OpenCV+Python简单实践
文章目录
- 一、基础练习
-
- 1.基础函数
- 2.找中心
- 3.修改
- 4.读取图片和视频
- 5.二值化
- 6.变换
- 二、进阶
-
- 1.转灰度
- 2.RGB转HSV
- 3.RGB转HSI
- 三、总结
- 四、参考
一、基础练习
1.基础函数
读取图片
img = cv.imread('../Resources/Photos/park.jpg')
转灰度图片
gray = cv.cvtColor(img, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
高斯滤波
blur = cv.GaussianBlur(img, (7,7), cv.BORDER_DEFAULT)
边缘检测
canny = cv.Canny(blur, 125, 175)
膨胀
dilated = cv.dilate(canny, (7,7), iterations=3)
腐蚀
eroded = cv.erode(dilated, (7,7), iterations=3)
改变图片尺寸
resized = cv.resize(img, (500,500), interpolation=cv.INTER_CUBIC)
裁剪图片
cropped = img[50:200, 200:400]
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
def stackImages(scale, imgArray):
"""
将多张图像压入同一个窗口显示
:param scale:float类型,输出图像显示百分比,控制缩放比例,0.5=图像分辨率缩小一半
:param imgArray:元组嵌套列表,需要排列的图像矩阵
:return:输出图像
"""
rows = len(imgArray)
cols = len(imgArray[0])
rowsAvailable = isinstance(imgArray[0], list)
width = imgArray[0][0].shape[1]
height = imgArray[0][0].shape[0]
if rowsAvailable:
for x in range(0, rows):
for y in range(0, cols):
if imgArray[x][y].shape[:2] == imgArray[0][0].shape[:2]:
imgArray[x][y] = cv.resize(imgArray[x][y], (0, 0), None, scale, scale)
else:
imgArray[x][y] = cv.resize(imgArray[x][y], (imgArray[0][0].shape[1], imgArray[0][0].shape[0]),
None, scale, scale)
if len(imgArray[x][y].shape) == 2: imgArray[x][y] = cv.cvtColor(imgArray[x][y], cv.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
imageBlank = np.zeros((height, width, 3), np.uint8)
hor = [imageBlank] * rows
hor_con = [imageBlank] * rows
for x in range(0, rows):
hor[x] = np.hstack(imgArray[x])
ver = np.vstack(hor)
else:
for x in range(0, rows):
if imgArray[x].shape[:2] == imgArray[0].shape[:2]:
imgArray[x] = cv2.resize(imgArray[x], (0, 0), None, scale, scale)
else:
imgArray[x] = cv2.resize(imgArray[x], (imgArray[0].shape[1], imgArray[0].shape[0]), None, scale, scale)
if len(imgArray[x].shape) == 2: imgArray[x] = cv2.cvtColor(imgArray[x], cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
hor = np.hstack(imgArray)
ver = hor
return ver
# Read in an image
# 读取图片
img = cv.imread('../Resources/Photos/park.jpg')
# Converting to grayscale
# 转灰度
gray = cv.cvtColor(img, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# Blur
# 高斯滤波
blur = cv.GaussianBlur(img, (7,7), cv.BORDER_DEFAULT)
# Edge Cascade
# Canny算子边缘检测
canny = cv.Canny(blur, 125, 175)
# Dilating the image
# 膨胀
dilated = cv.dilate(canny, (7,7), iterations=3)
# Eroding
# 腐蚀
eroded = cv.erode(dilated, (7,7), iterations=3)
# Resize
# 重新设置图片大小
resized = cv.resize(img, (500,500), interpolation=cv.INTER_CUBIC)
# Cropping
# 剪切图片
cropped = img[50:200, 200:400]
cv.putText(img, "Park", (0, 100), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 3.0, (255, 0, 0), 3)
cv.putText(gray, "Gray", (0, 100), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 3.0, (255, 0, 0), 3)
cv.putText(blur, "blur",(0, 100), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 3.0, (255, 0, 0), 3)
cv.putText(canny, "Canny Edges", (0, 100), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 3.0, (255, 0, 0), 3)
cv.putText(dilated, "Dilated", (0, 100), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 3.0, (255, 0, 0), 3)
cv.putText(eroded, "Eroded", (0, 100), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 3.0, (255, 0, 0), 3)
cv.putText(resized, "Resized", (0, 100), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 3.0, (255, 0, 0), 3)
cv.putText(cropped, "Cropped", (0, 100), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 3.0, (255, 0, 0), 3)
imgStack = stackImages(0.5,([img,gray,blur,canny],[dilated,eroded,resized,cropped]))
cv.imshow("imgStack", imgStack)
cv.waitKey(0)
2.找中心
读取图片
img = cv.imread('../Resources/Photos/cats.jpg')
图片变成全黑
blank = np.zeros(img.shape, dtype='uint8')
转为灰度
gray = cv.cvtColor(img, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
高斯滤波
blur = cv.GaussianBlur(gray, (5,5), cv.BORDER_DEFAULT)
边缘检测
canny = cv.Canny(blur, 125, 175)
二值化
ret, thresh = cv.threshold(canny, 125, 255, cv.THRESH_BINARY)
找中心
contours, hierarchies = cv.findContours(thresh, cv.RETR_LIST, cv.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
绘制
cv.drawContours(blank, contours, -1, (0,0,255), 5)
#pylint:disable=no-member
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
def stackImages(scale, imgArray):
"""
将多张图像压入同一个窗口显示
:param scale:float类型,输出图像显示百分比,控制缩放比例,0.5=图像分辨率缩小一半
:param imgArray:元组嵌套列表,需要排列的图像矩阵
:return:输出图像
"""
rows = len(imgArray)
cols = len(imgArray[0])
rowsAvailable = isinstance(imgArray[0], list)
width = imgArray[0][0].shape[1]
height = imgArray[0][0].shape[0]
if rowsAvailable:
for x in range(0, rows):
for y in range(0, cols):
if imgArray[x][y].shape[:2] == imgArray[0][0].shape[:2]:
imgArray[x][y] = cv.resize(imgArray[x][y], (0, 0), None, scale, scale)
else:
imgArray[x][y] = cv.resize(imgArray[x][y], (imgArray[0][0].shape[1], imgArray[0][0].shape[0]),
None, scale, scale)
if len(imgArray[x][y].shape) == 2: imgArray[x][y] = cv.cvtColor(imgArray[x][y], cv.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
imageBlank = np.zeros((height, width, 3), np.uint8)
hor = [imageBlank] * rows
hor_con = [imageBlank] * rows
for x in range(0, rows):
hor[x] = np.hstack(imgArray[x])
ver = np.vstack(hor)
else:
for x in range(0, rows):
if imgArray[x].shape[:2] == imgArray[0].shape[:2]:
imgArray[x] = cv2.resize(imgArray[x], (0, 0), None, scale, scale)
else:
imgArray[x] = cv2.resize(imgArray[x], (imgArray[0].shape[1], imgArray[0].shape[0]), None, scale, scale)
if len(imgArray[x].shape) == 2: imgArray[x] = cv2.cvtColor(imgArray[x], cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
hor = np.hstack(imgArray)
ver = hor
return ver
# 读取目标图片
img = cv.imread('../Resources/Photos/cats.jpg')
# 把图片RGB填充为0
blank = np.zeros(img.shape, dtype='uint8')
# 转为灰度图片
gray = cv.cvtColor(img, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 高斯滤波处理
blur = cv.GaussianBlur(gray, (5,5), cv.BORDER_DEFAULT)
# 边缘检测
canny = cv.Canny(blur, 125, 175)
# 二值化
ret, thresh = cv.threshold(canny, 125, 255, cv.THRESH_BINARY)
# 找到中心
contours, hierarchies = cv.findContours(thresh, cv.RETR_LIST, cv.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
print(f'{
len(contours)} contour(s) found!')
# 绘制边缘
cv.drawContours(blank, contours, -1, (0,0,255), 5)
cv.putText(img, "Cats", (0, 100), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 3.0, (255, 0, 0), 3)
cv.putText(gray, "Gray", (0, 100), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 3.0, (255, 0, 0), 3)
cv.putText(blur, "blur",(0, 100), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 3.0, (255, 0, 0), 3)
cv.putText(canny, "Canny Edges", (0, 100), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 3.0, (255, 0, 0), 3)
cv.putText(thresh, "thresh", (0, 100), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 3.0, (255, 0, 0), 3)
cv.putText(blank, "Contours Drawn", (0, 100), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1.0, (255, 0, 0), 3)
imgStack = stackImages(0.5,([img,gray,blur],[canny,thresh,blank]))
cv.imshow("imgStack", imgStack)
cv.waitKey(0)
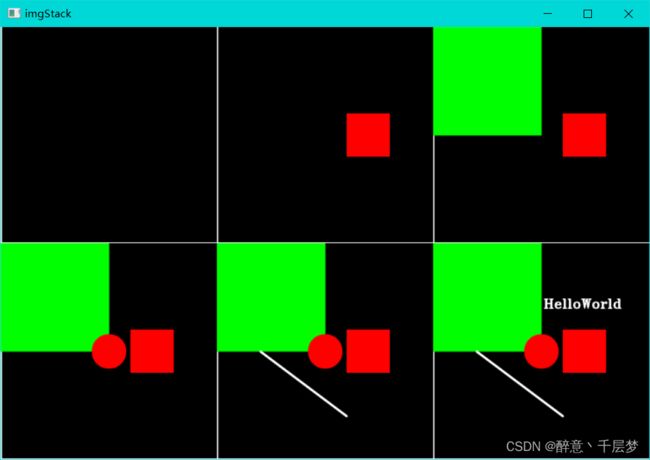
3.修改
把一个区域设置为指定颜色
img_2[200:300, 300:400]=0,0,255
画一个矩形
cv.rectangle(img_3, (0,0), (img_3.shape[1]//2, img_3.shape[0]//2), (0,255,0), thickness=-1)
画一个圆
cv.circle(img_4, (img_4.shape[1]//2, img_4.shape[0]//2), 40, (0,0,255), thickness=-1)
画一条直线
cv.line(img_5, (100,250), (300,400), (255,255,255), thickness=3)
显示字体
cv.putText(img_6, 'HelloWorld', (255,150), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_TRIPLEX, 1.0, (255,255,255), 2)
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
def stackImages(scale, imgArray):
"""
将多张图像压入同一个窗口显示
:param scale:float类型,输出图像显示百分比,控制缩放比例,0.5=图像分辨率缩小一半
:param imgArray:元组嵌套列表,需要排列的图像矩阵
:return:输出图像
"""
rows = len(imgArray)
cols = len(imgArray[0])
rowsAvailable = isinstance(imgArray[0], list)
width = imgArray[0][0].shape[1]
height = imgArray[0][0].shape[0]
if rowsAvailable:
for x in range(0, rows):
for y in range(0, cols):
if imgArray[x][y].shape[:2] == imgArray[0][0].shape[:2]:
imgArray[x][y] = cv.resize(imgArray[x][y], (0, 0), None, scale, scale)
else:
imgArray[x][y] = cv.resize(imgArray[x][y], (imgArray[0][0].shape[1], imgArray[0][0].shape[0]),
None, scale, scale)
if len(imgArray[x][y].shape) == 2: imgArray[x][y] = cv.cvtColor(imgArray[x][y], cv.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
imageBlank = np.zeros((height, width, 3), np.uint8)
hor = [imageBlank] * rows
hor_con = [imageBlank] * rows
for x in range(0, rows):
hor[x] = np.hstack(imgArray[x])
ver = np.vstack(hor)
else:
for x in range(0, rows):
if imgArray[x].shape[:2] == imgArray[0].shape[:2]:
imgArray[x] = cv2.resize(imgArray[x], (0, 0), None, scale, scale)
else:
imgArray[x] = cv2.resize(imgArray[x], (imgArray[0].shape[1], imgArray[0].shape[0]), None, scale, scale)
if len(imgArray[x].shape) == 2: imgArray[x] = cv2.cvtColor(imgArray[x], cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
hor = np.hstack(imgArray)
ver = hor
return ver
# 创造一个黑色背景板
img_1 = np.zeros((500,500,3), dtype='uint8')
# 绘制边缘线便于区分
cv.line(img_1, (0,0), (0,img_1.shape[0]), (255,255,255), thickness=3)
cv.line(img_1, (0,img_1.shape[0]), (img_1.shape[1],img_1.shape[0]), (255,255,255), thickness=3)
# 1. Paint the image a certain colour
# 把一个区域设置为指定颜色
img_2=img_1.copy()
img_2[200:300, 300:400]=0,0,255
# 2. Draw a Rectangle
# 画一个矩形
# 第一个参数为目标图片
# 第二个参数为矩形起始坐标,矩形左上角
# 第三个参数为矩形终止坐标,矩形右下角
# 第四个参数为颜色
# 第五个参数为线条宽度,-1表示填充
img_3=img_2.copy()
cv.rectangle(img_3, (0,0), (img_3.shape[1]//2, img_3.shape[0]//2), (0,255,0), thickness=-1)
# 3. Draw A circle
# 画一个圆
# 第一个参数为目标图片
# 第二个参数为圆心坐标
# 第三个参数为半径
# 第四个参数为颜色
# 第五个参数为线条宽度,-1表示填充
img_4=img_3.copy()
cv.circle(img_4, (img_4.shape[1]//2, img_4.shape[0]//2), 40, (0,0,255), thickness=-1)
# 4. Draw a line
# 画一条直线
# 第一个参数为目标图片
# 第二个参数为起始坐标
# 第三个参数为终止坐标
# 第四个参数为颜色
# 第五个参数为线条宽度
img_5=img_4.copy()
cv.line(img_5, (100,250), (300,400), (255,255,255), thickness=3)
# 5. Write text
# 在图片上写字
# 第一个参数为目标图片
# 第二个参数为显示内容
# 第三个参数为显示起始坐标
# 第四个参数为字体类型
# 第五个参数为字体大小
# 第六个参数为字体颜色
# 第七个参数为字体线条粗细
img_6=img_5.copy()
cv.putText(img_6, 'HelloWorld', (255,150), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_TRIPLEX, 1.0, (255,255,255), 2)
imgStack = stackImages(0.5,([img_1,img_2,img_3],[img_4,img_5,img_6]))
cv.imshow("imgStack", imgStack)
cv.waitKey(0)
4.读取图片和视频
读取图片
img = cv.imread('../Resources/Photos/cats.jpg')
cv.imshow('Cats', img)
打开视频
capture = cv.VideoCapture('../Resources/Videos/dog.mp4')
读取视频
while True:
# 循环读取每一帧
isTrue, frame = capture.read()
# if cv.waitKey(20) & 0xFF==ord('d'):
# This is the preferred way - if `isTrue` is false (the frame could
# not be read, or we're at the end of the video), we immediately
# break from the loop.
# 如果没有读取成功或者读取完毕直接退出
# 或者直接按下键盘的d退出
if isTrue:
cv.imshow('Video', frame)
if cv.waitKey(20) & 0xFF==ord('d'):
break
else:
break
源代码
#pylint:disable=no-member
import cv2 as cv
img = cv.imread('../Resources/Photos/cats.jpg')
cv.imshow('Cats', img)
cv.waitKey(0)
# Reading Videos
# 打开视频
capture = cv.VideoCapture('../Resources/Videos/dog.mp4')
while True:
# 循环读取每一帧
isTrue, frame = capture.read()
# if cv.waitKey(20) & 0xFF==ord('d'):
# This is the preferred way - if `isTrue` is false (the frame could
# not be read, or we're at the end of the video), we immediately
# break from the loop.
# 如果没有读取成功或者读取完毕直接退出
# 或者直接按下键盘的d退出
if isTrue:
cv.imshow('Video', frame)
if cv.waitKey(20) & 0xFF==ord('d'):
break
else:
break
# 释放
capture.release()
# 关闭窗口
cv.destroyAllWindows()
5.二值化
读取图片
img = cv.imread('../Resources/Photos/cats.jpg')
转灰度
gray = cv.cvtColor(img, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
二值化
threshold, thresh = cv.threshold(gray, 150, 255, cv.THRESH_BINARY )
threshold, thresh_inv = cv.threshold(gray, 150, 255, cv.THRESH_BINARY_INV )
adaptive_thresh1 = cv.adaptiveThreshold(gray, 255, cv.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C, cv.THRESH_BINARY_INV, 55, 1)
adaptive_thresh2 = cv.adaptiveThreshold(gray, 255, cv.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C, cv.THRESH_BINARY_INV, 55, 1)
效果
源码
#pylint:disable=no-member
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
def stackImages(scale, imgArray):
"""
将多张图像压入同一个窗口显示
:param scale:float类型,输出图像显示百分比,控制缩放比例,0.5=图像分辨率缩小一半
:param imgArray:元组嵌套列表,需要排列的图像矩阵
:return:输出图像
"""
rows = len(imgArray)
cols = len(imgArray[0])
rowsAvailable = isinstance(imgArray[0], list)
width = imgArray[0][0].shape[1]
height = imgArray[0][0].shape[0]
if rowsAvailable:
for x in range(0, rows):
for y in range(0, cols):
if imgArray[x][y].shape[:2] == imgArray[0][0].shape[:2]:
imgArray[x][y] = cv.resize(imgArray[x][y], (0, 0), None, scale, scale)
else:
imgArray[x][y] = cv.resize(imgArray[x][y], (imgArray[0][0].shape[1], imgArray[0][0].shape[0]),
None, scale, scale)
if len(imgArray[x][y].shape) == 2: imgArray[x][y] = cv.cvtColor(imgArray[x][y], cv.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
imageBlank = np.zeros((height, width, 3), np.uint8)
hor = [imageBlank] * rows
hor_con = [imageBlank] * rows
for x in range(0, rows):
hor[x] = np.hstack(imgArray[x])
ver = np.vstack(hor)
else:
for x in range(0, rows):
if imgArray[x].shape[:2] == imgArray[0].shape[:2]:
imgArray[x] = cv2.resize(imgArray[x], (0, 0), None, scale, scale)
else:
imgArray[x] = cv2.resize(imgArray[x], (imgArray[0].shape[1], imgArray[0].shape[0]), None, scale, scale)
if len(imgArray[x].shape) == 2: imgArray[x] = cv2.cvtColor(imgArray[x], cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
hor = np.hstack(imgArray)
ver = hor
return ver
# 读取图片
img = cv.imread('../Resources/Photos/cats.jpg')
# img = cv.imread('img_2.png')
# 转灰度
gray = cv.cvtColor(img, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# Simple Thresholding
# 二值化
# 第一个参数为目标图片
# 第二个参数为 阈值 threshold
# 第三参数为 最大值 maxval
# 第四个参数为类型
# THRESH_BINARY = 0, 大于thresh 为 maxval,否则为 0
# THRESH_BINARY_INV = 1, 大于thresh 为 0,否则为 maxval
# THRESH_TRUNC = 2, 大于thresh 为 thresh,否则为 0
# THRESH_TOZERO = 3, 大于thresh 不变,否则为 0
# THRESH_TOZERO_INV = 4, 大于thresh 为 0,否则 不变
# THRESH_MASK = 7,
# THRESH_OTSU = 8, 使用OTSU阈值
# THRESH_TRIANGLE = 16 使用三角形算法阈值
threshold, thresh = cv.threshold(gray, 150, 255, cv.THRESH_BINARY )
# 二值化
threshold, thresh_inv = cv.threshold(gray, 150, 255, cv.THRESH_BINARY_INV )
# Adaptive Thresholding
# 阈值自适应二值化
adaptive_thresh1 = cv.adaptiveThreshold(gray, 255, cv.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C, cv.THRESH_BINARY_INV, 55, 1)
adaptive_thresh2 = cv.adaptiveThreshold(gray, 255, cv.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C, cv.THRESH_BINARY_INV, 55, 1)
cv.putText(img, "Cats", (0, 100), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 3.0, (255, 0, 0), 3)
cv.putText(gray, "Gray", (0, 100), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 3.0, (255, 0, 0), 3)
cv.putText(thresh, "thresh",(0, 100), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 3.0, (255, 0, 0), 3)
cv.putText(thresh_inv, "thresh_inv", (0, 100), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 3.0, (255, 0, 0), 3)
cv.putText(adaptive_thresh1, "adaptive_thresh1", (0, 100), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 3.0, (255, 0, 0), 3)
cv.putText(adaptive_thresh2, "adaptive_thresh1", (0, 100), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1.0, (255, 0, 0), 3)
imgStack = stackImages(0.5,([img,gray,thresh],[thresh_inv,adaptive_thresh1,adaptive_thresh2]))
cv.imshow("imgStack", imgStack)
cv.waitKey(0)
6.变换
读取图片
img = cv.imread('../Resources/Photos/park.jpg')
缩放
def translate(img, x, y):
transMat = np.float32([[1,0,x],[0,1,y]])
dimensions = (img.shape[1], img.shape[0])
return cv.warpAffine(img, transMat, dimensions)
旋转
def rotate(img, angle, rotPoint=None):
(height,width) = img.shape[:2]
if rotPoint is None:
rotPoint = (width//2,height//2)
rotMat = cv.getRotationMatrix2D(rotPoint, angle, 1.0)
dimensions = (width,height)
return cv.warpAffine(img, rotMat, dimensions)
效果
源代码
#pylint:disable=no-member
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
def stackImages(scale, imgArray):
"""
将多张图像压入同一个窗口显示
:param scale:float类型,输出图像显示百分比,控制缩放比例,0.5=图像分辨率缩小一半
:param imgArray:元组嵌套列表,需要排列的图像矩阵
:return:输出图像
"""
rows = len(imgArray)
cols = len(imgArray[0])
rowsAvailable = isinstance(imgArray[0], list)
width = imgArray[0][0].shape[1]
height = imgArray[0][0].shape[0]
if rowsAvailable:
for x in range(0, rows):
for y in range(0, cols):
if imgArray[x][y].shape[:2] == imgArray[0][0].shape[:2]:
imgArray[x][y] = cv.resize(imgArray[x][y], (0, 0), None, scale, scale)
else:
imgArray[x][y] = cv.resize(imgArray[x][y], (imgArray[0][0].shape[1], imgArray[0][0].shape[0]),
None, scale, scale)
if len(imgArray[x][y].shape) == 2: imgArray[x][y] = cv.cvtColor(imgArray[x][y], cv.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
imageBlank = np.zeros((height, width, 3), np.uint8)
hor = [imageBlank] * rows
hor_con = [imageBlank] * rows
for x in range(0, rows):
hor[x] = np.hstack(imgArray[x])
ver = np.vstack(hor)
else:
for x in range(0, rows):
if imgArray[x].shape[:2] == imgArray[0].shape[:2]:
imgArray[x] = cv2.resize(imgArray[x], (0, 0), None, scale, scale)
else:
imgArray[x] = cv2.resize(imgArray[x], (imgArray[0].shape[1], imgArray[0].shape[0]), None, scale, scale)
if len(imgArray[x].shape) == 2: imgArray[x] = cv2.cvtColor(imgArray[x], cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
hor = np.hstack(imgArray)
ver = hor
return ver
img = cv.imread('../Resources/Photos/park.jpg')
#cv.imshow('Park', img)
# Translation
def translate(img, x, y):
transMat = np.float32([[1,0,x],[0,1,y]])
dimensions = (img.shape[1], img.shape[0])
return cv.warpAffine(img, transMat, dimensions)
# -x --> Left
# -y --> Up
# x --> Right
# y --> Down
# 缩放
translated = translate(img, -100, 100)
#cv.imshow('Translated', translated)
# Rotation
def rotate(img, angle, rotPoint=None):
(height,width) = img.shape[:2]
if rotPoint is None:
rotPoint = (width//2,height//2)
rotMat = cv.getRotationMatrix2D(rotPoint, angle, 1.0)
dimensions = (width,height)
return cv.warpAffine(img, rotMat, dimensions)
# 旋转
rotated = rotate(img, -45)
#cv.imshow('Rotated', rotated)
rotated_rotated = rotate(img, -90)
#cv.imshow('Rotated Rotated', rotated_rotated)
# Resizing
#
resized = cv.resize(img, (500,500), interpolation=cv.INTER_CUBIC)
#cv.imshow('Resized', resized)
# Flipping
# 旋转
flip = cv.flip(img, -1)
#cv.imshow('Flip', flip)
# Cropping
cropped = img[200:400, 300:400]
#cv.imshow('Cropped', cropped)
cv.putText(img, "img", (0, 100), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 3.0, (255, 0, 0), 3)
cv.putText(translated, "translated", (0, 100), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 3.0, (255, 0, 0), 3)
cv.putText(rotated, "rotated",(0, 100), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 3.0, (255, 0, 0), 3)
cv.putText(rotated_rotated, "rotated_rotated", (0, 100), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 3.0, (255, 0, 0), 3)
cv.putText(resized, "resized", (0, 100), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 3.0, (255, 0, 0), 3)
cv.putText(flip, "flip", (0, 100), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1.0, (255, 0, 0), 3)
imgStack = stackImages(0.5,([img,translated,rotated],[rotated_rotated,resized,flip]))
cv.imshow("imgStack", imgStack)
cv.waitKey(0)
二、进阶
1.转灰度
代码
img = cv.imread('../Resources/Photos/park.jpg')
gray = cv.cvtColor(img, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cv.imshow('Gray', gray)
2.RGB转HSV
代码
hsv = cv.cvtColor(img, cv.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
3.RGB转HSI
实现函数
def rgb2hsi(image):
b, g, r = cv.split(image) # 读取通道
r = r / 255.0 # 归一化
g = g / 255.0
b = b / 255.0
eps = 1e-6 # 防止除零
img_i = (r + g + b) / 3 # I分量
img_h = np.zeros(r.shape, dtype=np.float32)
img_s = np.zeros(r.shape, dtype=np.float32)
min_rgb = np.zeros(r.shape, dtype=np.float32)
# 获取RGB中最小值
min_rgb = np.where((r <= g) & (r <= b), r, min_rgb)
min_rgb = np.where((g <= r) & (g <= b), g, min_rgb)
min_rgb = np.where((b <= g) & (b <= r), b, min_rgb)
img_s = 1 - 3*min_rgb/(r+g+b+eps) # S分量
num = ((r-g) + (r-b))/2
den = np.sqrt((r-g)**2 + (r-b)*(g-b))
theta = np.arccos(num/(den+eps))
img_h = np.where((b-g) > 0, 2*np.pi - theta, theta) # H分量
img_h = np.where(img_s == 0, 0, img_h)
img_h = img_h/(2*np.pi) # 归一化
temp_s = img_s - np.min(img_s)
temp_i = img_i - np.min(img_i)
img_s = temp_s/np.max(temp_s)
img_i = temp_i/np.max(temp_i)
image_hsi = cv.merge([img_h, img_s, img_i])
return image_hsi
三、总结
图像不好学哦,还是得多多借助工具实现。
四、参考
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44926189/article/details/121131241