda install -c anaconda lxml
pyrcc5 -o libs/resources.py resources.qrc
2. 使用labellmg
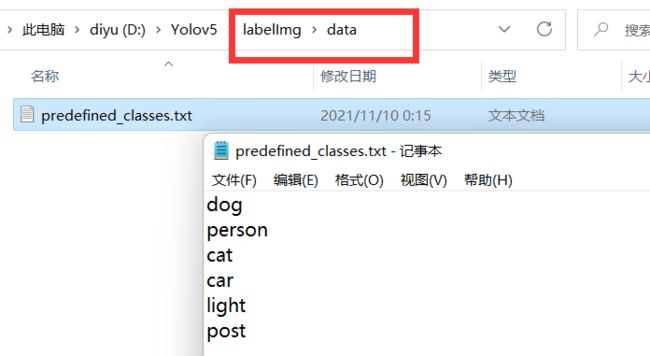
运行软件前可以更改下要标注的类别。
也可以进入软件后添加,不过那样每次进入软件都要添加,麻烦。
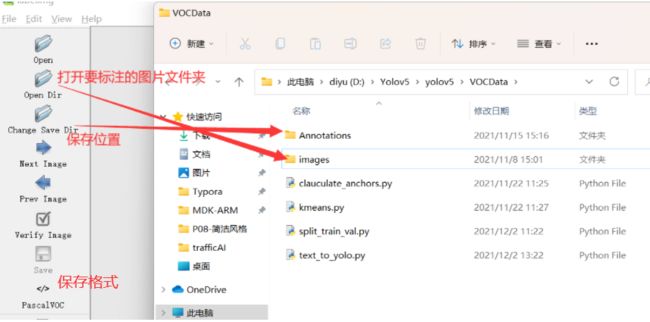
打开labellmg(要进入labellmg文件夹)
python labelImg.py #运行软件
勾选 auto save mode 自动保存
格式就默认是XML格式,可以更改成yolo,这里就使用默认的XML格式
点击左方边栏或者屏幕右键选择 Create RectBox 即可进行标注。
尽可能的完全拟合标注物体,建议放大标注
其它看个人标准。
四. 划分数据集以及配置文件修改
运行代码方式
第一种:使用pycharm、vscode、python自带的IDLE。如果出现缺少模块的情况(no module named),你可以安装模块,也可以使用后一种方法。
第二种:进入pytorch环境,进入代码所在目录,使用命令行形式运行(python + 程序名)
1. 划分训练集、验证集、测试集
在VOCData目录下创建程序 split_train_val.py 并运行
程序如下:(不需要更改)
# coding:utf-8
import os
import random
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
#xml文件的地址,根据自己的数据进行修改 xml一般存放在Annotations下
parser.add_argument('--xml_path', default='Annotations', type=str, help='input xml label path')
#数据集的划分,地址选择自己数据下的ImageSets/Main
parser.add_argument('--txt_path', default='ImageSets/Main', type=str, help='output txt label path')
opt = parser.parse_args()
trainval_percent = 1.0 # 训练集和验证集所占比例。 这里没有划分测试集
train_percent = 0.9 # 训练集所占比例,可自己进行调整
xmlfilepath = opt.xml_path
txtsavepath = opt.txt_path
total_xml = os.listdir(xmlfilepath)
if not os.path.exists(txtsavepath):
os.makedirs(txtsavepath)
num = len(total_xml)
list_index = range(num)
tv = int(num * trainval_percent)
tr = int(tv * train_percent)
trainval = random.sample(list_index, tv)
train = random.sample(trainval, tr)
file_trainval = open(txtsavepath + '/trainval.txt', 'w')
file_test = open(txtsavepath + '/test.txt', 'w')
file_train = open(txtsavepath + '/train.txt', 'w')
file_val = open(txtsavepath + '/val.txt', 'w')
for i in list_index:
name = total_xml[i][:-4] + '\n'
if i in trainval:
file_trainval.write(name)
if i in train:
file_train.write(name)
else:
file_val.write(name)
else:
file_test.write(name)
file_trainval.close()
file_train.close()
file_val.close()
file_test.close()
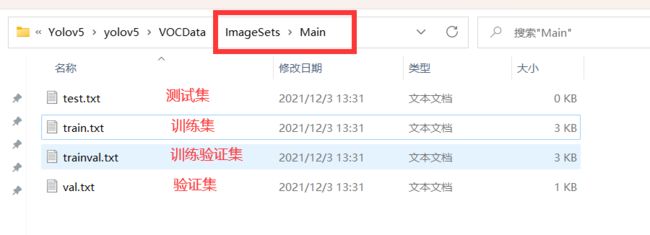
运行完毕后 会生成 ImagesSets\Main 文件夹,且在其下生成 测试集、训练集、验证集,存放图片的名字(无后缀.jpg)
由于没有分配测试集,所以测试集为空。
若要分配,更改第 14、15 行代码,更改所在比例即可。
2. XML格式转yolo_txt格式
在VOCData目录下创建程序 text_to_yolo.py 并运行
程序如下:
需要将第 7 行改成自己所标注的类别 以及 代码中各文件绝对路径
路径需为:d:\\images 或者 d:/images
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import os
from os import getcwd
sets = ['train', 'val', 'test']
classes = ["light", "post"] # 改成自己的类别
abs_path = os.getcwd()
print(abs_path)
def convert(size, box):
dw = 1. / (size[0])
dh = 1. / (size[1])
x = (box[0] + box[1]) / 2.0 - 1
y = (box[2] + box[3]) / 2.0 - 1
w = box[1] - box[0]
h = box[3] - box[2]
x = x * dw
w = w * dw
y = y * dh
h = h * dh
return x, y, w, h
def convert_annotation(image_id):
in_file = open('D:/Yolov5/yolov5/VOCData/Annotations/%s.xml' % (image_id), encoding='UTF-8')
out_file = open('D:/Yolov5/yolov5/VOCData/labels/%s.txt' % (image_id), 'w')
tree = ET.parse(in_file)
root = tree.getroot()
size = root.find('size')
w = int(size.find('width').text)
h = int(size.find('height').text)
for obj in root.iter('object'):
difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
#difficult = obj.find('Difficult').text
cls = obj.find('name').text
if cls not in classes or int(difficult) == 1:
continue
cls_id = classes.index(cls)
xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')
b = (float(xmlbox.find('xmin').text), float(xmlbox.find('xmax').text), float(xmlbox.find('ymin').text),
float(xmlbox.find('ymax').text))
b1, b2, b3, b4 = b
# 标注越界修正
if b2 > w:
b2 = w
if b4 > h:
b4 = h
b = (b1, b2, b3, b4)
bb = convert((w, h), b)
out_file.write(str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '\n')
wd = getcwd()
for image_set in sets:
if not os.path.exists('D:/Yolov5/yolov5/VOCData/labels/'):
os.makedirs('D:/Yolov5/yolov5/VOCData/labels/')
image_ids = open('D:/Yolov5/yolov5/VOCData/ImageSets/Main/%s.txt' % (image_set)).read().strip().split()
if not os.path.exists('D:/Yolov5/yolov5/VOCData/dataSet_path/'):
os.makedirs('D:/Yolov5/yolov5/VOCData/dataSet_path/')
list_file = open('dataSet_path/%s.txt' % (image_set), 'w')
for image_id in image_ids:
list_file.write('D:/Yolov5/yolov5/VOCData/images/%s.jpg\n' % (image_id))
convert_annotation(image_id)
list_file.close()
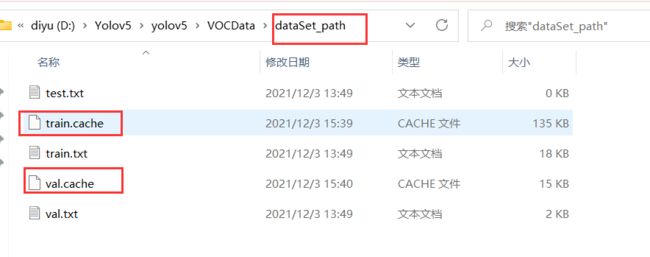
运行后会生成如下 labels 文件夹和 dataSet_path 文件夹。
其中 labels 中为不同图像的标注文件。每个图像对应一个txt文件,文件每一行为一个目标的信息,包括class, x_center, y_center, width, height格式,这种即为 yolo_txt格式
dataSet_path文件夹包含三个数据集的txt文件,train.txt等txt文件为划分后图像所在位置的绝对路径,如train.txt就含有所有训练集图像的绝对路径。
3. 配置文件
在 yolov5 目录下的 data 文件夹下 新建一个 myvoc.yaml文件(可以自定义命名),用记事本打开。
内容是:训练集以及验证集(train.txt和val.txt)绝对路径(通过 text_to_yolo.py 生成),然后是目标的类别数目和类别名称。
给出模板: 冒号后面需要加空格
train: D:/Yolov5/yolov5/VOCData/dataSet_path/train.txt
val: D:/Yolov5/yolov5/VOCData/dataSet_path/val.txt
# number of classes
nc: 2
# class names
names: ["light", "post"]
3. 聚类获得先验框
3.1 生成anchors文件
在VOCData目录下创建程序两个程序 kmeans.py 以及 clauculate_anchors.py
不需要运行 kmeans.py,运行 clauculate_anchors.py 即可。
kmeans.py 程序如下:这不需要运行,也不需要更改
如果报错,查看第 13 行内容
import numpy as np
def iou(box, clusters):
"""
Calculates the Intersection over Union (IoU) between a box and k clusters.
:param box: tuple or array, shifted to the origin (i. e. width and height)
:param clusters: numpy array of shape (k, 2) where k is the number of clusters
:return: numpy array of shape (k, 0) where k is the number of clusters
"""
x = np.minimum(clusters[:, 0], box[0])
y = np.minimum(clusters[:, 1], box[1])
if np.count_nonzero(x == 0) > 0 or np.count_nonzero(y == 0) > 0:
raise ValueError("Box has no area") # 如果报这个错,可以把这行改成pass即可
intersection = x * y
box_area = box[0] * box[1]
cluster_area = clusters[:, 0] * clusters[:, 1]
iou_ = intersection / (box_area + cluster_area - intersection)
return iou_
def avg_iou(boxes, clusters):
"""
Calculates the average Intersection over Union (IoU) between a numpy array of boxes and k clusters.
:param boxes: numpy array of shape (r, 2), where r is the number of rows
:param clusters: numpy array of shape (k, 2) where k is the number of clusters
:return: average IoU as a single float
"""
return np.mean([np.max(iou(boxes[i], clusters)) for i in range(boxes.shape[0])])
def translate_boxes(boxes):
"""
Translates all the boxes to the origin.
:param boxes: numpy array of shape (r, 4)
:return: numpy array of shape (r, 2)
"""
new_boxes = boxes.copy()
for row in range(new_boxes.shape[0]):
new_boxes[row][2] = np.abs(new_boxes[row][2] - new_boxes[row][0])
new_boxes[row][3] = np.abs(new_boxes[row][3] - new_boxes[row][1])
return np.delete(new_boxes, [0, 1], axis=1)
def kmeans(boxes, k, dist=np.median):
"""
Calculates k-means clustering with the Intersection over Union (IoU) metric.
:param boxes: numpy array of shape (r, 2), where r is the number of rows
:param k: number of clusters
:param dist: distance function
:return: numpy array of shape (k, 2)
"""
rows = boxes.shape[0]
distances = np.empty((rows, k))
last_clusters = np.zeros((rows,))
np.random.seed()
# the Forgy method will fail if the whole array contains the same rows
clusters = boxes[np.random.choice(rows, k, replace=False)]
while True:
for row in range(rows):
distances[row] = 1 - iou(boxes[row], clusters)
nearest_clusters = np.argmin(distances, axis=1)
if (last_clusters == nearest_clusters).all():
break
for cluster in range(k):
clusters[cluster] = dist(boxes[nearest_clusters == cluster], axis=0)
last_clusters = nearest_clusters
return clusters
if __name__ == '__main__':
a = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 7, 6, 8]])
print(translate_boxes(a))
运行:clauculate_anchors.py
会调用 kmeans.py 聚类生成新anchors的文件
程序如下:
需要更改第 9 、13行文件路径 以及 第 16 行标注类别名称
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# 根据标签文件求先验框
import os
import numpy as np
import xml.etree.cElementTree as et
from kmeans import kmeans, avg_iou
FILE_ROOT = "D:/Yolov5/yolov5/VOCData/" # 根路径
ANNOTATION_ROOT = "Annotations" # 数据集标签文件夹路径
ANNOTATION_PATH = FILE_ROOT + ANNOTATION_ROOT
ANCHORS_TXT_PATH = "D:/Yolov5/yolov5/VOCData/anchors.txt" #anchors文件保存位置
CLUSTERS = 9
CLASS_NAMES = ['light', 'post'] #类别名称
def load_data(anno_dir, class_names):
xml_names = os.listdir(anno_dir)
boxes = []
for xml_name in xml_names:
xml_pth = os.path.join(anno_dir, xml_name)
tree = et.parse(xml_pth)
width = float(tree.findtext("./size/width"))
height = float(tree.findtext("./size/height"))
for obj in tree.findall("./object"):
cls_name = obj.findtext("name")
if cls_name in class_names:
xmin = float(obj.findtext("bndbox/xmin")) / width
ymin = float(obj.findtext("bndbox/ymin")) / height
xmax = float(obj.findtext("bndbox/xmax")) / width
ymax = float(obj.findtext("bndbox/ymax")) / height
box = [xmax - xmin, ymax - ymin]
boxes.append(box)
else:
continue
return np.array(boxes)
if __name__ == '__main__':
anchors_txt = open(ANCHORS_TXT_PATH, "w")
train_boxes = load_data(ANNOTATION_PATH, CLASS_NAMES)
count = 1
best_accuracy = 0
best_anchors = []
best_ratios = []
for i in range(10): ##### 可以修改,不要太大,否则时间很长
anchors_tmp = []
clusters = kmeans(train_boxes, k=CLUSTERS)
idx = clusters[:, 0].argsort()
clusters = clusters[idx]
# print(clusters)
for j in range(CLUSTERS):
anchor = [round(clusters[j][0] * 640, 2), round(clusters[j][1] * 640, 2)]
anchors_tmp.append(anchor)
print(f"Anchors:{
anchor}")
temp_accuracy = avg_iou(train_boxes, clusters) * 100
print("Train_Accuracy:{:.2f}%".format(temp_accuracy))
ratios = np.around(clusters[:, 0] / clusters[:, 1], decimals=2).tolist()
ratios.sort()
print("Ratios:{}".format(ratios))
print(20 * "*" + " {} ".format(count) + 20 * "*")
count += 1
if temp_accuracy > best_accuracy:
best_accuracy = temp_accuracy
best_anchors = anchors_tmp
best_ratios = ratios
anchors_txt.write("Best Accuracy = " + str(round(best_accuracy, 2)) + '%' + "\r\n")
anchors_txt.write("Best Anchors = " + str(best_anchors) + "\r\n")
anchors_txt.write("Best Ratios = " + str(best_ratios))
anchors_txt.close()
会生成anchors文件。如果生成文件为空,重新运行即可。
第二行 Best Anchors 后面需要用到。
3.2 修改模型配置文件
选择一个模型,在yolov5目录下的model文件夹下是模型的配置文件,有n、s、m、l、x版本,逐渐增大(随着架构的增大,训练时间也是逐渐增大)。
这里选用 yolov5s.yaml
使用记事本打开 yolov5s.yaml。
修改两个参数。
把 nc 改成自己的标注类别数
修改anchors,根据 anchors.txt 中的 Best Anchors 修改,需要取整(四舍五入、向上、向下都可以)。
五. 模型训练
开始训练
我们可以看看 yolov5 目录下的 train.py 程序
我们一般需要注意这 七个参数
以上参数解释如下:
这个照搬别人的,参考链接在最后。
weights:权重文件路径
cfg:存储模型结构的配置文件
data:存储训练、测试数据的文件
epochs:指的就是训练过程中整个数据集将被迭代多少次,显卡不行你就调小点。
batch-size:一次看完多少张图片才进行权重更新,梯度下降的mini-batch,显卡不行你就调小点。
img-size:输入图片宽高,显卡不行你就调小点。
device:cuda device, i.e. 0 or 0,1,2,3 or cpu。选择使用GPU还是CPU
其它参数解释:
rect:进行矩形训练
resume:恢复最近保存的模型开始训练
nosave:仅保存最终checkpoint
notest:仅测试最后的epoch
evolve:进化超参数
bucket:gsutil bucket
cache-images:缓存图像以加快训练速度
name: 重命名results.txt to results_name.txt
adam:使用adam优化
multi-scale:多尺度训练,img-size +/- 50%
single-cls:单类别的训练集
进入pytorch环境,进入yolov5文件夹
训练命令如下:
如果出现缺少模块的情况(no module named),回到博客最开始部分,使用换源的方法补充安装yolov5的依赖。
python train.py --weights weights/yolov5s.pt --cfg models/yolov5s.yaml --data data/myvoc.yaml --epoch 200 --batch-size 8 --img 640 --device cpu
–weights weights/yolov5s.pt :这个也许你需要更改路径。我是将yolov5的pt文件都放在weights目录下,你可能没有,需要更改路径。
–epoch 200 :训练200次
–batch-size 8:训练8张图片后进行权重更新
–device cpu:使用CPU训练。
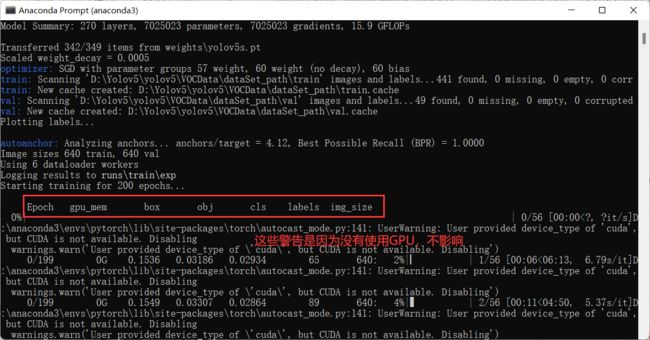
训练过程
如果你不想看到这些警告,网上是有办法消除的,自行寻找了。
如果你使用GPU训练也有类似下面这个,那是你 cuda 版本不对(不是>=10.1的版本),版本不对无法使用cuda。
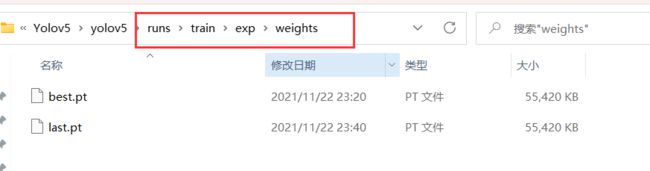
训练好的模型会被保存在 yolov5 目录下的 runs/train/weights/ 下
训练可视化
训练时或者训练后可以利用 tensorboard 查看训练可视化
tensorboard --logdir=runs
训练时间
我这里四百多张图片,使用CPU训练了一百二十几次(虽然设的200次,但我中途终止了),大概花了5、6个小时吧,半个月了忘了。
我同学 70张图片训练70次,使用CPU训练花了 一个多小时。
相关问题
如果出现缺少模块的情况(no module named)
回到博客最开始部分,使用换源的方法补充安装yolov5的依赖。
如果训练过程中出现 memory error
那是内存超了,减小 --epoch 以及 --batch-size 试试。
我同学将 --epoch 设为100次,–batch-size设为3才成功。
重复训练的话,你也许需要将这两个缓存清除掉。
六. 测试效果
我们使用刚刚训练出的最好的模型 best.pt 来测试,在yolov5目录下的 runs/train/exp/weights 。
python detect.py --weights runs/train/exp/weights/best.pt --source ../data/video/tram.mp4
七. 参考链接
YOLOv5训练自己的数据集(超详细完整版)_深度学习菜鸟的博客-CSDN博客_yolov5训练自己的数据